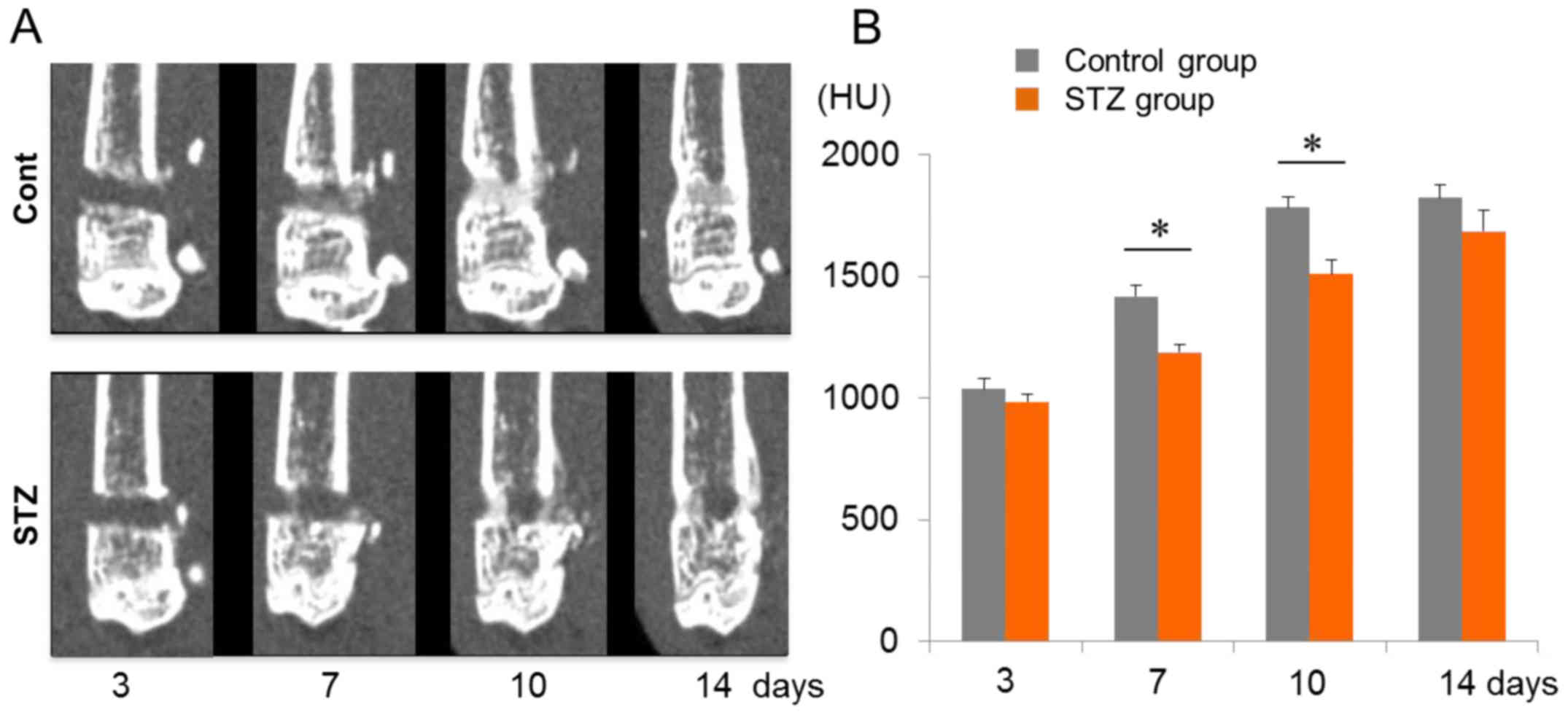
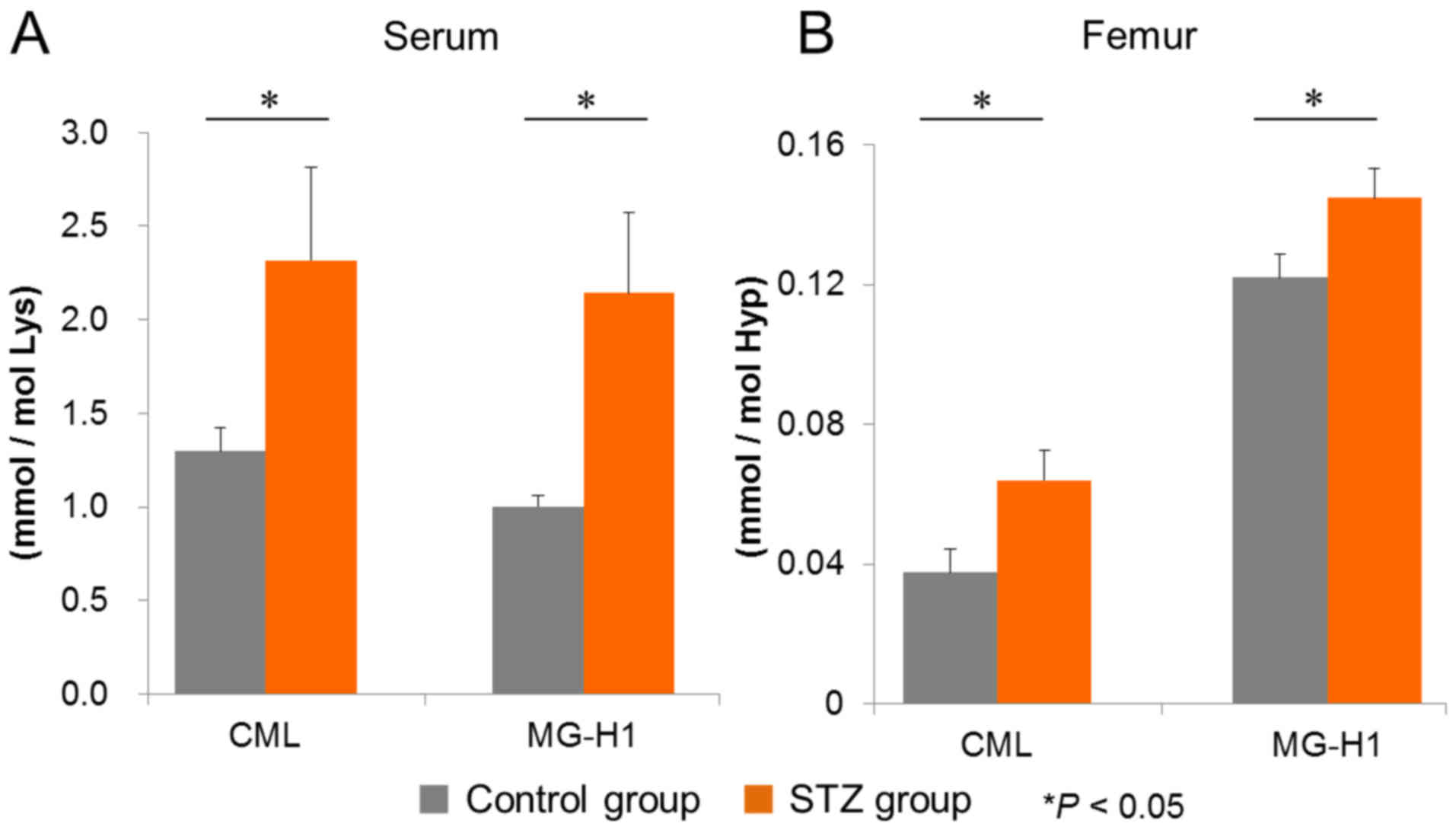
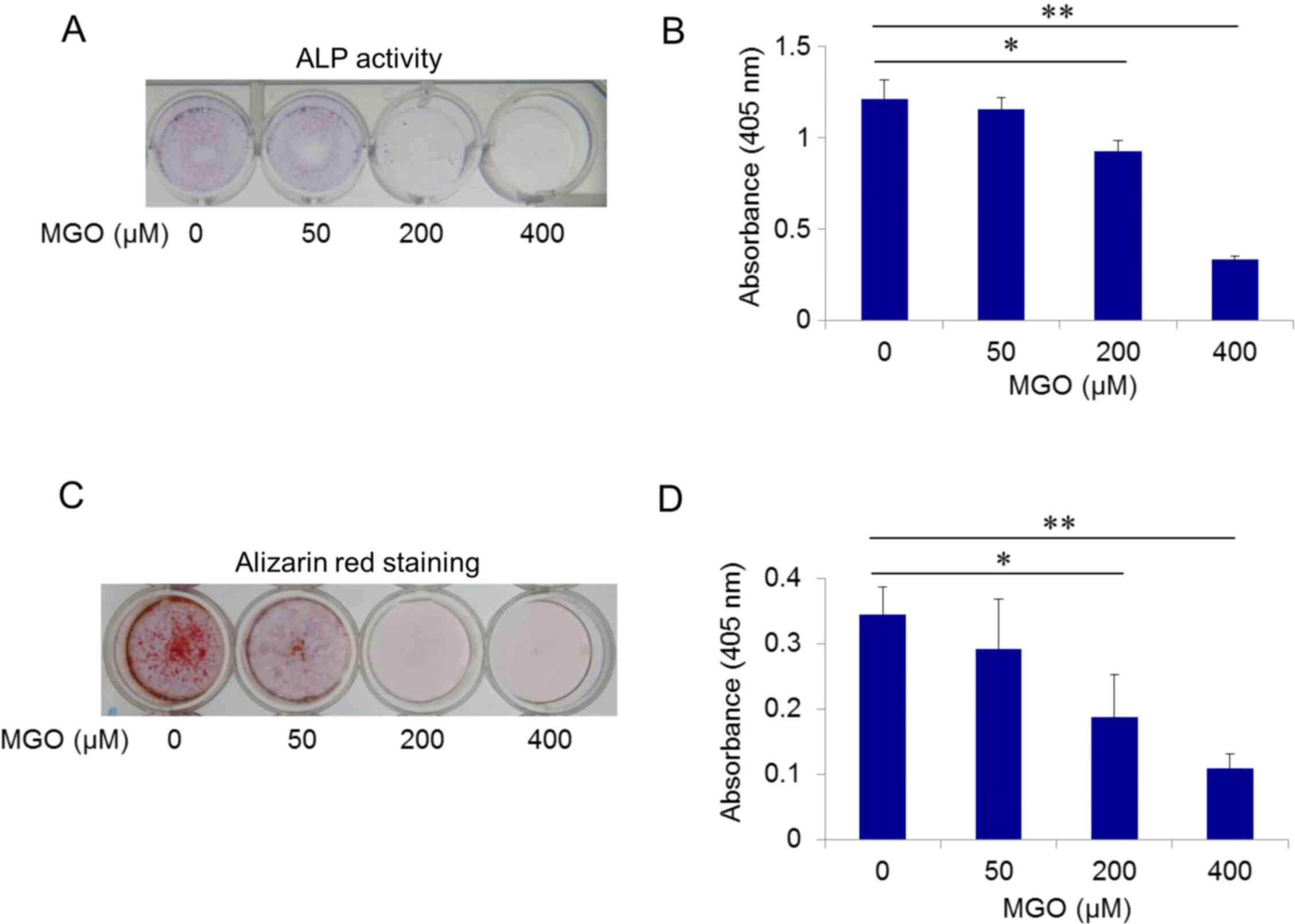
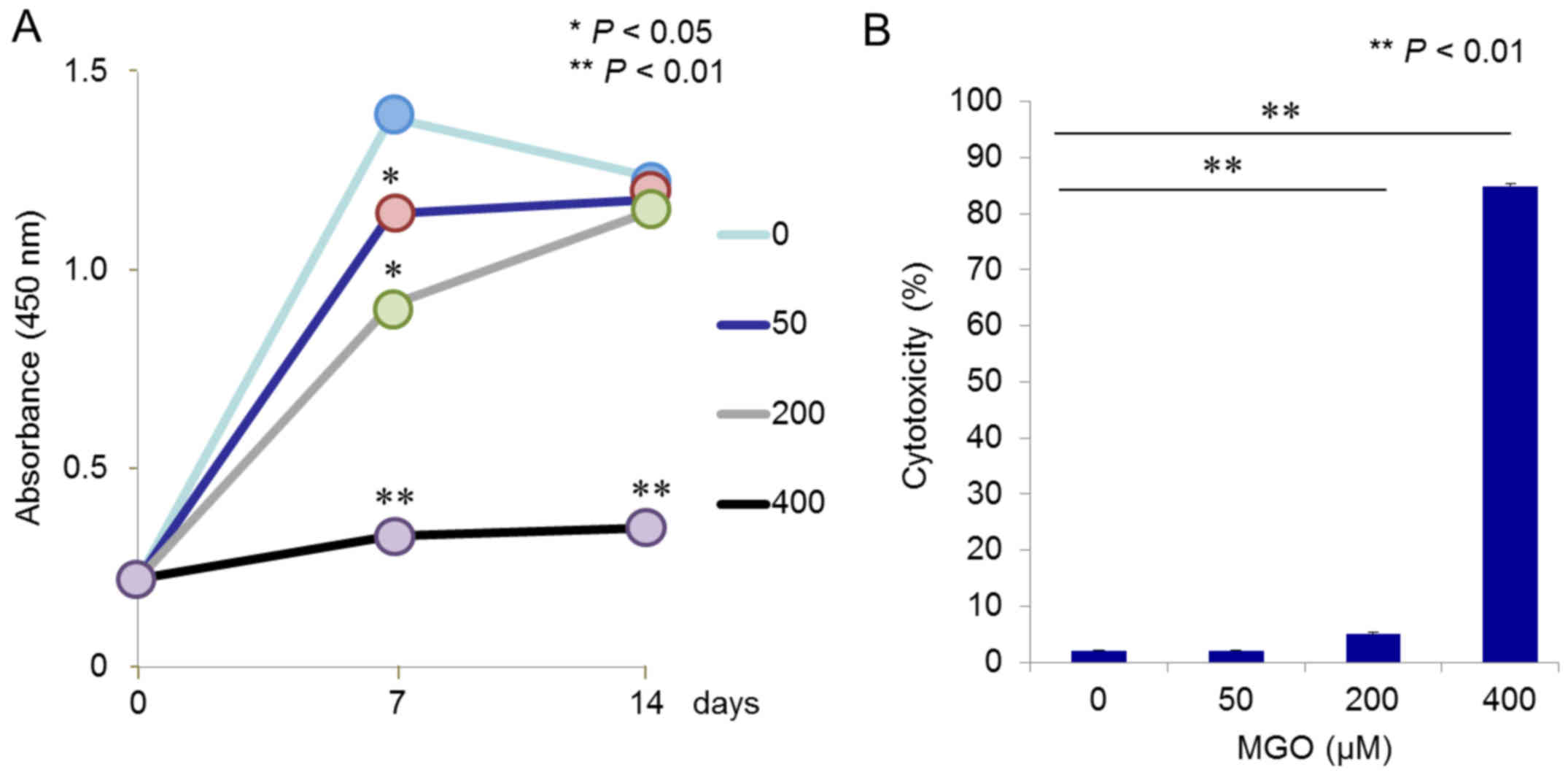
|
1
|
Vestergaard P: Discrepancies in bone
mineral density and fracture risk in patients with type 1 and type
2 diabetes-a meta- analysis. Osteoporosis Int. 18:427–444. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kayal RA, Alblowi J, McKenzie E,
Krothapalli N, Silkman L, Gerstenfeld L, Einhorn TA and Graves DT:
Diabetes causes the accelerated loss of cartilage during fracture
repair which is reversed by insulin treatment. Bone. 44:357–363.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Retzepi M and Donos N: The effect of
diabetes mellitus on osseous healing. Clin Oral Implants Res.
21:673–681. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Simpson CM, Calori GM and Giannoudis PV:
Diabetes and fracture healing: The skeletal effects of diabetic
drugs. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 11:215–220. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
de Liefde II, van der Klift M, de Laet CE,
van Daele PL, Hofman A and Pols HA: Bone mineral density and
fracture risk in type-2 diabetes mellitus: The Rotterdam study.
Osteoporosis Int. 16:1713–1720. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kayal RA, Tsatsas D, Bauer MA, Allen B,
Al-Sebaei MO, Kakar S, Leone CW, Morgan EF, Gerstenfeld LC, Einhorn
TA and Graves DT: Diminished bone formation during diabetic
fracture healing is related to the premature resorption of
cartilage associated with increased osteoclast activity. J Bone
Miner Res. 22:560–568. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kayal RA, Siqueira M, Alblowi J, McLean J,
Krothapalli N, Faibish D, Einhorn TA, Gerstenfeld LC and Graves DT:
TNF-alpha mediates diabetes-enhanced chondrocyte apoptosis during
fracture healing and stimulates chondrocyte apoptosis through
FOXO1. J Bone Miner Res. 25:1604–1615. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Loder RT: The influence of diabetes
mellitus on the healing of closed fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
210–216. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Folk JW, Starr AJ and Early JS: Early
wound complications of operative treatment of calcaneus fractures:
Analysis of 190 fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 13:369–372. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Botushanov NP and Orbetzova MM: Bone
mineral density and fracture risk in patients with type 1 and type
2 diabetes mellitus. Folia Med (Plovdiv). 51:12–17. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Stolzing A, Sellers D, Llewelyn O and
Scutt A: Diabetes induced changes in rat mesenchymal stem cells.
Cells Tissues Organs. 191:453–465. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sheweita SA and Khoshhal KI: Calcium
metabolism and oxidative stress in bone fractures: Role of
antioxidants. Curr Drug Metab. 8:519–525. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sanguineti R, Storace D, Monacelli F,
Federici A and Odetti P: Pentosidine effects on human osteoblasts
in vitro. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1126:166–172. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Alikhani M, Alikhani Z, Boyd C, MacLellan
CM, Raptis M, Liu R, Pischon N, Trackman PC, Gerstenfeld L and
Graves DT: Advanced glycation end products stimulate osteoblast
apoptosis via the MAP kinase and cytosolic apoptotic pathways.
Bone. 40:345–353. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brownlee M: Biochemistry and molecular
cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature. 414:813–820. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Westwood ME and Thornalley PJ: Molecular
characteristics of methylglyoxal-modified bovine and human serum
albumins. Comparison with glucose-derived advanced glycation end
product-modified serum albumins. J Protein Chem. 14:359–372. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Phillips SA and Thornalley PJ: The
formation of methylglyoxal from triose phosphates. Investigation
using a specific assay for methylglyoxal. Eur J Biochem.
212:101–105. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Silva Sousa M, Gomes RA, Ferreira AE,
Ponces Freire A and Cordeiro C: The glyoxalase pathway: The first
hundred years… and beyond. Biochem J. 453:1–15. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Thornalley PJ: Pharmacology of
methylglyoxal: Formation, modification of proteins and nucleic
acids, and enzymatic detoxification-a role in pathogenesis and
antiproliferative chemotherapy. Gen Pharmacol. 27:565–573. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kalapos MP: Methylglyoxal in living
organisms: Chemistry, biochemistry, toxicology and biological
implications. Toxicol Lett. 110:145–175. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vander Jagt DL and Hunsaker LA:
Methylglyoxal metabolism and diabetic complications: Roles of
aldose reductase, glyoxalase-I, betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase and
2-oxoaldehyde dehydrogenase. Chem Biol Interact. 143–144:341–351.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Scheijen JL and Schalkwijk CG:
Quantification of glyoxal, methylglyoxal and 3-deoxyglucosone in
blood and plasma by ultra performance liquid chromatography tandem
mass spectrometry: Evaluation of blood specimen. Clin Chem Lab Med.
52:85–91. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yamanaka M, Matsumura T, Ohno R, Fujiwara
Y, Shinagawa M, Sugawa H, Hatano K, Shirakawa J, Kinoshita H, Ito
K, et al: Non-invasive measurement of skin autofluorescence to
evaluate diabetic complications. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 58:135–140.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shirakawa J, Arakawa S, Tagawa T, Gotoh K,
Oikawa N, Ohno R, Shinagawa M, Hatano K, Sugawa H, Ichimaru K, et
al: Salacia chinensis L. extract ameliorates abnormal glucose
metabolism and improves the bone strength and accumulation of AGEs
in type 1 diabetic rats. Food Funct. 7:2508–2515. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Otsuka E, Yamaguchi A, Hirose S and
Hagiwara H: Characterization of osteoblastic differentiation of
stromal cell line ST2 that is induced by ascorbic acid. Am J
Physiol. 277:C132–C138. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yamaguchi A, Ishizuya T, Kintou N, Wada Y,
Katagiri T, Wozney JM, Rosen V and Yoshiki S: Effects of BMP-2,
BMP-4 and BMP-6 on osteoblastic differentiation of bone
marrow-derived stromal cell lines, ST2 and MC3T3-G2/PA6. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 220:366–371. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Suh KS, Choi EM, Rhee SY and Kim YS:
Methylglyoxal induces oxidative stress and mitochondrial
dysfunction in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. Free Radic Res.
48:206–217. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
McLellan AC, Thornalley PJ, Benn J and
Sonksen PH: Glyoxalase system in clinical diabetes mellitus and
correlation with diabetic complications. Clin Sci (Lond). 87:21–29.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lapolla A, Reitano R, Seraglia R, Sartore
G, Ragazzi E and Traldi P: Evaluation of advanced glycation end
products and carbonyl compounds in patients with different
conditions of oxidative stress. Mol Nutr Food Res. 49:685–690.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chaplen FW, Fahl WE and Cameron DC:
Evidence of high levels of methylglyoxal in cultured Chinese
hamster ovary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:5533–5538. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Webb-Robertson BJ, Lowry DF, Jarman KH,
Harbo SJ, Meng QR, Fuciarelli AF, Pounds JG and Lee KM: A study of
spectral integration and normalization in NMR-based metabonomic
analyses. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 39:830–836. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chan WH, Wu HJ and Shiao NH: Apoptotic
signaling in methylglyoxal-treated human osteoblasts involves
oxidative stress, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, caspase-3, and
p21-activated kinase 2. J Cell Biochem. 100:1056–1069. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ai-Aql ZS, Alagl AS, Graves DT,
Gerstenfeld LC and Einhorn TA: Molecular mechanisms controlling
bone formation during fracture healing and distraction
osteogenesis. J Dent Res. 87:107–118. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gerstenfeld LC, Wronski TJ, Hollinger JO
and Einhorn TA: Application of histomorphometric methods to the
study of bone repair. J Bone Miner Res. 20:1715–1722. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shin L and Peterson DA: Impaired
therapeutic capacity of autologous stem cells in a model of type 2
diabetes. Stem Cells Transl Med. 1:125–135. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Follak N, Kloting I and Merk H: Influence
of diabetic metabolic state on fracture healing in spontaneously
diabetic rats. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 21:288–296. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kawaguchi H, Kurokawa T, Hanada K, Hiyama
Y, Tamura M, Ogata E and Matsumoto T: Stimulation of fracture
repair by recombination human basic fibroblast growth factor in
normal and streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Endocrinology.
135:774–781. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bahney CS, Hu DP, Miclau T III and
Marcucio RS: The multifaceted role of the vasculature in
endochondral fracture repair. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
6:42015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liao YF, Chen LL, Zeng TS, Li YM, Fan Y,
Hu LJ and Ling Yue: Number of circulating endothelial progenitor
cells as a marker of vascular endothelial function for type 2
diabetes. Vasc Med. 15:279–285. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Okazaki K, Yamaguchi T, Tanaka K, Notsu M,
Ogawa N, Yano S and Sugimoto T: Advanced glycation end products
(AGEs), but not high glucose, inhibit the osteoblastic
differentiation of mouse stromal ST2 cells through the suppression
of osterix expression, and inhibit cell growth and increasing cell
apoptosis. Calcif Tissu Int. 91:286–296. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Xue J, Ray R, Singer D, Böhme D, Burz DS,
Rai V, Hoffmann R and Shekhtman A: The receptor for advanced
glycation end products (RAGE) specifically recognizes
methylglyoxal-derived AGEs. Biochemistry. 53:3327–3335. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Voziyan PA and Hudson BG: Pyridoxamine as
a multifunctional pharmaceutical: Targeting pathogenic glycation
and oxidative damage. Cell Mol Life Sci. 62:1671–1681. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Degenhardt TP, Alderson NL, Arrington DD,
Beattie RJ, Basgen JM, Steffes MW, Thorpe SR and Baynes JW:
Pyridoxamine inhibits early renal disease and dyslipidemia in the
streptozotocin-diabetic rat. Kidney Int. 61:939–950. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhu P, Lin H, Sun C, Lin F, Yu H, Zhuo X,
Zhou C and Deng Z: Synergistic effects of telmisartan and
pyridoxamine on early renal damage in spontaneously hypertensive
rats. Mol Med Rep. 5:655–662. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Waanders F, van den Berg E, Nagai R, van
Veen I, Navis G and van Goor H: Renoprotective effects of the
AGE-inhibitor pyridoxamine in experimental chronic allograft
nephropathy in rats. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 23:518–524. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Alderson NL, Chachich ME, Youssef NN,
Beattie RJ, Nachtigal M, Thorpe SR and Baynes JW: The AGE inhibitor
pyridoxamine inhibits lipemia and development of renal and vascular
disease in Zucker obese rats. Kidney Int. 63:2123–2133. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Tanimoto M, Gohda T, Kaneko S, Hagiwara S,
Murakoshi M, Aoki T, Yamada K, Ito T, Matsumoto M, Horikoshi S and
Tomino Y: Effect of pyridoxamine (K-163), an inhibitor of advanced
glycation end products, on type 2 diabetic nephropathy in
KK-A(y)/Ta mice. Metabolism. 56:160–167. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Williams ME, Bolton WK, Khalifah RG,
Degenhardt TP, Schotzinger RJ and McGill JB: Effects of
pyridoxamine in combined phase 2 studies of patients with type 1
and type 2 diabetes and overt nephropathy. Am J Nephrol.
27:605–614. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lewis EJ, Greene T, Spitalewiz S,
Blumenthal S, Berl T, Hunsicker LG, Pohl MA, Rohde RD, Raz I,
Yerushalmy Y, et al: Pyridorin in type 2 diabetic nephropathy. J Am
Soc Nephrol. 23:131–136. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Garg S, Syngle A and Vohra K: Efficacy and
tolerability of advanced glycation end-products inhibitor in
osteoarthritis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled
study. Clin J Pain. 29:717–724. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Nagaraj RH, Sarkar P, Mally A, Biemel KM,
Lederer MO and Padayatti PS: Effect of pyridoxamine on chemical
modification of proteins by carbonyls in diabetic rats:
Characterization of a major product from the reaction of
pyridoxamine and methylglyoxal. Arch Biochem Biophys. 402:110–119.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ruggiero-Lopez D, Lecomte M, Moinet G,
Patereau G, Lagarde M and Wiernsperger N: Reaction of metformin
with dicarbonyl compounds. Possible implication in the inhibition
of advanced glycation end product formation. Biochem Pharmacol.
58:1765–1773. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Effect of intensive blood-glucose control
with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2
diabetes (UKPDS 34). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group.
Lancet. 352:854–865. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kender Z, Fleming T, Kopf S, Torzsa P,
Grolmusz V, Herzig S, Schleicher E, Rácz K, Reismann P and Nawroth
PP: Effect of metformin on methylglyoxal metabolism in patients
with type 2 diabetes. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 122:316–319.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|