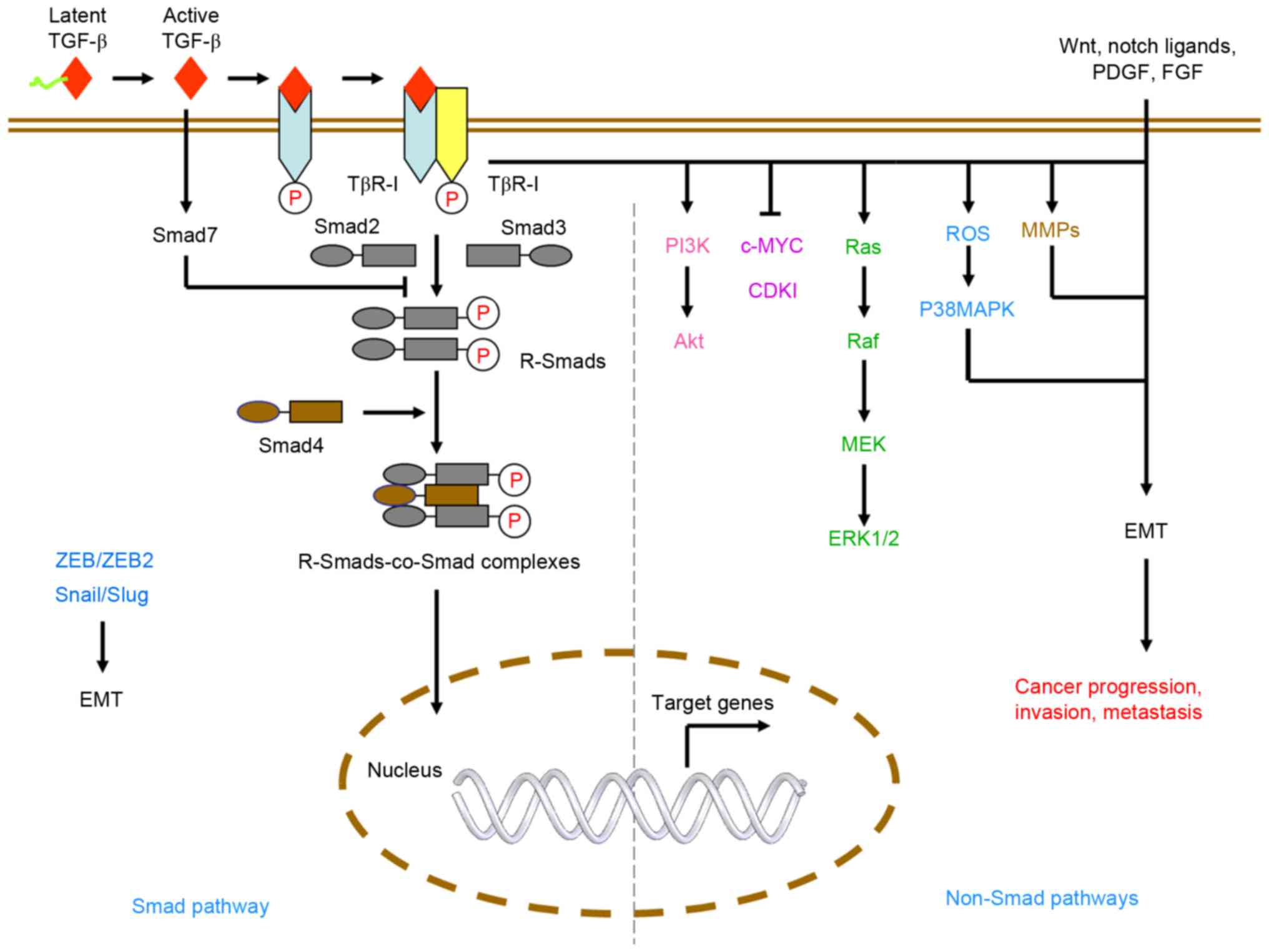
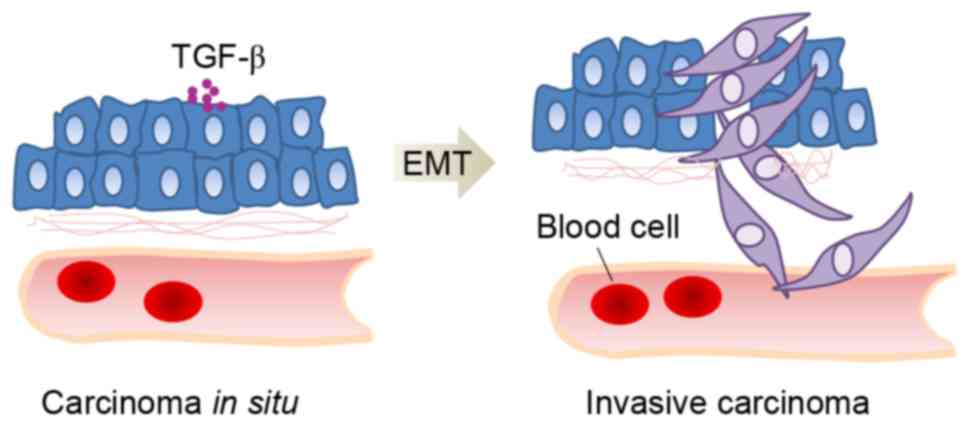
|
1
|
Morris SM, Carter KT, Baek JY, Koszarek A,
Yeh MM, Knoblaugh SE and Grady WM: TGF-β signaling alters the
pattern of liver tumorigenesis induced by Pten inactivation.
Oncogene. 34:3273–3282. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Horie Y, Suzuki A, Kataoka E, Sasaki T,
Hamada K, Sasaki J, Mizuno K, Hasegawa G, Kishimoto H, Iizuka M, et
al: Hepatocyte-specific Pten deficiency results in steatohepatitis
and hepatocellular carcinomas. J Clin Invest. 113:1774–1783. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Attisano L and Wrana JL: Signal
integration in TGF-β, WNT, and Hippo pathways. F1000Prime Rep.
5:172013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ikushima H and Miyazono K: TGFbeta
signalling: A complex web in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer.
10:415–424. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Derynck R, Akhurst RJ and Balmain A:
TGF-beta signaling in tumor suppression and cancer progression. Nat
Genet. 29:117–129. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kiyono K, Suzuki HI, Morishita Y, Komuro
A, Iwata C, Yashiro M, Hirakawa K, Kano MR and Miyazono K: c-Ski
overexpression promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis through
inhibition of transforming growth factor-beta signaling in
diffuse-type gastric carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 100:1809–1816. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Komuro A, Yashiro M, Iwata C, Morishita Y,
Johansson E, Matsumoto Y, Watanabe A, Aburatani H, Miyoshi H,
Kiyono K, et al: Diffuse-type gastric carcinoma: Progression,
angiogenesis, and transforming growth factor beta signaling. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 101:592–604. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Roberts AB and Wakefield LM: The two faces
of transforming growth factor beta in carcinogenesis. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 100:8621–8623. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Massagué J: TGF-beta signal transduction.
Annu Rev Biochem. 67:753–791. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Massagué J, Blain SW and Lo RS: TGFbeta
signaling in growth control, cancer, and heritable disorders. Cell.
103:295–309. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Y, Liu T, Tang W, Deng B, Chen Y, Zhu
J and Shen X: Hepatocellular carcinoma cells induce regulatory T
cells and lead to poor prognosis via production of transforming
growth factor-β1. Cell Physiol Biochem. 38:306–318. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shen H, Guan D, Shen J, Wang M, Chen X, Xu
T, Liu L and Shu Y: TGF-β1 induces erlotinib resistance in
non-small cell lung cancer by down-regulating PTEN. Biomed
Pharmacother. 77:1–6. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yoshimoto T, Fujita T, Kajiya M, Matsuda
S, Ouhara K, Shiba H and Kurihara H: Involvement of smad2 and
Erk/Akt cascade in TGF-β1-induced apoptosis in human gingival
epithelial cells. Cytokine. 75:165–173. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dai C, Yang J and Liu Y: Transforming
growth factor-beta1 potentiates renal tubular epithelial cell death
by a mechanism independent of Smad signaling. J Biol Chem.
278:12537–12545. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lyons RM, Gentry LE, Purchio AF and Moses
HL: Mechanism of activation of latent recombinant transforming
growth factor beta 1 by plasmin. J Cell Biol. 110:1361–1367. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Andreasen PA, Kjøller L, Christensen L and
Duffy MJ: The urokinase-type plasminogen activator system in cancer
metastasis: A review. Int J Cancer. 72:1–22. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yu Q and Stamenkovic I: Cell
surface-localized matrix metalloproteinase-9 proteolytically
activates TGF-beta and promotes tumor invasion and angiogenesis.
Genes Dev. 14:163–176. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mir FA, Contreras-Ruiz L and Masli S:
Thrombospondin-1-dependent immune regulation by transforming growth
factor-β2-exposed antigen-presenting cells. Immunology.
146:547–556. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Murphy-Ullrich JE and Poczatek M:
Activation of latent TGF-beta by thrombospondin-1: Mechanisms and
physiology. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 11:59–69. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dutta A, Li J, Fedele C, Sayeed A, Singh
A, Violette SM, Manes TD and Languino LR: αvβ6 integrin is required
for TGFβ1-mediated matrix metalloproteinase2 expression. Biochem J.
466:525–536. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Feng XH and Derynck R: Specificity and
versatility in tgf-beta signaling through Smads. Annu Rev Cell Dev
Biol. 21:659–693. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shi Y and Massagué J: Mechanisms of
TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell.
113:685–700. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Heldin CH, Miyazono K and ten Dijke P:
TGF-beta signalling from cell membrane to nucleus through SMAD
proteins. Nature. 390:465–471. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Park S, Jung HH, Park YH, Ahn JS and Im
YH: ERK/MAPK pathways play critical roles in EGFR ligands-induced
MMP1 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 407:680–686. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cheng X, Gao W, Dang Y, Liu X, Li Y, Peng
X and Ye X: Both ERK/MAPK and TGF-Beta/Smad signaling pathways play
a role in the kidney fibrosis of diabetic mice accelerated by blood
glucose fluctuation. J Diabetes Res. 2013:4637402013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yu JS, Ramasamy TS, Murphy N, Holt MK,
Czapiewski R, Wei SK and Cui W: PI3K/mTORC2 regulates TGF-β/Activin
signalling by modulating Smad2/3 activity via linker
phosphorylation. Nat Commun. 6:72122015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vo BT, Morton D Jr, Komaragiri S, Millena
AC, Leath C and Khan SA: TGF-β effects on prostate cancer cell
migration and invasion are mediated by PGE2 through activation of
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Endocrinology. 154:1768–1779. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Singha PK, Pandeswara S, Geng H, Lan R,
Venkatachalam MA and Saikumar P: TGF-β induced TMEPAI/PMEPA1
inhibits canonical Smad signaling through R-Smad sequestration and
promotes non-canonical PI3K/Akt signaling by reducing PTEN in
triple negative breast cancer. Genes Cancer. 5:320–336.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Reduced beta 2 glycoprotein I improve
diabetic nephropathy via inhibiting TGF-β1-p38 MAPK pathway
[Retraction]. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:197922015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen IT, Hsu PH, Hsu WC, Chen NJ and Tseng
PH: Polyubiquitination of transforming growth factor β-activated
Kinase 1 (TAK1) at lysine 562 residue regulates TLR4-mediated JNK
and p38 MAPK activation. Sci Rep. 5:123002015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Suzuki T, Dai P, Hatakeyama T, Harada Y,
Tanaka H, Yoshimura N and Takamatsu T: TGF-β signaling regulates
pancreatic β-Cell proliferation through control of cell cycle
regulator p27 expression. Acta Histochem Cytochem. 46:51–58. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Senturk S, Mumcuoglu M, Gursoy-Yuzugullu
O, Cingoz B, Akcali KC and Ozturk M: Transforming growth
factor-beta induces senescence in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
and inhibits tumor growth. Hepatology. 52:966–974. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang Y, Wu J, Lin B, Li X, Zhang H, Ding
H, Chen X, Lan L and Luo H: Galangin suppresses HepG2 cell
proliferation by activating the TGF-β receptor/Smad pathway.
Toxicology. 326:9–17. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Guo C, Liu S, Dong P, Zhao D, Wang C, Tao
Z and Sun MZ: Akbu-LAAO exhibits potent anti-tumor activity to
HepG2 cells partially through produced H2O2 via TGF-β signal
pathway. Sci Rep. 5:182152015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cheng L, Zhang C, Li D, Zou J and Wang J:
Transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) induces mouse
precartilaginous stem cell proliferation through TGF-β receptor II
(TGFRII)-Akt-β-catenin signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 15:12665–12676.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kudo-Saito C, Shirako H, Takeuchi T and
Kawakami Y: Cancer metastasis is accelerated through
immunosuppression during Snail-induced EMT of cancer cells. Cancer
Cell. 15:195–206. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hay ED: An overview of
epithelio-mesenchymal transformation. Acta Anat (Basel). 154:8–20.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Muthusamy BP, Budi EH, Katsuno Y, Lee MK,
Smith SM, Mirza AM, Akhurst RJ and Derynck R: ShcA protects against
epithelial-mesenchymal transition through compartmentalized
inhibition of TGF-β-Induced Smad activation. PLoS Biol.
13:e10023252015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xu J, Lamouille S and Derynck R:
TGF-beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Res.
19:156–172. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lee JY, Chang JW, Yang WS, Kim SB, Park
SK, Park JS and Lee SK: Albumin-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and ER stress are regulated through a common ROS-c-Src
kinase-mTOR pathway: Effect of imatinib mesylate. Am J Physiol
Renal Physiol. 300:F1214–1222. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Padua D, Zhang XH, Wang Q, Nadal C, Gerald
WL, Gomis RR and Massagué J: TGFbeta primes breast tumors for lung
metastasis seeding through angiopoietin-like 4. Cell. 133:66–77.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Naka K: TGF-β signaling in cancer stem
cells. Nihon Rinsho. 73:784–789. 2015.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
You H, Ding W and Rountree CB: Epigenetic
regulation of cancer stem cell marker CD133 by transforming growth
factor-beta. Hepatology. 51:1635–1644. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chanmee T, Ontong P, Mochizuki N,
Kongtawelert P, Konno K and Itano N: Excessive hyaluronan
production promotes acquisition of cancer stem cell signatures
through the coordinated regulation of Twist and the transforming
growth factor β (TGF-β)-Snail signaling axis. J Biol Chem.
289:26038–26056. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Fan QM, Jing YY, Yu GF, Kou XR, Ye F, Gao
L, Li R, Zhao QD, Yang Y, Lu ZH and Wei LX: Tumor-associated
macrophages promote cancer stem cell-like properties via
transforming growth factor-beta1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 352:160–168.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yu D, Shin HS, Lee YS and Lee YC: miR-106b
modulates cancer stem cell characteristics through TGF-β/Smad
signaling in CD44-positive gastric cancer cells. Lab Invest.
94:1370–1381. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
El Helou R, Wicinski J, Guille A, Adélaïde
J, Finetti P, Bertucci F, Chaffanet M, Birnbaum D, Charafe-Jauffret
E and Ginestier C: Brief reports: A distinct DNA methylation
signature defines breast cancer stem cells and predicts cancer
outcome. Stem Cells. 32:3031–3036. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang J, Shao N, Ding X, Tan B, Song Q,
Wang N, Jia Y, Ling H and Cheng Y: Crosstalk between transforming
growth factor-β signaling pathway and long non-coding RNAs in
cancer. Cancer Lett. 370:296–301. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Martin M and Herceg Z: From hepatitis to
hepatocellular carcinoma: A proposed model for cross-talk between
inflammation and epigenetic mechanisms. Genome Med. 4:82012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hernandez-Gea V, Toffanin S, Friedman SL
and Llovet JM: Role of the microenvironment in the pathogenesis and
treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology.
144:512–527. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Nana AW, Yang PM and Lin HY: Overview of
transforming growth factor β superfamily involvement in
glioblastoma initiation and progression. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
16:6813–6823. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Neuzillet C, de Gramont A,
Tijeras-Raballand A, de Mestier L, Cros J, Faivre S and Raymond E:
Perspectives of TGF-β inhibition in pancreatic and hepatocellular
carcinomas. Oncotarget. 5:78–94. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yang L, Pang Y and Moses HL: TGF-beta and
immune cells: An important regulatory axis in the tumor
microenvironment and progression. Trends Immunol. 31:220–227. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yang L: TGFbeta, a potent regulator of
tumor microenvironment and host immune response, implication for
therapy. Curr Mol Med. 10:374–380. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Chen J, Yao Y, Gong C, Yu F, Su S, Chen J,
Liu B, Deng H, Wang F, Lin L, et al: CCL18 from tumor-associated
macrophages promotes breast cancer metastasis via PITPNM3. Cancer
Cell. 19:541–555. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Pittet MJ: Behavior of immune players in
the tumor microenvironment. Curr Opin Oncol. 21:53–59. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Condeelis J and Pollard JW: Macrophages:
obligate partners for tumor cell migration, invasion and
metastasis. Cell. 124:263–266. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Storz P: Reactive oxygen species in tumor
progression. Front Biosci. 10:1881–1896. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Radisky DC, Levy DD, Littlepage LE, Liu H,
Nelson CM, Fata JE, Leake D, Godden EL, Albertson DG, Nieto MA, et
al: Rac1b and reactive oxygen species mediate MMP-3-induced EMT and
genomic instability. Nature. 436:123–127. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Pelicano H, Carney D and Huang P: ROS
stress in cancer cells and therapeutic implications. Drug Resist
Updat. 7:97–110. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Suh YA, Arnold RS, Lassegue B, Shi J, Xu
X, Sorescu D, Chung AB, Griendling KK and Lambeth JD: Cell
transformation by the superoxide-generating oxidase Mox1. Nature.
401:79–82. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kalluri R: Basement membranes: Structure,
assembly and role in tumour angiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer.
3:422–433. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Hasegawa Y, Takanashi S, Kanehira Y,
Tsushima T, Imai T and Okumura K: Transforming growth factor-beta1
level correlates with angiogenesis, tumor progression, and
prognosis in patients with nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer.
91:964–971. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Kang Y, Siegel PM, Shu W, Drobnjak M,
Kakonen SM, Cordón-Cardo C, Guise TA and Massagué J: A multigenic
program mediating breast cancer metastasis to bone. Cancer Cell.
3:537–549. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Sánchez-Elsner T, Botella LM, Velasco B,
Corbi A, Attisano L and Bernabéu C: Synergistic cooperation between
hypoxia and transforming growth factor-beta pathways on human
vascular endothelial growth factor gene expression. J Biol Chem.
276:38527–38535. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Zhao J, Cheng Q, Ye P, Yang G, Liu S, Ao
Q, Liu Y and Hu Y: Atorvastatin improves pathological changes in
the aged kidney by upregulating peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor expression and reducing matrix metalloproteinase-9 and
transforming growth factor-β1 levels. Exp Gerontol. 74:37–42. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Hua Y, Zhang W, Xie Z, Xu N and Lu Y:
MMP-2 is mainly expressed in arterioles and contributes to cerebral
vascular remodeling associated with TGF-β1 signaling. J Mol
Neurosci. 59:317–325. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Şekerci ÇA, Işbilen B, Işman F, Akbal C,
Şimşek F and Tarcan T: Urinary NGF, TGF-β1, TIMP-2 and bladder wall
thickness predict neurourological findings in children with
myelodysplasia. J Urol. 191:199–205. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Schwarte-Waldhoff I, Volpert OV, Bouck NP,
Sipos B, Hahn SA, Klein-Scory S, Lüttges J, Klöppel G, Graeven U,
Eilert-Micus C, et al: Smad4/DPC4-mediated tumor suppression
through suppression of angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
97:9624–9629. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Xu J, Acharya S, Sahin O, Zhang Q, Saito
Y, Yao J, Wang H, Li P, Zhang L, Lowery FJ, et al: 14-3-3ζ turns
TGF-β's function from tumor suppressor to metastasis promoter in
breast cancer by contextual changes of Smad partners from p53 to
Gli2. Cancer Cell. 27:177–192. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Akahira J, Sugihashi Y, Suzuki T, Ito K,
Niikura H, Moriya T, Nitta M, Okamura H, Inoue S, Sasano H, et al:
Decreased expression of 14-3-3 sigma is associated with advanced
disease in human epithelial ovarian cancer: Its correlation with
aberrant DNA methylation. Clin Cancer Res. 10:2687–2693. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|