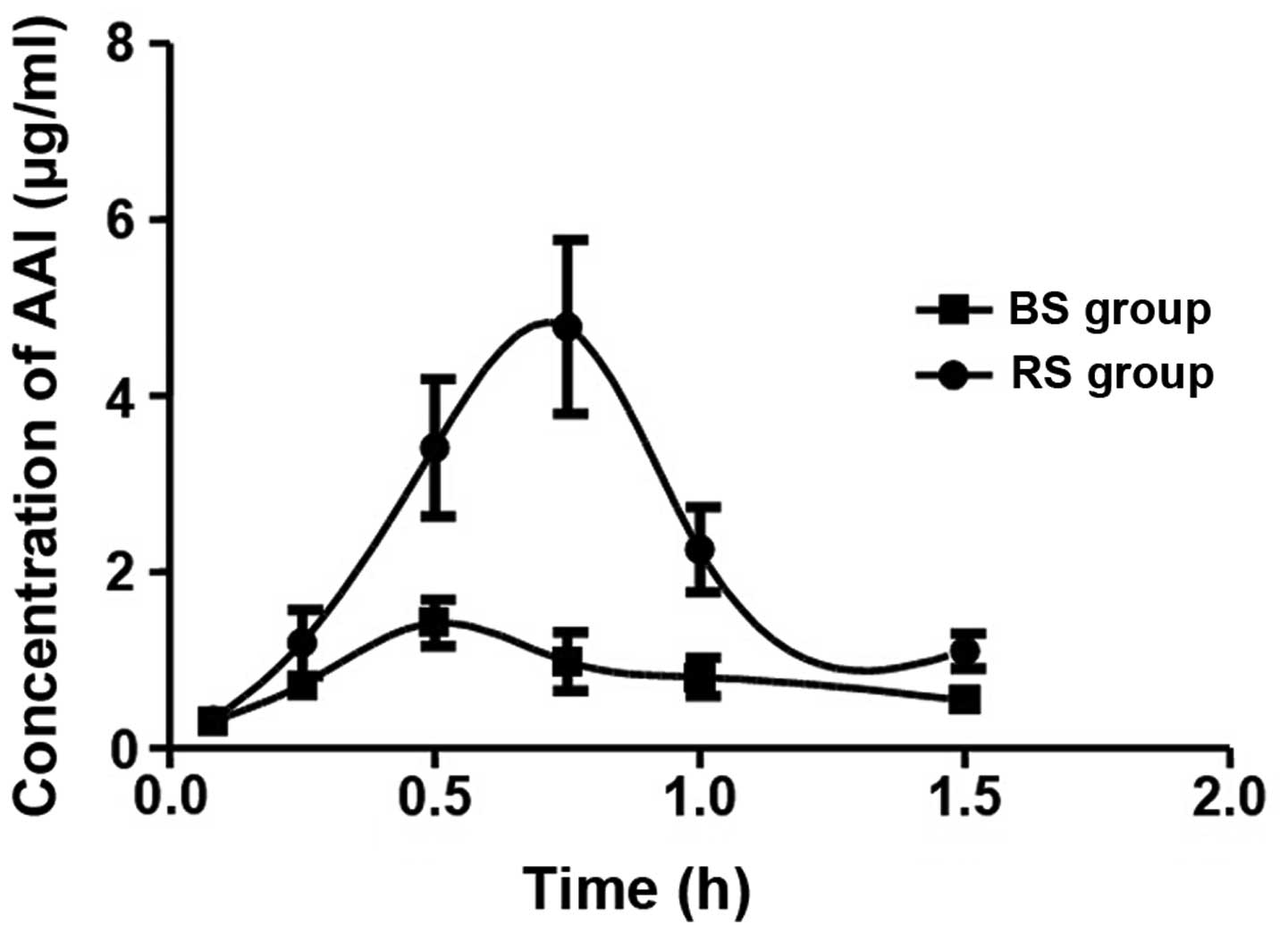
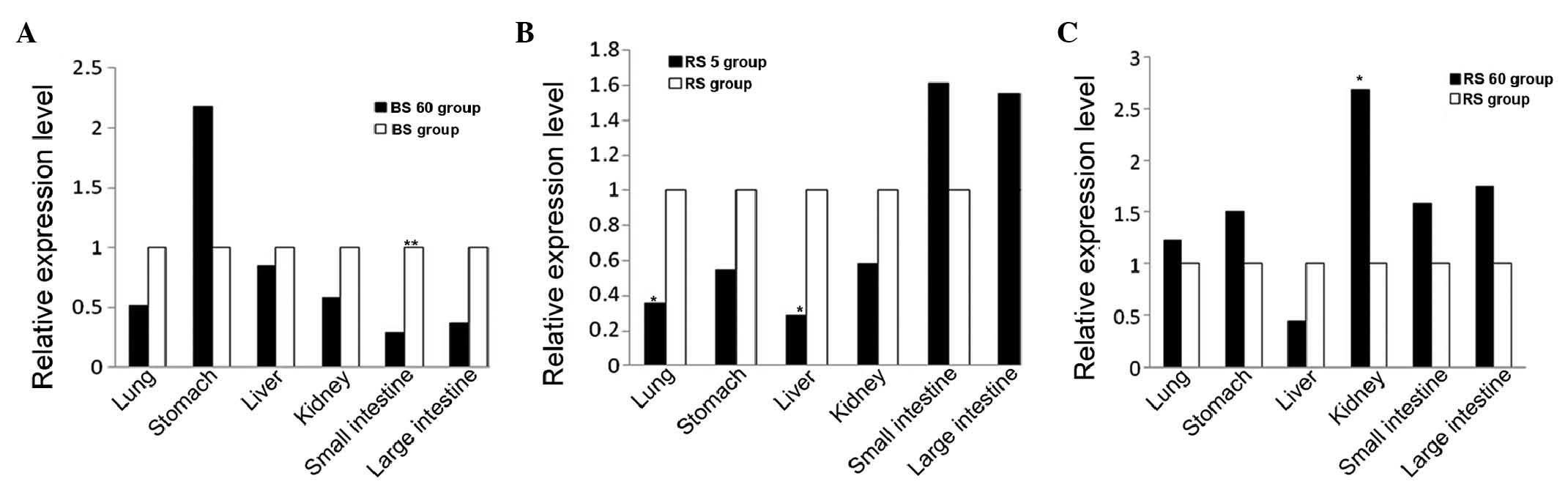
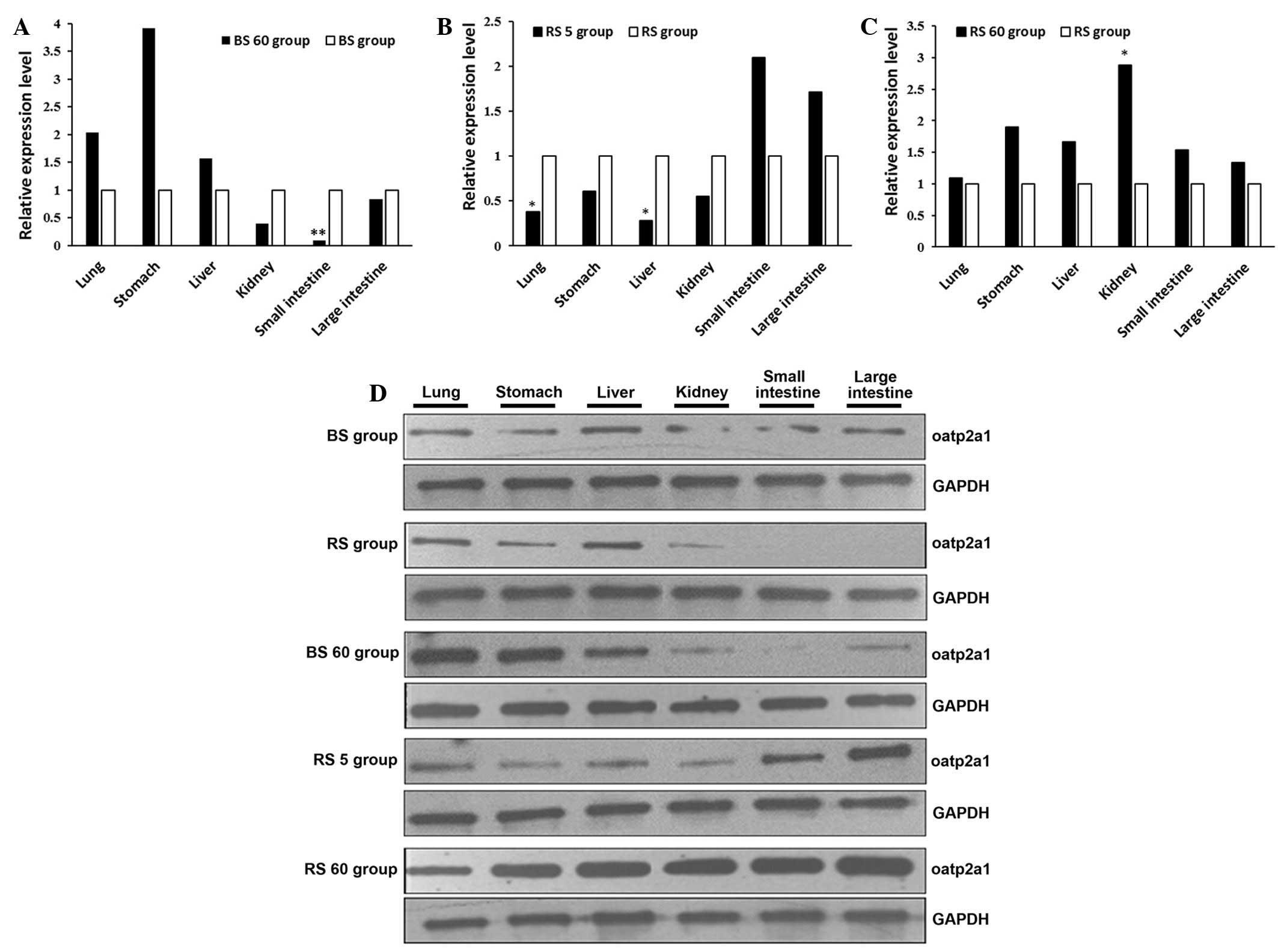
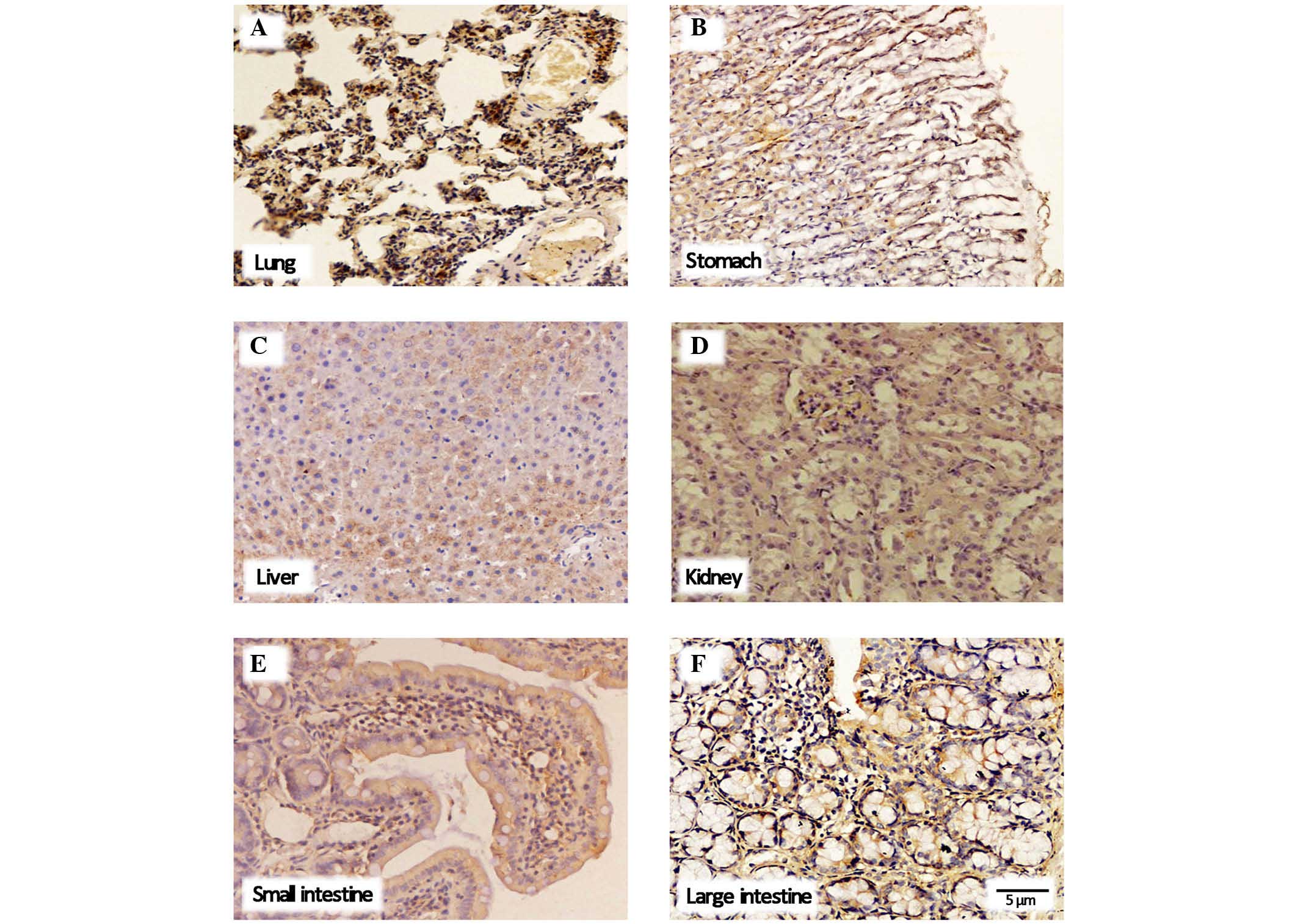
|
1
|
Cheung TP, Xue C, Leung K, Chan K and Li
CG: Aristolochic acids detected in some raw Chinese medicinal herbs
and manufactured herbal products-a consequence of inappropriate
nomenclature and imprecise labelling? Clin Toxicol (Phila).
44:371–378. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wang Y and Chan W: Determination of
aristolochic acids by high-performance liquid chromatography with
fluorescence detection. J Agric Food Chem. 62:5859–5864. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schaneberg BT and Khan IA: Analysis of
products suspected of containing Aristolochia or Asarum species. J
Ethnopharmacol. 94:245–249. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Adeyemi OO, Aigbe FR and Badru OA: The
antidiarrhoeal activity of the aqueous root extract of Aristolochia
ringens (Vahl.) Aristolochiaceae. Nig Q J Hosp Med. 22:29–33.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nitzsche D, Melzig MF and Arlt VM:
Evaluation of the cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of aristolochic
acid I-a component of Aristolochiaceae plant extracts used in
homeopathy. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 35:325–334. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang SM, Lai MN, Chen PC, Pu YS, Lai MK,
Hwang JS and Wang JD: Increased upper and lower tract urothelial
carcinoma in patients with end-stage renal disease: a nationwide
cohort study in Taiwan during 1997–2008. Biomed Res Int.
2014:1497502014.
|
|
7
|
Chau W, Ross R, Li JY, Yong TY, Klebe S
and Barbara JA: Nephropathy associated with use of a Chinese herbal
product containing aristolochic acid. Med J Aust. 194:367–368.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vanherweghem JL, Depierreux M, Tielemans
C, Abramowicz D, Dratwa M, Jadoul M, Richard C, Vandervelde D,
Verbeelen D and Vanhaelen-Fastre R: Rapidly progressive
interstitial renal fibrosis in young women: Association with
slimming regimen including Chinese herbs. Lancet. 341:387–391.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shibutani S, Dong H, Suzuki N, Ueda S,
Miller F and Grollman AP: Selective toxicity of aristolochic acids
I and II. Drug Metab Dispos. 35:1217–1222. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lai MN, Lai JN, Chen PC, Hsieh SC, Hu FC
and Wang JD: Risks of kidney failure associated with consumption of
herbal products containing Mu Tong or Fangchi: A population-based
case-control study. Am J Kidney Dis. 55:507–518. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schmeiser HH, Nortier JL, Singh R, Gamboa
da Costa G, Sennesael J, Cassuto-Viguier E, Ambrosetti D, Rorive S,
Pozdzik A, Phillips DH, et al: Exceptionally long-term persistence
of DNA adducts formed by carcinogenic aristolochic acid I in renal
tissue from patients with aristolochic acid nephropathy. Int J
Cancer. 135:502–507. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lan FL: On English translation of name of
sections in 'huangdi neijing suwen' with a comment on the English
translation of the section names in two books of English version.
Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 24:265–8. 2004.In Chinese.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xiong B and Qian H: Effects of Sijunzi
decoction and Yupingfeng powder on expression of janus
kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription signal
pathway in the brain of spleen-deficiency model rats. J Tradit Chin
Med. 33:78–84. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang X, Ren P, Wen AD, Wang LL, Zhang L
and Gao F: Pharmacokinetics of traditional Chinese syndrome and
recipe: A hypothesis and its verification (I). World J
Gastroenterol. 6:384–391. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ren P, Huang X, Li SQ, Xu SY, Wan MH, Zhou
YX, Zhou YW and Tang WF: Pharmacokinetic characteristics of ferulic
acid in patients with different syndromes of deficiency of spleen
qi, stagnation of liver qi and spleen deficiency, and excess of
stomach heat. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 4:147–151. 2006.In
Chinese. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu XN: Current concept of Spleen-Stomach
theory and Spleen deficiency syndrome in TCM. World J
Gastroenterol. 4:2–6. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ouyang S, Chen W and Kuang XB: Effects of
perindopril on expression of kidney aquaporin-2 and urine
aquaporin-2 excretion in chronic heart failure rats. Zhonghua Xin
Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 41:276–281. 2013.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhao WX, Gao J, Shi YY and Xu SQ: Effects
of different fluid resuscitation regimes on lung injury and
expression of pulmonary aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 5 in uncontrolled
hemorrhagic shock in rats. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue.
21:282–285. 2009.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu LX, Guo CX, Qu Q, Yu J, Chen WQ, Wang
G, Fan L, Li Q, Zhang W and Zhou HH: Effects of natural products on
the function of human organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B1.
Xenobiotica. 42:339–348. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Csanaky IL, Lu H, Zhang Y, Ogura K,
Choudhuri S and Klaassen CD: Organic anion-transporting polypeptide
1b2 (Oatp1b2) is important for the hepatic uptake of unconjugated
bile acids: Studies in Oatp1b2-null mice. Hepatology. 53:272–281.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Meyer zu Schwabedissen HE, Ware JA,
Finkelstein D, Chaudhry AS, Mansell S, Leon-Ponte M, Strom SC,
Zaher H, Schwarz UI, Freeman DJ, et al: Hepatic organic anion
transporting polypeptide transporter and thyroid hormone receptor
interplay determines cholesterol and glucose homeostasis.
Hepatology. 54:644–654. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kanai N, Lu R, Satriano JA, Bao Y, Wolkoff
AW and Schuster VL: Identification and characterization of a
prostaglandin transporter. Science. 268:866–869. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mandery K, Bujok K, Schmidt I, Wex T,
Treiber G, Malfertheiner P, Rau TT, Amann KU, Brune K, Fromm MF and
Glaeser H: Influence of cyclooxygenase inhibitors on the function
of the prostaglandin transporter organic anion-transporting
polypeptide 2A1 expressed in human gastroduodenal mucosa. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 332:345–351. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Nomura T, Chang HY, Lu R, Hankin J, Murphy
RC and Schuster VL: Prostaglandin signaling in the renal collecting
duct: Release, reuptake and oxidation in the same cell. J Biol
Chem. 280:28424–28429. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hu ZY: Disposition pathway-dependent
approach for predicting organic anion-transporting
polypeptide-mediated drug-drug interactions. Clin Pharmacokinet.
52:433–441. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shirasu T, Koyama H, Miura Y, Hoshina K,
Kataoka K and Watanabe T: Nanoparticles effectively target
rapamycin delivery to sites of experimental aortic aneurysm in
rats. PLoS One. 11:e01578132016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhao N, Zhang W, Guo Y, Jia H, Zha Q, Liu
Z, Xu S and Lu A: Effects on neuroendocrinoimmune network of
Lizhong Pill in the reserpine induced rats with spleen deficiency
in traditional Chinese medicine. J Ethnopharmacol. 133:454–459.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Corona-Meraz FI, Navarro-Hernández RE,
Ruíz-Quezada SL, Madrigal-Ruíz PM, Castro-Albarrán J,
Chavarría-Ávila E, Guzmán-Ornelas MO, Gómez-Bañuelos E, Petri MH,
Ramírez-Cedano JI, Aguilar-Aldrete ME, Ríos-Ibarra C and
Vázquez-Del Mercado M: Inverse relationship of the CMKLR1 relative
expression and chemerin serum levels in obesity with dysmetabolic
phenotype and insulin resistance. Mediators Inflamm.
2016:30853902016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li ZH, Wang J, Cai RL, Wang YW and Hu JP:
Establishment and evaluation of a rat model of ulcerative colitis
with syndrome of dampness stagnancy due to spleen deficiency. Zhong
Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 10:918–924. 2012.In Chinese. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li LS, Qu RY, Wang W and Guo H:
Significance of changes of gastrointestinal peptides in blood and
ileum of experimental spleen deficiency rats. World J
Gastroenterol. 9:553–556. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen Y, Sun BG, Zhang SJ, Chen ZX, Hardi
CF and Xiang T: Observations of TCRVβ gene expression in rats with
dampness syndrome. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2014:3736082014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Sponaas AM, Freitas do Rosario AP, Voisine
C, Mastelic B, Thompson J, Koernig S, Jarra W, Renia L, Mauduit M,
Potocnik AJ and Langhorne J: Migrating monocytes recruited to the
spleen play an important role in control of blood stage malaria.
Blood. 114:5522–5531. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Grant SJ, Schnyer RN, Chang DH, Fahey P
and Bensoussan A: Interrater reliability of chinese medicine
diagnosis in people with prediabetes. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2013:7108922013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fuchs TC, Mally A, Wool A, Beiman M and
Hewitt P: An exploratory evaluation of the utility of
transcriptional and urinary kidney injury biomarkers for the
prediction of aristolochic acid-induced renal injury in male rats.
Vet Pathol. 51:680–694. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
McDaniel LP, Elander ER, Guo X, Chen T,
Arlt VM and Mei N: Mutagenicity and DNA adduct formation by
aristolochic acid in the spleen of Big Blue® rats.
Environ Mol Mutagen. 53:358–368. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li J and Liu BY: Evaluation of clinical
therapeutic effect in Jing yue quan shu (Jingyue's Complete Works).
Zhonghua Yi Shi Za Zhi. 39:59–61. 2009.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pan AZ, Dong XA, Zhang SJ, Xiang T, Chen
ZX and Lin YW: Study on mRNA and protein expressions of organic
anion transporting polypeptide (oatp2b1) in rats with high fat diet
and overstrain induced Pi deficiency syndrome. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi
Jie He Za Zhi. 33:953–957. 2013.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Takanohashi T, Kubo S, Arisaka H, Shinkai
K and Ubukata K: Contribution of organic anion transporting
polypeptide (OATP) 1B1 and OATP1B3 to hepatic uptake of nateglinide
and the prediction of drug-drug interactions via these
transporters. J Pharm Pharmacol. 64:199–206. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Choi MK, Shin HJ, Choi YL, Deng JW, Shin
JG and Song IS: Differential effect of genetic variants of Na
(+)-taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide (NTCP) and organic
anion-transporting polypeptide 1B1 (OATP1B1) on the uptake of
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Xenobiotica. 41:24–34. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Dong X, Pan AZ and Sun BG: Organic anion
transporting polypeptide (oatp4a1) mRNA and protein expressions in
high fat and over-fatigue impairing Pi rats. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi
Jie He Za Zhi. 32:1223–1226. 2012.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|