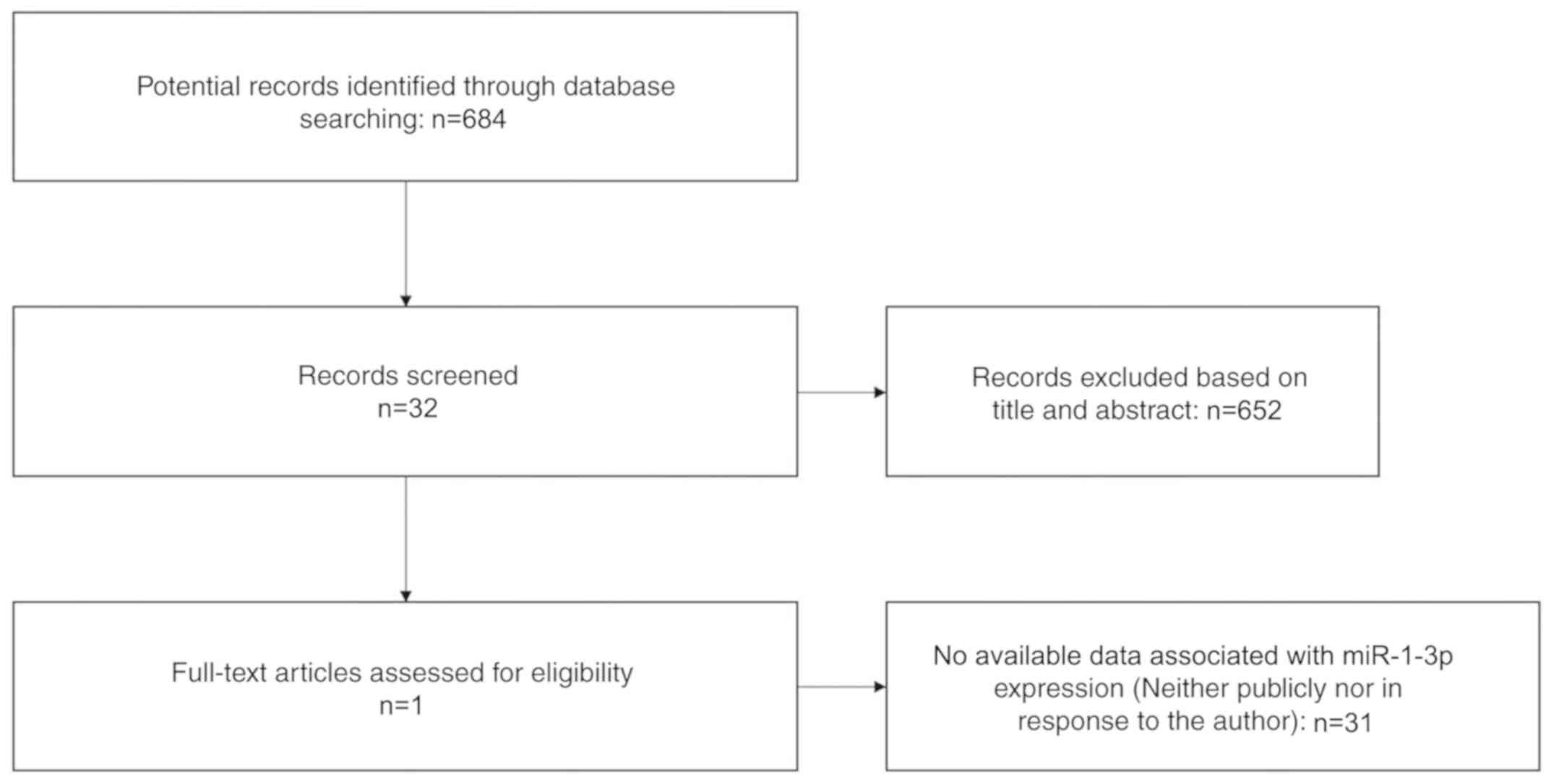
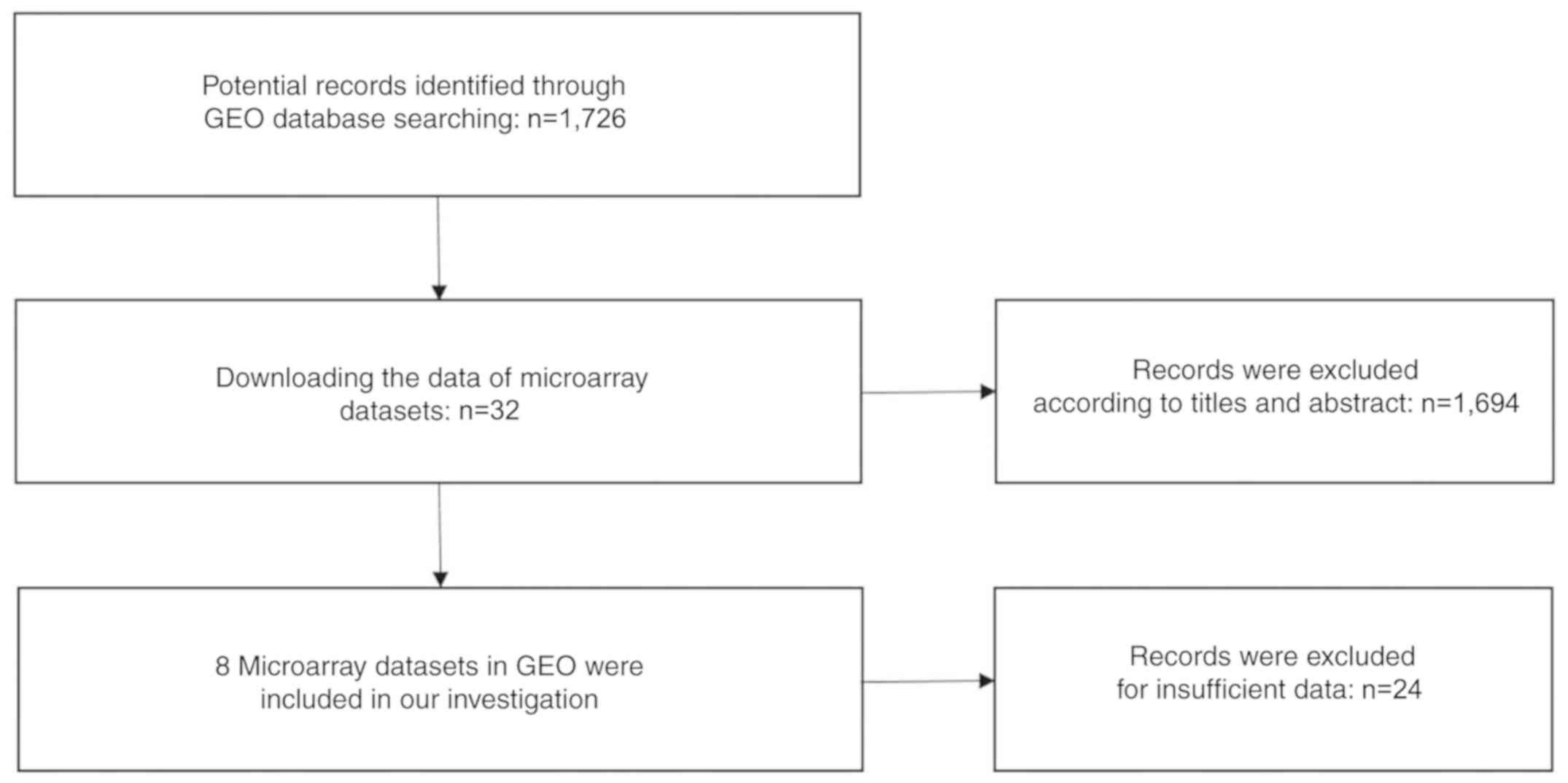
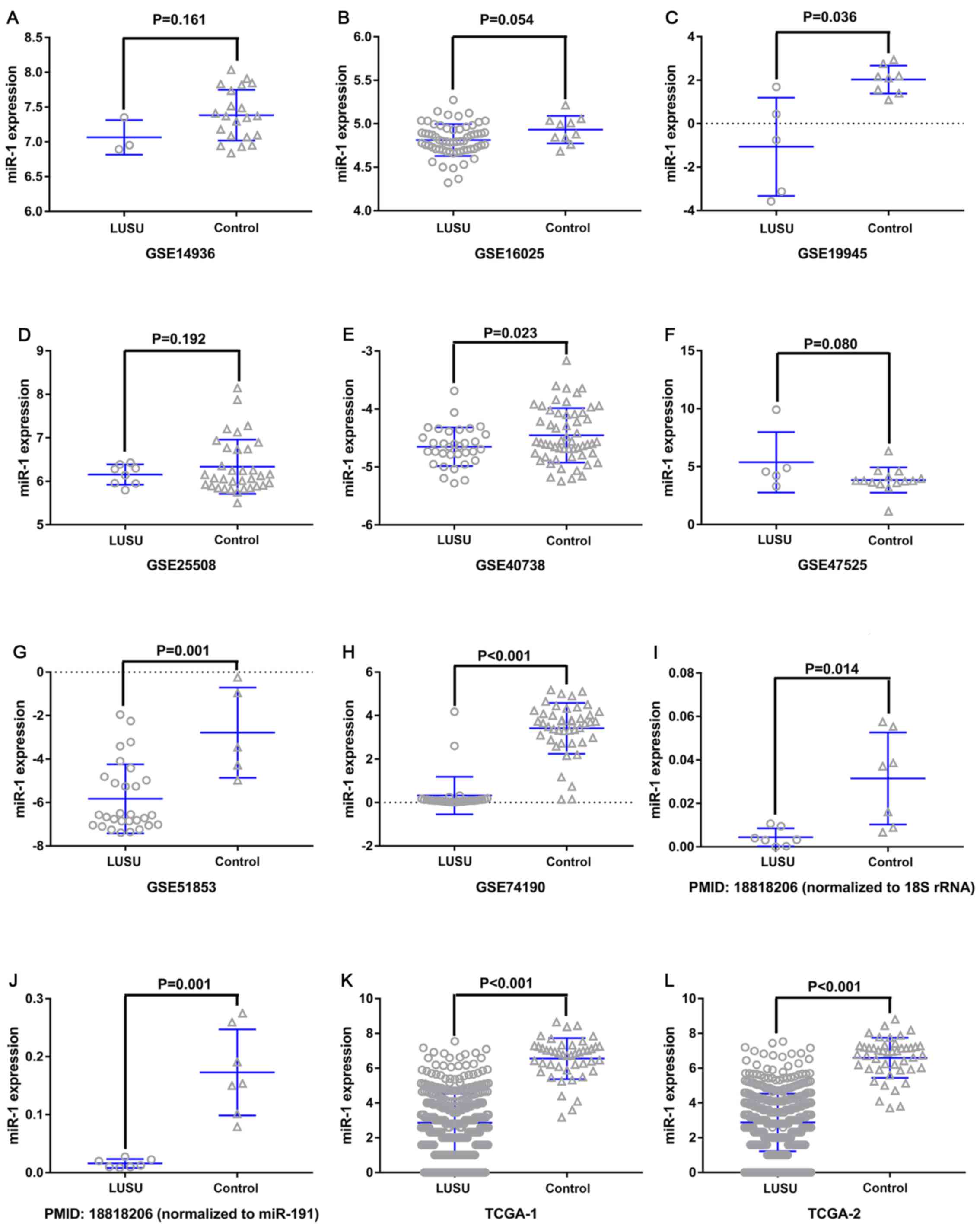
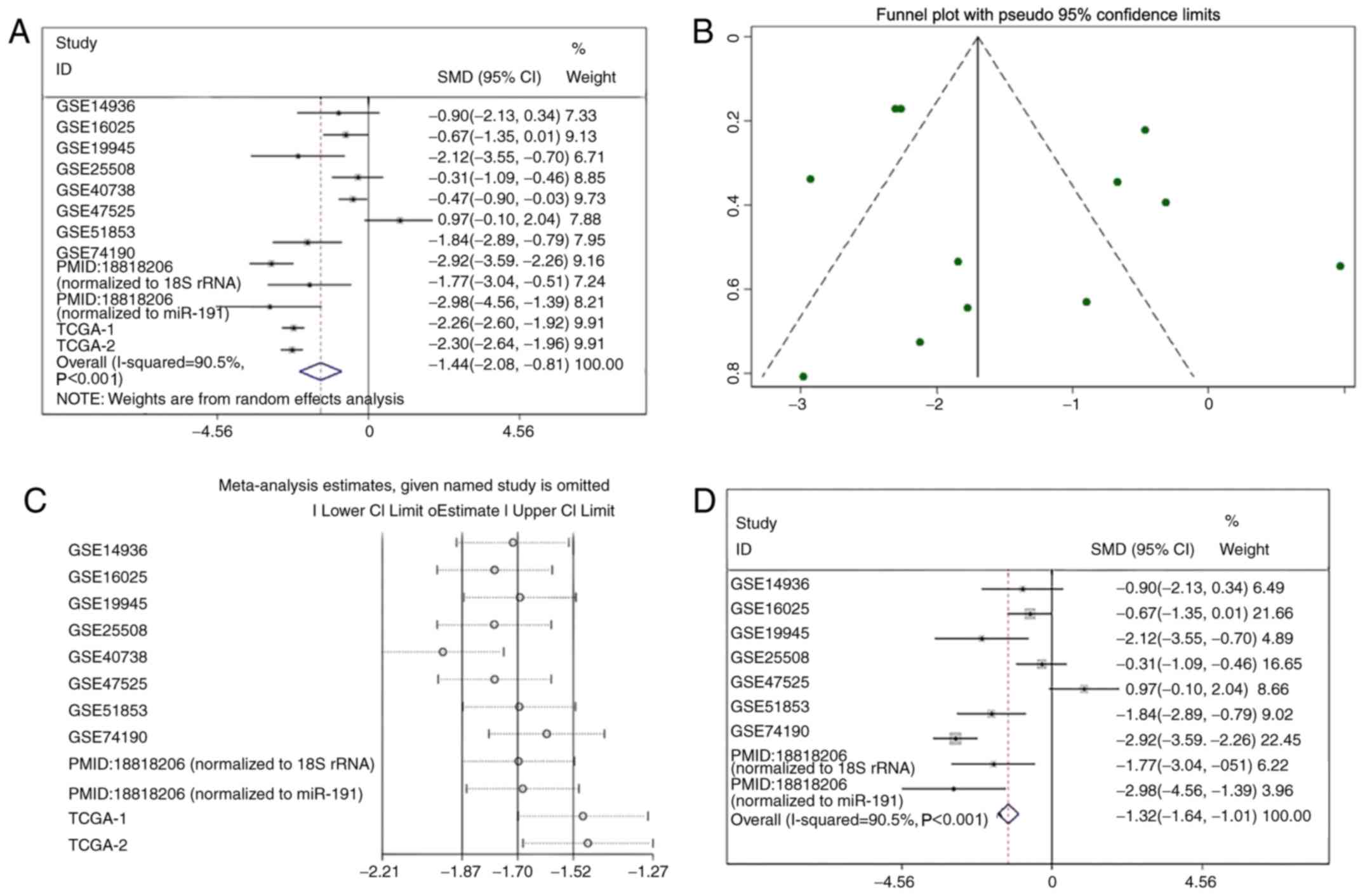
|
1
|
Chen M, Liu X, Du J, Wang XJ and Xia L:
Differentiated regulation of immune-response related genes between
LUAD and LUSC subtypes of lung cancers. Oncotarget. 8:133–144.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Freeman JR, Chu S, Hsu T and Huang YT:
Epigenome-wide association study of smoking and DNA methylation in
non-small cell lung neoplasms. Oncotarget. 7:69579–69591. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Peng L, Bian XW, Li DK, Xu C, Wang GM, Xia
QY and Xiong Q: Large-scale RNA-Seq transcriptome analysis of 4043
cancers and 548 normal tissue controls across 12 TCGA cancer types.
Sci Rep. 5:134132015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Czarnecka KH, Migdalska-Sęk M, Domańska D,
Pastusza-Lewandoska D, Dutkowska A, Kordiak J, Nawrot E,
Kiszałkiewicz J, Antczak A and Brzeziańska-Lasota E: FHIT promoter
methylation status, low protein and high mRNA levels in patients
with non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Oncol. 49:1175–1184. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chang JT, Lee YM and Huang RS: The impact
of the cancer genome atlas on lung cancer. Transl Res. 166:568–585.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang L, Chen Z, An L, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Guo
Y and Liu C: Analysis of long non-coding RNA expression profiles in
non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 38:2389–2400.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bittoni MA, Focht BC, Clinton SK,
Buckworth J and Harris RE: Prospective evaluation of C-reactive
protein, smoking and lung cancer death in the Third National Health
and Nutrition Examination Survey. Int J Oncol. 47:1537–1544. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Eldem V, Çelikkol Akçay U, Ozhuner E,
Bakır Y, Uranbey S and Unver T: Genome-wide identification of
miRNAs responsive to drought in peach (Prunus persica) by
high-throughput deep sequencing. PLoS One. 7:e502982012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ma N, Zhang W, Qiao C, Luo H, Zhang X, Liu
D, Zang S, Zhang L and Bai J: The tumor suppressive role of
MiRNA-509-5p by targeting FOXM1 in non-small cell lung cancer. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 38:1435–1446. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li P, Liu H, Wang Z, He F, Wang H, Shi Z,
Yang A and Ye J: MicroRNAs in laryngeal cancer: Implications for
diagnosis, prognosis and therapy. Am J Transl Res. 8:1935–1944.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang J, Li Y, Ding M, Zhang H, Xu X and
Tang J: Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of miR-22 in
regulating malignant progression in human cancer (Review). Int J
Oncol. 50:345–355. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gambari R, Brognara E, Spandidos DA and
Fabbri E: Targeting oncomiRNAs and mimicking tumor suppressor
miRNAs: Νew trends in the development of miRNA therapeutic
strategies in oncology (Review). Int J Oncol. 49:5–32. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Subramani R, Gangwani L, Nandy SB,
Arumugam A, Chattopadhyay M and Lakshmanaswamy R: Emerging roles of
microRNAs in pancreatic cancer diagnosis, therapy and prognosis
(Review). Int J Oncol. 47:1203–1210. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang P, Yang D, Zhang H, Wei X, Ma T,
Cheng Z, Hong Q, Hu J, Zhuo H, Song Y, et al: Early detection of
lung cancer in serum by a panel of MicroRNA biomarkers. Clin Lung
Cancer. 16:313–319.e1. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ma T, Zhao Y, Wei K, Yao G, Pan C, Liu B,
Xia Y, He Z, Qi X, Li Z, et al: MicroRNA-124 functions as a tumor
suppressor by regulating CDH2 and epithelial-mesenchymal transition
in non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 38:1563–1574.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Feng X, Jiang J, Shi S, Xie H, Zhou L and
Zheng S: Knockdown of miR-25 increases the sensitivity of liver
cancer stem cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis via PTEN/PI3K/Akt/Bad
signaling pathway. Int J Oncol. 49:2600–2610. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Meerson A and Yehuda H: Leptin and insulin
up-regulate miR-4443 to suppress NCOA1 and TRAF4, and decrease the
invasiveness of human colon cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 16:8822016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kumamoto T, Seki N, Mataki H, Mizuno K,
Kamikawaji K, Samukawa T, Koshizuka K, Goto Y and Inoue H:
Regulation of TPD52 by antitumor microRNA-218 suppresses cancer
cell migration and invasion in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Int J
Oncol. 49:1870–1880. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang Y, Chen L, Wu Z, Wang M, Jin F, Wang
N, Hu X, Liu Z, Zhang CY, Zen K, et al: miR-124-3p functions as a
tumor suppressor in breast cancer by targeting CBL. BMC Cancer.
16:8262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu X and Li Z: New insights into MicroRNAs
involves in drug resistance in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Am J
Transl Res. 7:2536–2542. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li Z, Yu X, Shen J, Law PT, Chan MT and Wu
WK: MicroRNA expression and its implications for diagnosis and
therapy of gallbladder cancer. Oncotarget. 6:13914–13921.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cui L, Li Y, Lv X, Li J, Wang X, Lei Z and
Li X: Expression of MicroRNA-301a and its functional roles in
malignant melanoma. Cell Physiol Biochem. 40:230–244. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang X, Zhang Y, Liu X, Fang A, Wang J,
Yang Y, Wang L, Du L and Wang C: Direct quantitative detection for
cell-free miR-155 in urine: A potential role in diagnosis and
prognosis for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Oncotarget.
7:3255–3266. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gao Y, Feng B, Han S, Lu L, Chen Y, Chu X,
Wang R and Chen L: MicroRNA-129 in human cancers: From
tumorigenesis to clinical treatment. Cell Physiol Biochem.
39:2186–2202. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Deng T, Yuan Y, Zhang C, Zhang C, Yao W,
Wang C, Liu R and Ba Y: Identification of circulating MiR-25 as a
potential biomarker for pancreatic cancer diagnosis. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 39:1716–1722. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lu L, Zhou L, Chen EZ, Sun K, Jiang P,
Wang L, Su X, Sun H and Wang H: A Novel YY1-miR-1 regulatory
circuit in skeletal myogenesis revealed by genome-wide prediction
of YY1-miRNA network. PLoS One. 7:e275962012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Han C, Shen JK, Hornicek FJ, Kan Q and
Duan Z: Regulation of microRNA-1 (miR-1) expression in human
cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1860:227–232. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Han C, Zhou Y, An Q, Li F, Li D, Zhang X,
Yu Z, Zheng L, Duan Z and Kan Q: MicroRNA-1 (miR-1) inhibits
gastric cancer cell proliferation and migration by targeting MET.
Tumour Biol. 36:6715–6723. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang W, Shen F and Wang C, Lu W, Wei J,
Shang A and Wang C: MiR-1-3p inhibits the proliferation and
invasion of bladder cancer cells by suppressing CCL2 expression.
Tumour Biol. 39:10104283176983832017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang Z, Wang J, Chen Z, Wang K and Shi L:
MicroRNA-1-3p inhibits proliferation and migration of oral squamous
cell carcinoma cells by targeting DKK1. Biochem Cell Biol.
96:355–364. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cui R, Meng W, Sun HL, Kim T, Ye Z, Fassan
M, Jeon YJ, Li B, Vicentini C, Peng Y, et al: MicroRNA-224 promotes
tumor progression in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 112:E4288–E4297. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang WC, Chin TM, Yang H, Nga ME, Lunny
DP, Lim EK, Sun LL, Pang YH, Leow YN, Malusay SR, et al:
Tumour-initiating cell-specific miR-1246 and miR-1290 expression
converge to promote non-small cell lung cancer progression. Nat
Commun. 7:117022016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang X, Wang C, Shan S, Liu X, Jiang Z
and Ren T: TLR4/ROS/miRNA-21 pathway underlies lipopolysaccharide
instructed primary tumor outgrowth in lung cancer patients.
Oncotarget. 7:42172–42182. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yu N, Zhang Q, Liu Q, Yang J and Zhang S:
A meta-analysis: microRNAs' prognostic function in patients with
nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer Med. 6:2098–2105. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gao L, Li SH, Tian YX, Zhu QQ, Chen G,
Pang YY and Hu XH: Role of downregulated miR-133a-3p expression in
bladder cancer: A bioinformatics study. Onco Targets Ther.
10:3667–3683. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu Y, Xing Z, Zhan P, Liu H, Ye W, Lv T
and Song Y: Is it feasible to detect epidermal growth factor
receptor mutations in circulating tumor cells in nonsmall cell lung
cancer?: A meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e51152016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang J, Yu Y, Li Y and Wei L: Diagnostic
value of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in hepatocellular carcinoma:
A meta-analysis with evidence from 1998 to 2016. Oncotarget.
8:75418–75426. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen WS, Li JJ, Hong L, Xing ZB, Wang F
and Li CQ: Comparison of MRI, CT and 18F-FDG PET/CT in the
diagnosis of local and metastatic of nasopharyngeal carcinomas: An
updated meta analysis of clinical studies. Am J Transl Res.
8:4532–4547. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ma X, Wang L, Wu H, Feng Y, Han X, Bu H
and Zhu Q: Spleen stiffness is superior to liver stiffness for
predicting esophageal varices in chronic liver disease: A
meta-analysis. PLoS One. 11:e01657862016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Love MI, Huber W and Anders S: Moderated
estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with
DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15:5502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang Y, Dang YW, Wang X, Yang X, Zhang R,
Lv ZL and Chen G: Comprehensive analysis of long non-coding RNA
PVT1 gene interaction regulatory network in hepatocellular
carcinoma using gene microarray and bioinformatics. Am J Transl
Res. 9:3904–3917. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zeng JH, Xiong DD, Pang YY, Zhang Y, Tang
RX, Luo DZ and Chen G: Identification of molecular targets for
esophageal carcinoma diagnosis using miRNA-seq and RNA-seq data
from The Cancer Genome Atlas: A study of 187 cases. Oncotarget.
8:35681–35699. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang Y, He RQ, Dang YW, Zhang XL, Wang X,
Huang SN, Huang WT, Jiang MT, Gan XN, Xie Y, et al: Comprehensive
analysis of the long noncoding RNA HOXA11-AS gene interaction
regulatory network in NSCLC cells. Cancer Cell Int. 16:892016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang Y, Huang JC, Cai KT, Yu XB, Chen YR,
Pan WY, He ZL, Lv J, Feng ZB and Chen G: Long non-coding RNA HOTTIP
promotes hepatocellular carcinoma tumorigenesis and development: A
comprehensive investigation based on bioinformatics, qRT-PCR and
meta-analysis of 393 cases. Int J Oncol. 51:1705–1721. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
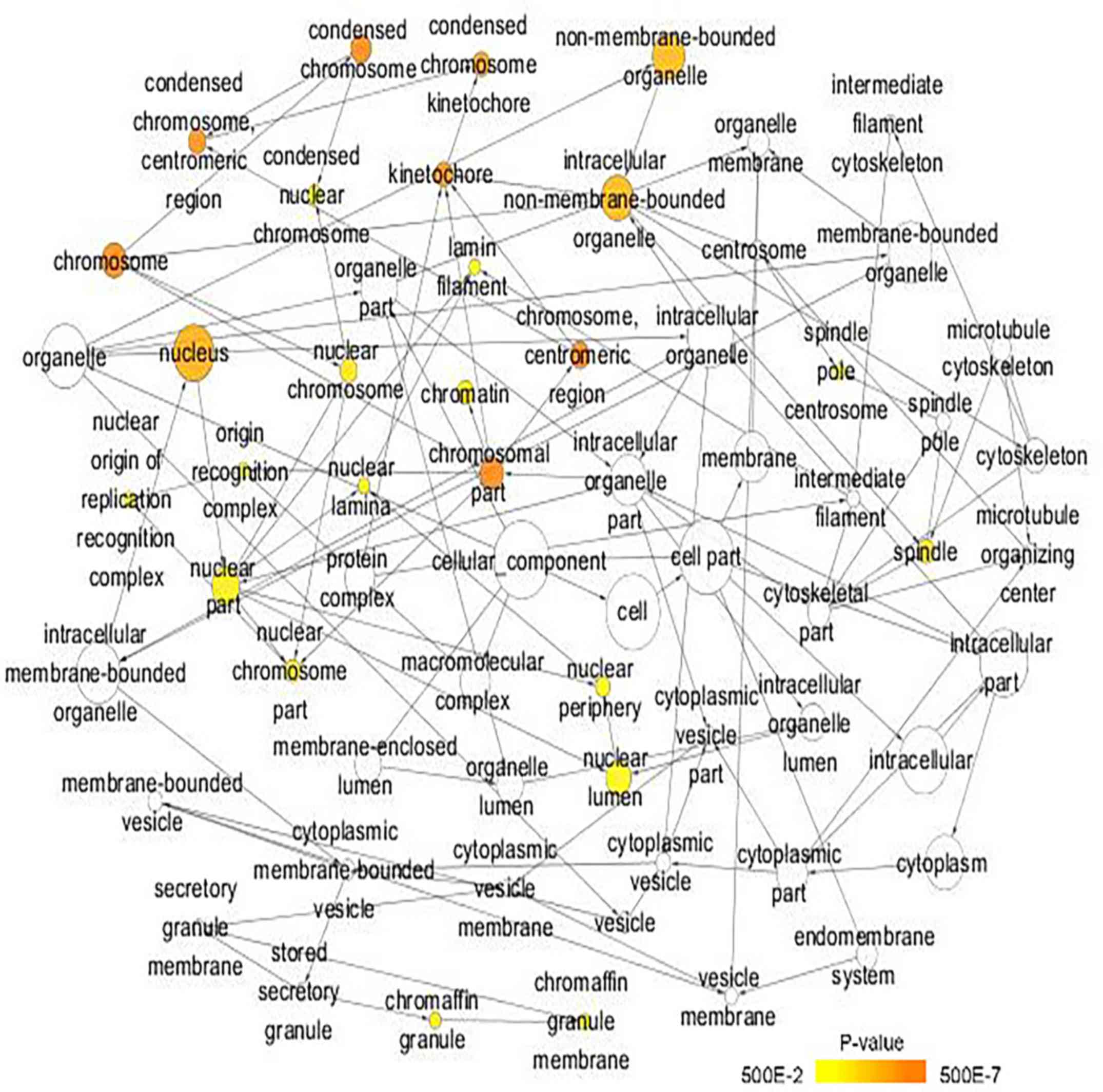
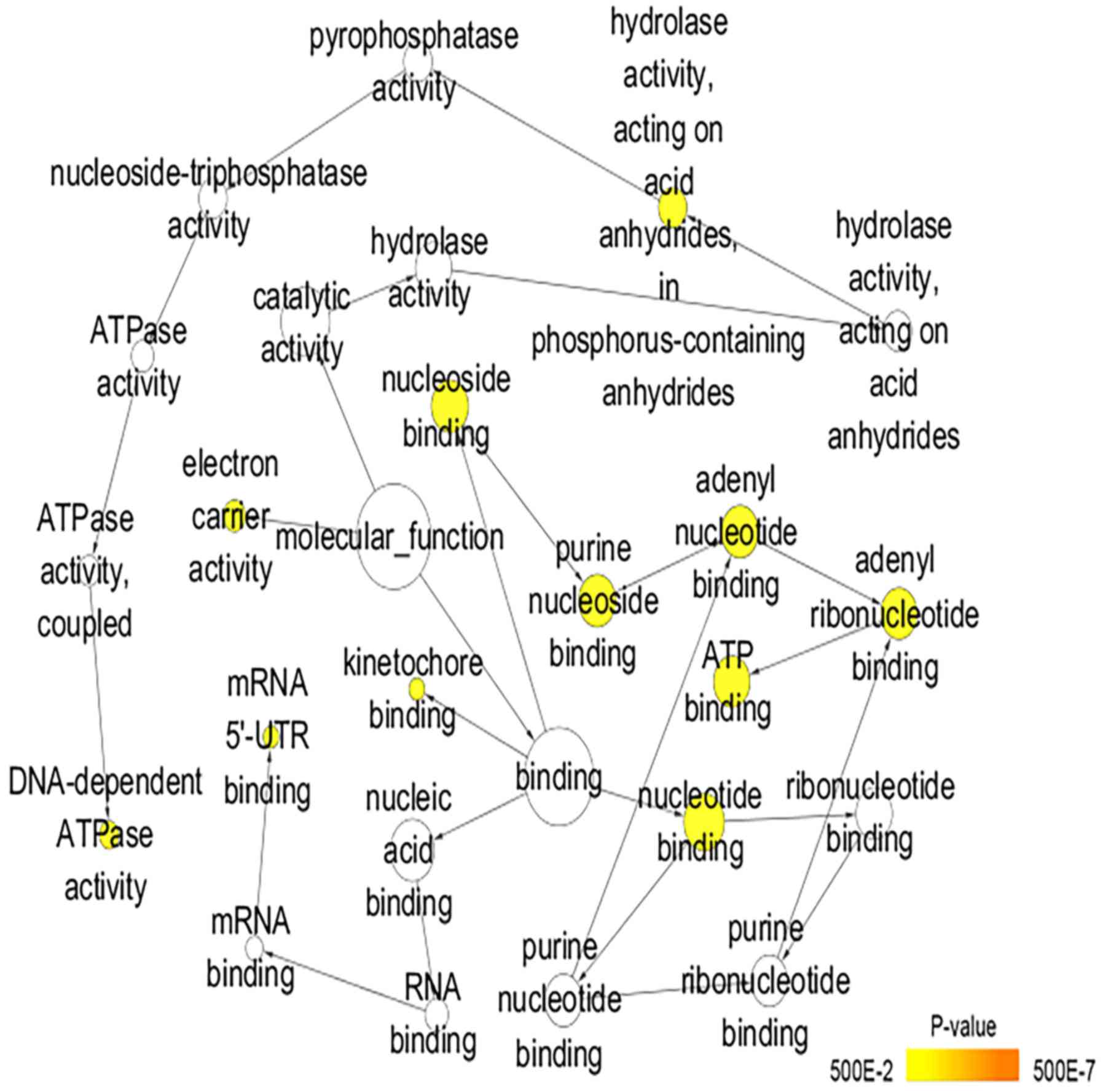
Maere S, Heymans K and Kuiper M: BiNGO: A
Cytoscape plugin to assess overrepresentation of Gene Ontology
categories in biological networks. Bioinformatics. 21:3448–3449.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Merico D, Isserlin R, Stueker O, Emili A
and Bader GD: Enrichment map: A network-based method for gene-set
enrichment visualization and interpretation. PLoS One.
5:e139842010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Seike M, Goto A, Okano T, Bowman ED,
Schetter AJ, Horikawa I, Mathe EA, Jen J, Yang P, Sugimura H, et
al: MiR-21 is an EGFR-regulated anti-apoptotic factor in lung
cancer in never-smokers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:12085–12090.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Raponi M, Dossey L, Jatkoe T, Wu X, Chen
G, Fan H and Beer DG: MicroRNA classifiers for predicting prognosis
of squamous cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 69:5776–5783. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
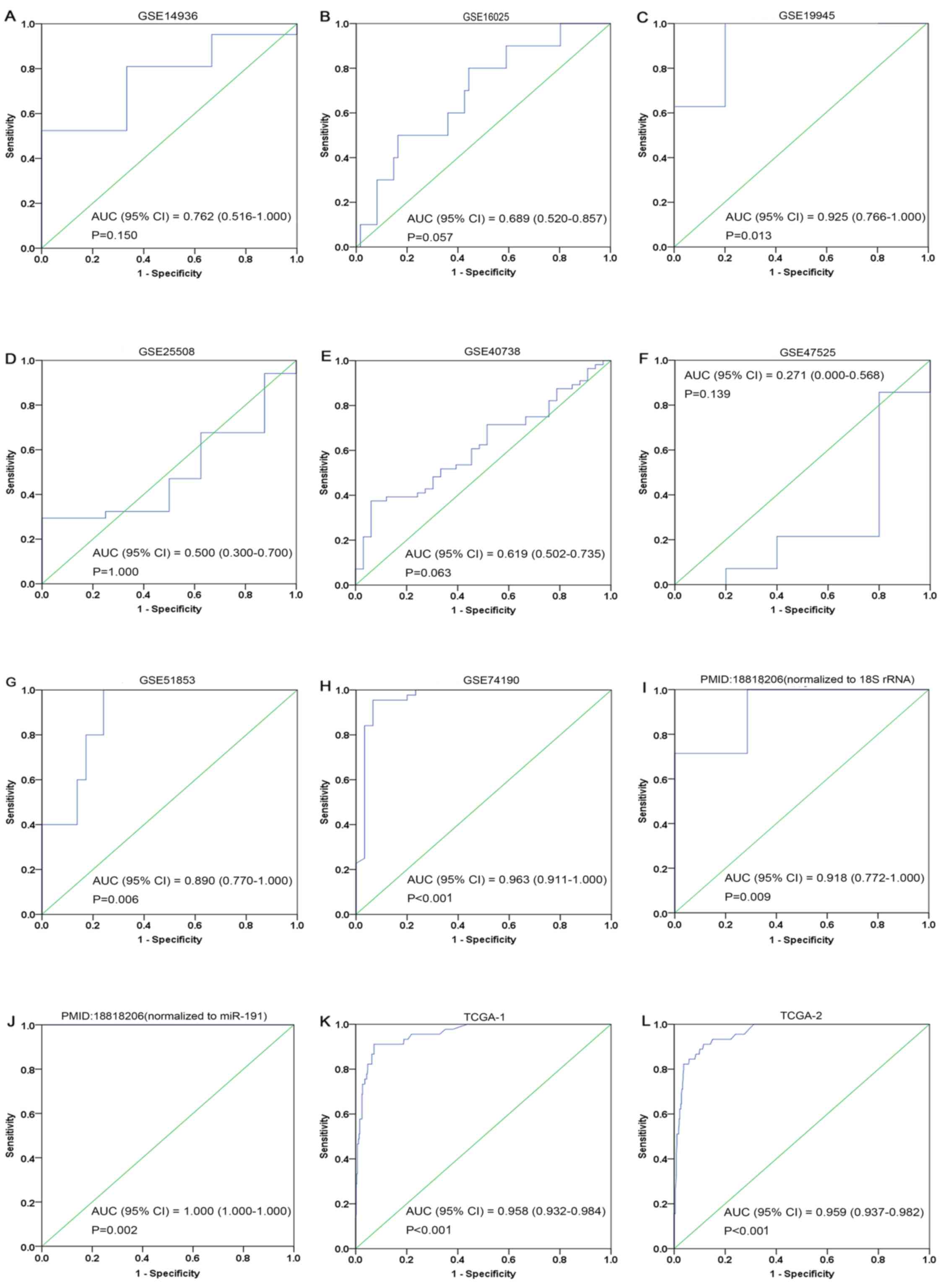
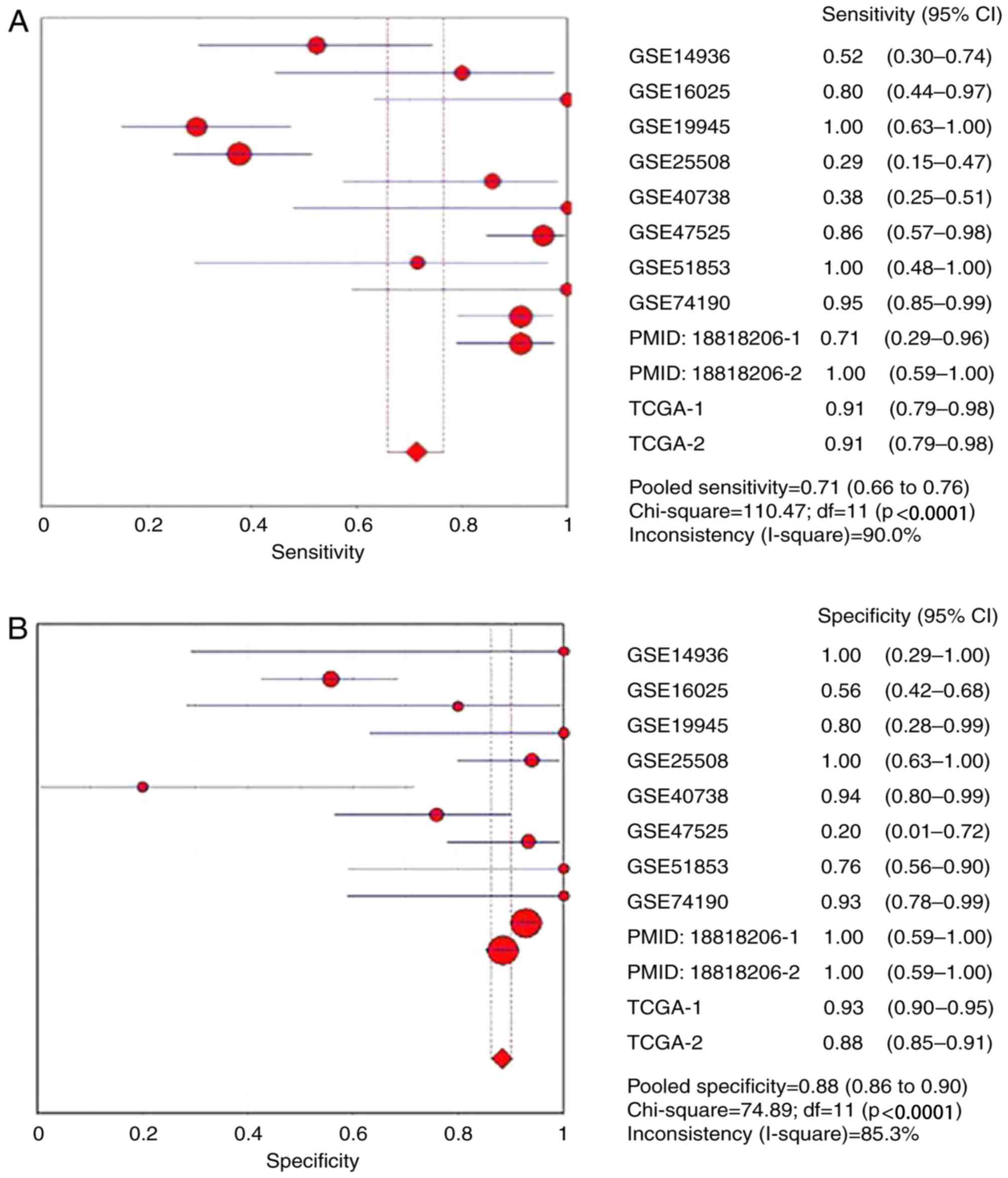
Ohba T and Nagano H: A small-cell lung
cancer subtype with good prognosis found by a three miRNA
signature. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE19945Oct
1st–2017
|
|
51
|
Nymark P, Guled M, Borze I, Faisal A,
Lahti L, Salmenkivi K, Kettunen E, Anttila S and Knuutila S:
Integrative analysis of microRNA, mRNA and aCGH data reveals
asbestos- and histology-related changes in lung cancer. Genes
Chromosomes Cancer. 50:585–597. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Patnaik SK, Kannisto ED, Mallick R,
Vachani A and Yendamuri S: Whole blood microRNA expression may not
be useful for screening non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One.
12:e01819262017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
van Jaarsveld MT, Wouters MD, Boersma AW,
Smid M, van Ijcken WF, Mathijssen RH, Hoeijmakers JH, Martens JW,
van Laere S, Wiemer EA and Pothof J: DNA damage responsive
microRNAs misexpressed in human cancer modulate therapy
sensitivity. Mol Oncol. 8:458–468. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Arima C, Kajino T, Tamada Y, Imoto S,
Shimada Y, Nakatochi M, Suzuki M, Isomura H, Yatabe Y, Yamaguchi T,
et al: Lung adenocarcinoma subtypes definable by lung
development-related miRNA expression profiles in association with
clinicopathologic features. Carcinogenesis. 35:2224–2231. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Jin Y, Liu YL and Lu SH: The miRNA
expression profiles in three subtypes of lung carcinomas.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE74190Oct
12th–2017
|
|
56
|
Liu T, Hu K, Zhao Z, Chen G, Ou X, Zhang
H, Zhang X, Wei X, Wang D, Cui M and Liu C: MicroRNA-1
down-regulates proliferation and migration of breast cancer stem
cells by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Oncotarget.
6:41638–41649. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Xie M, Dart DA, Guo T, Xing XF, Cheng XJ,
Du H, Jiang WG, Wen XZ and Ji JF: MicroRNA-1 acts as a tumor
suppressor microRNA by inhibiting angiogenesis-related growth
factors in human gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 21:41–54. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Xu X, Wu X, Jiang Q, Sun Y, Liu H, Chen R
and Wu S: Downregulation of microRNA-1 and microRNA-145 contributes
synergistically to the development of colon cancer. Int J Mol Med.
36:1630–1638. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Mataki H, Enokida H, Chiyomaru T, Mizuno
K, Matsushita R, Goto Y, Nishikawa R, Higashimoto I, Samukawa T,
Nakagawa M, et al: Downregulation of the microRNA-1/133a cluster
enhances cancer cell migration and invasion in lung-squamous cell
carcinoma via regulation of Coronin1C. J Hum Genet. 60:53–61. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Liu J, Zhang C and Feng Z: Tumor
suppressor p53 and its gain-of-function mutants in cancer. Acta
Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 46:170–179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zhong G, Chen X, Fang X, Wang D, Xie M and
Chen Q: Fra-1 is upregulated in lung cancer tissues and inhibits
the apoptosis of lung cancer cells by the P53 signaling pathway.
Oncol Rep. 35:447–453. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhang HY, Yang W and Lu JB: Knockdown of
GluA2 induces apoptosis in non-small-cell lung cancer A549 cells
through the p53 signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 14:1005–1010. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Jung IL, Kang HJ, Kim KC and Kim IG:
PTEN/pAkt/p53 signaling pathway correlates with the radioresponse
of non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Mol Med. 25:517–523.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhang C, Liu J, Tan C, Yue X, Zhao Y, Peng
J, Wang X, Laddha SV, Chan CS, Zheng S, et al: microRNA-1827
represses MDM2 to positively regulate tumor suppressor p53 and
suppress tumorigenesis. Oncotarget. 7:8783–8796. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Perdas E, Stawski R, Nowak D and Zubrzycka
M: Potential of liquid biopsy in papillary thyroid carcinoma in
context of miRNA, BRAF and p53 mutation. Curr Drug Targets.
19:1721–1729. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Xiao S, Wang R, Wu X, Liu W and Ma S: The
long noncoding RNA TP73-AS1 interacted with miR-124 to modulate
glioma growth by targeting inhibitor of apoptosis-stimulating
protein of p53. DNA Cell Biol. 37:117–125. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
He L, He X, Lim LP, de Stanchina E, Xuan
Z, Liang Y, Xue W, Zender L, Magnus J, Ridzon D, et al: A microRNA
component of the p53 tumour suppressor network. Nature.
447:1130–1134. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|