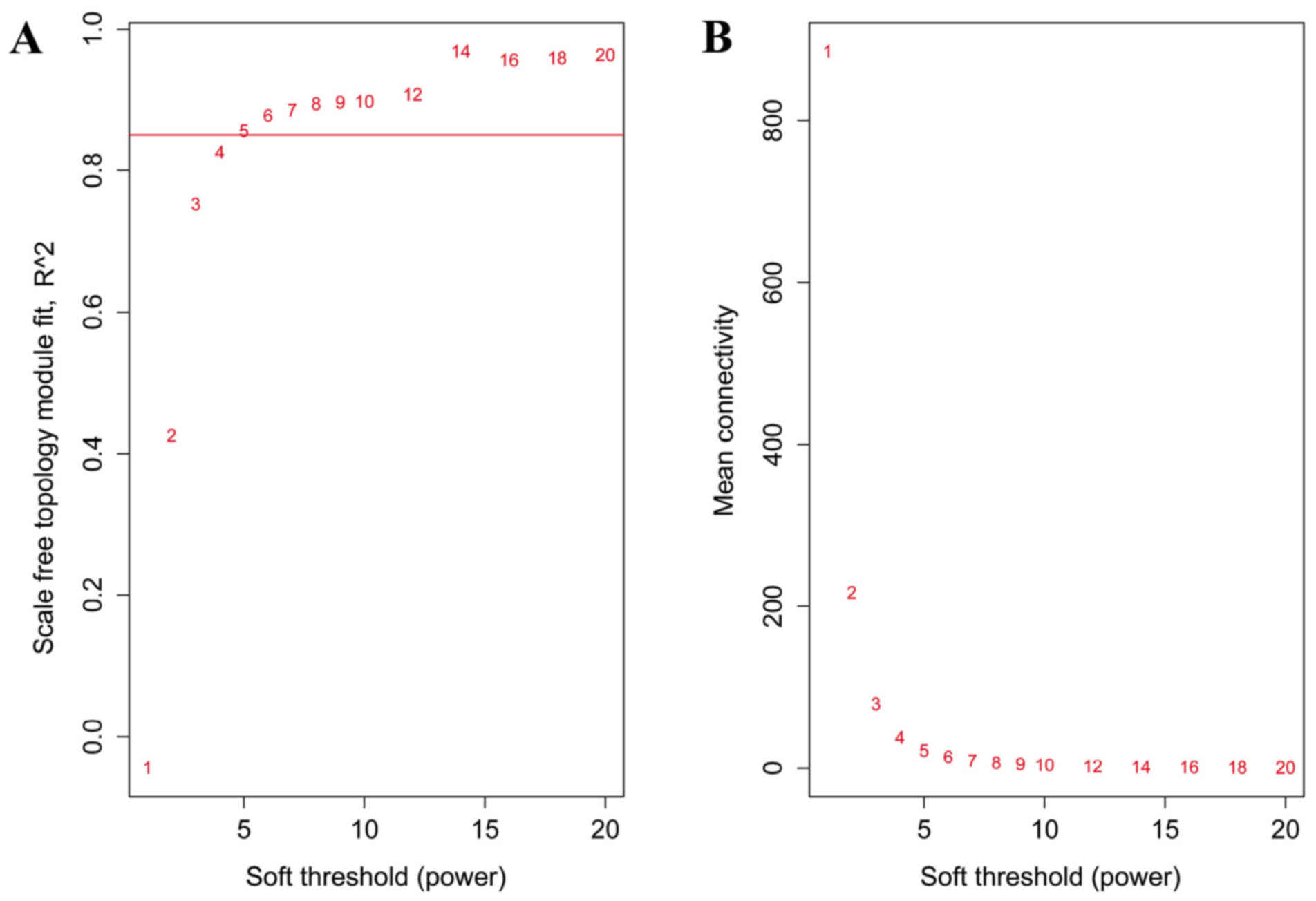
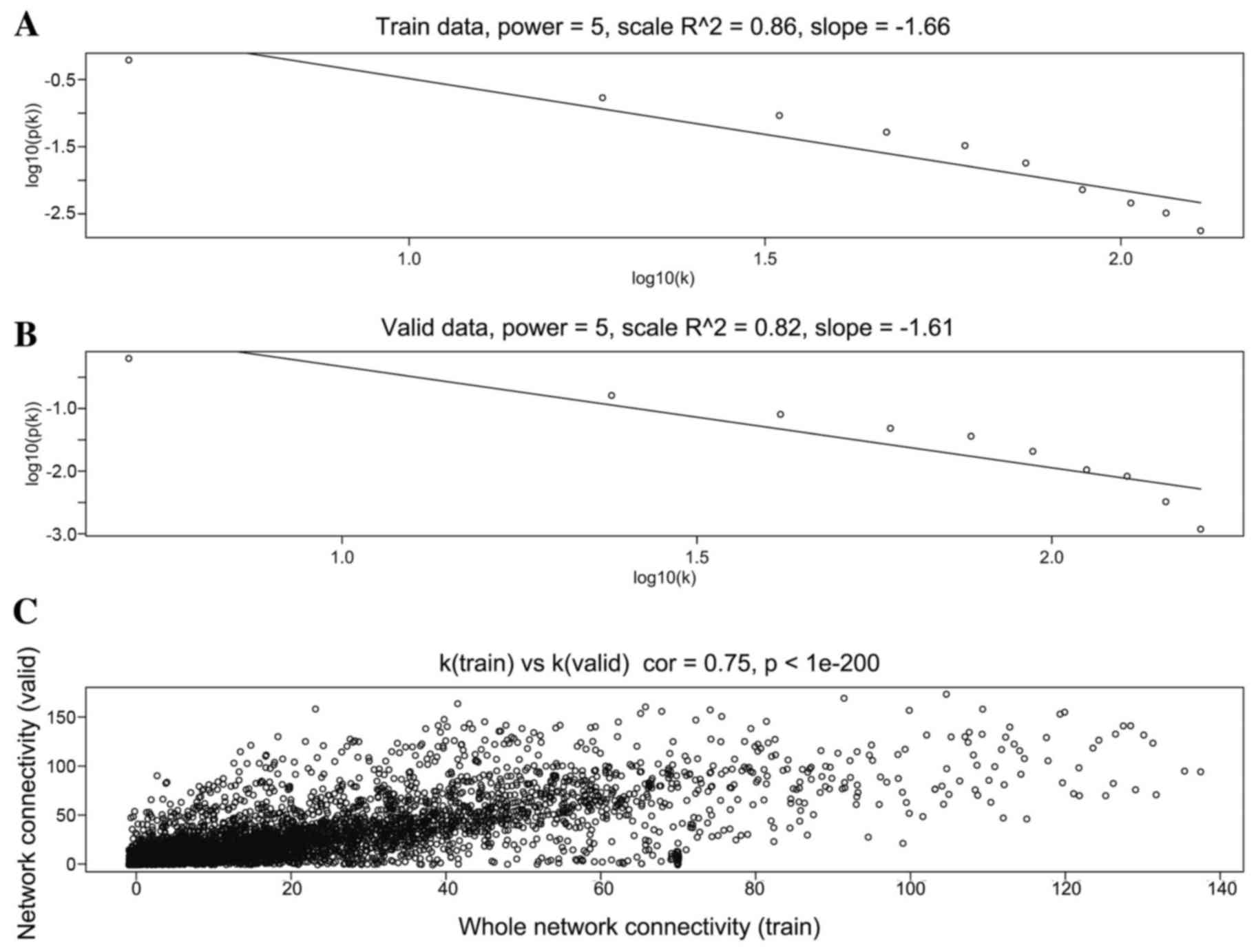
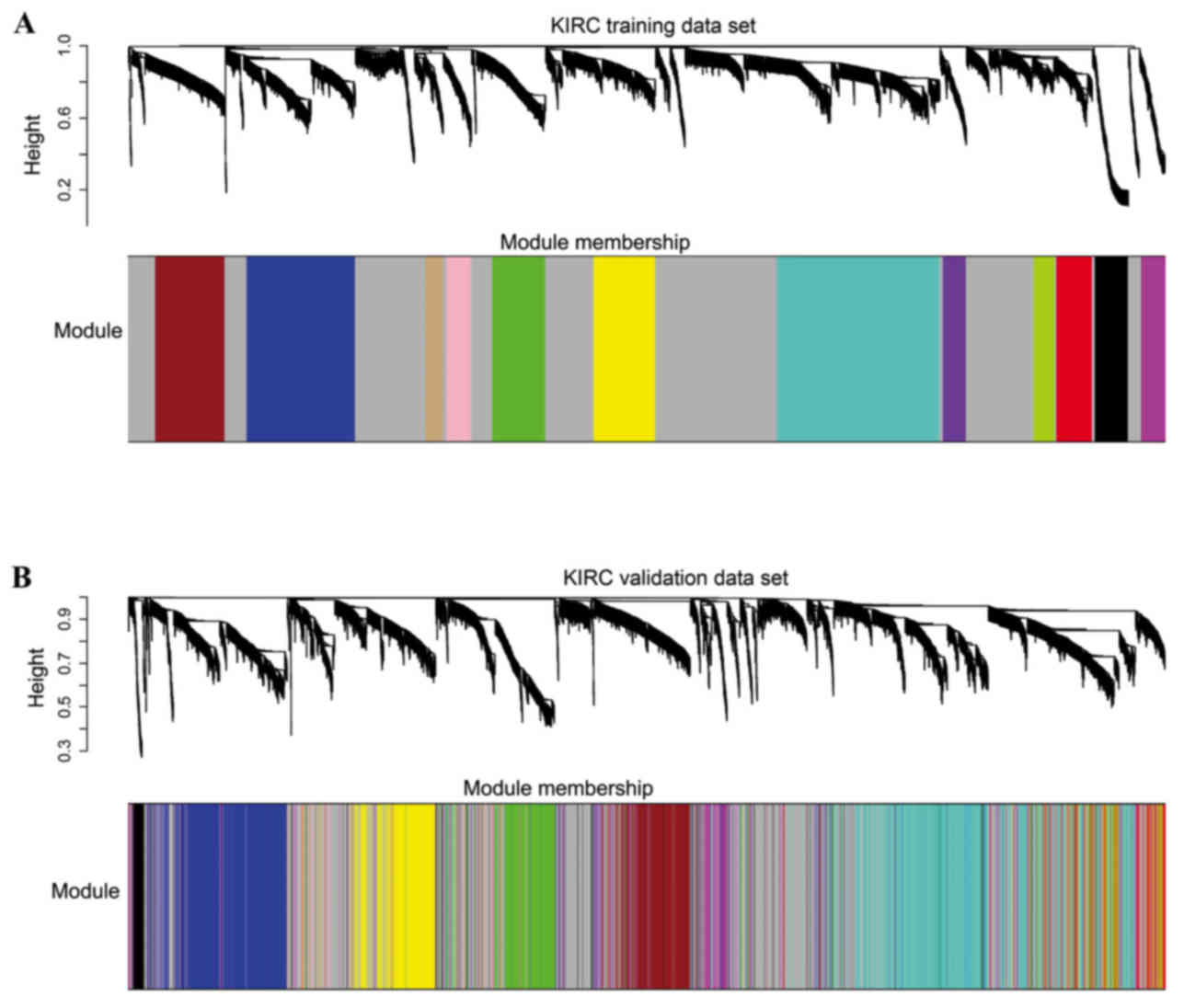
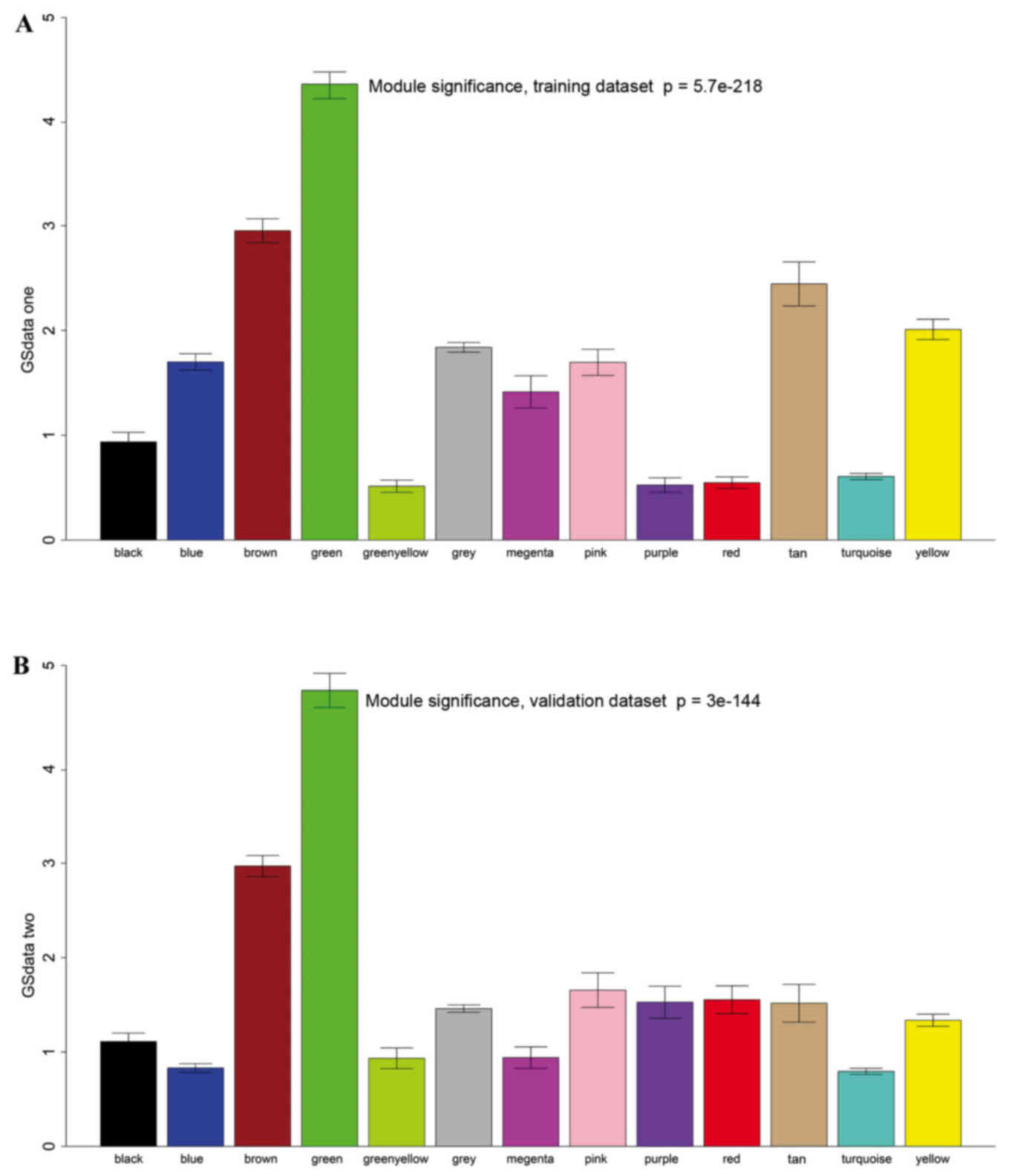
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Linehan WM: Genetic basis of kidney
cancer: Role of genomics for the development of disease-based
therapeutics. Genome Res. 22:2089–2100. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mickisch GH: Principles of nephrectomy for
malignant disease. BJU Int. 89:488–495. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Janzen NK, Kim HL, Figlin RA and
Belldegrun AS: Surveillance after radical or partial nephrectomy
for localized renal cell carcinoma and management of recurrent
disease. Urol Clin North Am. 30:843–852. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Robb VA, Magdalena K, Klein-Szanto AJ and
Henske EP: Activation of the mTOR signaling pathway in renal clear
cell carcinoma. J Urol. 177:346–352. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Guo G, Gui Y, Gao S, Tang A, Hu X, Huang
Y, Jia W, Li Z, He M, Sun L, et al: Frequent mutations of genes
encoding ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis pathway components in clear
cell renal cell carcinoma. Nat Genet. 44:17–19. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Dormoy V, Danilin S, Lindner V, Thomas L,
Rothhut S, Coquard C, Helwig JJ, Jacqmin D, Lang H and Massfelder
T: The sonic hedgehog signaling pathway is reactivated in human
renal cell carcinoma and plays orchestral role in tumor growth. Mol
Cancer. 8:1232009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tang SW, Chang WH, Su YC, Chen YC, Lai YH,
Wu PT, Hsu CI, Lin WC, Lai MK and Lin JY: MYC pathway is activated
in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and essential for proliferation
of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 273:35–43.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lebdai S, Verhoest G, Parikh H, Jacquet
SF, Bensalah K, Chautard D, Leclercq N Rioux, Azzouzi AR and Bigot
P: Identification and validation of TGFBI as a promising prognosis
marker of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Urol Oncol.
33:69.e11–e18. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Liu X, Wang J and Sun G: Identification of
key genes and pathways in renal cell carcinoma through expression
profiling data. Kidney Blood Press Res. 40:288–297. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Valletti A, Gigante M, Palumbo O, Carella
M, Divella C, Sbisà E, Tullo A, Picardi E, D'Erchia AM, Battaglia
M, et al: Genome-wide analysis of differentially expressed genes
and splicing isoforms in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. PLoS One.
8:e784522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Langfelder P and Horvath S: WGCNA: An R
package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC
Bioinformatics. 9:5592008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for annotation,
visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 4:P32003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kidokoro T, Tanikawa C, Furukawa Y,
Katagiri T, Nakamura Y and Matsuda K: CDC20, a potential cancer
therapeutic target, is negatively regulated by p53. Oncogene.
27:1562–1571. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gardner FP, Joseph RW, Serie D, Hilton TW,
Parasramka M, Eckel-Passow J, Cheville J and Bradley C: Association
of topoisomerase II expression and cancer-specific death in
patients with surgically resected clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
J Clin Oncol. 31 Suppl 6:abstr 446. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen D, Maruschke M, Riesenberg R,
Zimmermann W, Stief CG and Buchner A: MP29-03 TET3, hells, TOP2A
and ATAD2 are novel independent prognostic markers in advanced
renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 191:e3052014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wong N, Yeo W, Wong WL, Wong NL, Chan KY,
Mo FK, Koh J, Chan SL, Chan AT, Lai PB, et al: TOP2A overexpression
in hepatocellular carcinoma correlates with early age onset,
shorter patients survival and chemoresistance. Int J Cancer.
124:644–652. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lan J, Huang HY, Lee SW, Chen TJ, Tai HC,
Hsu HP, Chang KY and Li CF: TOP2A overexpression as a poor
prognostic factor in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Tumour
Biol. 35:179–187. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jain M, Zhang L, He M, Zhang YQ, Shen M
and Kebebew E: TOP2A is overexpressed and a therapeutic target for
adrenocortical carcinoma. Endocr Relat Cancer. 20:361–370. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Subhash VV, Tan SH, Tan WL, Yeo MS, Xie C,
Wong FY, Kiat ZY, Lim R and Yong WP: GTSE1 expression represses
apoptotic signaling and confers cisplatin resistance in gastric
cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 15:5502015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu Q, Su PF, Zhao S and Shyr Y:
Transcriptome-wide signatures of tumor stage in kidney renal clear
cell carcinoma: Connecting copy number variation, methylation and
transcription factor activity. Genome Med. 6:1172014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rath O and Kozielski F: Kinesins and
cancer. Nature Rev Cancer. 12:527–539. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sakowicz R, Finer JT, Beraud C, Crompton
A, Lewis E, Fritsch A, Lee Y, Mak J, Moody R, Turincio R, et al:
Antitumor activity of a kinesin inhibitor. Cancer Res.
64:3276–3280. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Taniwaki M, Takano A, Ishikawa N, Yasui W,
Inai K, Nishimura H, Tsuchiya E, Kohno N, Nakamura Y and Daigo Y:
Activation of KIF4A as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic
target for lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 13:6624–6631. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gnjatic S, Cao Y, Reichelt U, Yekebas EF,
Nölker C, Marx AH, Erbersdobler A, Nishikawa H, Hildebrandt Y,
Bartels K, et al: NY-CO-58/KIF2C is overexpressed in a variety of
solid tumors and induces frequent T cell responses in patients with
colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 127:381–393. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Minakawa Y, Kasamatsu A, Koike H, Higo M,
Nakashima D, Kouzu Y, Sakamoto Y, Ogawara K, Shiiba M, Tanzawa H
and Uzawa K: Kinesin family member 4A: A potential predictor for
progression of human oral cancer. PLoS One. 8:e859512013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jiang P and Zhang D: Maternal embryonic
leucine zipper kinase (MELK): A novel regulator in cell cycle
control, embryonic development, and cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
14:21551–21560. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ganguly R, Mohyeldin A, Thiel J, Kornblum
HI, Beullens M and Nakano I: MELK-a conserved kinase: Functions,
signaling, cancer, and controversy. Clin Transl Med. 4:112015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pickard MR, Green AR, Ellis IO, Caldas C,
Hedge VL, Mourtada-Maarabouni M and Williams GT: Dysregulated
expression of Fau and MELK is associated with poor prognosis in
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 11:R602009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chung S and Nakamura Y: MELK inhibitor,
novel molecular targeted therapeutics for human cancer stem cells.
Cell Cycle. 12:1655–1656. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hsu PK, Chen HY, Yeh YC, Yen CC, Wu YC,
Hsu CP, Hsu WH and Chou TY: TPX2 expression is associated with cell
proliferation and patient outcome in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. J Gastroenterol. 49:1231–1240. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yan L, Li S, Xu C, Zhao X, Hao B, Li H and
Qiao B: Target protein for Xklp2 (TPX2), a microtubule-related
protein, contributes to malignant phenotype in bladder carcinoma.
Tumor Biol. 34:4089–4100. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Jiang P, Shen K, Wang X, Song H, Yue Y and
Liu T: TPX2 regulates tumor growth in human cervical carcinoma
cells. Mol Med Rep. 9:2347–2351. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Huang Y, Guo W and Kan H: TPX2 Is a
prognostic marker and contributes to growth and metastasis of human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 15:18148–18161. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|