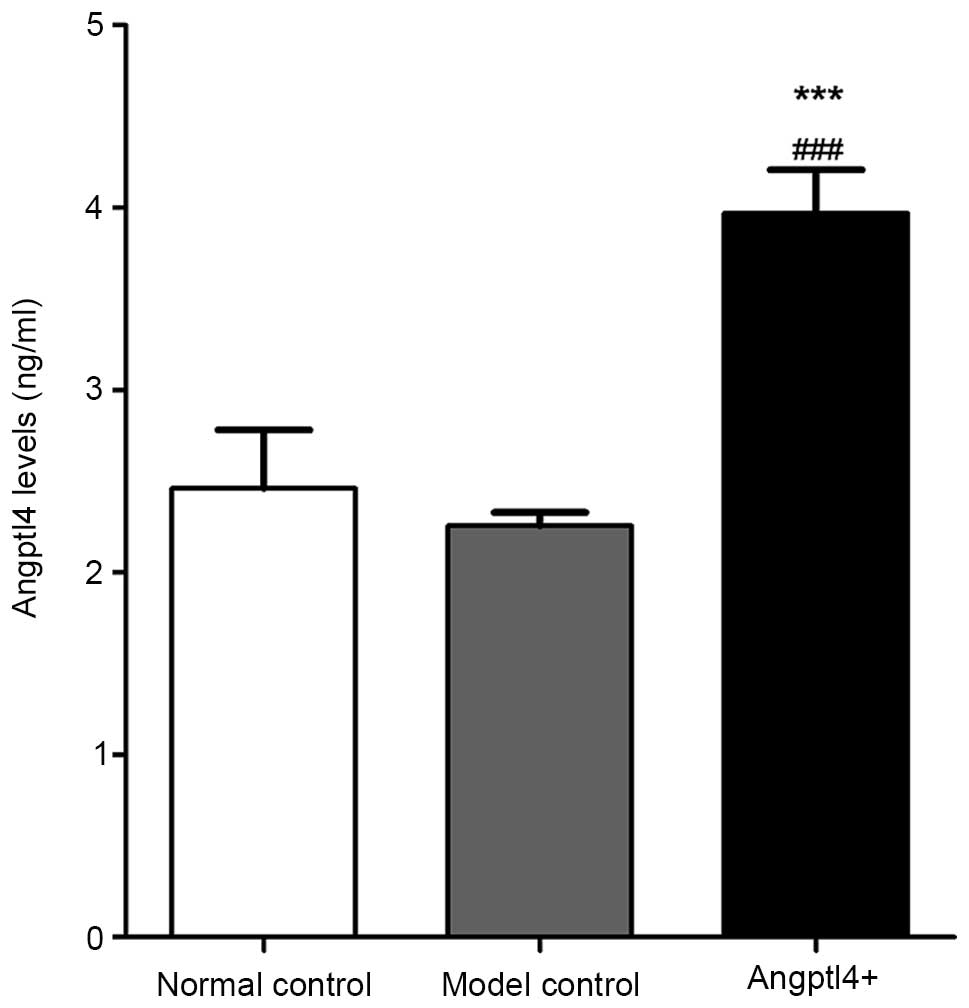
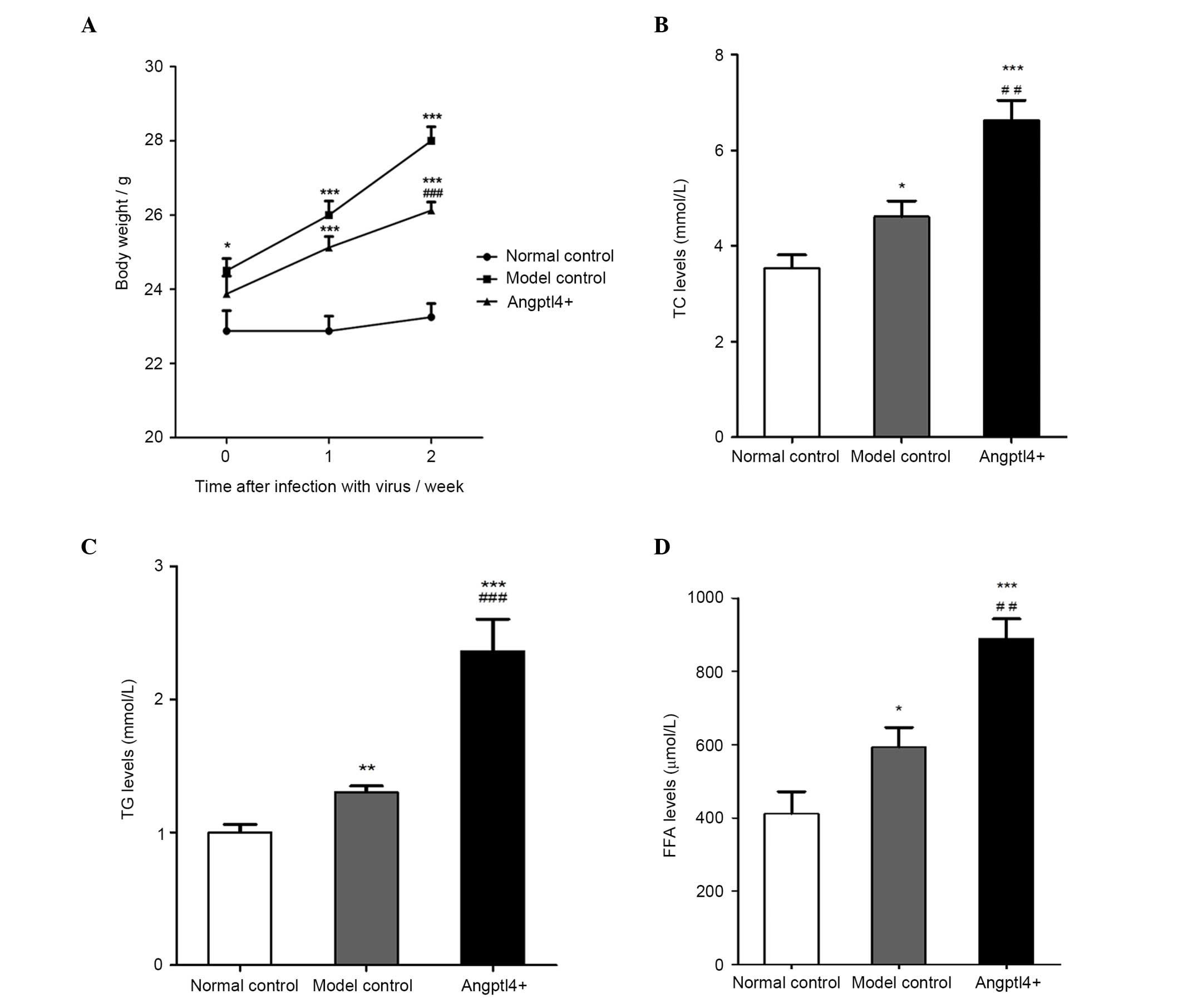
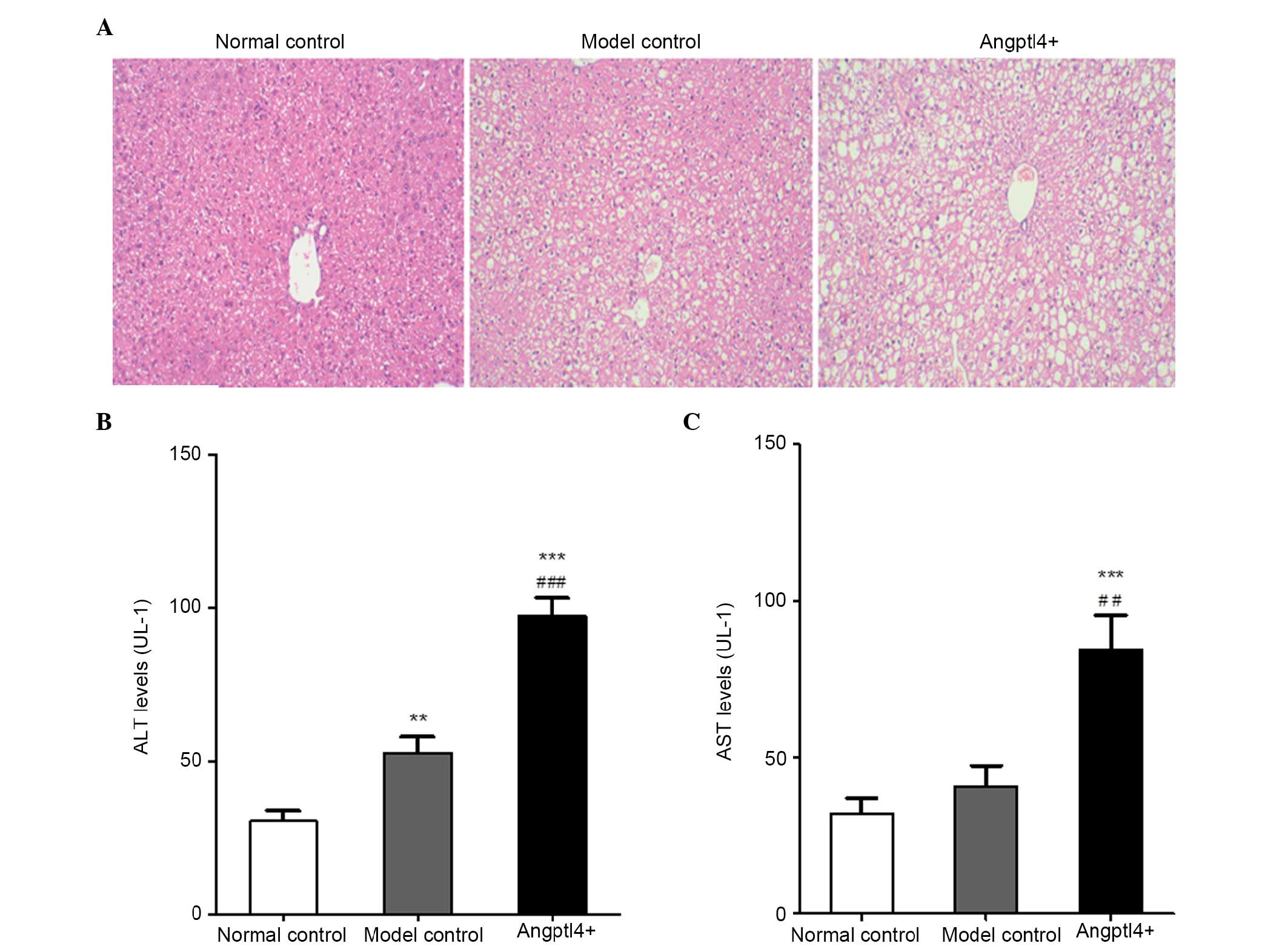
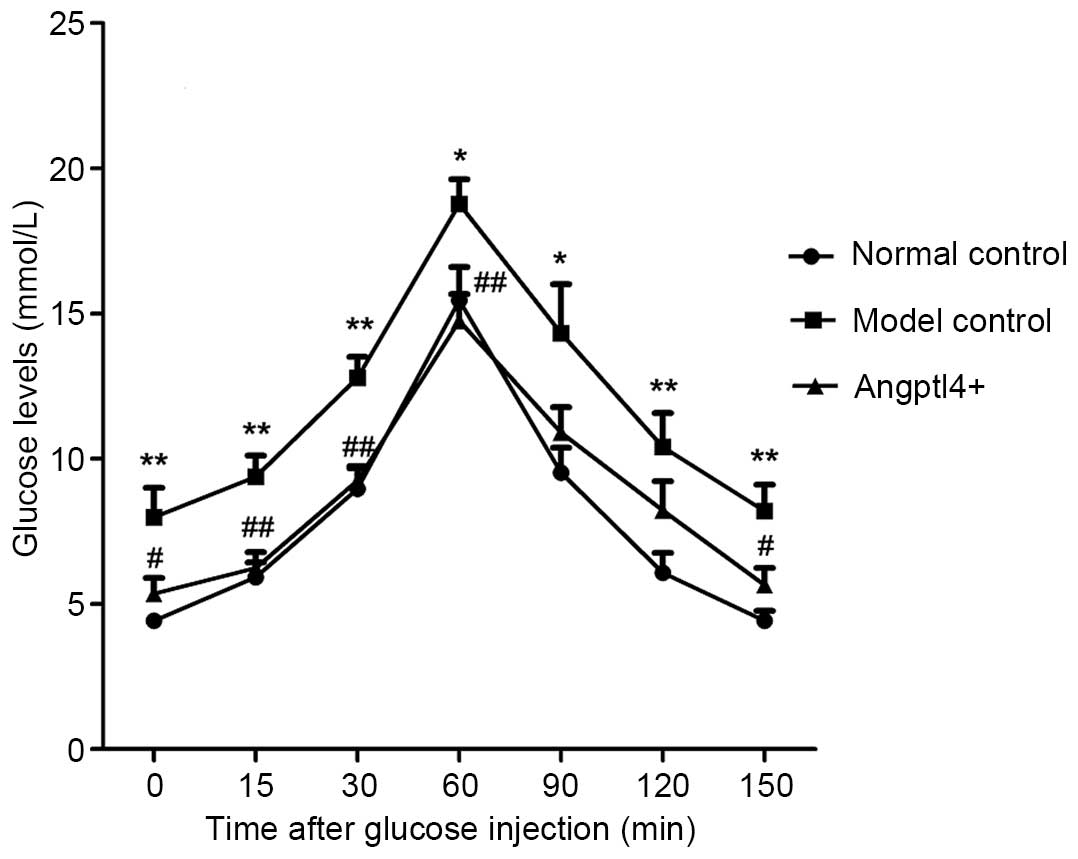
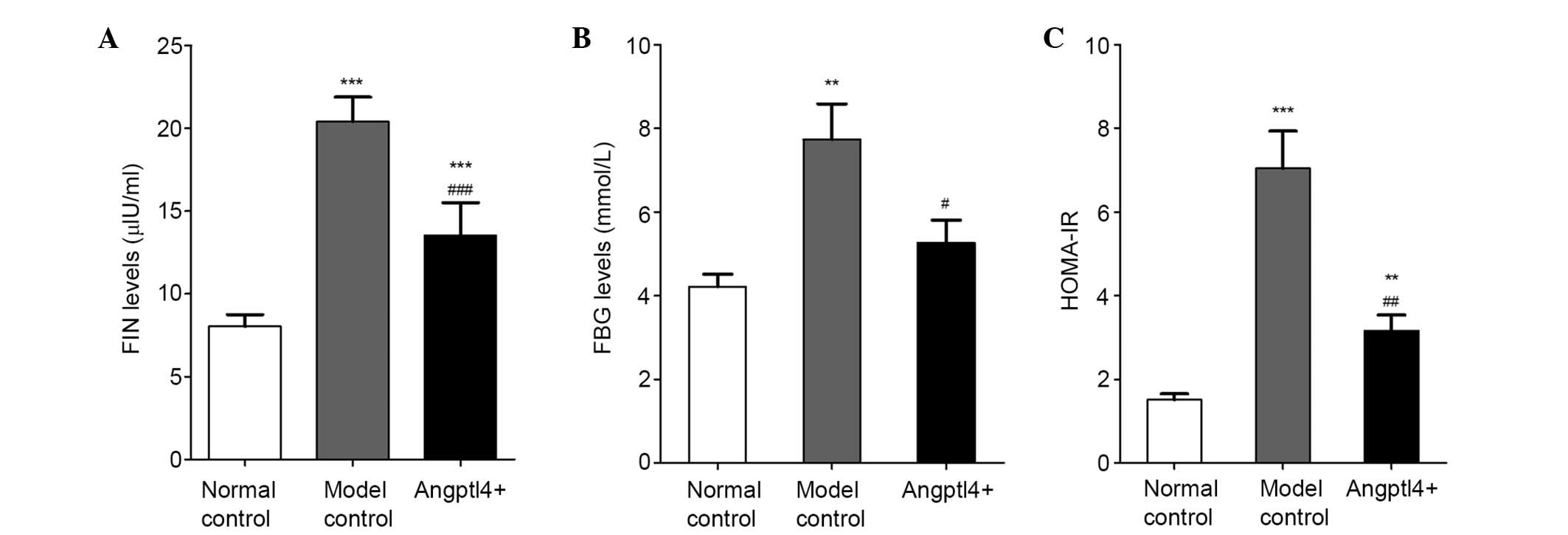
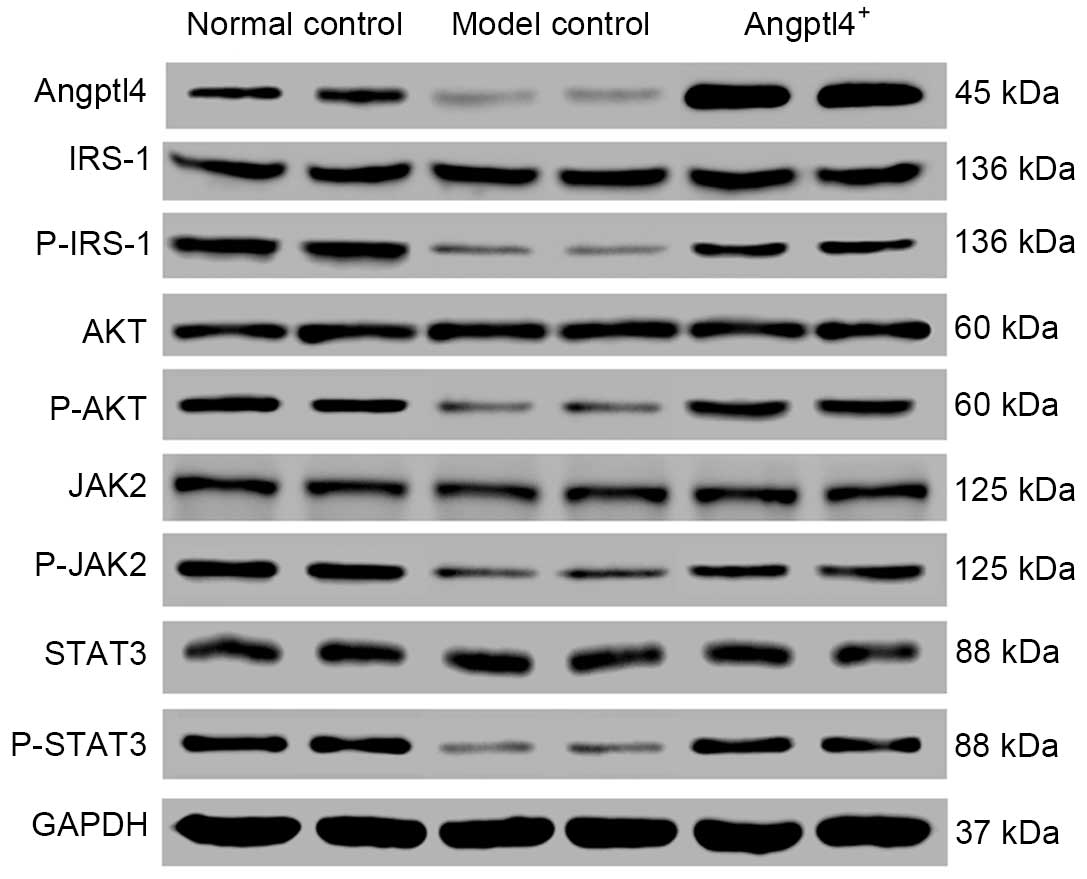
|
1
|
Kershaw EE and Flier JS: Adipose tissue as
an endocrine organ. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 89:2548–2556. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Friedman JM and Halaas JL: Leptin and the
regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature. 395:763–770. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Matsuzawa Y, Funahashi T, Kihara S and
Shimomura I: Adiponectin and metabolic syndrome. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 24:29–33. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Yoon JC, Chickering TW, Rosen ED, Dussault
B, Qin Y, Soukas A, Friedman JM, Holmes WE and Spiegelman BM:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma target genen
encoding a novel angiopoietin-related protein associated with
adipose differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 20:5343–5349. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kersten S, Mandard S, Tan NS, Escher P,
Metzger D, Chambon P, Gonzalez FJ, Desvergne B and Wahli W:
Characterization of the fasting-induced adipose factor FIAF, a
novel peroxisome proliferator activated receptor target gene. J
Biol Chem. 275:28488–28493. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Koster A, Chao YB, Mosior M, Ford A,
Gonzalez-DeWhitt PA, Hale JE, Li D, Qiu Y, Fraser CC, Yang DD, et
al: Transgenic angiopoietin-like (angptl)4 overexpression and
targeted disrupt ion of angptl4 and angptl3: Regulation of
triglyceride metabolism. Endocrinology. 146:4943–4950. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ge H, Cha JY, Gopal H, Harp C, Yu X, Repa
JJ and Li C: Differential regulation and properties of
angiopoietin-like proteins 3 and 4. J Lipid Res. 46:1484–1490.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sanderson LM, Degenhardt T, Koppen A,
Kalkhoven E, Desvergne B, Müller M and Kersten S: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor beta/delta (PPARbeta/delta) but not
PPARalpha serves as a plasma free fatty acid sensor in liver. Mol
Cell Biol. 29:6257–6267. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mattijssen F and Kersten S: Regulation of
triglyceride metabolism by Angiopoietin-like proteins. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1821:782–789. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Merkel M, Eckel RH and Goldberg IJ:
Lipoprotein lipase: Genetics, lipid uptake, and regulation. J Lipid
Res. 43:1997–2006. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Le Jan S, Amy C, Cazes A, Monnot C,
Lamandé N, Favier J, Philippe J, Sibony M, Gasc JM, Corvol P and
Germain S: Angiopoietin-like 4 is a proangiogenic factor produced
during ischemia and in conventional renal cell carcinoma. Am J
Pathol. 162:1521–1528. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu A, Lam MC, Chan KW, Wang Y, Zhang J,
Hoo RL, Xu JY, Chen B, Chow WS, Tso AW and Lam KS:
Angiopoietin-like protein4 decreases blood glucose and improves
glucose tolerance but induces hyperlipidemia and hepatic steatosis
in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:6086–6091. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Mandard S, Zandbergen F, van Straten E,
Wahli W, Kuipers F, Müller M and Kersten S: The fasting-induced
adipose factor/angiopoietin-like protein 4 is physically associated
with lipoproteins and governs plasma lipid levels and adiposity. J
Biol Chem. 281:934–944. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Reitman S and Frankel S: A colorimetric
method for the determination of serum glutamic oxalacetic and
glutamic pyruvic transaminases. Am J Clin Pathol. 28:56–63. 1957.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cusi K, Maezono K, Oaman A, Pendergrass M,
Patti ME, Pratipanawatr T, DeFronzo RA, Kahn CR and Mandarino LJ:
Insulin resistance differentially affects the pi3-kinase- and MAP
kinase-mediated signaling in human muscle. J Clin Invest.
105:311–320. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang WZ, Zhao SM and Gao SZ: Research
progress on leptin-mediated JAK/STAT signaling pathway in lipid
metabolism. Chin J Cell Biol. 33:584–589. 2011.
|
|
17
|
Kim HK, Youn BS, Shin MS, Namkoong C, Park
KH, Baik JH, Kim JB, Park JY, Lee KU, Kim YB and Kim MS:
Hypothalamic Angptl4/Fiaf is a novel regulator of food intake and
body weight. Diabetes. 59:2772–2780. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yoshida K, Shimizugawa T, Ono M and
Furukawa H: Angiopoietin-like protein 4 is a potent
hyperlipidemia-inducing factor in mice and inhibitor of lipoprotein
lipase. J Lipid Res. 43:1770–1772. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Oike Y, Akao M, Kubota Y and Suda T:
Angiopoietin-like proteins: Potential new targets for metabolic
syndrome therapy. Trends Mol Med. 11:473–479. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee CH, Olson P and Evans RM: Minireview:
Lipid metabolism, metabolic diseases, and peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors. Endocrinology. 144:2201–2207.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guilherme A, Virbasius JV, Puri V and
Czech MP: Adipocyte dysfunctions linking obesity to insulin
resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:367–377.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Samuel VT, Petersen KF and Shulman GI:
Lipid-induced insulin resistance: Unravelling the mechanism.
Lancet. 375:2267–2277. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gray NE, Lam LN, Yang K, Zhou AY, Koliwad
S and Wang JC: Angiopoietin-like 4 (Angptl4) protein is a
physiological mediator of intracellular lipolysis in murine
adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 287:8444–8456. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ono H, Shimano H, Katagiri H, Yahagi N,
Sakoda H, Onishi Y, Anai M, Ogihara T, Fujishiro M, Viana AY, et
al: Hepatic Akt activation induces marked hypoglycemia,
hepatomegaly, and hypertriglyceridemia with sterol regulatory
element binding protein involvement. Diabetes. 52:2905–2913. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Stiles B, Wang Y, Stahl A, Bassilian S,
Lee WP, Kim YJ, Sherwin R, Devaskar S, Lesche R, Magnuson MA and Wu
H: Liver-specific deletion of negative regulator Pten results in
fatty liver and insulin hypersensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:2082–2087. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Mizutani N, Ozaki N, Seino Y, Fukami A,
Sakamoto E, Fukuyama T, Sugimura Y, Nagasaki H, Arima H and Oiso Y:
Reduction of insulin signaling upregulates angiopoietin-like
protein 4 through elevated free fatty acids in diabetic mice. Exp
Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 120:139–144. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yamada T, Ozaki N, Kato Y, Miura Y and
Oiso Y: Insulin downregulates angiopoietin-like protein 4 mRNA in
3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 347:1138–1144. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Prudente S, Morini E and Trischitta V:
Insulin signaling regulating genes: Effect on T2DM and
cardiovascular risk. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 5:682–693. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Karlsson HK and Zierath JR: Insulin
signaling and glucose transport in insulin resistant human skeletal
muscle. Cell Biochem Biophys. 48:103–113. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hou M, Cui J, Liu J, Liu F, Jiang R, Liu
K, Wang Y, Yin L, Liu W and Yu B: Angiopoietin-like 4 confers
resistance to hypoxia/serum deprivation-induced apoptosis through
PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 signaling pathways in mesenchymal stem cells.
PLoS One. 9:e858082014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chong HC, Chan JS, Goh CQ, Gounko NV, Luo
B, Wang X, Foo S, Wong MT, Choong C, Kersten S and Tan NS:
Angiopoietin-like 4 stimulates STAT3-mediated iNOS expression and
enhances angiogenesis to accelerate wound healing in diabetic mice.
Mol Ther. 22:1593–1604. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yan ZK, Yang ZJ and Chen F: Effect of
electroacupuncture stimulation of 'Housanli' (ST 36) and 'Zhongwan'
(CV 12) on serum leptin and hepatocellular JAK 2-STAT 3 signaling
in obese rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 40:1–5. 2015.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|