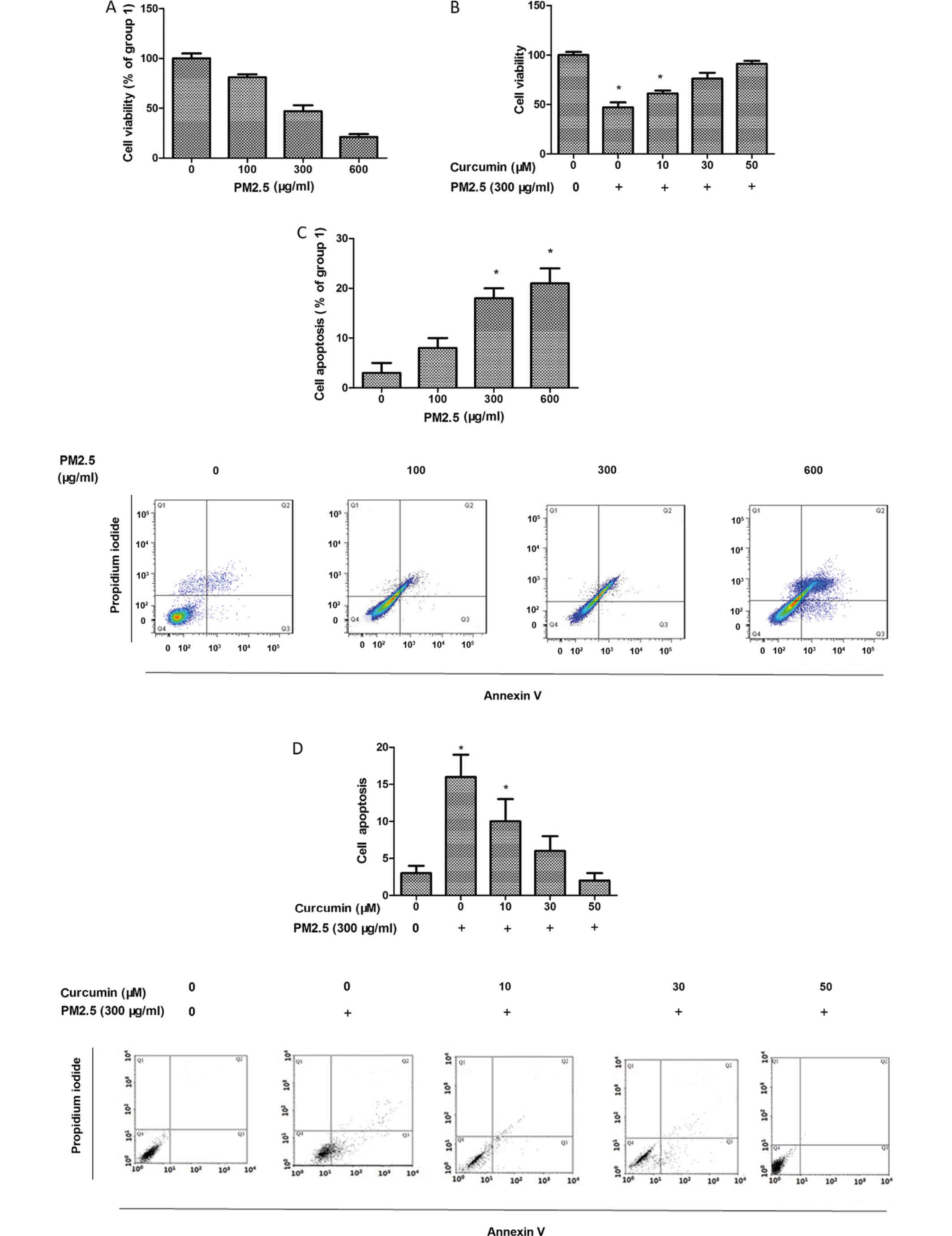
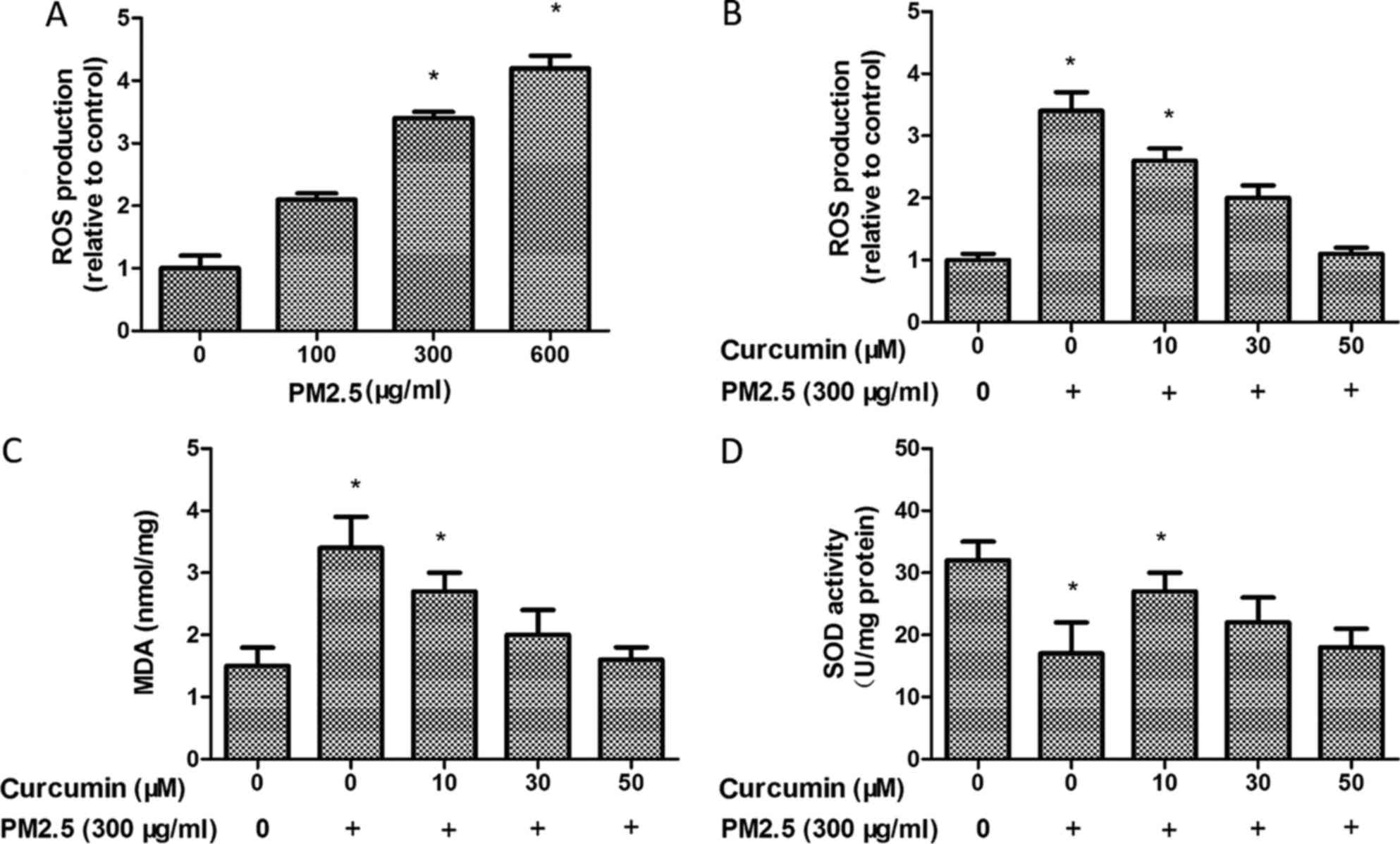
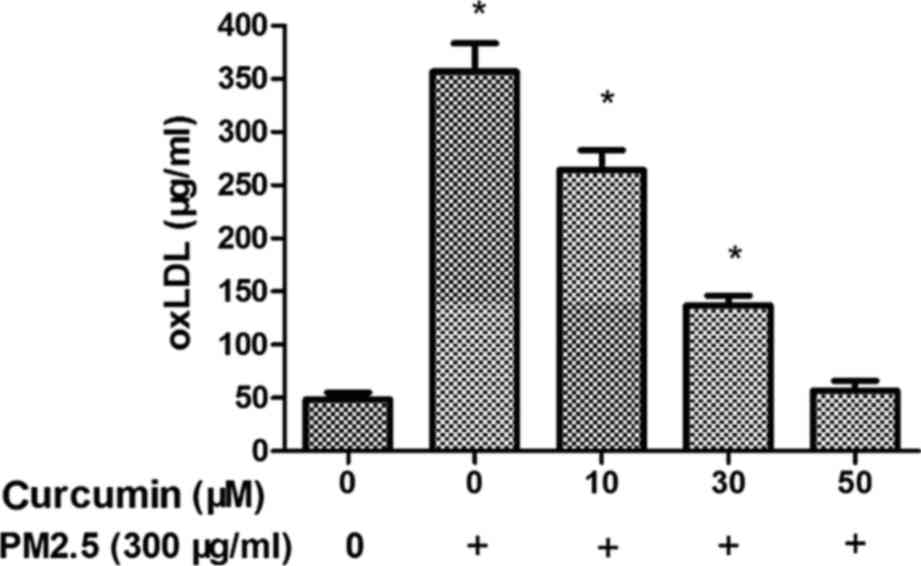
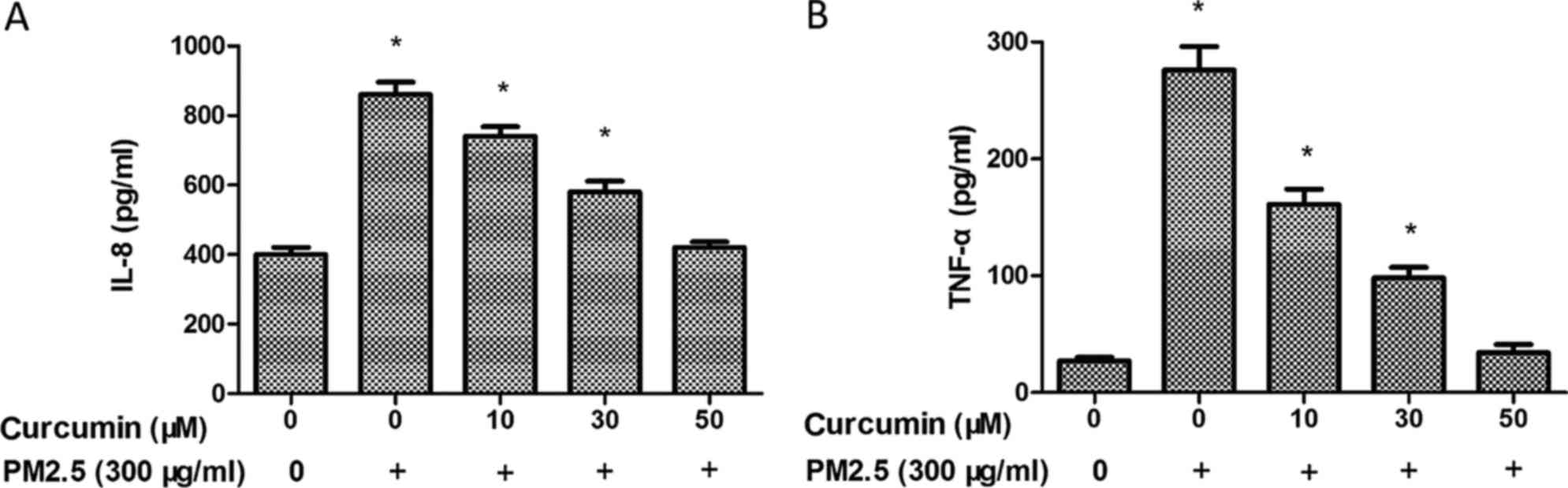
|
1
|
Lee YJ, Kim NY, Suh YA and Lee C:
Involvement of ROS in curcumin-induced autophagic cell death.
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 15:1–7. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zheng A, Li H, Wang X, Feng Z, Xu J, Cao
K, Zhou B, Wu J and Liu J: Anticancer effect of a curcumin
derivative B63: ROS production and mitochondrial dysfunction. Curr
Cancer Drug Targets. 14:156–166. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Garige M and Walters E: Curcumin inhibits
development and cell adhesion in Dictyostelium discoideum:
Implications for YakA signaling and GST enzyme function. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 467:275–281. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tapia E, Soto V, Ortiz-Vega KM,
Zarco-Márquez G, Molina-Jijón E, Cristóbal-García M, Santamaría J,
García-Niño WR, Correa F, Zazueta C and Pedraza-Chaverri: Curcumin
induces Nrf2 nuclear translocation and prevents glomerular
hypertension, hyperfiltration, oxidant stress, and the decrease in
antioxidant enzymes in 5/6 nephrectomized rats. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2012:2690392012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cao F, Liu T, Xu Y, Xu D and Feng S:
Curcumin inhibits cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in
human osteoclastoma cell through MMP-9, NF-κB and JNK signaling
pathways. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:6037–6045. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Katsori AM, Palagani A, Bougarne N,
Hadjipavlou-Litina D, Haegeman G and Vanden Berghe W: Inhibition of
the NF-κB signaling pathway by a novel heterocyclic curcumin
analogue. Molecules. 20:863–878. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Royt M, Mukherjee S, Sarkar R and Biswas
J: Curcumin sensitizes chemotherapeutic drugs via modulation of
PKC, telomerase, NF-kappaB and HDAC in breast cancer. Ther Deliv.
2:1275–1293. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kioumourtzoglou MA, Schwartz JD, Weisskopf
MG, Melly SJ, Wang Y, Dominici F and Zanobetti A: Long-term PM2.5
exposure and neurological hospital admissions in the northeastern
united states. Environ Health Perspect. 124:23–29. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Buczyńska AJ, Krata A, Van Grieken R,
Brown A, Polezer G, De Wael K and Potgieter-Vermaak S: Composition
of PM2.5 and PM1 on high and low pollution event days and its
relation to indoor air quality in a home for the elderly. Sci Total
Environ. 490:134–143. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mohammed MO, Song WW, Ma WL, Li WL, Li YF,
Khan AU, Ibrahim MA, Maarouf OA, Ahmed AA and Ambuchi JJ: Potential
toxicological and cardiopulmonary effects of PM2.5 exposure and
related mortality: Findings of recent studies published during
2003–2013. Biomed Environ Sci. 29:66–79. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Y, Yang W, Han B, Zhang W, Chen M and
Bai Z: Gravimetric analysis for PM2.5 mass concentration based on
year-round monitoring at an urban site in Beijing. J Environ Sci
(China). 40:154–160. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fang X, Li R, Xu Q, Bottai M, Fang F and
Cao Y: A two-stage method to estimate the contribution of road
traffic to PM2.5 concentrations in Beijing, China. Int J Environ
Res Public Health. 13:pii: E124. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Han L, Zhou W and Li W: Fine particulate
(PM2.5) dynamics during rapid urbanization in Beijing, 1973–2013.
Sci Rep. 6:236042016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Duan L, Xiu G, Feng L, Cheng N and Wang C:
The mercury species and their association with carbonaceous
compositions, bromine and iodine in PM2.5 in Shanghai. Chemosphere.
146:263–271. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhao M, Qiao T, Huang Z, Zhu M, Xu W, Xiu
G, Tao J and Lee S: Comparison of ionic and carbonaceous
compositions of PM2.5 in 2009 and 2012 in Shanghai, China. Sci
Total Environ. 536:695–703. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Haikerwal A, Akram M, Del Monaco A, Smith
K, Sim MR, Meyer M, Tonkin AM, Abramson MJ and Dennekamp M: Impact
of fine particulate Matter (PM2.5) exposure during wildfires on
cardiovascular health outcomes. J Am Heart Assoc. 4:pii: e001653.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Niu J, Liberda EN, Qu S, Guo X, Li X,
Zhang J, Meng J, Yan B, Li N, Zhong M, et al: The role of metal
components in the cardiovascular effects of PM2.5. PLoS One.
8:e837822013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Montiel-Dávalos A, Alfaro-Moreno E and
López-Marure R: PM2.5 and PM10 induce the expression of adhesion
molecules and the adhesion of monocytic cells to human umbilical
vein endothelial cells. Inhal Toxicol. 19:(Suppl 1). S91–S98. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yang GZ, Wang ZJ, Bai F, Qin XJ, Cao J, Lv
JY and Zhang MS: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate protects HUVECs from
PM2.5-induced oxidative stress injury by activating critical
antioxidant pathways. Molecules. 20:6626–6639. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gimbrone MA Jr and García-Cardeña G:
Endothelial cell dysfunction and the pathobiology of
atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 118:620–636. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Soares SR, Carvalho-Oliveira R,
Ramos-Sanchez E, Catanozi S, da Silva LF, Mauad T, Gidlund M, Goto
H and Garcia ML: Air pollution and antibodies against modified
lipoproteins are associated with atherosclerosis and vascular
remodeling in hyperlipemic mice. Atherosclerosis. 207:368–373.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Takenaka T, Takahashi K, Kobayashi T,
Oshima E, Iwasaki S and Suzuki H: Oxidized low density lipoprotein
(Ox-LDL) as a marker of atherosclerosis in hemodialysis (HD)
patients. Clin Nephrol. 58:33–37. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang GF, Shi CG, Sun MZ, Wang L, Wu SX,
Wang HF, Xu ZQ and Chen DM: Tetramethylpyrazine attenuates
atherosclerosis development and protects endothelial cells from
ox-LDL. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 27:199–210. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bo L, Jiang S, Xie Y, Kan H, Song W and
Zhao J: Effect of vitamin e and omega-3 fatty acids on protecting
ambient PM2.5-induced inflammatory response and oxidative stress in
vascular endothelial cells. PLoS One. 11:e01522162016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li R, Kou X, Xie L, Cheng F and Geng H:
Effects of ambient PM2.5 on pathological injury, inflammation,
oxidative stress, metabolic enzyme activity, and expression of
c-fos and c-jun in lungs of rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int.
22:20167–20176. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang HP, Zheng FL, Zhao JH, Guo DX and
Chen XL: Genistein inhibits ox-LDL-induced VCAM-1, ICAM-1 and MCP-1
expression of HUVECs through heme oxygenase-1. Arch Med Res.
44:13–20. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Deng X, Rui W, Zhang F and Ding W: PM2.5
induces Nrf2-mediated defense mechanisms against oxidative stress
by activating PIK3/AKT signaling pathway in human lung alveolar
epithelial A549 cells. Cell Biol Toxicol. 29:143–157. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Su R, Jin X, Zhang W, Li Z, Liu X and Ren
J: Particulate matter exposure induces the autophagy of macrophages
via oxidative stress-mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Chemosphere.
167:444–453. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang X, Chen M, Zhong M, Hu Z, Qiu L,
Rajagopalan S, Fossett NG, Chen LC and Ying Z: Exposure to
concentrated ambient PM2.5 shortens lifespan and induces
inflammation-associated signaling and oxidative stress in
drosophila. Toxicol Sci. 156:199–207. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hong Z, Guo Z, Zhang R, Xu J, Dong W,
Zhuang G and Deng C: Airborne fine particulate matter induces
oxidative stress and inflammation in human nasal epithelial cells.
Tohoku J Exp Med. 239:117–125. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang W, Deng Z, Feng Y, Liao F, Zhou F,
Feng S and Wang X: PM2.5 induced apoptosis in endothelial cell
through the activation of the p53-bax-caspase pathway. Chemosphere.
177:135–143. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Deng X, Zhang F, Wang L, Rui W, Long F,
Zhao Y, Chen D and Ding W: Airborne fine particulate matter induces
multiple cell death pathways in human lung epithelial cells.
Apoptosis. 19:1099–1112. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Soberanes S, Urich D, Baker CM, Burgess Z,
Chiarella SE, Bell EL, Ghio AJ, De Vizcaya-Ruiz A, Liu J, Ridge KM,
et al: Mitochondrial complex III-generated oxidants activate ASK1
and JNK to induce alveolar epithelial cell death following exposure
to particulate matter air pollution. J Biol Chem. 284:2176–2186.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rice MB, Cavallari J, Fang S and
Christiani D: Acute decrease in HDL cholesterol associated with
exposure to welding fumes. J Occup Environ Med. 53:17–21. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yan B, Li J, Guo J, Ma P, Wu Z, Ling Z,
Guo H, Hiroshi Y, Yanagi U, Yang X, et al: The toxic effects of
indoor atmospheric fine particulate matter collected from allergic
and non-allergic families in Wuhan on mouse peritoneal macrophages.
J Appl Toxicol. 36:596–608. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yeatts K, Svendsen E, Creason J, Alexis N,
Herbst M, Scott J, Kupper L, Williams R, Neas L, Cascio W, et al:
Coarse particulate matter (PM2.5–10) affects heart rate
variability, blood lipids, and circulating eosinophils in adults
with asthma. Environ Health Perspect. 115:709–714. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Brucker N, Moro AM, Charão MF, Durgante J,
Freitas F, Baierle M, Nascimento S, Gauer B, Bulcão RP, Bubols GB,
et al: Biomarkers of occupational exposure to air pollution,
inflammation and oxidative damage in taxi drivers. Sci Total
Environ. 463–464:884–493. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Li Q, Wang Y, Li H, Shen G and Hu S:
Ox-LDL influences peripheral Th17/Treg balance by modulating Treg
apoptosis and Th17 proliferation in atherosclerotic cerebral
infarction. Cell Physiol Biochem. 33:1849–1862. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kafoury RM and Madden MC: Diesel exhaust
particles induce the over expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha
(TNF-alpha) gene in alveolar macrophages and failed to induce
apoptosis through activation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB).
Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2:107–13. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gu LZ, Sun H and Chen JH: Histone
deacetylases 3 deletion restrains PM2.5-induced mice lung injury by
regulating NF-κB and TGF-β/Smad2/3 signaling pathways. Biomed
Pharmacother. 85:756–762. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|