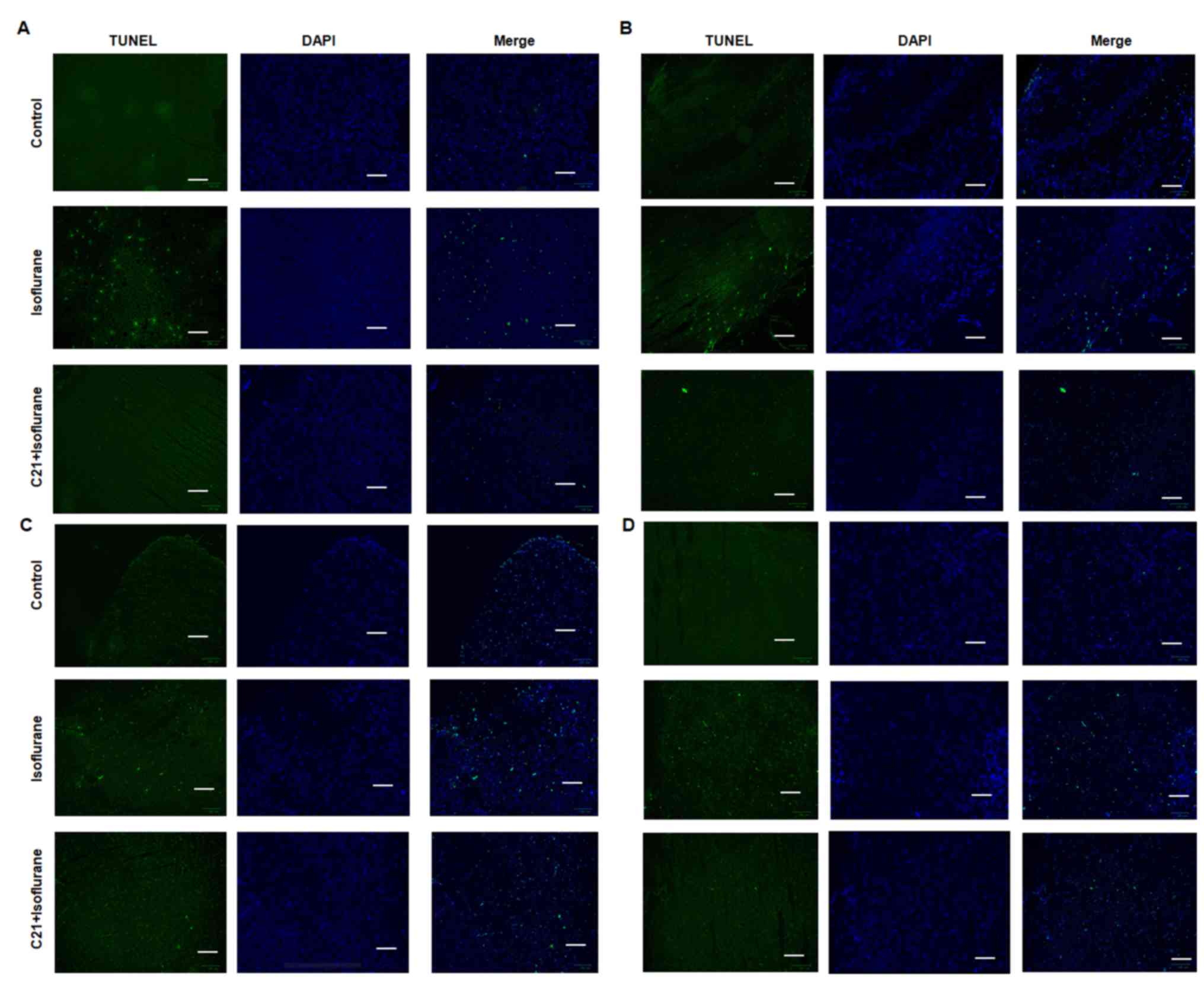
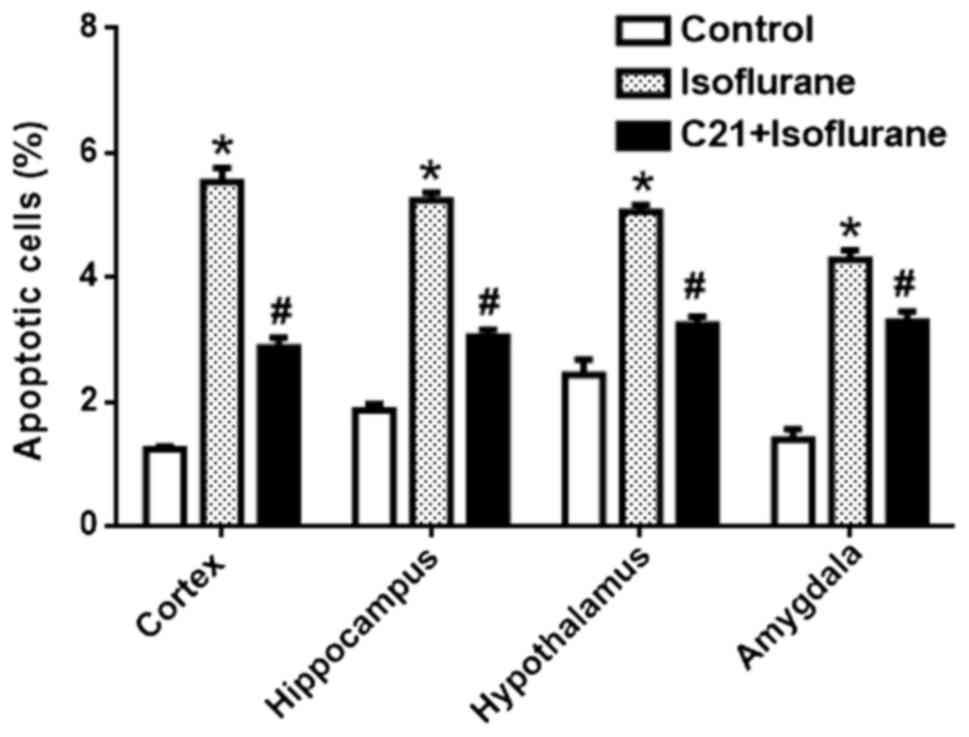
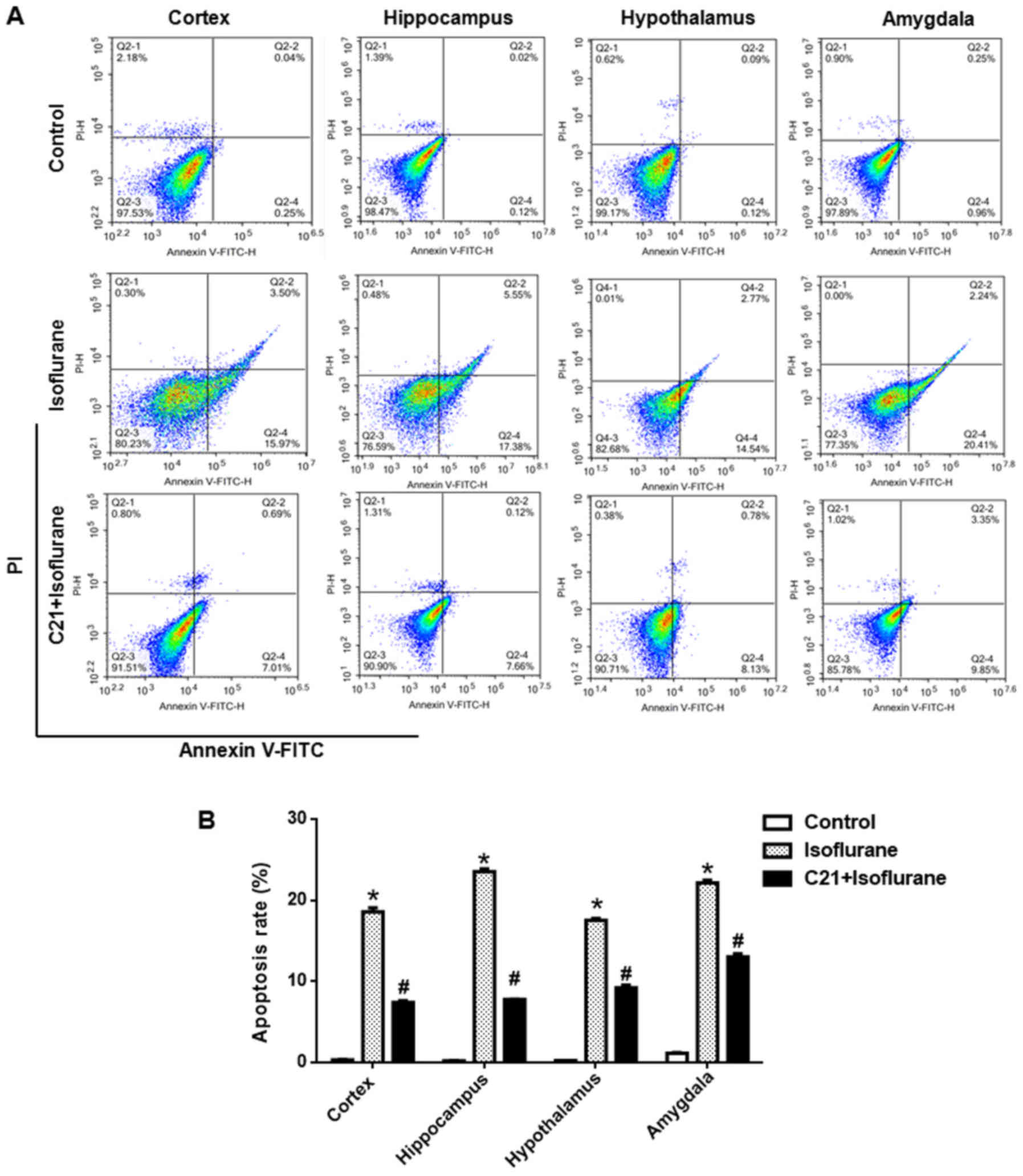
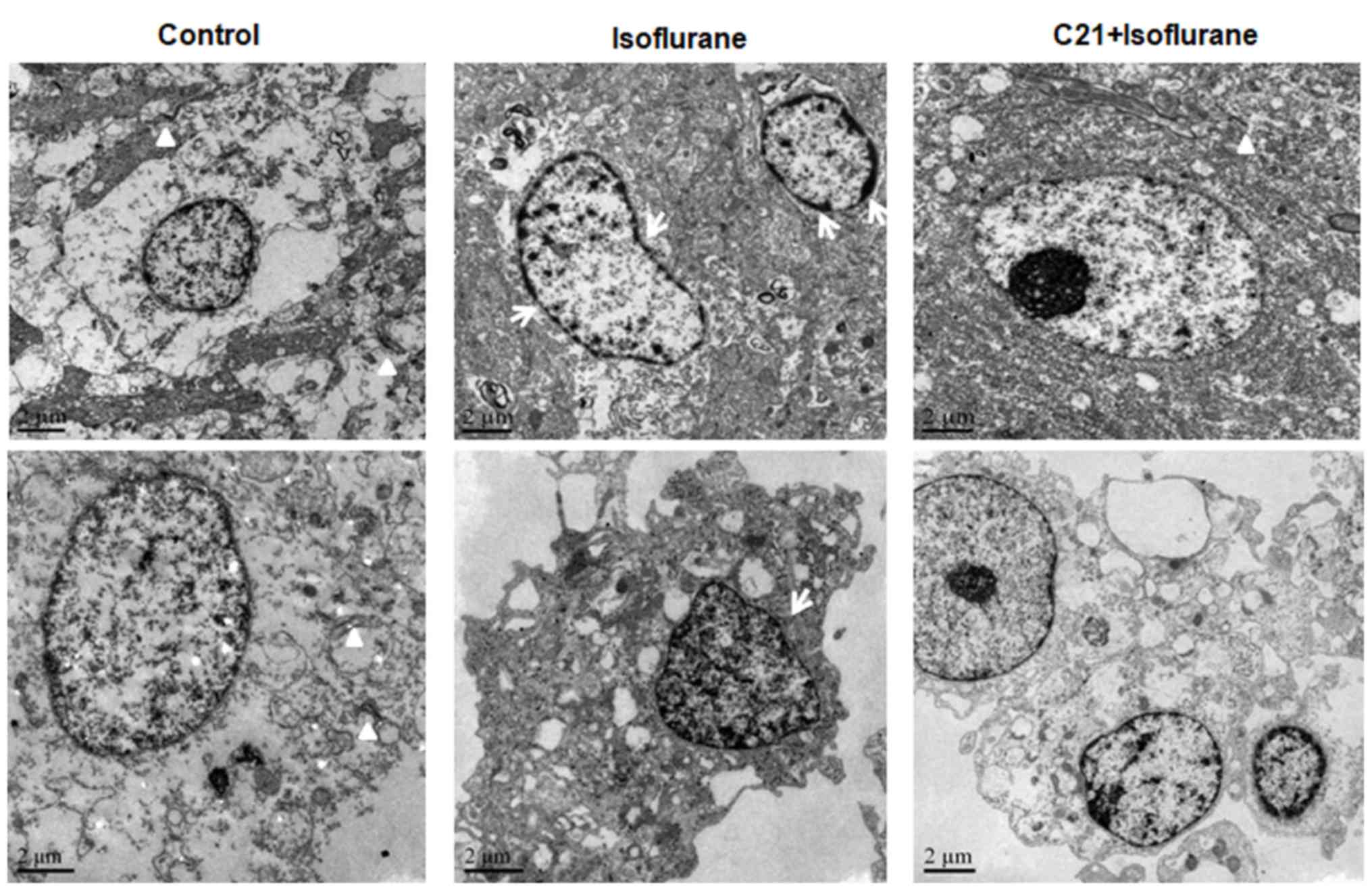
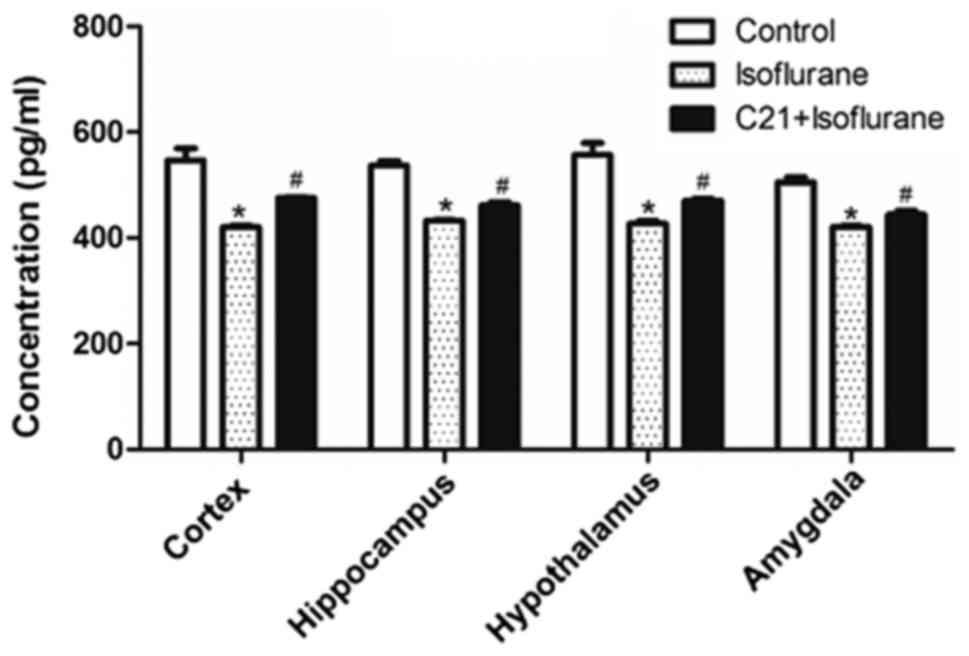
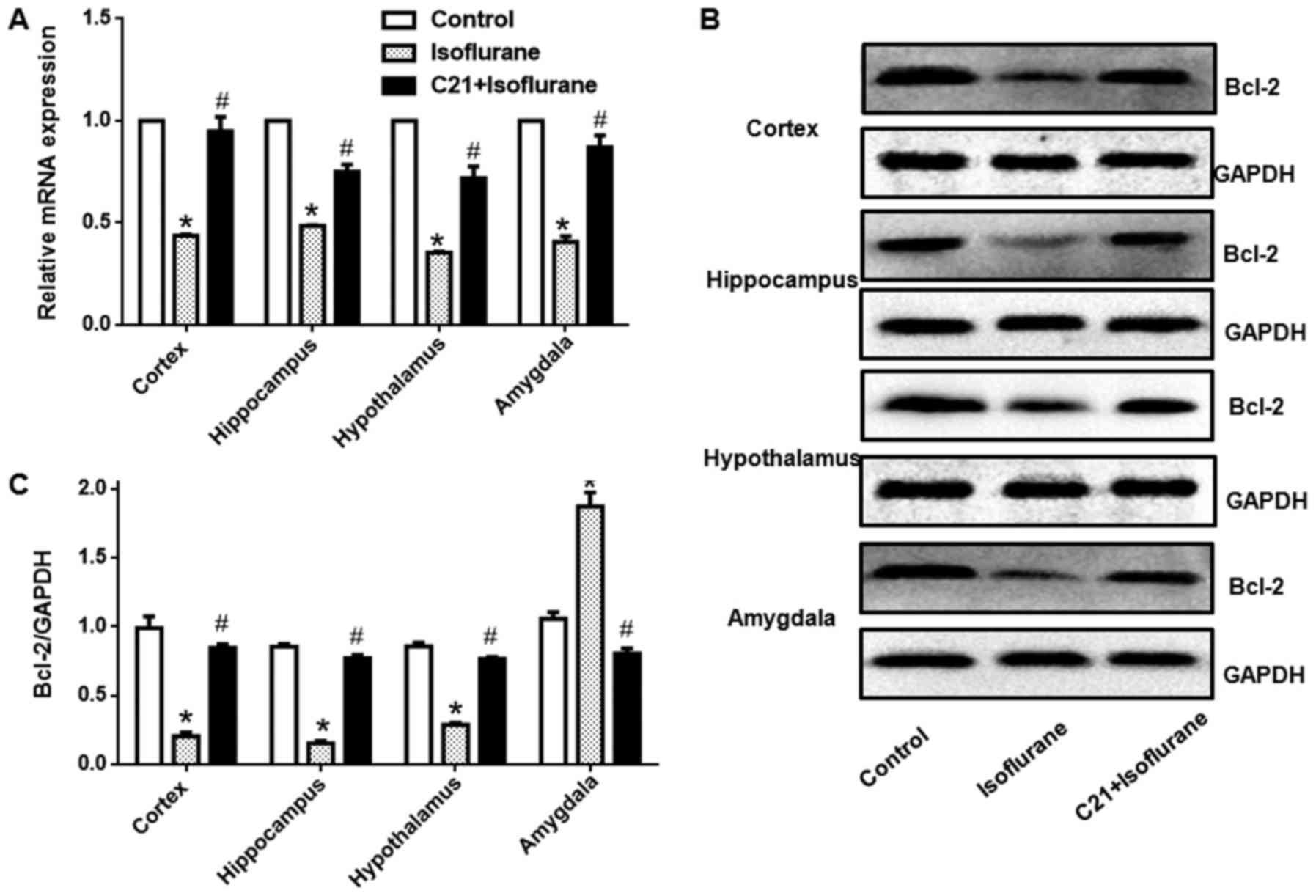
|
1
|
Deng M, Hofacer RD, Jiang C, Joseph B,
Hughes EA, Jia B, Danzer SC and Loepke AW: Brain regional
vulnerability to anaesthesia-induced neuroapoptosis shifts with age
at exposure and extends into adulthood for some regions. Br J
Anaesth. 113:443–451. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang J, Dong Y, Zhou C, Zhang Y and Xie
Z: Anesthetic sevoflurane reduces levels of hippocalcin and
postsynaptic density protein 95. Mol Neurobiol. 51:853–863. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhao T, Li Y, Wei W, Savage S, Zhou L and
Ma D: Ketamine administered to pregnant rats in the second
trimester causes long-lasting behavioral disorders in offspring.
Neurobiol Dis. 68:145–155. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cheng Y, He L, Prasad V, Wang S and Levy
RJ: Anesthesia-induced neuronal apoptosis in the developing retina:
A window of opportunity. Anesth Analg. 121:1325–1335. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Noguchi KK, Johnson SA, Dissen GA, Martin
LD, Manzella FM, Schenning KJ, Olney JW and Brambrink AM:
Isoflurane exposure for three hour triggers apoptotic cell death in
neonatal macaque brain. Br J Anaesth. 119:524–531. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhu G, Liu Y, Wang Y, Bi X and Baudry M:
Different patterns of electrical activity lead to long-term
potentiation by activating different intracellular pathways. J
Neurosci. 35:621–633. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhao DA, Bi LY, Huang Q, Zhang FM and Han
ZM: Isoflurane provides neuroprotection in neonatal hypoxic
ischemic brain injury by suppressing apoptosis. Braz J Anesthesiol.
66:613–621. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sosunov SA, Ameer X, Niatsetskaya ZV,
Utkina-Sosunova I, Ratner VI and Ten VS: Isoflurane anesthesia
initiated at the onset of reperfusion attenuates oxidative and
hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. PLoS One. 10:e01204562015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kalkman CJ, Peelen L, Moons KG, Veenhuizen
M, Bruens M, Sinnema G and de Jong TP: Behavior and development in
children and age at the time of first anesthetic exposure.
Anesthesiology. 110:805–812. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Flick RP, Wilder RT, Sprung J, Katusic SK,
Voigt R, Colligan R, Schroeder DR, Weaver AL and Warner DO:
Anesthesia and cognitive performance in children: No evidence for a
causal relationship. Are the conclusions justified by the data?
Response to Bartels et al, 2009. Twin Res Hum Genet.
12:611–614. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li X, Wei K, Hu R, Zhang B, Li L, Wan L,
Zhang C and Yao W: Upregulation of Cdh1 attenuates
isoflurane-induced neuronal apoptosis and long-term cognitive
impairments in developing rats. Front Cell Neurosci. 11:3682017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Villela D, Leonhardt J, Patel N, Joseph J,
Kirsch S, Hallberg A, Unger T, Bader M, Santos RA, Sumners C and
Steckelings UM: Angiotensin type 2 receptor (AT2R) and receptor
Mas: A complex liaison. Clin Sci. 128:227–234. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Valero-Esquitino V, Lucht K, Namsolleck P,
Monnet-Tschudi F, Stubbe T, Lucht F, Liu M, Ebner F, Brandt C,
Danyel LA, et al: Direct angiotensin type 2 receptor (AT2R)
stimulation attenuates T-cell and microglia activation and prevents
demyelination in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice.
Clin Sci (Lond). 128:95–109. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang Y, Del Borgo M, Lee HW, Baraldi D,
Hirmiz B, Gaspari TA, Denton KM, Aguilar MI, Samuel CS and Widdop
RE: Anti-fibrotic potential of AT2 receptor agonists.
Front Pharmacol. 8:5642017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bennion DM, Isenberg JD, Harmel AT, DeMars
K, Dang AN, Jones CH, Pignataro ME, Graham JT, Steckelings UM,
Alexander JC, et al: Post-stroke angiotensin II type 2 receptor
activation provides long-term neuroprotection in aged rats. PLoS
One. 12:e01807382017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pandey A and Gaikwad AB: Compound 21 and
Telmisartan combination mitigates type 2 diabetic nephropathy
through amelioration of caspase mediated apoptosis. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 487:827–833. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Um HD: Bcl-2 family proteins as regulators
of cancer cell invasion and metastasis: A review focusing on
mitochondrial respiration and reactive oxygen species. Oncotarget.
7:5193–5203. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zheng JH, Follis Viacava A, Kriwacki RW
and Moldoveanu T: Discoveries and controversies in BCL-2
protein-mediated apoptosis. FEBS J. 283:2690–2700. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C (T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang YL, Chen X and Wang ZP: Detrimental
effects of postnatal exposure to propofol on memory and hippocampal
LTP in mice. Brain Res. 1622:321–327. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang YL, Li F and Chen X: Pten
inhibitor-bpV ameliorates early postnatal propofol exposure-induced
memory deficit and impairment of hippocampal LTP. Neurochem Res.
40:1593–1599. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li J, Yang S and Zhu G: Postnatal calpain
inhibition elicits cerebellar cell death and motor dysfunction.
Oncotarget. 8:87997–88007. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Koulis C, Chow BS, McKelvey M, Steckelings
UM, Unger T, Thallas-Bonke V, Thomas MC, Cooper ME, Jandeleit-Dahm
KA and Allen TJ: AT2R agonist, compound 21, is reno-protective
against type 1 diabetic nephropathy. Hypertension. 65:1073–1081.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Iwanami J, Mogi M, Tsukuda K, Steckelings
UM, Unger T, Thallas-Bonke V, Thomas MC, Cooper ME, Jandeleit-Dahm
KA, Allen TJ, et al: Possible synergistic effect of direct
angiotensin II type 2 receptor stimulation by compound 21 with
memantine on prevention of cognitive decline in type 2 diabetic
mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 724:9–15. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Min LJ, Mogi M, Tsukuda K, Jing F, Ohshima
K, Nakaoka H, Kan-No H, Wang XL, Chisaka T, Bai HY, et al: Direct
stimulation of angiotensin II type 2 receptor initiated after
stroke ameliorates ischemic brain damage. Am J Hypertens.
27:1036–1044. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Iwanami J, Mogi M, Tsukuda K, Wang XL,
Nakaoka H, Kan-no H, Chisaka T, Bai HY, Shan BS, Kukida M and
Horiuchi M: Direct angiotensin II type 2 receptor stimulation by
compound 21 prevents vascular dementia. J Am Soc Hypertens.
9:250–256. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu G, Wang Y, Li J and Wang J: Chronic
treatment with ginsenoside Rg1 promotes memory and hippocampal
long-term potentiation in middle-aged mice. Neuroscience.
292:81–89. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Finkel T and Holbrook NJ: Oxidants,
oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature. 408:239–247.
2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhu G, Wang X, Wu S, Li X and Li Q:
Neuroprotective effects of puerarin on
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine induced Parkinson's
disease model in mice. Phytother Res. 28:179–186. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ozaki M, Deshpande SS, Angkeow P, Bellan
J, Lowenstein CJ, Dinauer MC, Goldschmidt-Clermont PJ and Irani K:
Inhibition of the Rac1 GTPase protects against nonlethal
ischemia/reperfusion-induced necrosis and apoptosis in vivo. FASEB
J. 14:418–429. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lennon SV, Martin SJ and Cotter TG:
Dose-dependent induction of apoptosis in human tumour cell lines by
widely diverging stimuli. Cell Prolif. 24:203–214. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li W, Li DY, Zhao SM, Zheng ZJ, Hu J, Li
ZZ and Xiong SB: Rutin attenuates isoflurane-induced neuroapoptosis
via modulating JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in the hippocampi of
neonatal rats. Exp Ther Med. 13:2056–2064. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Monsalve FA, Pyarasani RD, Delgado-Lopez F
and Moore-Carrasco R: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
targets for the treatment of metabolic diseases. Mediators Inflamm.
2013:5496272013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Qian G, Fan W, Ahlemeyer B, Karnati S and
Baumgart-Vogt E: Peroxisomes in different skeletal cell types
during intramembranous and endochondral ossification and their
regulation during osteoblast differentiation by distinct peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors. PLoS One. 10:e01434392015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fong WH, Tsai HD, Chen YC, Wu JS and Lin
TN: Anti-apoptotic actions of PPAR-gamma against ischemic stroke.
Mol Neurobiol. 41:180–186. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Crisafulli C, Bruscoli S, Esposito E,
Mazzon E, Di Paola R, Genovese T, Bramanti P, Migliorati G and
Cuzzocrea S: PPAR-α contributes to the anti-inflammatory activity
of 17β-estradiol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 331:796–807. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|