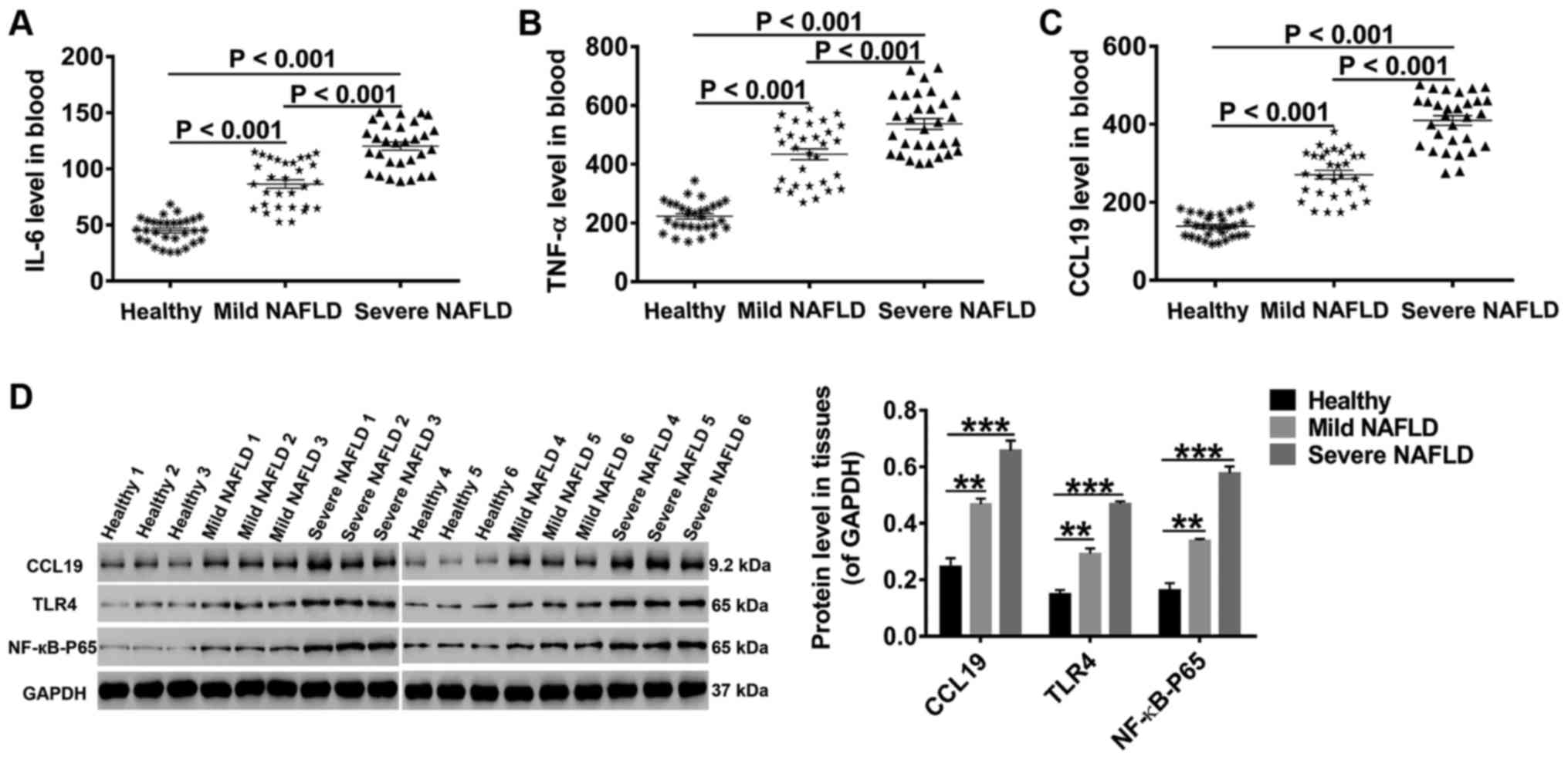
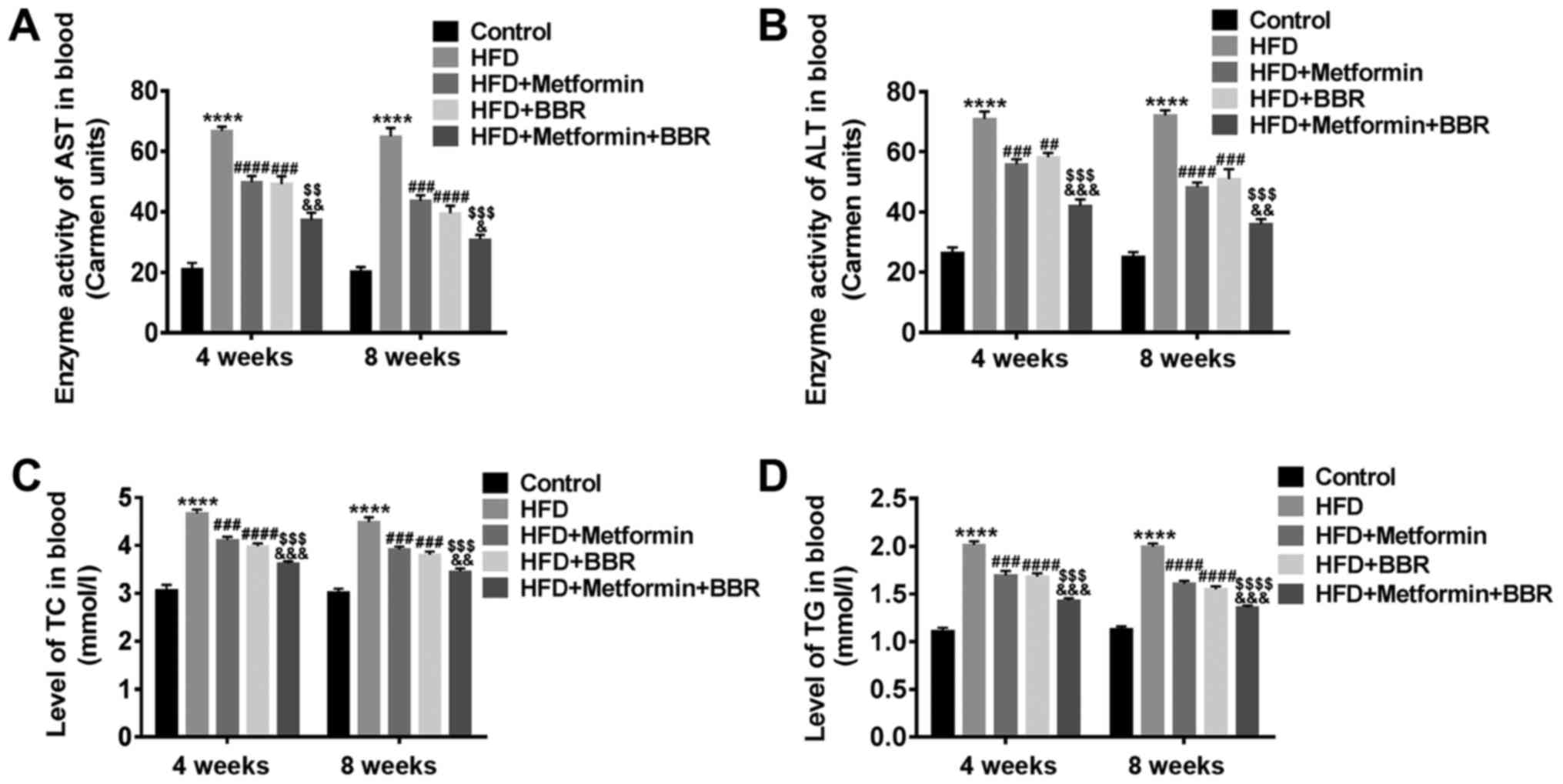
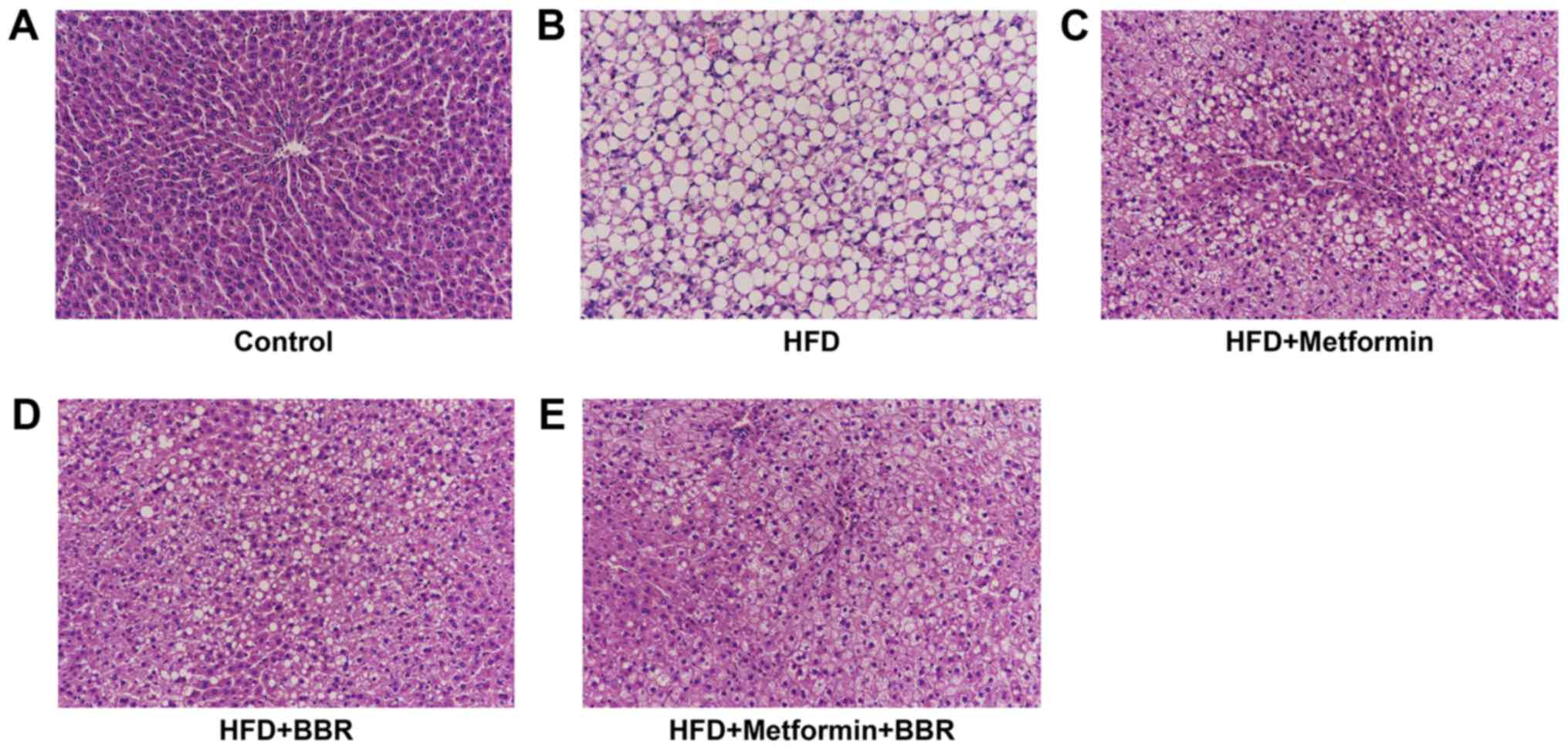
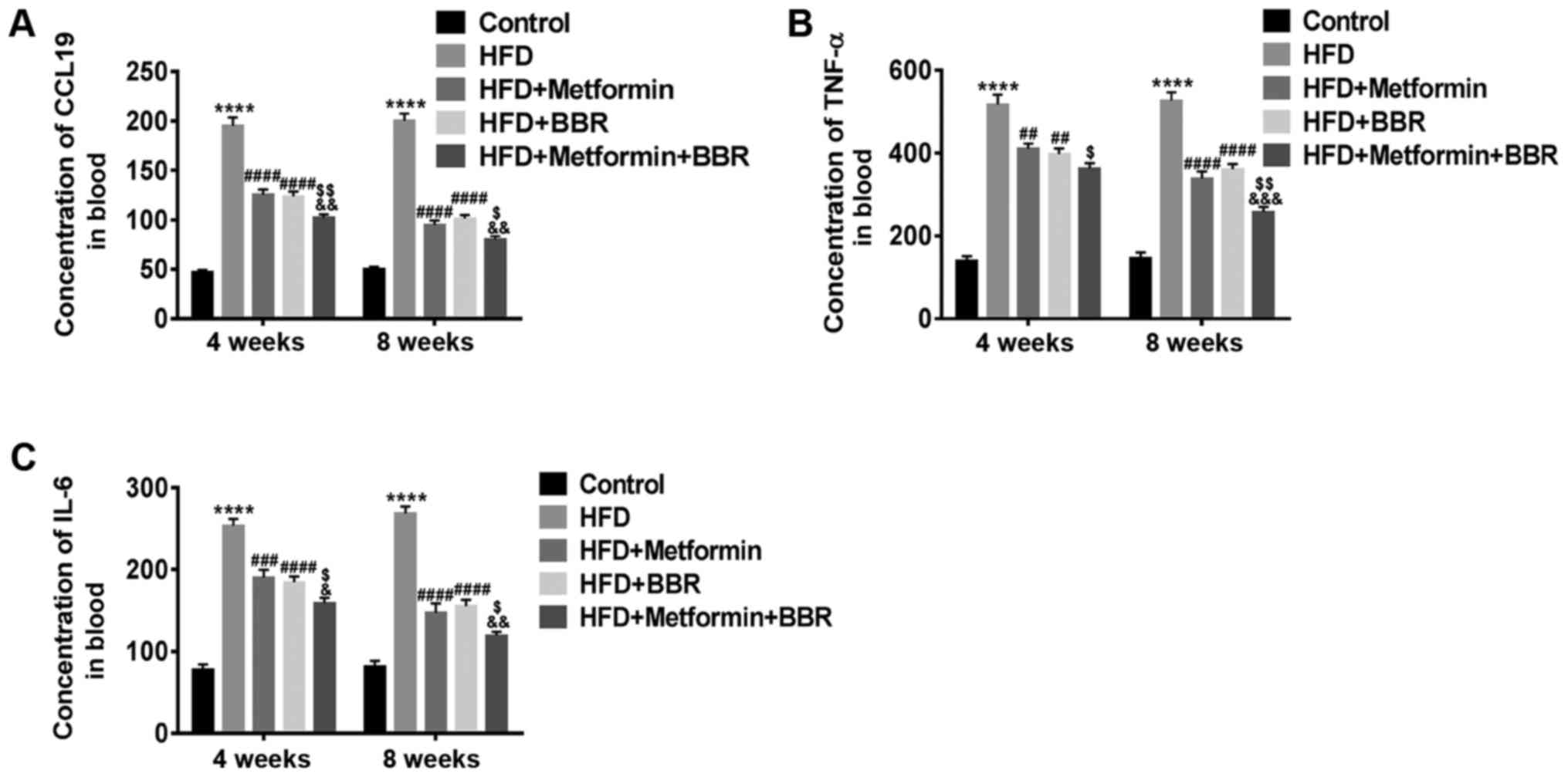
|
1
|
Angulo P: Nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease. N Engl J Med. 346:1221–1231. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ding RB, Bao J and Deng CX: Emerging roles
of SIRT1 in fatty liver diseases. Int J Biol Sci. 13:852–867. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vernon G, Baranova A and Younossi ZM:
Systematic review: The epidemiology and natural history of
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
in adults. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 34:274–285. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Alisi A, Cianfarani S, Manco M, Agostoni C
and Nobili V: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolic
syndrome in adolescents: Pathogenetic role of genetic background
and intrauterine environment. Ann Med. 44:29–40. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Perticone M, Cimellaro A, Maio R, Caroleo
B, Sciacqua A, Sesti G and Perticone F: Additive effect of
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease on metabolic syndrome-related
endothelial dysfunction in hypertensive patients. Int J Mol Sci.
17:4562016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cohen JC, Horton JD and Hobbs HH: Human
fatty liver disease: Old questions and new insights. Science.
332:1519–1523. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu KT, Kuo PL, Su SB, Chen YY, Yeh ML,
Huang CI, Yang JF, Lin CI, Hsieh MH, Hsieh MY, et al: Nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease severity is associated with the ratios of total
cholesterol and triglycerides to high-density lipoprotein
cholesterol. J Clin Lipidol. 10:420–425. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kotronen A, Peltonen M, Hakkarainen A,
Sevastianova K, Bergholm R, Johansson LM, Lundbom N, Rissanen A,
Ridderstråle M, Groop L, et al: Prediction of non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease and liver fat using metabolic and genetic factors.
Gastroenterology. 137:865–872. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, Chen Y, Shen X,
Fenyk-Melody J, Wu M, Ventre J, Doebber T, Fujii N, et al: Role of
AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J
Clin Invest. 108:1167–1174. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Walker AK and Näär AM: SREBPs: Regulators
of cholesterol/lipids as therapeutic targets in metabolic
disorders, cancers and viral diseases. Clin Lipidol. 7:27–36. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Horton JD: Sterol regulatory
element-binding proteins: Transcriptional activators of lipid
synthesis. Biochem Soc Trans. 30:1091–1095. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bricambert J, Miranda J, Benhamed F,
Girard J, Postic C and Dentin R: Salt-inducible kinase 2 links
transcriptional coactivator p300 phosphorylation to the prevention
of ChREBP-dependent hepatic steatosis in mice. J Clin Invest.
120:4316–4331. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kiziltas S, Ata P, Colak Y, Mesçi B,
Senates E, Enc F, Ulasoglu C, Tuncer I and Oguz A: TLR4 gene
polymorphism in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in
comparison to healthy controls. Metab Syndr Relat Disord.
12:165–170. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao CY, Yan L, Wang YD, Wang W, Zhou JY
and Zhen Z: Role of resistin in inflammation of hepatocytes in
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi.
17:683–687. 2009.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pietilä TE, Veckman V, Lehtonen A, Lin R,
Hiscott J and Julkunen I: Multiple NF-kappaB and IFN regulatory
factor family transcription factors regulate CCL19 gene expression
in human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. J Immunol. 178:253–261.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zuany-Amorim C, Hastewell J and Walker C:
Toll-like receptors as potential therapeutic targets for multiple
diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 1:797–807. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS and
Spiegelman BM: Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha:
Direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science.
259:87–91. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pinto Lde F, Compri CM, Fornari JV,
Bartchewsky W, Cintra DE, Trevisan M, Carvalho Pde O, Ribeiro ML,
Velloso LA, Saad MJ, et al: The immunosuppressant drug,
thalidomide, improves hepatic alterations induced by a high-fat
diet in mice. Liver Int. 30:603–610. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
El-Assal O, Feng H, Kim WH, Radaeva S and
Gao B: IL-6-deficient mice are susceptible to ethanol-induced
hepatic steatosis: IL-6 protects against ethanol-induced oxidative
stress and mitochondrial permeability transition in the liver. Cell
Mol Immunol. 1:205–211. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Teoh N, Field J and Farrell G:
Interleukin-6 is a key mediator of the hepatoprotective and
pro-proliferative effects of ischaemic preconditioning in mice. J
Hepatol. 45:20–27. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Peters M, Blinn G, Jostock T, Schirmacher
P, Meyer zum Büschenfelde KH, Galle PR and Rose-John S: Combined
interleukin 6 and soluble interleukin 6 receptor accelerates murine
liver regeneration. Gastroenterology. 119:1663–1671. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Blindenbacher A, Wang X, Langer I, Savino
R, Terracciano L and Heim MH: Interleukin 6 is important for
survival after partial hepatectomy in mice. Hepatology. 38:674–682.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Klein C, Wüstefeld T, Assmus U, Roskams T,
Rose-John S, Müller M, Manns MP, Ernst M and Trautwein C: The
IL-6-gp130-STAT3 pathway in hepatocytes triggers liver protection
in T cell-mediated liver injury. J Clin Invest. 115:860–869. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mas E, Danjoux M, Garcia V, Carpentier S,
Ségui B and Levade T: IL-6 deficiency attenuates murine
diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. PLoS One. 4:e79292009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wieckowska A, Papouchado BG, Li Z, Lopez
R, Zein NN and Feldstein AE: Increased hepatic and circulating
interleukin-6 levels in human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am J
Gastroenterol. 103:1372–1379. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lavine JE, Schwimmer JB, Van Natta ML,
Molleston JP, Murray KF, Rosenthal P, Abrams SH, Scheimann AO,
Sanyal AJ, Chalasani N, et al: Effect of vitamin E or metformin for
treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children and
adolescents: The TONIC randomized controlled trial. JAMA.
305:1659–1668. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yin J, Xing H and Ye J: Efficacy of
berberine in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cell Mol
Immunol. 57:712–717. 2008.
|
|
28
|
Kong W, Wei J, Abidi P, Lin M, Inaba S, Li
C, Wang Y, Wang Z, Si S, Pan H, et al: Berberine is a novel
cholesterol-lowering drug working through a unique mechanism
distinct from statins. Nat Med. 10:1344–1351. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kong WJ, Zhang H, Song DQ, Xue R, Zhao W,
Wei J, Wang YM, Shan N, Zhou ZX, Yang P, et al: Berberine reduces
insulin resistance through protein kinase C-dependent up-regulation
of insulin receptor expression. Metabolism. 58:109–119. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Brusq JM, Ancellin N, Grondin P, Guillard
R, Martin S, Saintillan Y and Issandou M: Inhibition of lipid
synthesis through activation of AMP kinase: An additional mechanism
for the hypolipidemic effects of berberine. J Lipid Res.
47:1281–1288. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chang X, Yan H, Fei J, Jiang M, Zhu H, Lu
D and Gao X: Berberine reduces methylation of the MTTP promoter and
alleviates fatty liver induced by a high-fat diet in rats. J Lipid
Res. 51:2504–2515. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yuan X, Wang J, Tang X, Li Y, Xia P and
Gao X: Berberine ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by a
global modulation of hepatic mRNA and lncRNA expression profiles. J
Transl Med. 13:242015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yan HM, Xia MF, Wang Y, Chang XX, Yao XZ,
Rao SX, Zeng MS, Tu YF, Feng R, Jia WP, et al: Efficacy of
berberine in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS
One. 10:e01341722015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mazza A, Fruci B, Garinis GA, Giuliano S,
Malaguarnera R and Belfiore A: The role of metformin in the
management of NAFLD. Exp Diabetes Res. 2012:7164042012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Luther SA, Bidgol A, Hargreaves DC,
Schmidt A, Xu Y, Paniyadi J, Matloubian M and Cyster JG: Differing
activities of homeostatic chemokines CCL19, CCL21 and CXCL12 in
lymphocyte and dendritic cell recruitment and lymphoid neogenesis.
Journal of Immunology. 169:424–433. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Yanagawa Y and Onoé K: CCL19 induces rapid
dendritic extension of murine dendritic cells. Blood.
100:1948–1956. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sano T, Iwashita M, Nagayasu S, Yamashita
A, Shinjo T, Hashikata A, Asano T, Kushiyama A, Ishimaru N,
Takahama Y and Nishimura F: Protection from diet-induced obesity
and insulin resistance in mice lacking CCL19-CCR7 signaling.
Obesity (Silver Spring). 23:1460–1471. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Borai IH, Shaker Y, Kamal MM, Ezzat WM,
Ashour E, Afify M, Gouda W and Elbrashy MM: Evaluation of
biomarkers in egyptian patients with different grades of
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 5:109–118.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lee SH, Yun SJ, Kim DH, Jo HH and Park YS:
Severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease on sonography and risk
of coronary heart disease. J Clin Ultrasound. 45:391–399. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hong J, Kang B, Kim A, Hwang S, Ahn J, Lee
S, Kim J, Park JH and Cheon DS: Development of a highly sensitive
real-time one step RT-PCR combined complementary locked primer
technology and conjugated minor groove binder probe. Virol J.
8:3302011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang Q, Zhao Y, Zhang DB and Sun LJ:
Effect of Sinai san decoction on the development of non-alcoholic
steatohepatitis in rats. World J Gastroenterol. 11:1392–1395. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Brunt EM, Janney CG, Di Bisceglie AM,
Neuschwander-Tetri BA and Bacon BR: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A
proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. Am J
Gastroenterol. 94:2467–2474. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Haukeland JW, Damås JK, Konopski Z, Løberg
EM, Haaland T, Goverud I, Torjesen PA, Birkeland K, Bjøro K and
Aukrust P: Systemic inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease is characterized by elevated levels of CCL2. J Hepatol.
44:1167–1174. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cynis H, Kehlen A, Haegele M, Hoffmann T,
Heiser U, Fujii M, Shibazaki Y, Yoneyama H, Schilling S and Demuth
HU: Inhibition of Glutaminyl Cyclases alleviates CCL2-mediated
inflammation of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Int J
Exp Pathol. 94:217–225. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kirovski G, Gäbele E, Dorn C, Moleda L,
Niessen C, Weiss TS, Wobser H, Schacherer D, Buechler C, Wasmuth HE
and Hellerbrand C: Hepatic steatosis causes induction of the
chemokine RANTES in the absence of significant hepatic
inflammation. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 3:675–680. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shimizu Y, Murata H, Kashii Y, Hirano K,
Kunitani H, Higuchi K and Watanabe A: CC-chemokine receptor 6 and
its ligand macrophage inflammatory protein 3alpha might be involved
in the amplification of local necroinflammatory response in the
liver. Hepatology. 34:311–319. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen W, Wang X, Huang LI and Liu BO:
Hepcidin in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease regulated by the
TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 11:73–76. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hassan K, Bhalla V, El Regal ME and
A-kader HH: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A comprehensive
review of a growing epidemic. World J Gastroenterol.
20:12082–12101. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang J, Tan Y, Yao F and Zhang Q:
Polydatin alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats by
inhibiting the expression of TNF-α and SREBP-1c. Mol Med Rep.
6:815–820. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Long YC and Zierath JR: AMP-activated
protein kinase signaling in metabolic regulation. J Clin Invest.
116:1776–1783. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kohjima M, Higuchi N, Kato M, Kotoh K,
Yoshimoto T, Fujino T, Yada M, Yada R, Harada N, Enjoji M, et al:
SREBP-1c, regulated by the insulin and AMPK signaling pathways,
plays a role in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Mol Med.
21:507–511. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|