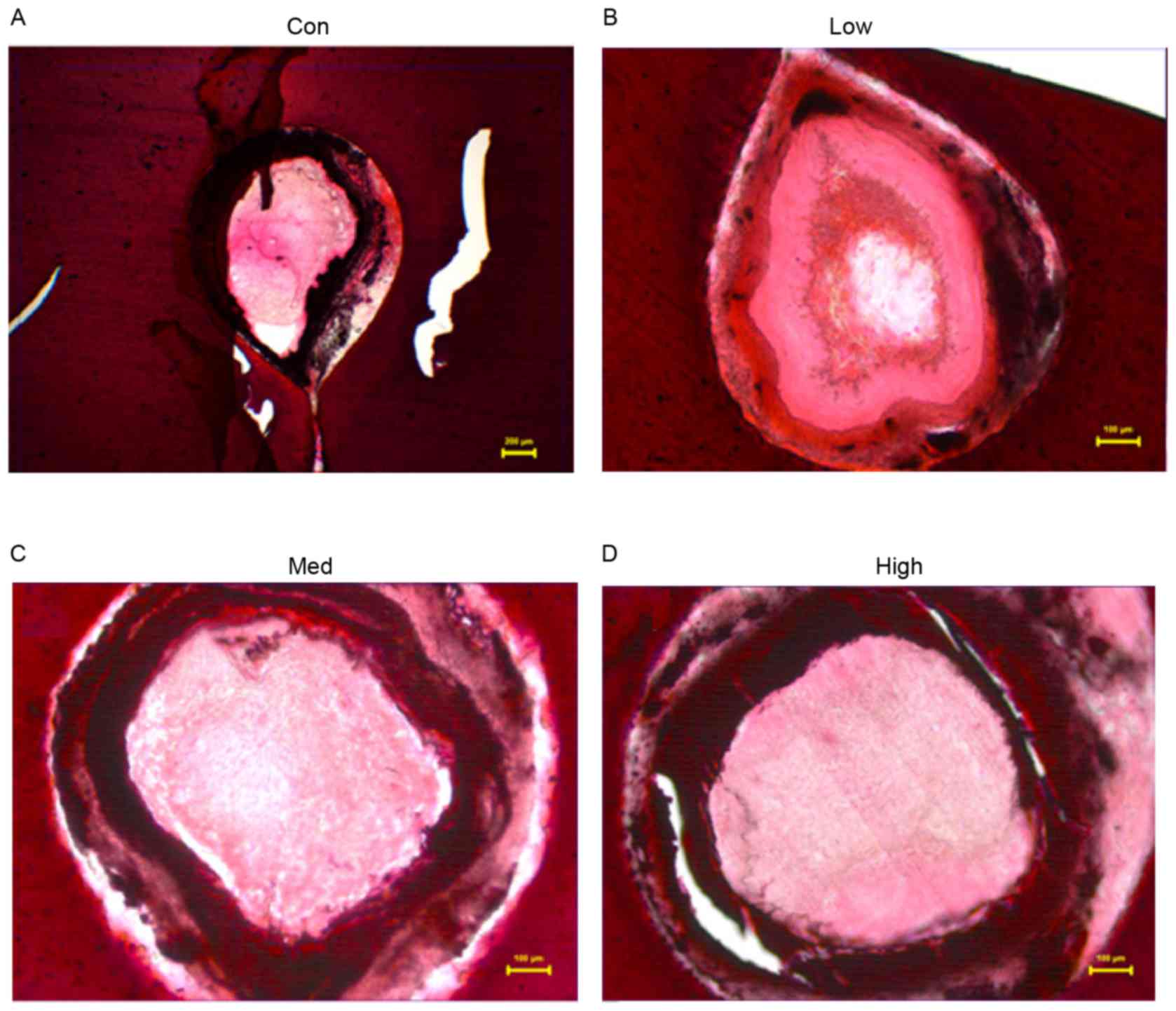
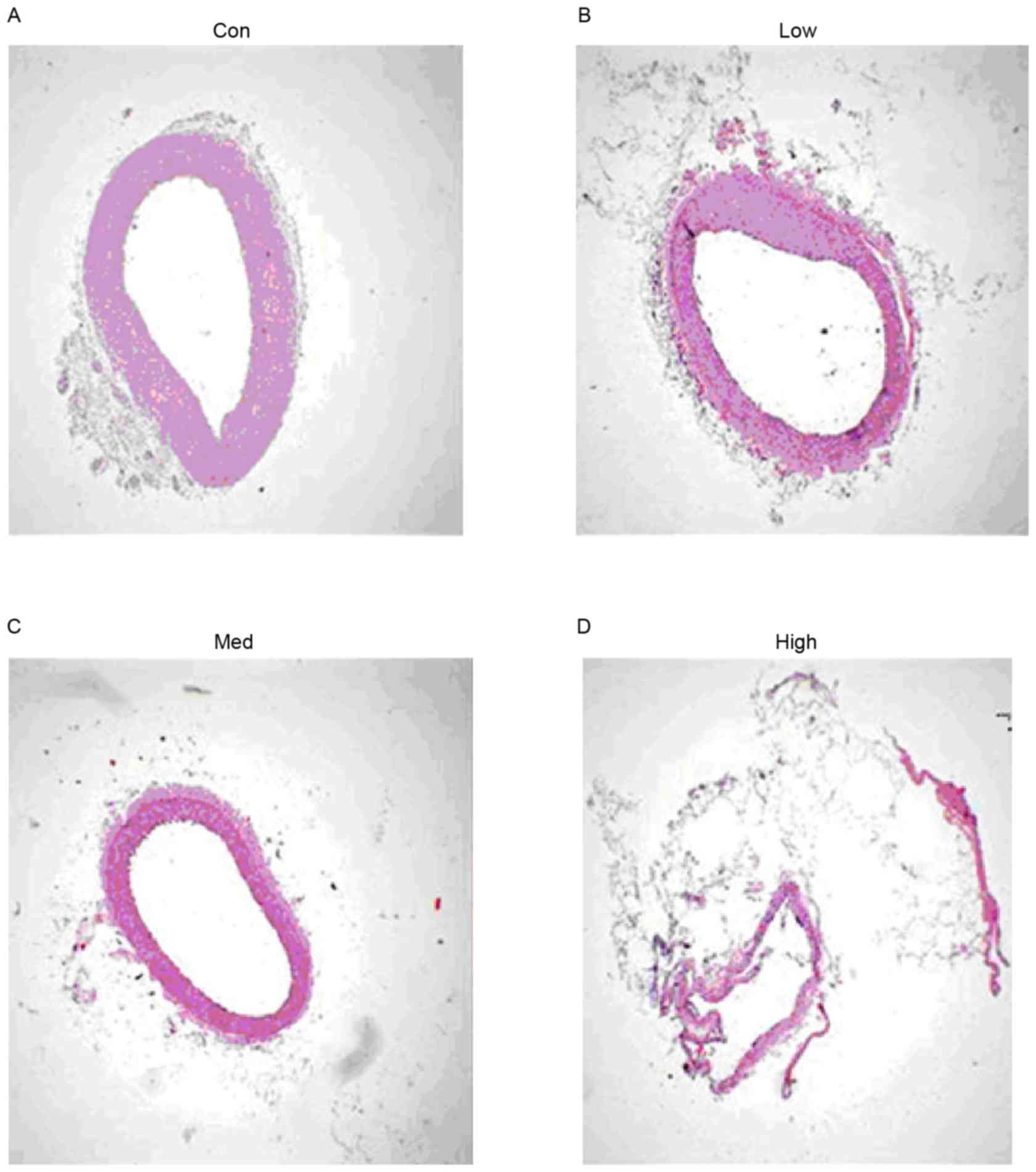
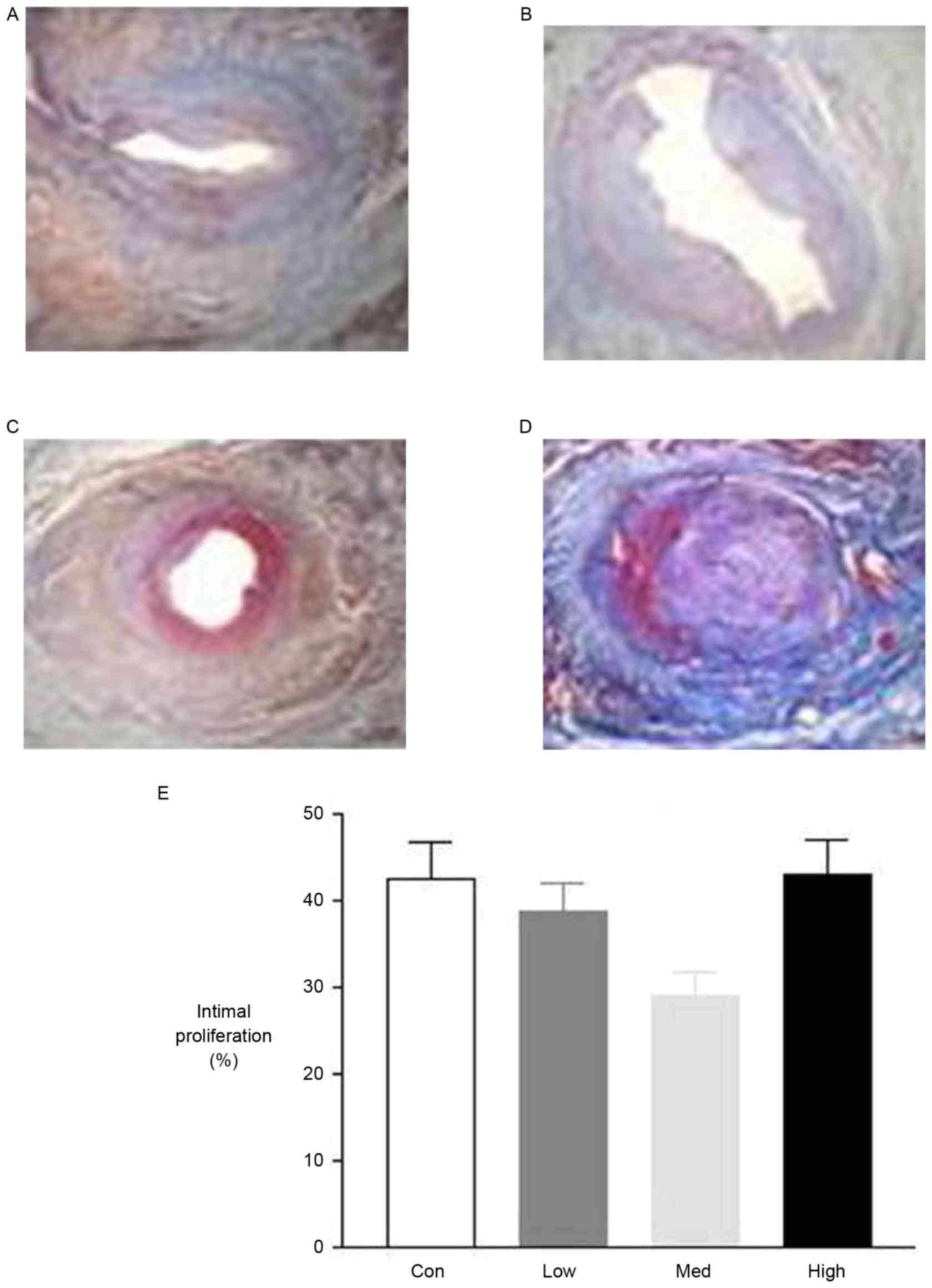
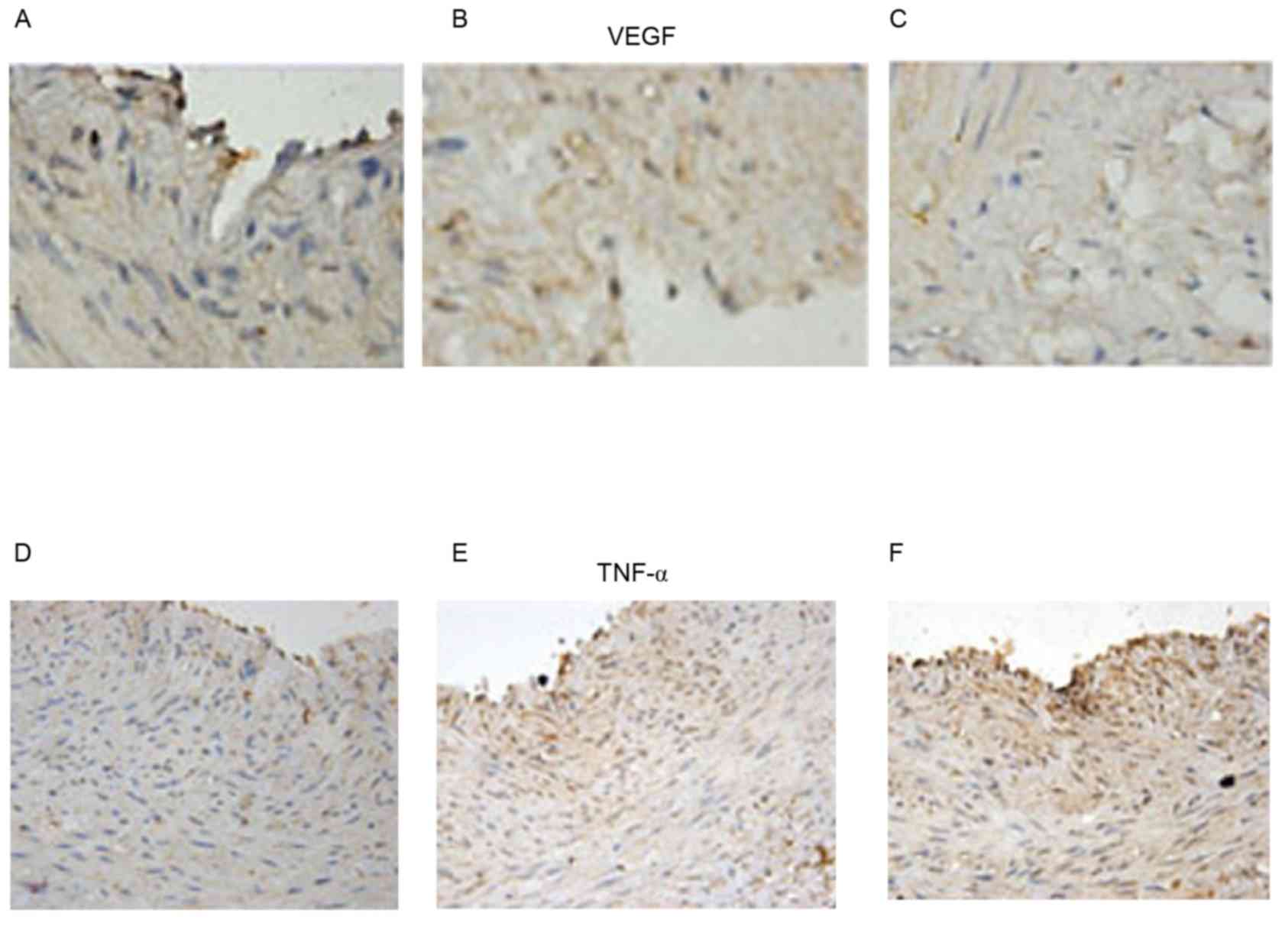
|
1
|
Traverse JH, McKenna DH, Harvey K,
Jorgenso BC, Olson RE, Bostrom N, Kadidlo D, Lesser JR, Jagadeesan
V, Garberich R and Henry TD: Results of a phase 1, randomized,
double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of bone marrow mononuclear
stem cell administration in patients following ST-elevation
myocardial infarction. Am Heart J. 160:428–434. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ince H, Petzsch M, Kleine HD, Eckard H,
Rehders T, Burska D, Kische S, Freund M and Nienaber CA: Prevention
of left ventricular remodeling with granulocyte colony-stimulating
factor after acute myocardial infarction: Final 1-year results of
the front-integrated revascularization and stem cell liberation in
evolving acute myocardial infarction by granulocyte
colony-stimulating factor (FIRSTLINE-AMI) trial. Circulation 112 (9
Suppl). I73–I80. 2005.
|
|
3
|
Ince H, Petzsch M, Kleine HD, Schmidt H,
Rehders T, Körber T, Schümichen C, Freund M and Nienaber CA:
Preservation from left ventricular remodeling by front-integrated
revascularization and stem cell liberation in evolving acute
myocardial infarction by use of granulocyte-colony-stimulating
factor (FIRSTLINE-AMI). Circulation. 112:3097–3106. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Takano H, Hasegawa H, Kuwabara Y, Nakayama
T, Matsuno K, Miyazaki Y, Yamamoto M, Fujimoto Y, Okada H, Okubo S,
et al: Feasibility and safety of granulocyte colony-stimulating
factor treatment in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Int
J Cardiol. 122:41–47. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Valgimigli M, Rigolin GM, Cittanti C,
Malagutti P, Curello S, Percoco G, Bugli AM, Della Porta M,
Bragotti LZ, Ansani L, et al: Use of granulocyte-colony stimulating
factor during acute myocardial infarction to enhance bone marrow
stem cell mobilization in humans: Clinical and angiographic safety
profile. Eur Heart J. 26:1838–1845. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zohlnhöfer D, Ott I, Mehilli J, Schömig K,
Michalk F, Ibrahim T, Meisetschläger G, von Wedel J, Bollwein H,
Seyfarth M, et al: Stem cell mobilization by granulocyte
colony-stimulating factor in patients with acute myocardial
infarction: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 295:1003–1010.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brunner S, Huber BC, Fischer R, Groebner
M, Hacker M, David R, Zaruba MM, Vallaster M, Rischpler C, Wilke A,
et al: G-CSF treatment after myocardial infarction: Impact on bone
marrow-derived vs cardiac progenitor cells. Exp Hematol.
36:695–702. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hasegawa H, Takano H, Iwanaga K, Ohtsuka
M, Qin Y, Niitsuma Y, Ueda K, Toyoda T, Tadokoro H and Komuro I:
Cardioprotective effects of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor
in swine with chronic myocardial ischemia. J Am Coll Cardiol.
47:842–849. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kagawa R, Moritake K, Shima T and Okada Y:
Validity of B-mode ultrasonographic findings in patients undergoing
carotid endarterectomy in comparison with angiographic and
clinicopathologic features. Stroke. 27:700–705. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Handa N, Matsumoto M, Maeda H, Hougaku H,
Ogawa S, Fukunaga R, Yoneda S, Kimura K and Kamada T: Ultrasonic
evaluation of early carotid atherosclerosis. Stroke. 21:1567–1572.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ripa RS, Jørgensen E, Wang Y, Thune JJ,
Nilsson JC, Søndergaard L, Johnsen HE, Køber L, Grande P and
Kastrup J: Stem cell mobilization induced by subcutaneous
granulocyte-colony stimulating factor to improve cardiac
regeneration after acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction: Result
of the double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled stem cells in
myocardial infarction (STEMMI) trial. Circulation. 113:1983–1992.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Powell TM, Paul JD, Hill JM, Thompson M,
Benjamin M, Rodrigo M, McCoy JP, Read EJ, Khuu HM, Leitman SF, et
al: Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor mobilizes functional
endothelial progenitor cells in patients with coronary artery
disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 25:296–301. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hill JM, Syed MA, Arai AE, Powell TM, Paul
JD, Zalos G, Read EJ, Khuu HM, Leitman SF, Horne M, et al: Outcomes
and risks of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in patients with
coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 46:1643–1648. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kang HJ, Lee HY, Na SH, Chang SA, Park KW,
Kim HK, Kim SY, Chang HJ, Lee W, Kang WJ, et al: Differential
effect of intracoronary infusion of mobilized peripheral blood stem
cells by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on left ventricular
function and remodeling in patients with acute myocardial
infarction versus old myocardial infarction: The MAGIC Cell-3-DES
randomized, controlled trial. Circulation 114 (1 Suppl). I145–I151.
2006.
|
|
15
|
Tse G, Hothi SS, Grace AA and Huang CL:
Ventricular arrhythmogenesis following slowed conduction in
heptanol-treated, Langendorff-perfused mouse hearts. J Physiol Sci.
62:79–92. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tse G, Tse V, Yeo JM and Sun B: Atrial
anti-arrhythmic effects of heptanol in Langendorff-perfused mouse
hearts. PLoS One. 11:e01488582016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tse G, Yeo JM, Tse V and Sun B: Gap
junction inhibition by heptanol increases ventricular
arrhythmogenicity by decreasing conduction velocity without
affecting repolarization properties or myocardial refractoriness in
Langendorff-perfused mouse hearts. Mol Med Rep. 14:4069–4074. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tse G, Wong ST, Tse V and Yeo JM:
Restitution analysis of alternans using dynamic pacing and its
comparison with S1S2 restitution in heptanol-treated, hypokalaemic
Langendorff-perfused mouse hearts. Biomed Rep. 4:673–680. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tse G, Tse V and Yeo JM: Ventricular
anti-arrhythmic effects of heptanol in hypokalaemic,
Langendorff-perfused mouse hearts. Biomed Rep. 4:313–324. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tse G, Sun B, Wong ST, Tse V and Yeo JM:
Anti-arrhythmic effects of hypercalcemia in hyperkalemic,
Langendorff-perfused mouse hearts. Biomed Rep. 5:301–310. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Choy L, Yeo JM, Tse V, Chan SP and Tse G:
Cardiac disease and arrhythmogenesis: Mechanistic insights from
mouse models. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 12:1–10. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tse G, Wong ST, Tse V, Lee YT, Lin HY and
Yeo JM: Cardiac dynamics: Alternans and arrhythmogenesis. J
Arrhythm. 32:411–417. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tse G, Lai ET, Yeo JM and Yan BP:
Electrophysiological mechanisms of Bayés syndrome: Insights from
clinical and mouse studies. Front Physiol. 7:1882016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tse G, Lai ET, Lee AP, Yan BP and Wong SH:
Electrophysiological mechanisms of gastrointestinal
arrhythmogenesis: Lessons from the heart. Front Physiol. 7:2302016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tse G, Fiona Chan YW, Keung W and Yan BP:
Electrophysiological mechanisms of long and short QT syndromes:
Insights from mouse models. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 14:8–13.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tse G, Lai TH, Yeo JM, Tse V and Wong SH:
Mechanisms of electrical activation and conduction in the
gastrointestinal system: Lessons from cardiac electrophysiology.
Front Physiol. 7:1822016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tse G, Lai ET, Tse V and Yeo JM: Molecular
and electrophysiological mechanisms underlying cardiac
arrhythmogenesis in diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Res.
2016:28487592016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tse G, Yan BP, Chan YW, Tian XY and Huang
Y: Reactive oxygen species, endoplasmic reticulum stress and
mitochondrial dysfunction: The link with cardiac arrhythmogenesis.
Front Physiol. 7:3132016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen Z, Sun B, Tse G, Jiang J and Xu W:
Reversibility of both sinus node dysfunction and reduced HCN4 mRNA
expression level in an atrial tachycardia pacing model of
tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome in rabbit hearts. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 9:8526–8531. 2016.
|
|
30
|
Tse G, Yeo JM, Chan YW, Lai ET and Yan BP:
What is the arrhythmic substrate in viral myocarditis? Insights
from clinical and animal studies. Front Physiol. 7:3082016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tse G and Yeo JM: Conduction abnormalities
and ventricular arrhythmogenesis: The roles of sodium channels and
gap junctions. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 9:75–82. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tse G: Mechanisms of cardiac arrhythmias.
J Arrhythm. 32:75–81. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Vassiliou V, Chin C, Perperoglou A, Tse G,
Ali A, Raphael C, Jabbour A, Newby D, Pennell D, Dweck M and Prasad
S: 93 ejection fraction by cardiovascular magnetic resonance
predicts adverse outcomes post aortic valve replacement. Heart. 100
(Suppl 3):A53–A54. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Tse G, Ali A, Prasad SK, Vassiliou V and
Raphael CE: Atypical case of post-partum cardiomyopathy: An overlap
syndrome with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy? BJR
Case Rep. 1:201501822015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tse G, Ali A, Alpendurada F, Prasad S,
Raphael CE and Vassiliou V: Tuberculous constrictive pericarditis.
Res Cardiovasc Med. 4:e296142015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tse G: Both transmural dispersion of
repolarization and of refractoriness are poor predictors of
arrhythmogenicity: A role for iCEB (QT/QRS)? J Geriatr Cardiol.
13:813–814. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tse G, Wong ST, Tse V and Yeo JM:
Monophasic action potential recordings: Which is the recording
electrode? J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 27:457–462. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tse G and Yan BP: Novel arrhythmic risk
markers incorporating QRS dispersion: QRSd ×
(Tpeak-Tend)/QRS and QRSd ×
(Tpeak-Tend)/(QT × QRS). Ann Noninvasive
Electrocardiol. 22:Nov;2016.(doi: 10.1111/anec.12397). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tse G: Novel conduction-repolarization
indices for the stratification of arrhythmic risk. J Geriatr
Cardiol. 13:811–812. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tse G: (Tpeak-Tend)/QRS and
(Tpeak-Tend)/(QT × QRS): Novel markers for predicting arrhythmic
risk in Brugada syndrome. Europace. 19:6962017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tse G and Yan BP: Traditional and novel
electrocardiographic markers for predicting arrhythmic risk and
sudden cardiac death. Europace. 19:712–721. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Tse G, Wong ST, Tse V and Yeo JM:
Depolarization vs. repolarization: What is the mechanism of
ventricular arrhythmogenesis underlying sodium channel
haploinsufficiency in mouse hearts? Acta Physiol (Oxf).
218:234–235. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tse G, Wong ST, Tse V and Yeo JM:
Variability in local action potential durations, dispersion of
repolarization and wavelength restitution in aged wild-type and
Scn5a+/− mouse hearts modelling human Brugada syndrome.
J Geriatr Cardiol. 13:930–931. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tse G, Wong ST, Tse V and Yeo JM:
Determination of action potential wavelength restitution in
Scn5a+/− mouse hearts modelling human Brugada syndrome.
J Physiol. 14:595–596. 2017.
|
|
45
|
Murugan D, Lau YS, Lau WC, Mustafa MR and
Huang Y: Angiotensin 1–7 protects against angiotensin II-induced
endoplasmic reticulum stress and endothelial dysfunction via mas
receptor. PLoS One. 10:e01454132015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wei LH, Huang XR, Zhang Y, Li YQ, Chen HY,
Heuchel R, Yan BP, Yu CM and Lan HY: Deficiency of Smad7 enhances
cardiac remodeling induced by angiotensin II infusion in a mouse
model of hypertension. PLoS One. 8:e701952013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wong WT, Tian XY and Huang Y: Endothelial
dysfunction in diabetes and hypertension: Cross talk in RAS, BMP4,
and ROS-dependent COX-2-derived prostanoids. J Cardiovasc
Pharmacol. 61:204–214. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ma S, Tian XY, Zhang Y, Mu C, Shen H,
Bismuth J, Pownall HJ, Huang Y and Wong WT: E-selectin-targeting
delivery of microRNAs by microparticles ameliorates endothelial
inflammation and atherosclerosis. Sci Rep. 6:229102016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lin Z, Pan X, Wu F, Ye D, Zhang Y, Wang Y,
Jin L, Lian Q, Huang Y, Ding H, et al: Fibroblast growth factor 21
prevents atherosclerosis by suppression of hepatic sterol
regulatory element-binding protein-2 and induction of adiponectin
in mice. Circulation. 131:1861–1871. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yuen CY, Wong SL, Lau CW, Tsang SY, Xu A,
Zhu Z, Ng CF, Yao X, Kong SK, Lee HK and Huang Y: From skeleton to
cytoskeleton: Osteocalcin transforms vascular fibroblasts to
myofibroblasts via angiotensin II and toll-like receptor 4. Circ
Res. 111:e55–e66. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhang H, Liu J, Qu D, Wang L, Luo JY, Lau
CW, Liu P, Gao Z, Tipoe GL, Lee HK, et al: Inhibition of miR-200c
restores endothelial function in diabetic mice through suppression
of COX-2. Diabetes. 65:1196–1207. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Cheang WS, Tian XY, Wong WT, Lau CW, Lee
SS, Chen ZY, Yao X, Wang N and Huang Y: Metformin protects
endothelial function in diet-induced obese mice by inhibition of
endoplasmic reticulum stress through 5′adenosine
monophosphate-activated protein kinase-peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor δ pathway. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 34:830–836. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Morrow JP, Katchman A, Son NH, Trent CM,
Khan R, Shiomi T, Huang H, Amin V, Lader JM, Vasquez C, et al: Mice
with cardiac overexpression of peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor γ have impaired repolarization and spontaneous fatal
ventricular arrhythmias. Circulation. 124:2812–2821. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Xie L, Feng H, Li S, Meng G, Liu S, Tang
X, Ma Y, Han Y, Xiao Y, Gu Y, et al: SIRT3 mediates the antioxidant
effect of hydrogen sulfide in endothelial cells. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 24:329–343. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Xu A and Huang Y: A tireless giant in
vascular research. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 67:359–360. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Chen Y, Liu J, Zheng Y, Wang J, Wang Z, Gu
S, Tan J, Jing Q and Yang H: Uncoupling protein 3 mediates
H2O2 preconditioning-afforded
cardioprotection through the inhibition of MPTP opening. Cardiovasc
Res. 105:192–202. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhang Y, Liu J, Luo JY, Tian XY, Cheang
WS, Xu J, Lau CW, Wang L, Wong WT, Wong CM, et al: Upregulation of
angiotensin (1–7)-mediated signaling preserves endothelial function
through reducing oxidative stress in diabetes. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 23:880–892. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Li Y, Fukuda N, Yokoyama S, Kusumi Y,
Hagikura K, Kawano T, Takayama T, Matsumoto T, Satomi A, Honye J,
et al: Effects of G-CSF on cardiac remodeling and arterial
hyperplasia in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 549:98–106. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Hansson GK: Immune mechanisms in
atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 21:1876–1890. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Haghighat A, Weiss D, Whalin MK, Cowan DP
and Taylor WR: Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and
granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor exacerbate
atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Circulation.
115:2049–2054. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Hasegawa H, Takano H, Ohtsuka M, Ueda K,
Niitsuma Y, Qin Y, Tadokoro H, Shiomi M and Komuro I: G-CSF
prevents the progression of atherosclerosis and neointimal
formation in rabbits. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 344:370–376.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Cho HJ, Kim TY, Cho HJ, Park KW, Zhang SY,
Kim JH, Kim SH, Hahn JY, Kang HJ, Park YB and Kim HS: The effect of
stem cell mobilization by granulocyte-colony stimulating factor on
neointimal hyperplasia and endothelial healing after vascular
injury with bare-metal versus paclitaxel-eluting stents. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 48:366–374. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kong D, Melo LG, Gnecchi M, Zhang L,
Mostoslavsky G, Liew CC, Pratt RE and Dzau VJ: Cytokine-induced
mobilization of circulating endothelial progenitor cells enhances
repair of injured arteries. Circulation. 110:2039–2046. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Sehara Y, Hayashi T, Deguchi K, Zhang H,
Tsuchiya A, Yamashita T, Lukic V, Nagai M, Kamiya T and Abe K:
G-CSF enhances stem cell proliferation in rat hippocampus after
transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. Neurosci Lett.
418:248–252. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Sato T, Suzuki H, Kusuyama T, Omori Y,
Soda T, Tsunoda F, Shoji M, Iso Y, Koba S, Geshi E, et al: G-CSF
after myocardial infarction accelerates angiogenesis and reduces
fibrosis in swine. Int J Cardiol. 127:166–173. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Ripa RS, Wang Y, Jørgensen E, Johnsen HE,
Hesse B and Kastrup J: Intramyocardial injection of vascular
endothelial growth factor-A165 plasmid followed by
granulocyte-colony stimulating factor to induce angiogenesis in
patients with severe chronic ischaemic heart disease. Eur Heart J.
27:1785–1792. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Lim SY, Kim YS, Ahn Y, Jeong MH, Rok LS,
Kim JH, Kim KH, Park HW, Kim W, Cho JG, et al: The effects of
granulocyte-colony stimulating factor in bare stent and
sirolimus-eluting stent in pigs following myocardial infarction.
Int J Cardiol. 118:304–311. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|