|
1
|
Dar A, Faizi S, Naqvi S, Roome T,
Zikr-ur-Rehman S, Ali M, Firdous S and Moin ST: Analgesic and
antioxidant activity of mangiferin and its derivatives: The
structure activity relationship. Biol Pharm Bull. 28:596–600. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Duang XY, Wang Q, Zhou XD and Huang DM:
Mangiferin: A possible strategy for periodontal disease to therapy.
Med Hypotheses. 76:486–488. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Guha S, Ghosal S and Chattopadhyay U:
Antitumor, immunomodulatory and anti-HIV effect of mangiferin, a
naturally occurring glucosylxanthone. Chemotherapy. 42:443–451.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ajila CM, Rao LJ and Rao UJ:
Characterization of bioactive compounds from raw and ripe Mangifera
indica L. peel extracts. Food Chem Toxicol. 48:3406–3411. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Iseda S: On mangiferin, the coloring
matter of mango (Mangifera indica Linn). V. Identification of sugar
component and the structure of mangiferin. Bull Chem Soc Jpn.
30:629–633. 1957. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang Z, Deng J, Wang Q, Li X and Wei H:
Improvement in the solubility of mangiferin by HP-β-CD inclusion.
Chin Tradit Patent Med. 2008.
|
|
7
|
Han D, Chen C, Cong Z, Yu Z and Xing T:
Determination of mangiferin in rat plasma by liquid-liquid
extraction with UPLC-MS/MS. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 51:260–263. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu R, Liu Z, Zhang C and Zhang B:
Gelucire44/14 as a novel absorption enhancer for drugs with
different hydrophilicities: In vitro and in vivo improvement on
transcorneal permeation. J Pharm Sci. 100:3186–3196. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ma H, Chen H, Sun L, Tong L and Zhang T:
Improving permeability and oral absorption of mangiferin by
phospholipid complexation. Fitoterapia. 93:54–61. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Saleh F, Mumu SJ, Ara F, Hafez MA and Ali
L: Non-adherence to self-care practices & medication and health
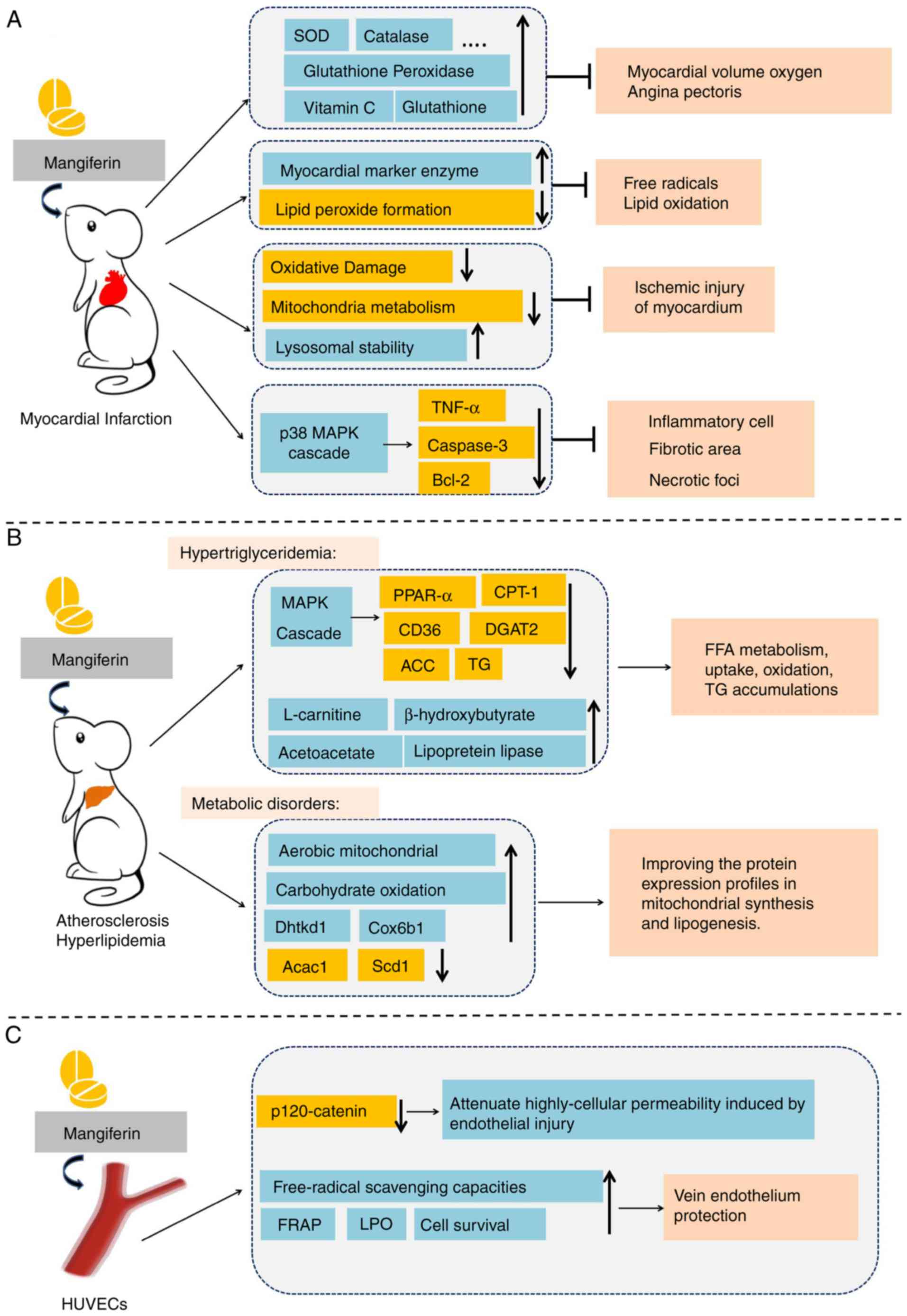
related quality of life among patients with type 2 diabetes: A
cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health. 14:4312014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kueh YC, Morris T and Ismail AA: The
effect of diabetes knowledge and attitudes on self-management and
quality of life among people with type 2 diabetes. Psychol Health
Med. 22:138–144. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ogurtsova K, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Huang
Y, Linnenkamp U, Guariguata L, Cho NH, Cavan D, Shaw JE and
Makaroff LE: IDF diabetes atlas: Global estimates for the
prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.
128:40–50. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
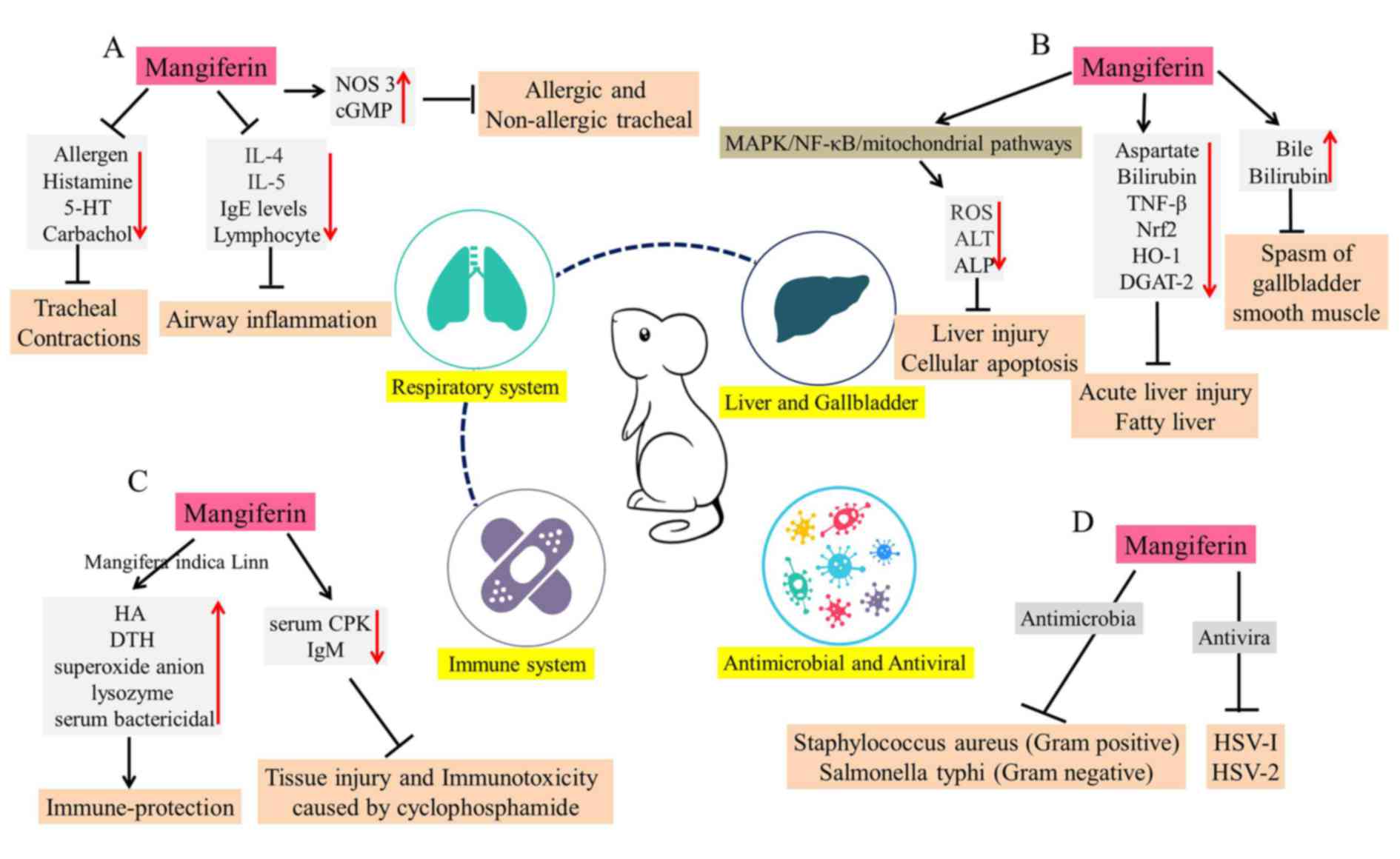
|
|
13
|
Xu Y, Wang L, He J, Bi Y, Li M, Wang T,
Wang L, Jiang Y, Dai M, Lu J, et al: Prevalence and control of
diabetes in Chinese adults. JAMA. 310:948–959. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Barker A, Langenberg C and Wareham NJ:
Genetic determinants of glucose homeostasis. Best Pract Res Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 26:159–170. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Saltiel AR and Kahn CR: Insulin signalling
and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature.
414:799–806. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Göke B: Islet cell function: Alpha and
beta cells-partners towards normoglycaemia. Int J Clin Pract Suppl.
62:2–7. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Cusi K: The role of adipose tissue and
lipotoxicity in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Curr Diab Rep.
10:306–315. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Scheen AJ: Pathophysiology of type 2
diabetes. Acta Clin Belg. 58:335–341. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Avogaro A, Giorda C, Maggini M, Mannucci
E, Raschetti R, Lombardo F, Spila-Alegiani S, Turco S, Velussi M
and Ferrannini E: Diabetes and Informatics Study Group, Association
of Clinical Diabetologists, Istituto Superiore di Sanità: Incidence
of coronary heart disease in type 2 diabetic men and women: Impact
of microvascular complications, treatment, and geographic location.
Diabetes Care. 30:1241–1247. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Connelly K, Kelly D and Gilbert R:
Clinically relevant models of diabetic cardiac complications. Circ
Res. 101:e782007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
De Mattia G, Bravi MC, Laurenti O, Moretti
A, Cipriani R, Gatti A, Mandosi E and Morano S: Endothelial
dysfunction and oxidative stress in type 1 and type 2 diabetic
patients without clinical macrovascular complications. Diabetes Res
Clin Pract. 79:337–342. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Happich M, Breitscheidel L, Meisinger C,
Ulbig M, Falkenstein P, Benter U and Watkins J: Cross-sectional
analysis of adult diabetes type 1 and type 2 patients with diabetic
microvascular complications from a German retrospective
observational study. Curr Med Res Opin. 23:1367–1374. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cohen A and Horton ES: Progress in the
treatment of type 2 diabetes: New pharmacologic approaches to
improve glycemic control. Curr Med Res Opin. 23:905–917. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Carpino PA and Goodwin B: Diabetes area
participation analysis: A review of companies and targets described
in the 2008–2008 patent literature. Expert Opin Ther Pat.
20:1627–1651. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sellamuthu PS, Arulselvan P, Fakurazi S
and Kandasamy M: Beneficial effects of mangiferin isolated from
Salacia chinensis on biochemical and hematological parameters in
rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Pak J Pharm Sci.
27:161–167. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sellamuthu PS, Muniappan BP, Perumal SM
and Kandasamy M: Antihyperglycemic effect of mangiferin in
streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. J Health Sci. 55:206–214.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Saleh S, El-Maraghy N, Reda E and Barakat
W: Modulation of diabetes and dyslipidemia in diabetic
insulin-resistant rats by mangiferin: Role of adiponectin and
TNF-α. An Acad Bras Cienc. 86:1935–1948. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Muruganandan S, Srinivasan K, Gupta S,
Gupta PK and Lal J: Effect of mangiferin on hyperglycemia and
atherogenicity in streptozotocin diabetic rats. J Ethnopharmacol.
97:497–501. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Miura T, Iwamoto N, Kato M, Ichiki H, Kubo
M, Komatsu Y, Ishida T, Okada M and Tanigawa K: The suppressive
effect of mangiferin with exercise on blood lipids in type 2
diabetes. Biol Pharm Bull. 24:1091–1092. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Miura T, Ichiki H, Hashimoto I, Iwamoto N,
Kato M, Kubo M, Ishihara E, Komatsu Y, Okada M, Ishida T and
Tanigawa K: Antidiabetic activity of a xanthone compound,
mangiferin. Phytomedicine. 8:85–87. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kumar SR, Ray MI, Ujwala M, Borde MK and
Deshmukh YA: Natural dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitor mangiferin
mitigates diabetes- and metabolic syndrome-induced changes in
experimental rats. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 9:261–272. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang HL, Li CY, Zhang B, Liu YD, Lu BM,
Shi Z, An N, Zhao LK, Zhang JJ, Bao JK and Wang Y: Mangiferin
facilitates islet regeneration and β-cell proliferation through
upregulation of cell cycle and β-cell regeneration regulators. Int
J Mol Sci. 15:9016–9035. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Duran-Salgado MB and Rubio-Guerra AF:
Diabetic nephropathy and inflammation. World J Diabetes. 5:393–398.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pal PB, Sinha K and Sil PC: Mangiferin
attenuates diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting oxidative stress
mediated signaling cascade, TNFα related and mitochondrial
dependent apoptotic pathways in streptozotocin-induced diabetic
rats. PLoS One. 9:e1072202014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu YW, Zhu X, Zhang L, Lu Q, Wang JY,
Zhang F, Guo H, Yin JL and Yin XX: Up-regulation of glyoxalase 1 by
mangiferin prevents diabetic nephropathy progression in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 721:355–364.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhu X, Cheng YQ, Du L, Li Y, Zhang F, Guo
H, Liu YW and Yin XX: Mangiferin attenuates renal fibrosis through
down-regulation of osteopontin in diabetic rats. Phytother Res.
29:295–302. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gaede P, Vedel P, Larsen N, Jensen GV,
Parving HH and Pedersen O: Multifactorial intervention and
cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J
Med. 348:383–393. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kannel WB and McGee DL: Diabetes and
cardiovascular disease: The Framingham Study. JAMA. 241:2035–2038.
1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Manson JE, Colditz GA, Stampfer MJ,
Willett WC, Krolewski AS, Rosner B, Arky RA, Speizer FE and
Hennekens CH: A prospective study of maturity-onset diabetes
mellitus and risk of coronary heart disease and stroke in women.
Arch Intern Med. 151:1141–1147. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ramasamy R, Yan SF and Schmidt AM:
Receptor for AGE (RAGE): Signaling mechanisms in the pathogenesis
of diabetes and its complications. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1243:88–102.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Suchal K, Malik S, Khan SI, Malhotra RK,
Goyal SN, Bhatia J, Kumari S, Ojha S and Arya DS: Protective effect
of mangiferin on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: Role of AGE-RAGE/MAPK
pathways. Sci Rep. 7:420272017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hou J, Zheng D, Fung G, Deng H, Chen L,
Liang J, Jiang Y and Hu Y: Mangiferin suppressed advanced glycation
end products (AGEs) through NF-κB deactivation and displayed
anti-inflammatory effects in streptozotocin and high fat
diet-diabetic cardiomyopathy rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
94:332–340. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hou J, Zheng D, Zhong G and Hu Y:
Mangiferin mitigates diabetic cardiomyopathy in
streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 91:759–763.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Basha B, Samuel SM, Triggle CR and Ding H:
Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus: possible involvement
of endoplasmic reticulum stress? Exp Diabetes Res. 2012:4818402012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Song J, Li J, Hou F, Wang X and Liu B:
Mangiferin inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated
thioredoxin-interacting protein/NLRP3 inflammasome activation with
regulation of AMPK in endothelial cells. Metabolism. 64:428–437.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Barascu A, Besson P, Le Floch O, Bougnoux
P and Jourdan ML: CDK1-cyclin B1 mediates the inhibition of
proliferation induced by omega-3 fatty acids in MDA-MB-231 breast
cancer cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 38:196–208. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Miyazaki T and Arai S: Two distinct
controls of mitotic cdk1/cyclin B1 activity requisite for cell
growth prior to cell division. Cell Cycle. 6:1419–1425. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Porter LA and Donoghue DJ: Cyclin B1 and
CDK1: Nuclear localization and upstream regulators. Prog Cell Cycle
Res. 5:335–347. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hu X and Moscinski LC: Cdc2: A monopotent
or pluripotent CDK? Cell Prolif. 44:205–211. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Peng ZG, Yao YB, Yang J, Tang YL and Huang
X: Mangiferin induces cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase through
ATR-Chk1 pathway in HL-60 leukemia cells. Genet Mol Res.
14:4989–5002. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yao YB, Peng ZG, Liu ZF, Yang J and Luo J:
Effects of mangiferin on cell cycle status and CDC2/Cyclin B1
expression of HL-60 cells. Zhong Yao Cai. 33:81–85. 2010.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
du Plessis-Stoman D, du Preez J and van de
Venter M: Combination treatment with oxaliplatin and mangiferin
causes increased apoptosis and downregulation of NFκB in cancer
cell lines. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 8:177–184.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Dolcet X, Llobet D, Pallares J and
Matias-Guiu X: NF-kB in development and progression of human
cancer. Virchows Archiv. 446:475–382. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
García-Rivera D, Delgado R, Bougarne N,
Haegeman G and Berghe WV: Gallic acid indanone and mangiferin
xanthone are strong determinants of immunosuppressive anti-tumour
effects of Mangifera indica L. bark in MDA-MB231 breast cancer
cells. Cancer Lett. 305:21–31. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Shi W, Deng J, Tong R, Yang Y, He X, Lv J,
Wang H, Deng S, Qi P, Zhang D and Wang Y: Molecular mechanisms
underlying mangiferin-induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in
A549 human lung carcinoma cells. Mol Med Rep. 13:3423–3432. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Telang M, Dhulap S, Mandhare A and Hirwani
R: Therapeutic and cosmetic applications of mangiferin: A patent
review. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 23:1561–1580. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Pomerantz JL and Baltimore D: Two pathways
to NF-kappaB. Mol Cell. 10:693–695. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kawasaki H, Toyoda M, Shinohara H, Okuda
J, Watanabe I, Yamamoto T, Tanaka K, Tenjo T and Tanigawa N:
Expression of survivin correlates with apoptosis, proliferation,
and angiogenesis during human colorectal tumorigenesis. Cancer.
91:2026–2032. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Budihardjo I, Oliver H, Lutter M, Luo X
and Wang X: Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during
apoptosis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 15:269–290. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Pan LL, Wang AY, Huang YQ, Luo Y and Ling
M: Mangiferin induces apoptosis by regulating Bcl-2 and Bax
expression in the CNE2 nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:7065–7068. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kim H, Kim H, Mosaddik A, Gyawali R, Ahn
KS and Cho SK: Induction of apoptosis by ethanolic extract of mango
peel and comparative analysis of the chemical constitutes of mango
peel and flesh. Food Chem. 133:416–422. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Lv J, Wang Z, Zhang L, Wang HL, Liu Y, Li
C, Deng J, Wang Y and Bao JK: Mangiferin induces apoptosis and cell
cycle arrest in MCF-7 cells both in vitro and in vivo. J Anim Vet
Adv. 12:352–359. 2013.
|
|
63
|
Zou B, Wang H, Liu Y, Qi P, Lei T, Sun M
and Wang Y: Mangiferin induces apoptosis in human ovarian
adenocarcinoma OVCAR3 cells via the regulation of Notch3. Oncol
Rep. 38:1431–1441. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Saha S, Sadhukhan P and Sil PC:
Mangiferin: A xanthonoid with multipotent anti-inflammatory
potential. Biofactors. 42:459–474. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Bera S, Chaudhuri S and Dutta D:
Assessment of free-radical scavenging activities of mangiferin from
Curcuma amada obtained by non-conventional extraction methods: A
comparative study. Indian J Biotechnol. 14:179–185. 2015.
|
|
66
|
Abdul-Muneer PM, Chandra N and Haorah J:
Interactions of oxidative stress and neurovascular inflammation in
the pathogenesis of traumatic brain injury. Mol Neurobiol.
51:966–979. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Fujiwara N, Som AT, Pham LD, Lee BJ,
Mandeville ET, Lo EH and Arai K: A free radical scavenger edaravone
suppresses systemic inflammatory responses in a rat transient focal
ischemia model. Neurosci Lett. 633:7–13. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Ren Y, Wei B, Song X, An N, Zhou Y, Jin X
and Zhang Y: Edaravone's free radical scavenging mechanisms of
neuroprotection against cerebral ischemia: Review of the
literature. Int J Neurosci. 125:555–565. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Lewén A, Matz P and Chan PH: Free radical
pathways in CNS injury. J Neurotrauma. 17:871–890. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Fu Y, Liu H, Song C, Zhang F, Liu Y, Wu J,
Wen X, Liang C, Ma K, Li L, et al: Mangiferin regulates cognitive
deficits and heme oxygenase-1 induced by lipopolysaccharide in
mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 29:950–956. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Jangra A, Lukhi MM, Sulakhiya K, Baruah CC
and Lahkar M: Protective effect of mangiferin against
lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive and anxiety-like behaviour in
mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 740:337–347. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Bhatia HS, Candelario-Jalil E, de Oliveira
AC, Olajide OA, Martínez-Sánchez G and Fiebich BL: Mangiferin
inhibits cyclooxygenase-2 expression and prostaglandin E 2
production in activated rat microglial cells. Arch Biochem Biophys.
477:253–258. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Márquez L, García-Bueno B, Madrigal JL and
Leza JC: Mangiferin decreases inflammation and oxidative damage in
rat brain after stress. Eur J Nutr. 51:729–739. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Wang Z, Guo S, Wang J, Shen Y, Zhang J and
Wu Q: Nrf2/HO-1 mediates the neuroprotective effect of mangiferin
on early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage by attenuating
mitochondria-related apoptosis and neuroinflammation. Sci Rep.
7:118832017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Yang Z, Weian C, Susu H and Hanmin W:
Protective effects of mangiferin on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion
injury and its mechanisms. Eur J Pharmacol. 771:145–151. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Prabhu S, Jainu M, Sabitha KE and Devi CS:
Role of mangiferin on biochemical alterations and antioxidant
status in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats. J
Ethnopharmacol. 107:126–133. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Prabhu S, Jainu M, Sabitha KE and Devi CS:
Cardioprotective effect of mangiferin on isoproterenol induced
myocardial infarction in rats. Indian J Exp Biol. 44:209–215.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Prabhu S, Jainu M, Sabitha KE and Devi
Shyamala CS: Effect of mangiferin on mitochondrial energy
production in experimentally induced myocardial infarcted rats.
Vascul Pharmacol. 44:519–525. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Prabhu S, Narayan S and Devi C: Mechanism
of protective action of mangiferin on suppression of inflammatory
response and lysosomal instability in rat model of myocardial
infarction. Phytother Res. 23:756–760. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Zheng D, Hou J, Xiao Y, Zhao Z and Chen L:
Cardioprotective effect of mangiferin on left ventricular
remodeling in rats. Pharmacology. 90:78–87. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Arozal W, Suyatna FD, Juniantito V,
Rosdiana DS, Amurugam S, Aulia R, Monayo ER and Siswandi R: The
effects of mangiferin (Mangifera indica L) in doxorubicin-induced
cardiotoxicity in rats. Drug Res (Stuttg). 65:574–580. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Nordestgaard BG and Varbo A: Triglycerides
and cardiovascular disease. Lancet. 384:626–635. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Alberto Nú?ez-Sellés J: Antioxidant
therapy: myth or reality? J Braz Chem Soc. 16:699–710. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Pardo-Andreu GL, Paim BA, Castilho RF,
Velho JA, Delgado R, Vercesi AE and Oliveira HC: Mangifera indica
L: extract (Vimang) and its main polyphenol mangiferin prevent
mitochondrial oxidative stress in atherosclerosis-prone
hypercholesterolemic mouse. Pharmacol Res. 57:332–338. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Guo F, Huang C, Liao X, Wang Y, He Y, Feng
R, Li Y and Sun C: Beneficial effects of mangiferin on
hyperlipidemia in high-fat-fed hamsters. Mol Nutr Food Res.
55:1809–1818. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Niu Y, Li S, Na L, Feng R, Liu L, Ying L
and Sun C: Mangiferin decreases plasma free fatty acids through
promoting its catabolism in liver by activation of AMPK. PLoS One.
7:e307822012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Na L, Zhang Q, Jiang S, Du S, Zhang W, Li
Y, Sun C and Niu Y: Mangiferin supplementation improves serum lipid
profiles in overweight patients with hyperlipidemia: A double-blind
randomized controlled trial. Sci Rep. 5:103442015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Apontes P, Liu Z, Su K, Benard O, Youn DY,
Li X, Li W, Mirza RH, Bastie CC, Jelicks LA, et al: Mangiferin
stimulates carbohydrate oxidation and protects against metabolic
disorders induced by high-fat diets. Diabetes. 63:3626–3636. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Lim J, Liu Z, Apontes P, Feng D, Pessin
JE, Sauve AA, Angeletti RH and Chi Y: Dual mode action of
mangiferin in mouse liver under high fat diet. PLoS One.
9:e901372014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Takagi A and Tada Y: Medical applicability
of cultured vascular endothelial cells in cardiovascular surgery.
Jpn J Cardiovasc Surg. 19:45–52. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Lahera V, Navarro-Cid J, Maeso R and
Cachofeiro V: Participation of endothelium-derived vasoconstrictor
factors in arterial hypertension. Rev Esp Cardiol. 52 Suppl
3:S4–S11. 1999.(In Spanish).
|
|
92
|
He Q, Ai J and Huang Y: Relationship
between endothelial damage and p120-catenin in paraquat
intoxication and the protective effect of mangiferin. Zhonghua Wei
Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 26:369–373. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Luo F, Lv Q, Zhao Y, Hu G, Huang G, Zhang
J, Sun C, Li X and Chen K: Quantification and purification of
mangiferin from Chinese Mango (Mangifera indica L.) cultivars and
its protective effect on human umbilical vein endothelial cells
under H(2)O(2)-induced stress. Int J Mol Sci. 13:11260–11274. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Venugopal R, Sakthisekaran D, Rajkapoor B
and Nishigaki I: In vitro protective effect of mangiferin against
glycated protein-iron chelate induced toxicity in human umbilical
vein endothelial cells. J Biol Sci. 7:1227–1232. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Vieira AB, Coelho LP, Insuela DB, Carvalho
VF, dos Santos MH, Silva PM and Martins MA: Mangiferin prevents
guinea pig tracheal contraction via activation of the nitric
oxide-cyclic GMP pathway. Plos One. 8:e717592013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Rivera DG, Hernández I, Merino N, Luque Y,
Álvarez A, Martín Y, Amador A, Nuevas L and Delgado R: Mangifera
indica L. extract (Vimang) and mangiferin reduce the airway
inflammation and Th2 cytokines in murine model of allergic asthma.
J Pharm Pharmacol. 63:1336–1345. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Cohen JC, Horton JD and Hobbs HH: Human
fatty liver disease. Old questions and new insights. Science.
332:1519–1523. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Guo Y and Xia C: Research progress of
pharmacological action and clinical application in tibetan medicine
‘Zangyinchen’. Asia Pac Tradit Med. 2016.
|
|
99
|
Tan L, Feng-Zu HU and Dong Q: Simultaneous
determination of three iridoid glycosides and three flavonoids in
Swertia mussotii Franch. from Qinghai by UPLC. Chin J Pharm Anal.
2017.
|
|
100
|
Pal PB, Sinha K and Sil PC: Mangiferin, a
natural xanthone, protects murine liver in Pb(II) induced hepatic
damage and cell death via MAP kinase, NF-κB and mitochondria
dependent pathways. PLoS One. 8:e568942013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Rasool M, Sabina EP, Mahinda PS and
Gnanaselvi BC: Mangiferin, a natural polyphenol protects the
hepatic damage in mice caused by CCl 4 intoxication. Comp Clin
Pathol. 21:865–872. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Pan CW, Pan ZZ, Hu JJ, Chen WL, Zhou GY,
Lin W, Jin LX and Xu CL: Mangiferin alleviates lipopolysaccharide
and D-galactosamine-induced acute liver injury by activating the
Nrf2 pathway and inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Eur J
Pharmacol. 770:85–91. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Xing X, Li D, Chen D, Zhou L, Chonan R,
Yamahara J, Wang J and Li Y: Mangiferin treatment inhibits hepatic
expression of acyl-coenzyme A: Diacylglycerol acyltransferase-2 in
fructose-fed spontaneously hypertensive rats: A link to
amelioration of fatty liver. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 280:207–215.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
He F, Zeng X, Wei G, Wen Y, Su H, Wei B,
et al: Choleretic action and spasmolysis of gallbladder smooth
muscle of mangiferin. China Pharmacist. 2014.
|
|
105
|
Makare N, Bodhankar S and Rangari V:
Immunomodulatory activity of alcoholic extract of Mangifera indica
L. in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 78:133–137. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Sahu S, Das BK, Pradhan J, Mohapatra BC,
Mishra BK and Sarangi N: Effect of Magnifera indica kernel as a
feed additive on immunity and resistance to Aeromonas hydrophila in
Labeo rohita fingerlings. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 23:109–118. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
García D, Leiro J, Delgado R, Sanmartín ML
and Ubeira FM: Mangifera indica L. extract (Vimang) and mangiferin
modulate mouse humoral immune responses. Phytother Res.
17:1182–1187. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Muruganandan S, Lal J and Gupta PK:
Immunotherapeutic effects of mangiferin mediated by the inhibition
of oxidative stress to activated lymphocytes, neutrophils and
macrophages. Toxicology. 215:57–68. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Miura T, Ichiki H, Iwamoto N, Kato M, Kubo
M, Sasaki H, Okada M, Ishida T, Seino Y and Tanigawa K:
Antidiabetic activity of the rhizoma of Anemarrhena asphodeloides
and active components, mangiferin and its glucoside. Biol Pharm
Bull. 24:1009–1011. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Kim CY, Ahn MJ and Kim J: Preparative
isolation of mangiferin from anemarrhena asphodeloides rhizomes by
centrifugal partition chromatography. J Liq Chromatogr Relat
Technol. 29:869–875. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Maji HS, Maji S, Roy R, Sen A and Biswas
T: Isolation of mangiferin from flowering buds of mangifera indica
l and its evaluation of in vitro antibacterial activity. JPA.
4:49–56. 2015.
|
|
112
|
Zheng MS and Lu ZY: Antiviral effect of
mangiferin and isomangiferin on herpes simplex virus. Chin Med J
(Engl). 103:160–165. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Zhu XM, Song JX, Huang ZZ, Wu YM and Yu
MJ: Antiviral activity of mangiferin against herpes simplex virus
type 2 in vitro. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 14:452–454. 1993.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
García D, Escalante M, Delgado R, Ubeira
FM and Leiro J: Anthelminthic and antiallergic activities of
Mangifera indica L. stem bark components Vimang and mangiferin.
Phytother Res. 17:1203–1208. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Ochocka R, Hering A, Stefanowicz-Hajduk J,
Cal K and Barańska H: The effect of mangiferin on skin:
Penetration, permeation and inhibition of ECM enzymes. PLoS One.
12:e01815422017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|