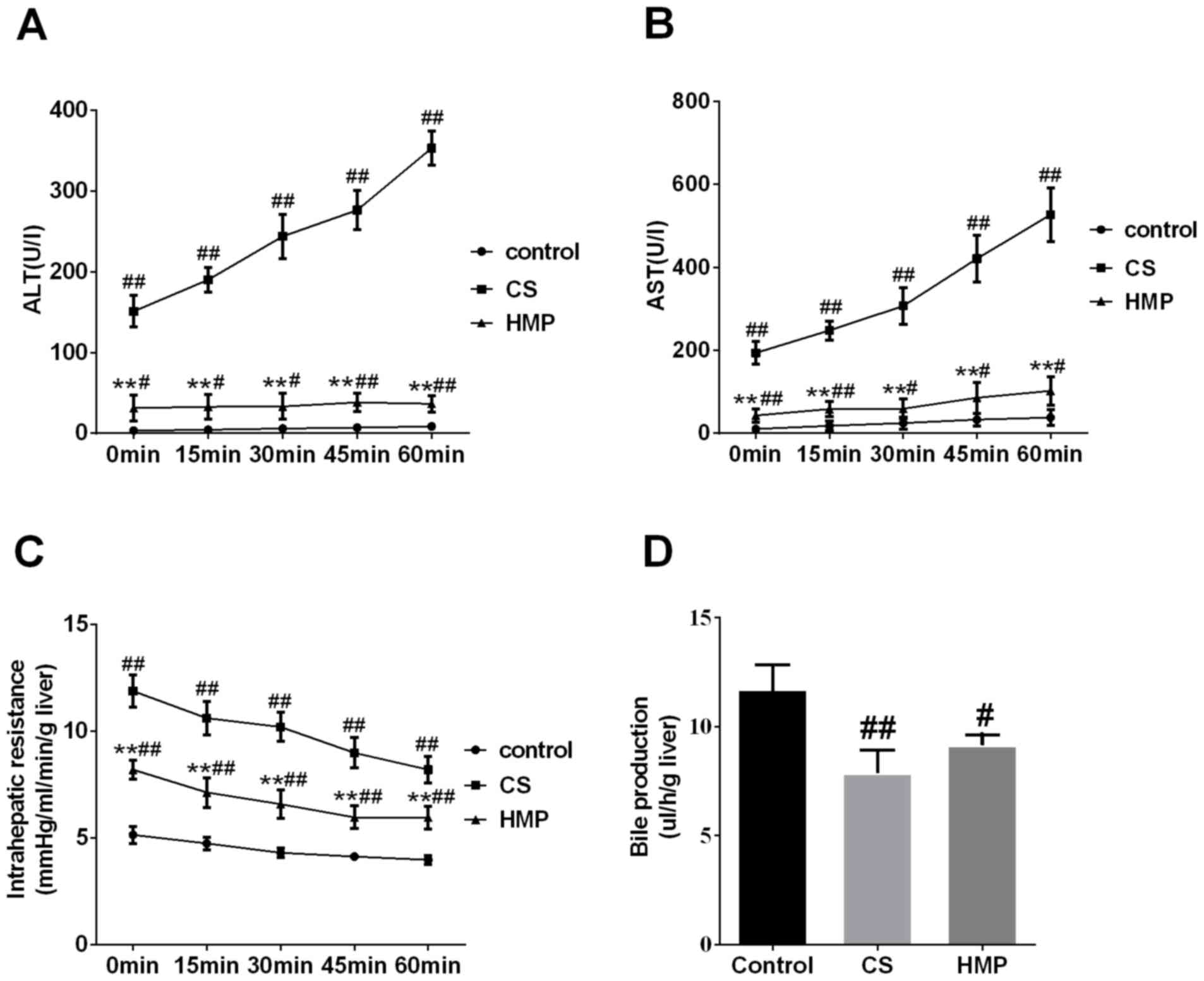
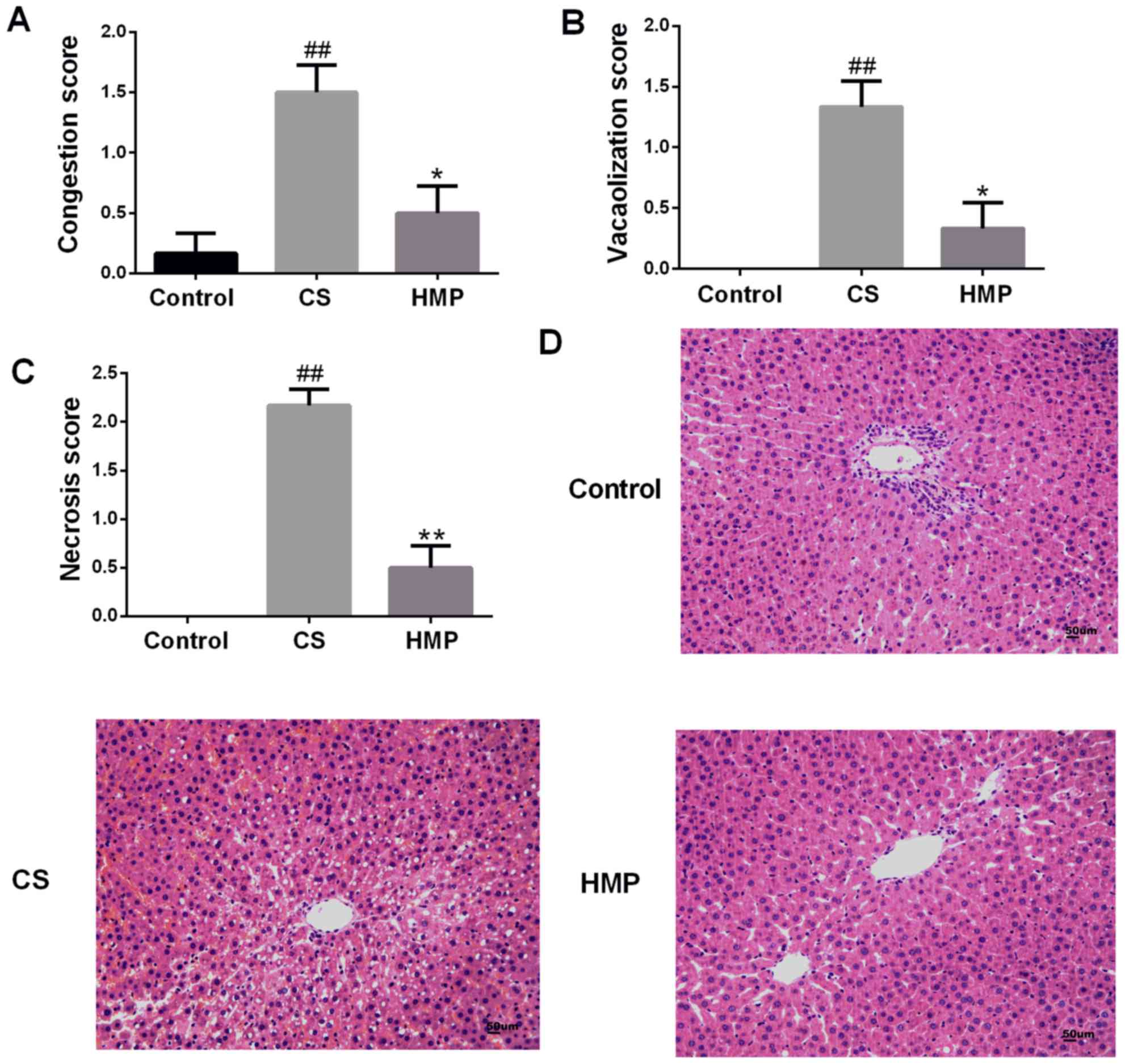
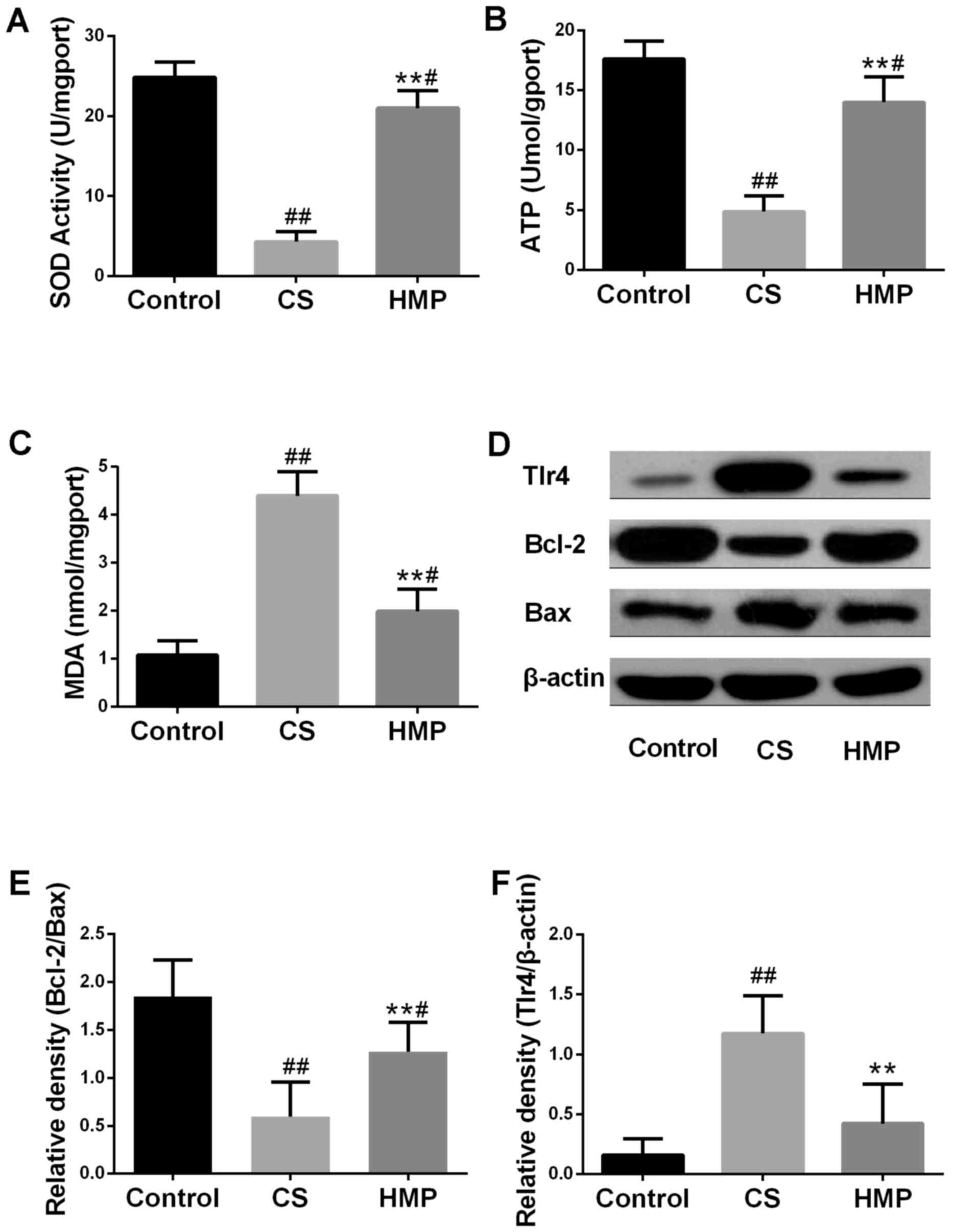
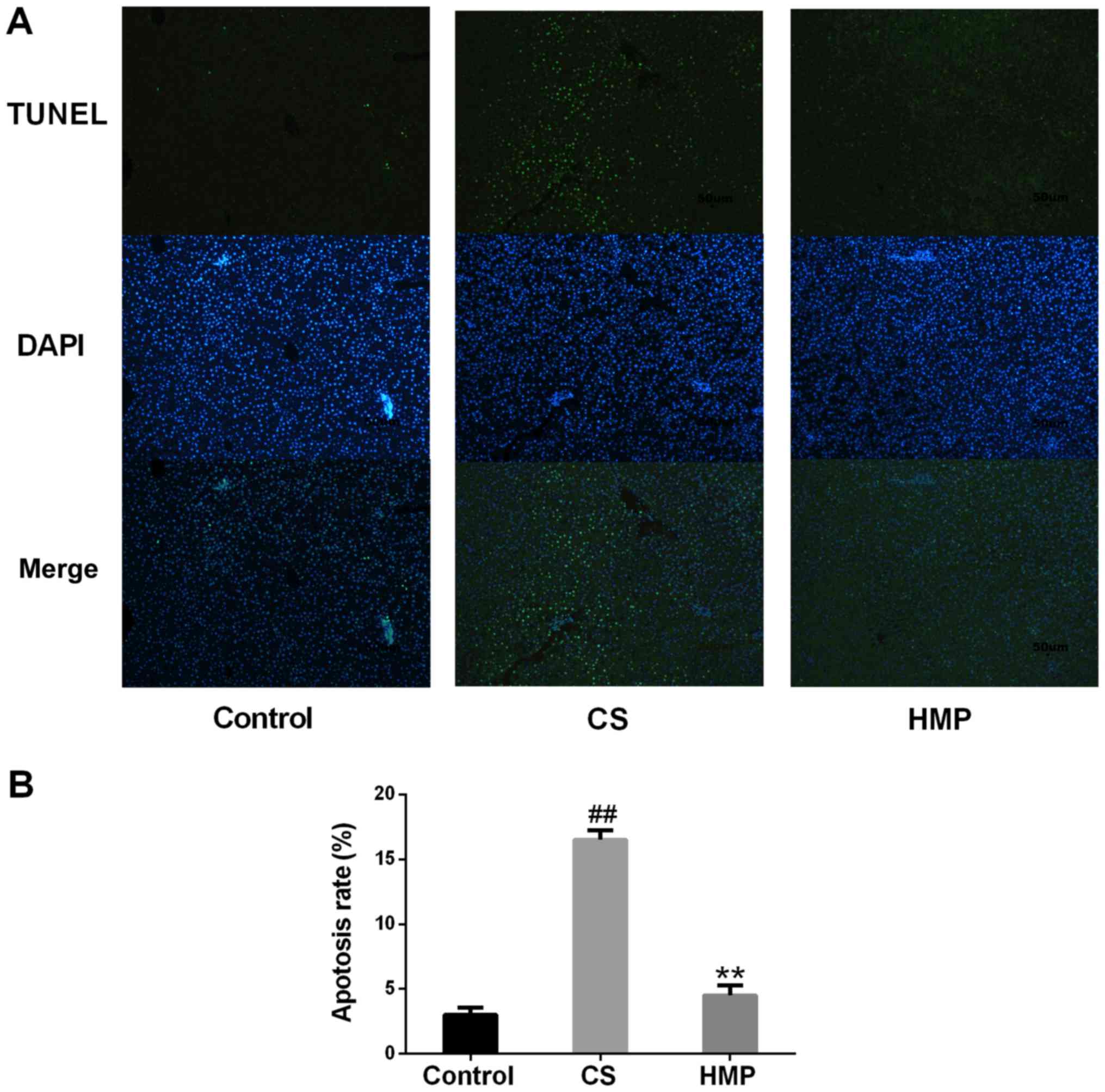
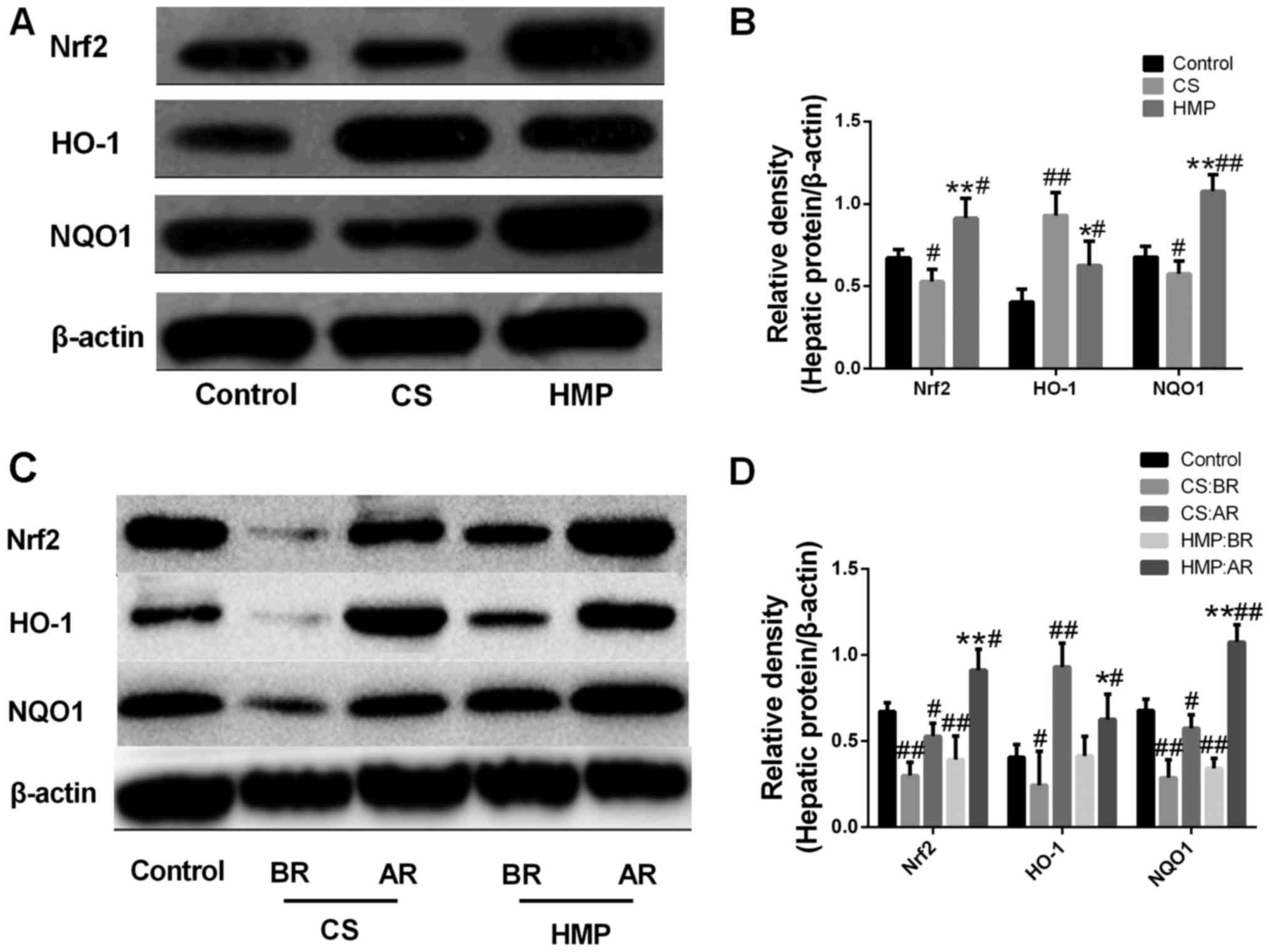
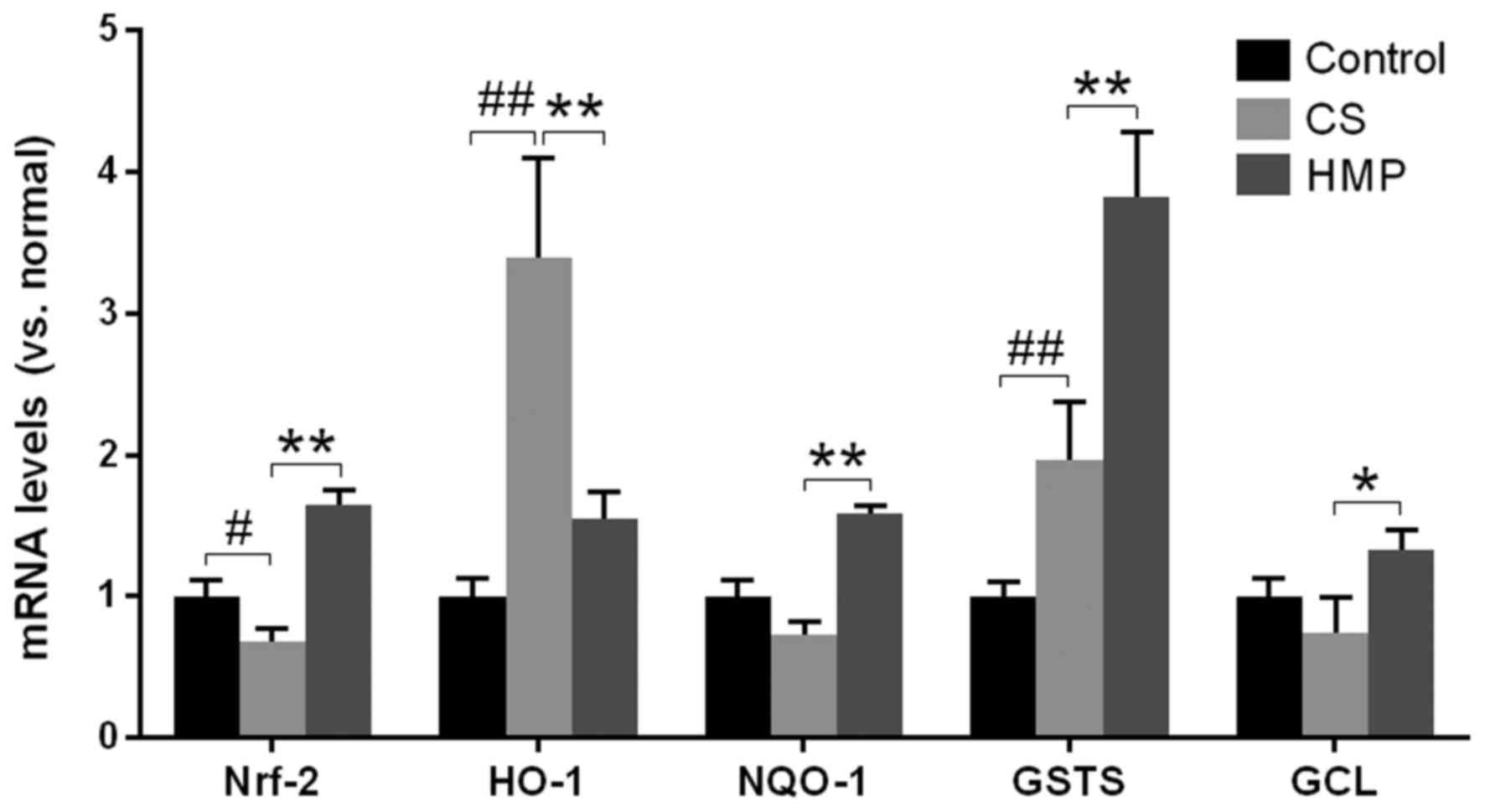
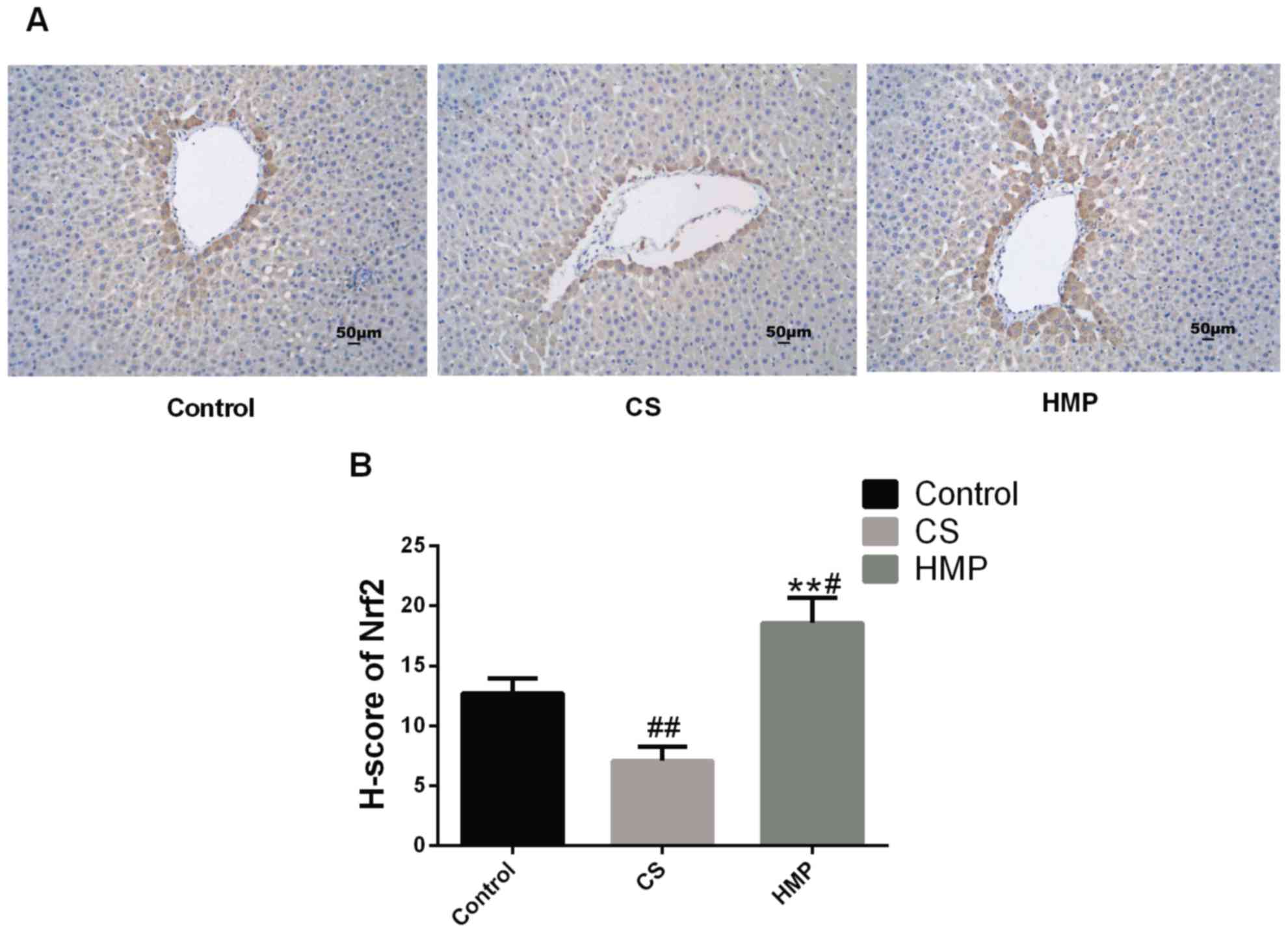
|
1
|
O'Leary JG, Lepe R and Davis GL:
Indications for liver transplantation. Gastroenterology.
134:1764–1776. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Monbaliu D, Pirenne J and Talbot D: Liver
transplantation using donation after cardiac death donors. J
Hepatol. 56:474–485. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Neyrinck A, Van Raemdonck D and Monbaliu
D: Donation after circulatory death: Current status. Curr Opin
Anaesthesiol. 26:382–390. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jay CL, Lyuksemburg V, Ladner DP, Wang E,
Caicedo JC, Holl JL, Abecassis MM and Skaro AI: Ischemic
cholangiopathy after controlled donation after cardiac death liver
transplantation: A meta-analysis. Ann Surg. 253:259–264. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fujita S, Mizuno S, Fujikawa T, Reed AI,
Kim RD, Howard RJ and Hemming AW: Liver transplantation from
donation after cardiac death: A single center experience.
Transplantation. 84:46–49. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Manzarbeitia CY, Ortiz JA, Jeon H,
Rothstein KD, Martinez O, Araya VR, Munoz SJ and Reich DJ:
Long-term outcome of controlled, non-heart-beating donor liver
transplantation. Transplantation. 78:211–215. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Morrissey PE and Monaco AP: Donation after
circulatory death: Current practices, ongoing challenges, and
potential improvements. Transplantation. 97:258–264. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Henry SD and Guarrera JV: Protective
effects of hypothermic ex vivo perfusion on ischemia/reperfusion
injury and transplant outcomes. Transplantation Rev (Orlando).
26:163–175. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Schreinemachers MJ, Doorschodt BM and van
Gulik TM: Machine perfusion preservation of the liver: A worthwhile
clinical activity? Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 12:224–230. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ma Q and He X: Molecular Basis of
Electrophilic and Oxidative Defense: Promises and Perils of Nrf2.
Pharmacol Rev. 64:1055–1081. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kensler TW, Wakabayashi N and Biswal S:
Cell survival responses to environmental stresses via the
Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 47:89–116.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Itoh K, Wakabayashi N, Katoh Y, Ishii T,
Igarashi K, Engel JD and Yamamoto M: Keap1 represses nuclear
activation of antioxidant responsive elements by Nrf2 through
binding to the amino-terminal Neh2 domain. Genes Dev. 13:76–86.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kang MI, Kobayashi A, Wakabayashi N, Kim
SG and Yamamoto M: Scaffolding of Keap1 to the actin cytoskeleton
controls the function of Nrf2 as key regulator of cytoprotective
phase 2 genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:2046–2051. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang DD and Hannink M: Distinct cysteine
residues in keap1 are required for Keap1-dependent ubiquitination
of Nrf2 and for stabilization of Nrf2 by chemopreventiveagents and
oxidative stress. Mol Cell Biol. 23:8137–8151. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kurokawa H, Motohashi H, Sueno S, Kimura
M, Takagawa H, Kanno Y, Yamamoto M and Tanaka T: Structural basis
of alternative DNA recognition by Maf transcription factors. Mol
Cell Biol. 29:6232–6244. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kudoh K, Uchinami H, Yoshioka M, Seki E
and Yamamoto Y: Nrf2 activation protects the liver from
ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Ann Surg. 260:118–127. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee LY, Harberg C, Matkowskyj KA, Cook S,
Roenneburg D, Werner S, Johnson J and Foley DP: Overactivation of
the nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2-antioxidant
response element pathway in hepatocytes decreases hepatic
ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Liver Transplant. 22:91–102.
2016. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Tanaka Y, Maher JM, Chen C and Klaassen
CD: Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion induces renal heme oxygenase-1 via
NF-E2-related factor 2 in rats and mice. Mol Pharmacol. 71:817–825.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fukuda Y, Kaishima M, Ohnishi T, Tohyama
K, Chisaki I, Nakayama Y, Ogasawara-Shimizu M and Kawamata Y: Fluid
shear stress stimulates MATE2-K expression via Nrf2 pathway
activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 484:358–364. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nigro P, Abe J and Berk BC: Flow shear
stress and atherosclerosis: A matter of site specificity. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 15:1405–1414. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zakkar M, Angelini GD and Emanueli C:
Regulation of vascular endothelium inflammatory signalling by shear
stress. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 14:181–186. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
National Research Council, . Guide for the
care and use of laboratory animals. 8th edition. The National
Academies press; Washington, DC: 2011, PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Carnevale ME, Balaban CL, Guibert EE,
Bottai H and Rodriguez JV: Hypothermic machine perfusion versus
cold storage in the rescuing of livers from non-heart-beating donor
rats. Artif Organs. 37:985–991. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rodriguez J, Guibert EE, Quintana A,
Scandizzi A and Almada L: Role of sodium nitroprusside in the
improvement of rat liver preservation in University of Wisconsin
solution: A study in the isolated perfused liver model. J Surg Res.
87:201–208. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dutkowski P, Schönfeld S, Odermatt B,
Heinrich T and Junginger T: Rat liver preservation by hypothermic
oscillating liver perfusion compared to simple cold storage.
Cryobiology. 36:61–70. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zeng C, Hu X, He W, Wang Y, Li L, Xiong Y
and Ye Q: Hypothermic machine perfusion ameliorates inflammation
during ischemia-reperfusion injury via sirtuin-1-mediated
deacetylation of nuclear factor-κB p65 in rat livers donated after
circulatory death. Mol Med Rep. 16:8649–8656. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schlegel A, Kron P, Graf R, Dutkowski P
and Clavien PA: Warm vs. cold perfusion techniques to rescue rodent
liver grafts. J Hepatol. 61:1267–1275. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pizarro MD, Rodriguez JV, Mamprin ME,
Fuller BJ, Mann BE, Motterlini R and Guibert EE: Protective effects
of a carbon monoxide-releasing molecule (CORM-3) during hepatic
cold preservation. Cryobiology. 58:248–255. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Srinivasan PK, Yagi S, Doorschodt B, Nagai
K, Afify M, Uemoto S and Tolba R: Impact ofvenous systemic oxygen
persufflation supplemented with nitric oxide gas on cold-stored,
warm ischemia-damaged experimental liver grafts. Liver Transpl.
18:219–225. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Minor T and Manekeller S: Assessment of
hepatic integrity after ischemic preservation by isolated perfusion
in vitro: The role of albumin. Cryobiology. 54:188–195. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Boyer JL: Bile formation and secretion.
Compr Physiol. 3:1035–1078. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Suzuki S, Toledo-Pereyra LH, Rodriguez FJ
and Cejalvo D: Neutrophil Infiltration As An Important Factor in
Liver Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury. Transplantation.
55:1265–1272. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Funel N, Giovannetti E, Chiaro MD, Pollina
L, Mosca F, Peters G, Campani D and Boggi U: Molecular mechanisms
underlying the synergistic interaction of the novel anticancer drug
celandine with gemcitabine in preclinical models of pancreatic
cancer. Polski Tygodnik Lekarski. 11:23–40. 2011.
|
|
34
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sun K, Liu ZS and Sun Q: Role of
mitochondria in cell apoptosis during hepaticischemia-reperfusion
injury and protective effect of ischemic postconditioning. World J
Gastroenterol. 10:1934–1938. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang L, Li C, Quan R and Xie S: The
effect of electroacupuncture on neuronal apoptosis and related
functions in rats with acute spinal cord injury. Chin Med.
5:199–210. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Radak Z, Zhao Z, Koltai E, Ohno H and
Atalay M: Oxygen consumption and usage during physical exercise:
The balance between oxidative stress and ROS-dependent adaptive
signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal. 18:1208–1246. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cardoso AR, Kakimoto PA and Kowaltowski
AJ: Diet-sensitive sources of reactive oxygen species in liver
mitochondria: Role of very long chain Acyl-CoA dehydrogenases. PLoS
One. 8:e770882013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Reuter S, Gupta SC, Chaturvedi MM and
Aggarwal BB: Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: How are
they linked? Free Radic Biol Med. 49:1603–1616. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chao DT and Korsmeyer SJ: BCL-2 family:
Regulators of cell death. Annu Rev Immunol. 16:395–419. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL and Korsmeyer SJ:
Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that
accelerates programmed cell death. Cell. 74:609–619. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Klune JR and Tsung A: Molecular biology of
liver ischemia/reperfusion injury: Established mechanisms and
recent advancements. Surg Clin North Am. 90:665–677. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Weigand K, Brost S, Steinebrunner N,
Büchler M, Schemmer P and Müller M: Ischemia/reperfusion injury in
liver surgery and transplantation: Pathophysiology. HPB Surg.
2012:1767232012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Marecki H, Bozorgzadeh A, Porte RJ,
Leuvenink HG, Uygun K and Martins PN: Liver ex situ machine
perfusion preservation: A review of the methodology and results of
large animal studies and clinical trials. Liver Transpl.
23:679–695. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Montalvo-Jave EE, Escalante-Tattersfield
T, Ortega-Salgado JA, Piña E and Geller DA: Factors in the
pathophysiology of the liver ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Surg
Res. 147:153–159. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kaczorowski DJ, Tsung A and Billiar TR:
Innate immune mechanisms in ischemia/reperfusion. Front Biosci
(Elite Ed). 1:91–98. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zeng XP, Li XJ, Zhang QY, Liu QW, Li L,
Xiong Y, He CX, Wang YF and Ye QF: Tert-Butylhydroquinone protects
liver against ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats through
Nrf2-activating anti-oxidative activity. Transplant Proc.
49:366–372. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Tao X, Sun X, Xu L, Yin L, Han X, Qi Y, Xu
Y, Zhao Y, Wang C and Peng J: Total flavonoids from Rosa laevigata
Michx fruit ameliorates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury through
inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation in rats. Nutrients.
8:E4182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chou YH, Ho FM, Liu DZ, Lin SY, Tsai LH,
Chen CH, Ho YS, Hung LF and Liang YC: The possible role of heat
shock factor-1 in the negative regulation of heme oxygenase-1. Int
J Biochem Cell Biol. 37:604–615. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Pastukh V, Ruchko M, Gorodnya O, Wilson GL
and Gillespie MN: Sequence-specific oxidative base modifications in
hypoxia-inducible genes. Free Radic Biol Med. 43:1616–1626. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hsieh CY, Hsiao HY, Wu WY, Liu CA, Tsai
YC, Chao YJ, Wang DL and Hsieh HJ: Regulation of shear-induced
nuclear translocation of the Nrf2 transcription factor in
endothelial cells. J Biomed Sci. 16:122009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
St Peter SD, Imber CJ and Friend PJ: Liver
and kidney preservation by perfusion. Lancet. 359:604–613. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|