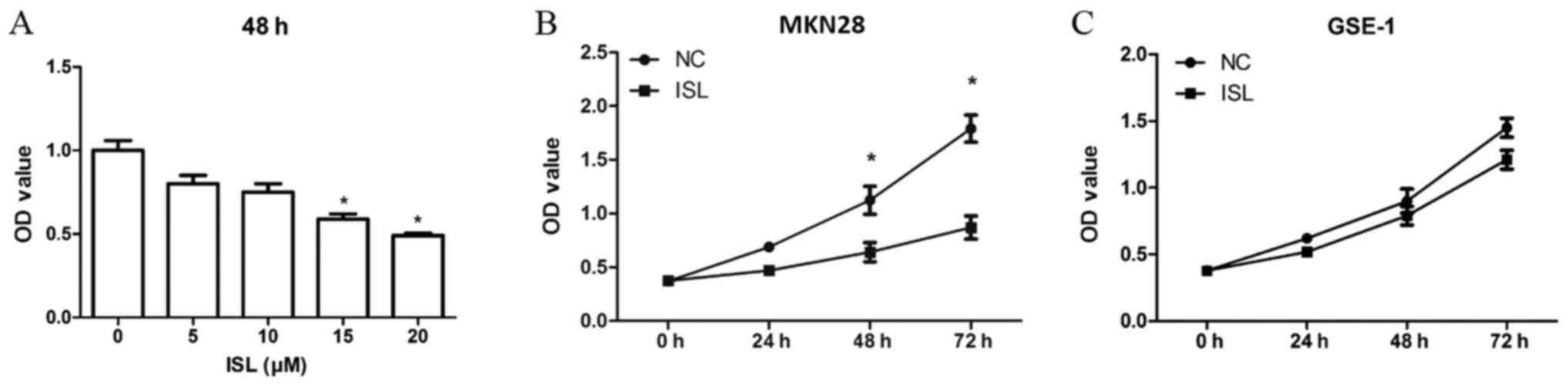
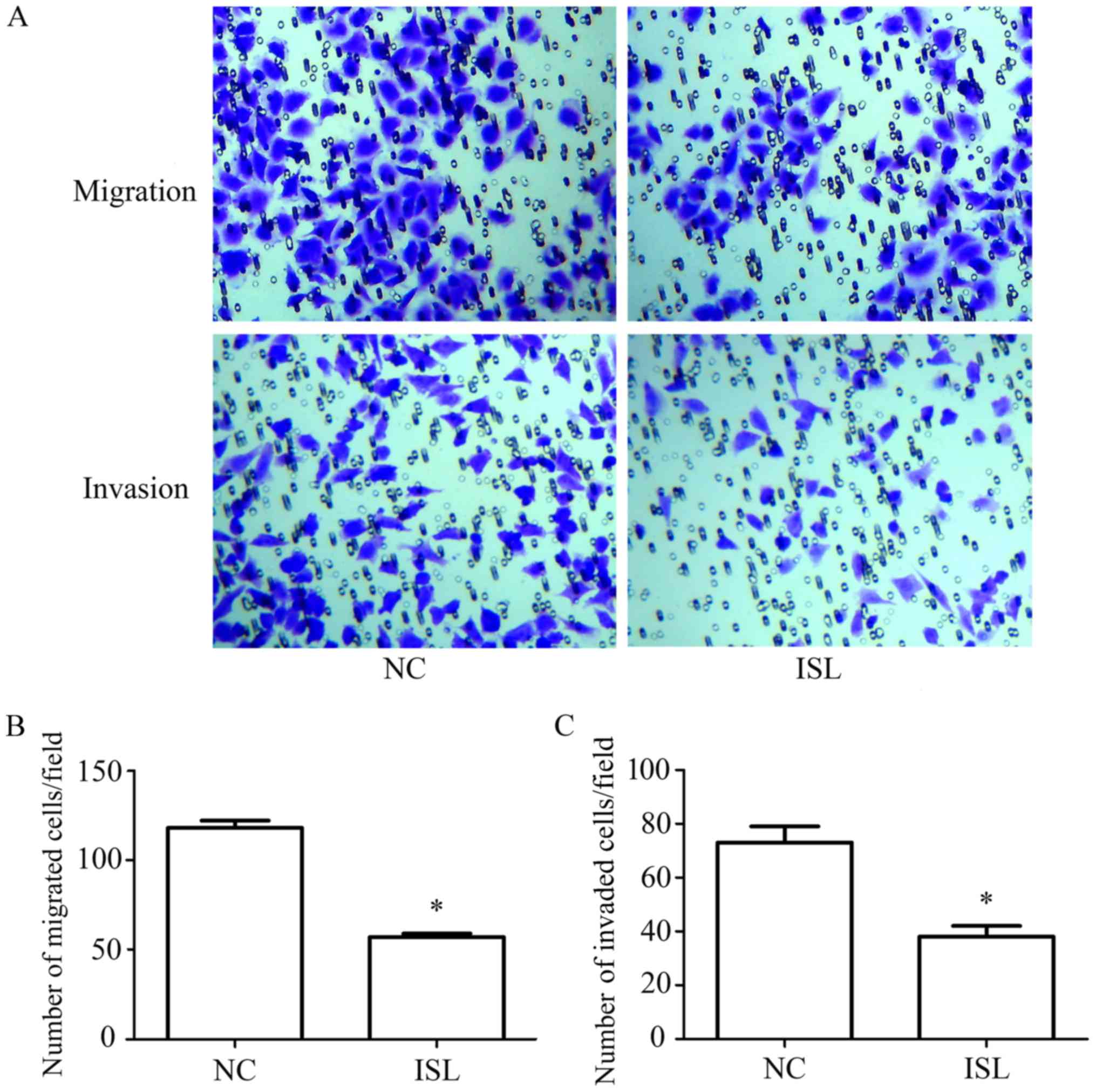
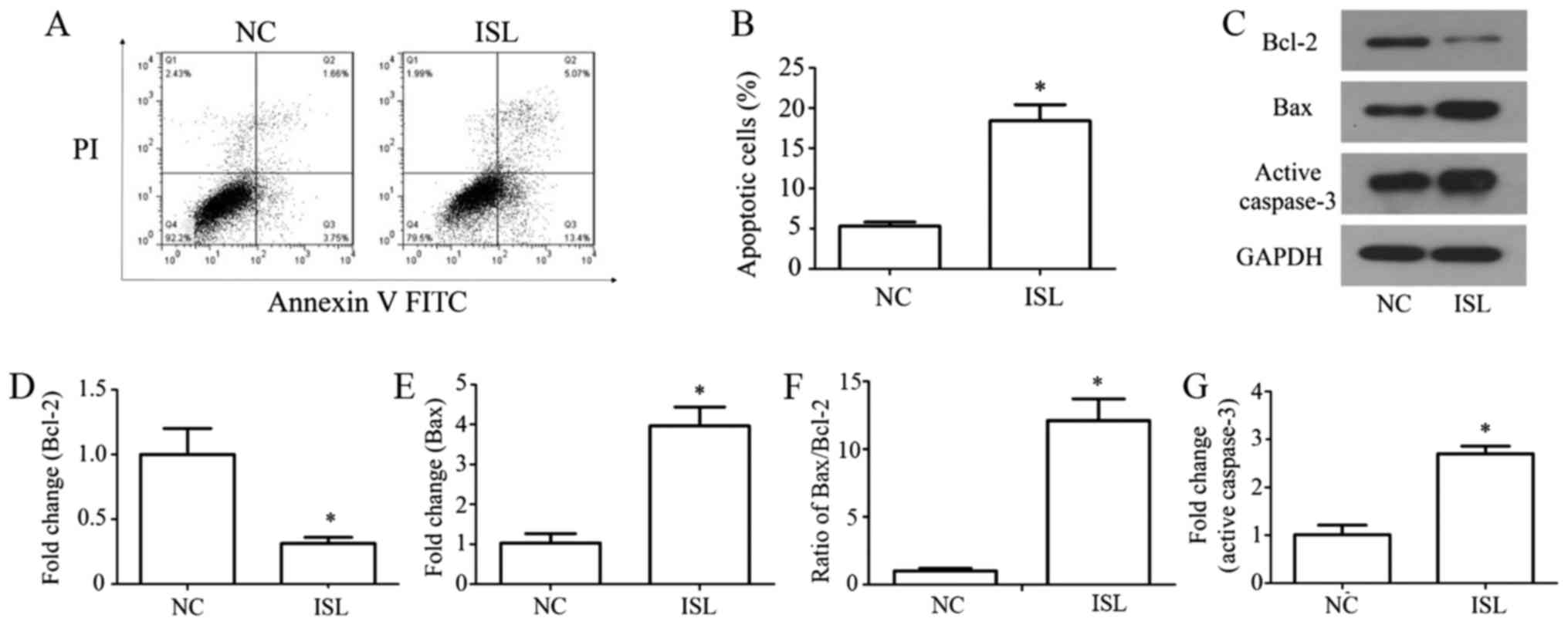
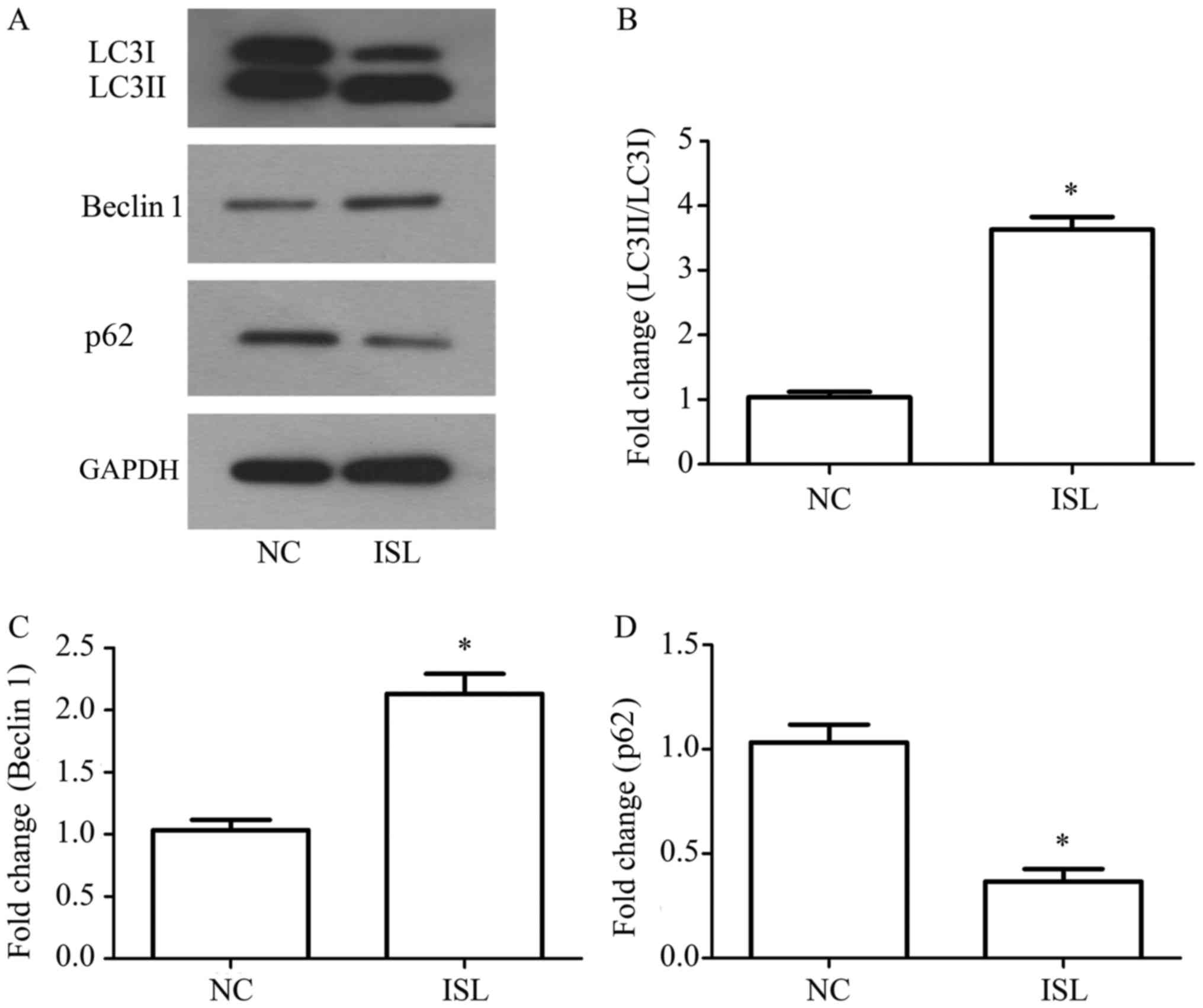
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lin X, Zhao Y, Song WM and Zhang B:
Molecular classification and prediction in gastric cancer. Comput
Struct Biotechnol J. 13:448–458. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu W, Yang Q, Liu B and Zhu Z: Serum
proteomics for gastric cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 431:179–184. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Asghari MH, Moloudizargari M, Ghobadi E,
Fallah M and Abdollahi M: Melatonin as a multifunctional
anti-cancer molecule: Implications in gastric cancer. Life Sci.
185:38–45. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zheng R, Deng Q, Liu Y and Zhao P:
Curcumin inhibits gastric carcinoma cell growth and induces
apoptosis by suppressing the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway.
Med Sci Monit. 23:163–171. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zheng YB, Xiao GC, Tong SL, Ding Y, Wang
QS, Li SB and Hao ZN: Paeoniflorin inhibits human gastric carcinoma
cell proliferation through up-regulation of microRNA-124 and
suppression of PI3K/Akt and STAT3 signaling. World J Gastroenterol.
21:7197–7207. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shen H, Zhao S, Xu Z, Zhu L, Han Y and Ye
J: Evodiamine inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in
gastric cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 10:367–371. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yeh Feng C, Wang KC, Chiang LC, Shieh DE,
Yen MH and Chang San J: Water extract of licorice had anti-viral
activity against human respiratory syncytial virus in human
respiratory tract cell lines. J Ethnopharmacol. 148:466–473. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Si L, Yang X, Yan X, Wang Y and Zheng Q:
Isoliquiritigenin induces apoptosis of human bladder cancer T24
cells via a cyclin-dependent kinase-independent mechanism. Oncol
Lett. 14:241–249. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Peng F, Du Q, Peng C, Wang N, Tang H, Xie
X, Shen J and Chen J: A review: The pharmacology of
isoliquiritigenin. Phytother Res. 29:969–977. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhao Z, Park SM, Guan L, Wu Y, Lee JR, Kim
SC, Kim YW and Zhao R: Isoliquiritigenin attenuates oxidative
hepatic damage induced by carbon tetrachloride with or without
buthionine sulfoximine. Chem Biol Interact. 225:13–20. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yadav VR, Prasad S, Sung B and Aggarwal
BB: The role of chalcones in suppression of NF-κB-mediated
inflammation and cancer. Int Immunopharmacol. 11:295–309. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen XY, Li DF, Han JC, Wang B, Dong ZP,
Yu LN, Pan ZH, Qu CJ, Chen Y, Sun SG and Zheng QS: Reprogramming
induced by isoliquiritigenin diminishes melanoma cachexia through
mTORC2-AKT-GSK3β signaling. Oncotarget. 8:34565–34575.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Z, Wang N, Liu P, Chen Q, Situ H, Xie
T, Zhang J, Peng C, Lin Y and Chen J: MicroRNA-25 regulates
chemoresistance-associated autophagy in breast cancer cells, a
process modulated by the natural autophagy inducer
isoliquiritigenin. Oncotarget. 5:7013–7026. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao H, Yuan X, Li D, Chen H, Jiang J,
Wang Z, Sun X and Zheng Q: Isoliquiritigen enhances the antitumour
activity and decreases the genotoxic effect of cyclophosphamide.
Molecules. 18:8786–8798. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim DH, Park JE, Chae IG, Park G, Lee S
and Chun KS: Isoliquiritigenin inhibits the proliferation of human
renal carcinoma Caki cells through the ROS-mediated regulation of
the Jak2/STAT3 pathway. Oncol Rep. 38:575–583. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yoshida T, Horinaka M, Takara M,
Tsuchihashi M, Mukai N, Wakada M and Sakai T: Combination of
isoliquiritigenin and tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand induces apoptosis in colon cancer HT29
cells. Environ Health Prev Med. 13:281–287. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kwon GT, Cho HJ, Chung WY, Park KK, Moon A
and Park JH: Isoliquiritigenin inhibits migration and invasion of
prostate cancer cells: Possible mediation by decreased JNK/AP-1
signaling. J Nutr Biochem. 20:663–676. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hsia SM, Yu CC, Shih YH, Chen Yuanchien M,
Wang TH, Huang YT and Shieh TM: Isoliquiritigenin as a cause of DNA
damage and inhibitor of ataxia-telangiectasia mutated expression
leading to G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis in oral squamous cell
carcinoma. Head Neck. 38 Suppl 1:E360–E371. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hsu YL, Chia CC, Chen PJ, Huang SE, Huang
SC and Kuo PL: Shallot and licorice constituent isoliquiritigenin
arrests cell cycle progression and induces apoptosis through the
induction of ATM/p53 and initiation of the mitochondrial system in
human cervical carcinoma HeLa cells. Mol Nutr Food Res. 53:826–835.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ma J, Fu NY, Pang DB, Wu WY and Xu AL:
Apoptosis induced by isoliquiritigenin in human gastric cancer
MGC-803 cells. Planta Med. 67:754–757. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lin M, Wu D and Huang Y: Natural compounds
ursolic acid and isoliquiritigenin target GRP78 to enhance human
gastric cancer cell chemosensitivity by 5-fluorouracil. FASEB J.
30:1193–1194. 2016.
|
|
24
|
Wu CH, Chen HY, Wang CW, Shieh TM, Huang
TC, Lin LC, Wang KL and Hsia SM: Isoliquiritigenin induces
apoptosis and autophagy and inhibits endometrial cancer growth in
mice. Oncotarget. 7:73432–73447. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen G, Zhu L, Liu Y, Zhou Q, Chen H and
Yang J: Isoliquiritigenin, a flavonoid from licorice, plays a dual
role in regulating gastrointestinal motility in vitro and in vivo.
Phytother Res. 23:498–506. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jergens A, Young J, Moore D, Wang C,
Hostetter J, Augustine L, Allenspach K, Schmitz S and Mosher C:
Bcl-2/caspase 3 mucosal imbalance favors T cell resistance to
apoptosis in dogs with inflammatory bowel disease. Vet Immunol
Immunopathol. 158:167–174. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Renault TT, Floros KV, Elkholi R, Corrigan
KA, Kushnareva Y, Wieder SY, Lindtner C, Serasinghe MN, Asciolla
JJ, Buettner C, et al: Mitochondrial shape governs BAX-induced
membrane permeabilization and apoptosis. Mol Cell. 57:69–82. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fang H, Wu Y, Guo J, Rong J, Ma L, Zhao Z,
Zuo D and Peng S: T-2 toxin induces apoptosis in differentiated
murine embryonic stem cells through reactive oxygen
species-mediated mitochondrial pathway. Apoptosis. 17:895–907.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Maiuri MC, Criollo A, Tasdemir E, Vicencio
JM, Tajeddine N, Hickman JA, Geneste O and Kroemer G: BH3-only
proteins and BH3 mimetics induce autophagy by competitively
disrupting the interaction between Beclin 1 and Bcl-2/Bcl-X(L).
Autophagy. 3:374–376. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shvets E, Abada A, Weidberg H and Elazar
Z: Dissecting the involvement of LC3B and GATE-16 in p62
recruitment into autophagosomes. Autophagy. 7:683–688. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wei Y, An Z, Zou Z, Sumpter R, Su M, Zang
X, Sinha S, Gaestel M and Levine B: The stress-responsive kinases
MAPKAPK2/MAPKAPK3 activate starvation-induced autophagy through
Beclin 1 phosphorylation. elife. 4:e052892015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Wang Z, Wang N, Han S, Wang D, Mo S, Yu L,
Huang H, Tsui K, Shen J and Chen J: Dietary compound
isoliquiritigenin inhibits breast cancer neoangiogenesis via
VEGF/VEGFR-2 signaling pathway. PLoS One. 8:e685662013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen T, Deng S and Lin R: The inhibitory
effect of Isoliquiritigenin on the proliferation of human arterial
smooth muscle cell. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 18:572017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen G, Hu X, Zhang W, Xu N, Wang FQ, Jia
J, Zhang WF, Sun ZJ and Zhao YF: Mammalian target of rapamycin
regulates isoliquiritigenin-induced autophagic and apoptotic cell
death in adenoid cystic carcinoma cells. Apoptosis. 17:90–101.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wu S, Xue J, Yang Y, Zhu H, Chen F, Wang
J, Lou G, Liu Y, Shi Y, Yu Y, et al: Isoliquiritigenin inhibits
interferon-γ-inducible genes expression in hepatocytes through
down-regulating activation of JAK1/STAT1, IRF3/MyD88, ERK/MAPK,
JNK/MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem.
37:501–514. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Safdari Y, Khalili M, Ebrahimzadeh MA,
Yazdani Y and Farajnia S: Natural inhibitors of PI3K/AKT signaling
in breast cancer: emphasis on newly-discovered molecular mechanisms
of action. Pharmacol Res. 93:1–10. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang ZG, Wang Y, Huang Y, Lu Q, Zheng L,
Hu D, Feng WK, Liu YL, Ji KT, Zhang HY, et al: bFGF regulates
autophagy and ubiquitinated protein accumulation induced by
myocardial ischemia/reperfusion via the activation of the
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Sci Rep. 5:92872015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dillon RL, White DE and Muller WJ: The
phosphatidyl inositol 3-kinase signaling network: Implications for
human breast cancer. Oncogene. 26:1338–1345. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen L, Wang J, Wang B, Yang J, Gong Z,
Zhao X, Zhang C and Du K: MiR-126 inhibits vascular endothelial
cell apoptosis through targeting PI3K/Akt signaling. Ann Hematol.
95:365–374. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Arsham AM, Plas DR, Thompson CB and Simon
MC: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling is neither required
for hypoxic stabilization of HIF-1 alpha nor sufficient for
HIF-1-dependent target gene transcription. J Biol Chem.
277:15162–15170. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sharma S, Guru SK, Manda S, Kumar A,
Mintoo MJ, Prasad VD, Sharma PR, Mondhe DM, Bharate SB and Bhushan
S: A marine sponge alkaloid derivative 4-chloro fascaplysin
inhibits tumor growth and VEGF mediated angiogenesis by disrupting
PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling cascade. Chem Biol Interact. 275:47–60.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cheng TC, Din ZH, Su JH, Wu YJ and Liu CI:
sinulariolide suppresses cell migration and invasion by inhibiting
matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9 and urokinase through the
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in human bladder cancer cells. Mar
Drugs. 15:pii: E238. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Capes-Davis A, Theodosopoulos G, Atkin I,
Drexler HG, Kohara A, MacLeod RA, Masters JR, Nakamura Y, Reid YA,
Reddel RR and Freshney RI: Check your cultures! A list of
cross-contaminated or misidentified cell lines. Int J Cancer.
127:1–8. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|