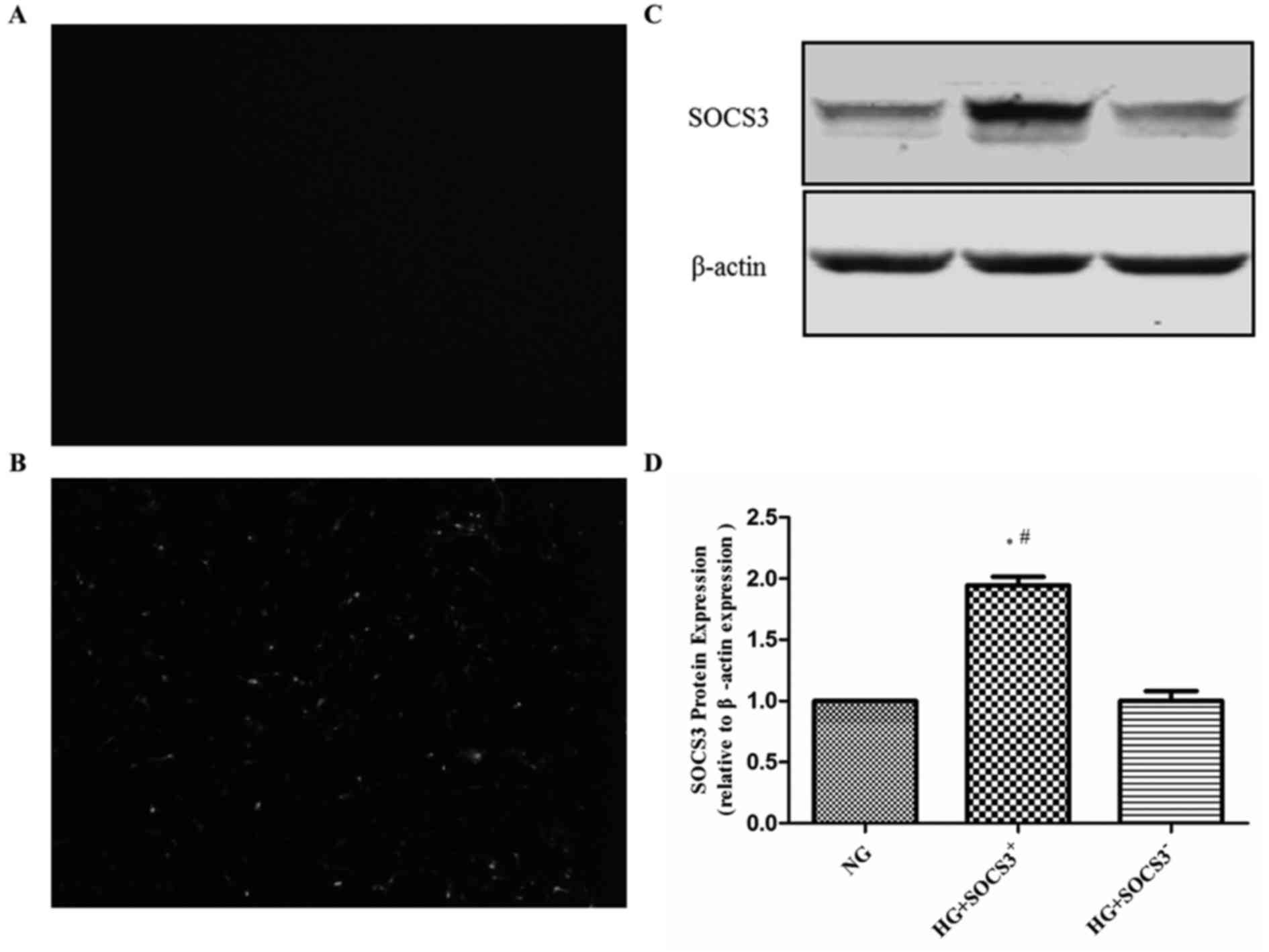
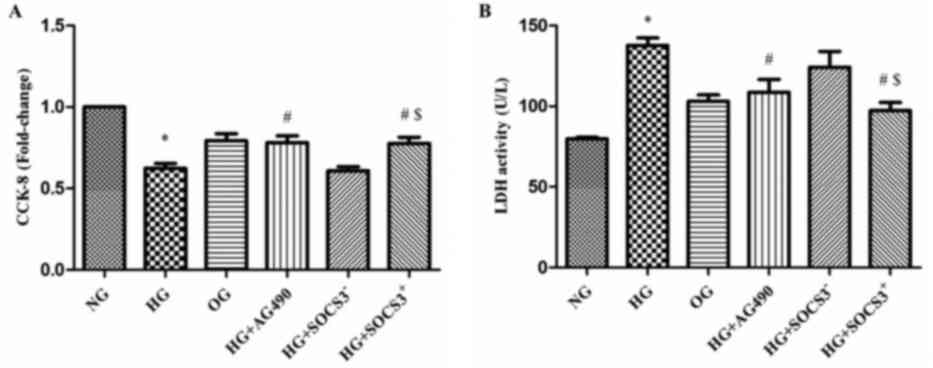
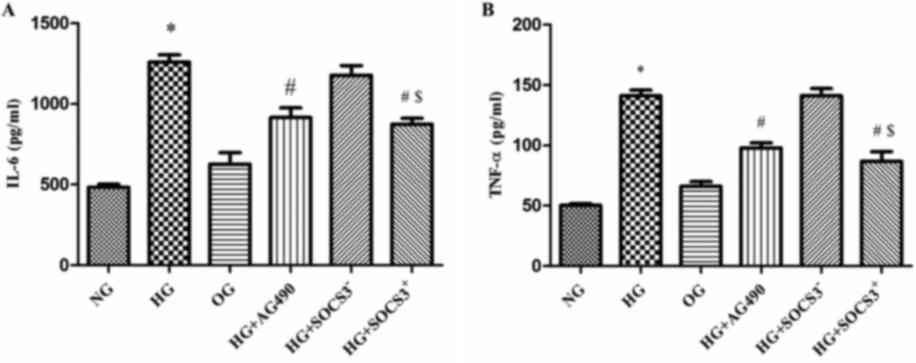
|
1
|
Klein OL, Krishnan JA, Glick S and Smith
LJ: Systematic review of the association between lung function and
type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med. 27:977–987. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang HJ, Huang YL, Shih YY, Wu HY, Peng CT
and Lo WY: MicroRNA-146a decreases high glucose/thrombin-induced
endothelial inflammation by inhibiting NAPDH oxidase 4 expression.
Mediators Inflamm. 2014:3795372014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hsia CC and Raskin P: Lung involvement in
diabetes: Does it matter? Diabetes Care. 31:828–829. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Orasanu G and Plutzky J: The pathologic
continuum of diabetic vascular disease. J Am CollCardiol. 53:(5
Suppl). S35–S42. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Pradhan AD, Manson JE, Rifai N, Buring JE
and Ridker PM: C-reactive protein, interleukin 6, and risk of
developing type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA. 286:327–334. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee YS and Jun HS: Anti-inflammatory
effects of GLP-1-based therapies beyond glucose control. Mediators
Inflamm. 2016:30946422016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang X, Bao W, Liu J, Ouyang YY, Wang D,
Rong S, Xiao X, Shan ZL, Zhang Y, Yao P and Liu LG: Inflammatory
markers and risk of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Diabetes Care. 36:166–175. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Williams MD and Nadler JL: Inflammatory
mechanisms of diabetic complications. Curr Diab Rep. 7:242–248.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Stuart MJ and Baune BT: Depression and
type 2 diabetes: Inflammatory mechanisms of a psychoneuroendocrine
co-morbidity. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 36:658–676. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu Q, Xing L, Wang L, Yao F, Liu S, Hao
J, Liu W and Duan H: Therapeutic effects of suppressors of cytokine
signaling in diabetic nephropathy. J Histochem Cytochem.
62:119–128. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hu C, Sun L, Xiao L, Han Y, Fu X, Xiong X,
Xu X, Liu Y, Yang S, Liu F and Kanwar YS: Insights into the
mechanisms involved in the expression and regulation of
extracellular matrix proteins in diabetic nephropathy. Curr Med
Chem. 22:2858–2870. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Marrero MB, Banes-Berceli AK, Stern DM and
Eaton DC: Role of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway in diabetic
nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 290:F762–F768. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dalpke A, Heeg K, Bartz H and Baetz A:
Regulation of innate immunity by suppressor of cytokine signaling
(SOCS) proteins. Immunobiology. 213:225–235. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Inagaki-Ohara K, Kondo T, Ito M and
Yoshimura A: SOCS, inflammation, and cancer. JAKSTAT.
2:e240532013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Krebs DL and Hilton DJ: SOCS proteins:
Negative regulators of cytokine signaling. Stem Cells. 19:378–387.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yasukawa H, Sasaki A and Yoshimura A:
Negative regulation of cytokine signaling pathways. Annu Rev
Immunol. 18:143–164. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Suchy D, Łabuzek K, Machnik G, Kozłowski M
and Okopień B: SOCS and diabetes-ups and downs of a turbulent
relationship. Cell Biochem Funct. 31:181–195. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Piessevaux J, Lavens D, Peelman F and
Tavernier J: The many faces of the SOCS box. Cytokine Growth Factor
Rev. 19:371–381. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yoshimura A, Suzuki M, Sakaguchi R, Hanada
T and Yasukawa H: SOCS, inflammation, and autoimmunity. Front
Immunol. 3:202012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sasaki A, Yasukawa H, Suzuki A, Kamizono
S, Syoda T, Kinjyo I, Sasaki M, Johnston JA and Yoshimura A:
Cytokine-inducible SH2 protein-3 (CIS3/SOCS3) inhibits Janus
tyrosine kinase by binding through the N-terminal kinase inhibitory
region as well as SH2 domain. Genes Cells. 4:339–351. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Carow B and Rottenberg ME: SOCS3, a major
regulator of infection and inflammation. Front Immunol. 5:582014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Feng X, Tang H, Leng J and Jiang Q:
Suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) and type 2 diabetes. Mol
Biol Rep. 41:2265–2274. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Alisson-Silva F, Freire-de-Lima L, Donadio
JL, Lucena MC, Penha L, Sá-Diniz JN, Dias WB and Todeschini AR:
Increase of O-glycosylated oncofetal fibronectin in high
glucose-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cultured human
epithelial cells. PLoS One. 8:e604712013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang JS, Chuang LY, Guh JY, Huang YJ and
Hsu MS: Antioxidants attenuate high glucose-induced hypertrophic
growth in renal tubular epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 293:F1072–F1082. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang X, Shaw S, Amiri F, Eaton DC and
Marrero MB: Inhibition of the Jak/STAT signaling pathway prevents
the high glucose-induced increase in tgf-beta and fibronectin
synthesis in mesangial cells. Diabetes. 51:3505–3509. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shi Y, Zhang Y, Wang C, Du C, Zhao S, Qi
Z, Zhang Q and Duan H: Suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 reduces
high glucose-induced TGF-beta1 and fibronectin synthesis in human
mesangial cells. FEBS Lett. 582:3484–3488. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nakashima T, Yokoyama A, Onari Y, Shoda H,
Haruta Y, Hattori N, Naka T and Kohno N: Suppressor of cytokine
signaling 1 inhibits pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis. J Allergy
Clin Immunol. 121:1269–1276. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Severgnini M, Takahashi S, Tu P, Perides
G, Homer RJ, Jhung JW, Bhavsar D, Cochran BH and Simon AR:
Inhibition of the Src and Jak kinases protects against
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Am J RespirCrit Care
Med. 171:858–867. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ortiz-Muñoz G, Lopez-Parra V, Lopez-Franco
O, Fernandez-Vizarra P, Mallavia B, Flores C, Sanz A, Blanco J,
Mezzano S, Ortiz A, et al: Suppressors of cytokine signaling
abrogate diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 21:763–772. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gao H, Hoesel LM, Guo RF, Rancilio NJ,
Sarma JV and Ward PA: Adenoviral-mediated overexpression of SOCS3
enhances IgG immune complex-induced acute lung injury. J Immunol.
177:612–620. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yan C, Ward PA, Wang X and Gao H: Myeloid
depletion of SOCS3 enhances LPS-induced acute lung injury through
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein δ pathway. FASEB J. 27:2967–2976.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Qin H, Roberts KL, Niyongere SA, Cong Y,
Elson CO and Benveniste EN: Molecular mechanism of
lipopolysaccharide-induced SOCS-3 gene expression in macrophages
and microglia. J Immunol. 179:5966–5976. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Venieratos PD, Drossopoulou GI,
Kapodistria KD, Tsilibary EC and Kitsiou PV: High glucose induces
suppression of insulin signalling and apoptosis via upregulation of
endogenous IL-1beta and suppressor of cytokine signalling-1 in
mouse pancreatic beta cells. Cell Signal. 22:791–800. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Goodman RB, Pugin J, Lee JS and Matthay
MA: Cytokine-mediated inflammation in acute lung injury. Cytokine
Growth Factor Rev. 14:523–535. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Croker BA, Krebs DL, Zhang JG, Wormald S,
Willson TA, Stanley EG, Robb L, Greenhalgh CJ, Förster I, Clausen
BE, et al: SOCS3 negatively regulates IL-6 signaling in vivo. Nat
Immunol. 4:540–545. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Alexander WS and Hilton DJ: The role of
suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins in regulation of
the immune response. Annu Rev Immunol. 22:503–529. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shi YH, Zhao S, Wang C, Li Y and Duan HJ:
Fluvastatin inhibits activation of JAK and STAT proteins in
diabetic rat glomeruli and mesangial cells under high glucose
conditions. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 28:1938–1946. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Manea SA, Manea A and Heltianu C:
Inhibition of JAK/STAT signaling pathway prevents
high-glucose-induced increase in endothelin-1 synthesis in human
endothelial cells. Cell Tissue Res. 340:71–79. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hernández-Vargas P, López-Franco O,
Sanjuán G, Rupérez M, Ortiz-Muñoz G, Suzuki Y, Aguado-Roncero P,
Pérez-Tejerizo G, Blanco J, Egido J, et al: Suppressors of cytokine
signaling regulate angiotensin II-activated Janus kinase-signal
transducers and activators of transcription pathway in renal cells.
J Am SocNephrol. 16:1673–1683. 2005.
|
|
40
|
Gómez-Guerrero C, López-Franco O, Sanjuán
G, Hernández-Vargas P, Suzuki Y, Ortiz-Muñoz G, Blanco J and Egido
J: Suppressors of cytokine signaling regulate Fc receptor signaling
and cell activation during immune renal injury. J Immunol.
172:6969–6977. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Suzuki A, Hanada T, Mitsuyama K, Yoshida
T, Kamizono S, Hoshino T, Kubo M, Yamashita A, Okabe M, Takeda K,
et al: CIS3/SOCS3/SSI3 plays a negative regulatory role in STAT3
activation and intestinal inflammation. J Exp Med. 193:471–481.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wong PK, Egan PJ, Croker BA, O'Donnell K,
Sims NA, Drake S, Kiu H, McManus EJ, Alexander WS, Roberts AW and
Wicks IP: SOCS-3 negatively regulates innate and adaptive immune
mechanisms in acute IL-1-dependent inflammatory arthritis. J Clin
Invest. 116:1571–1581. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|