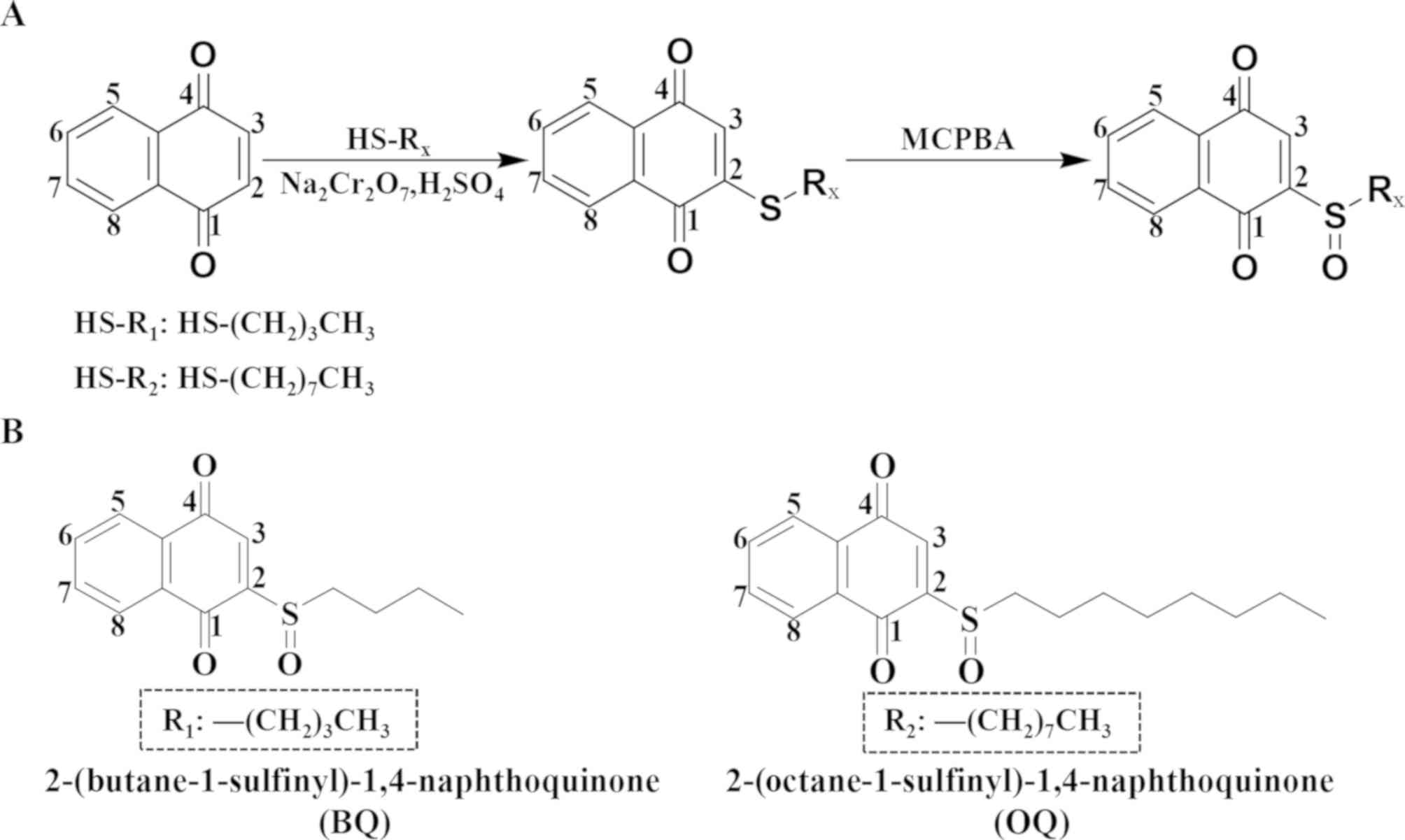
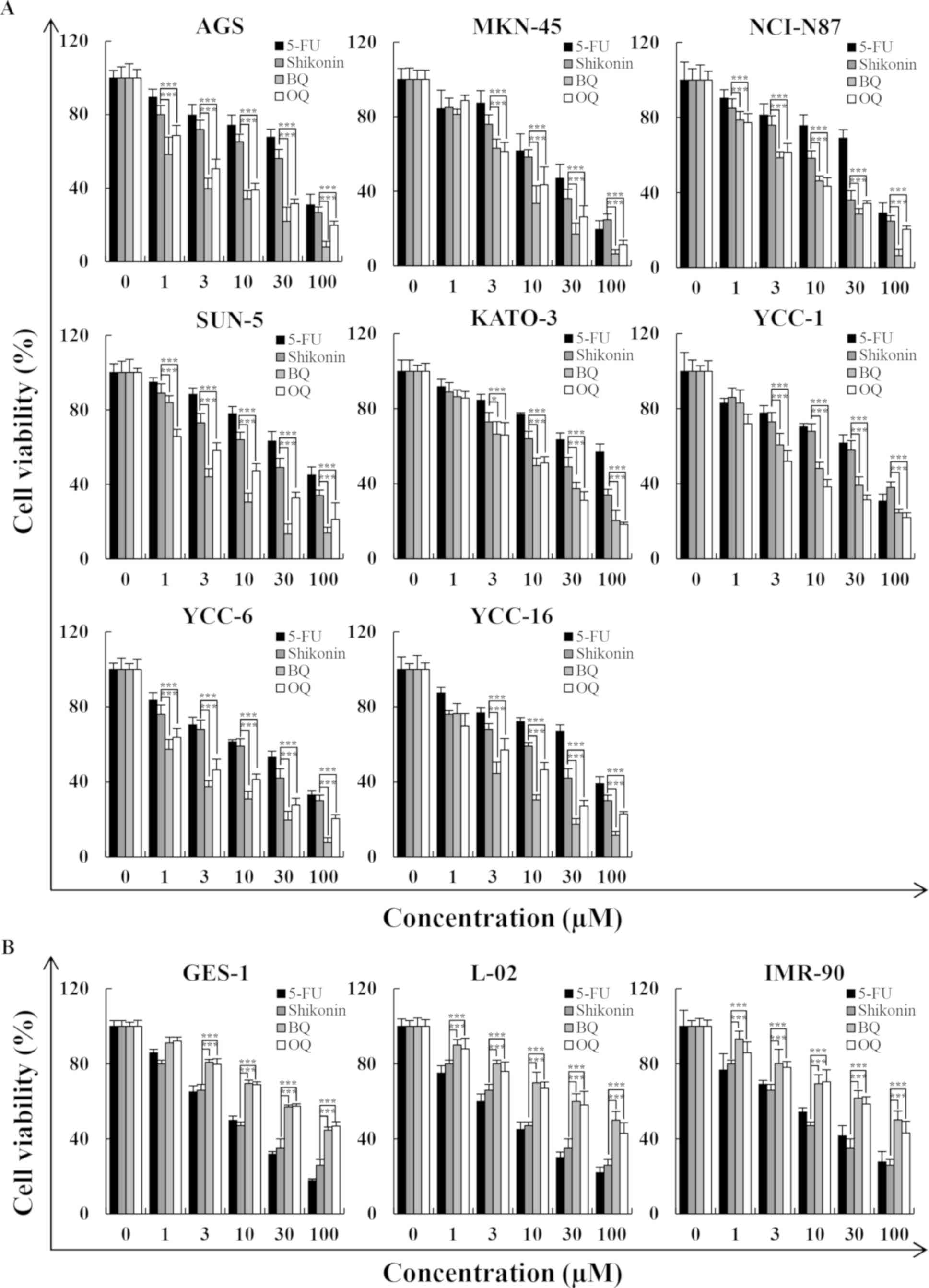
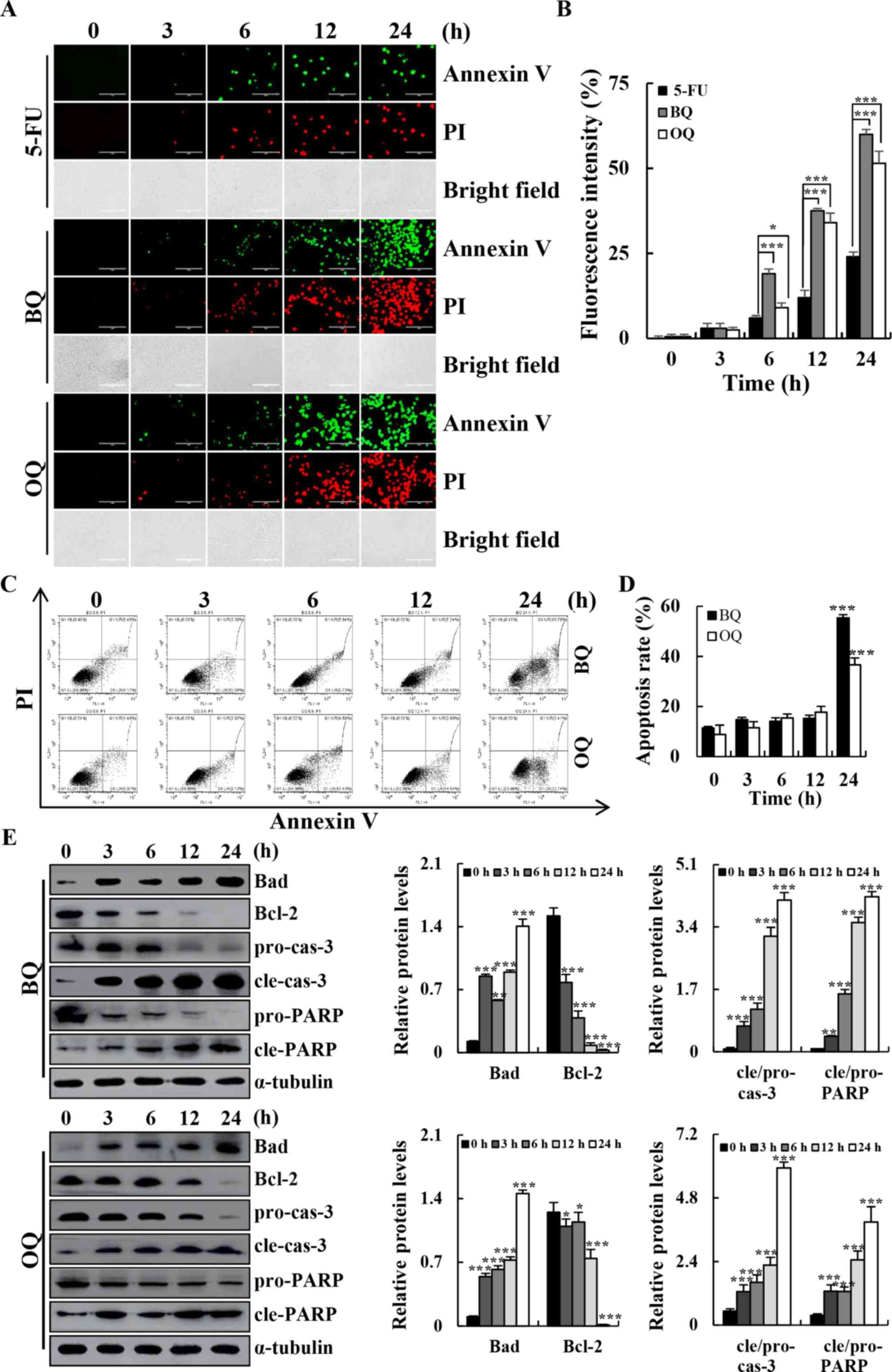
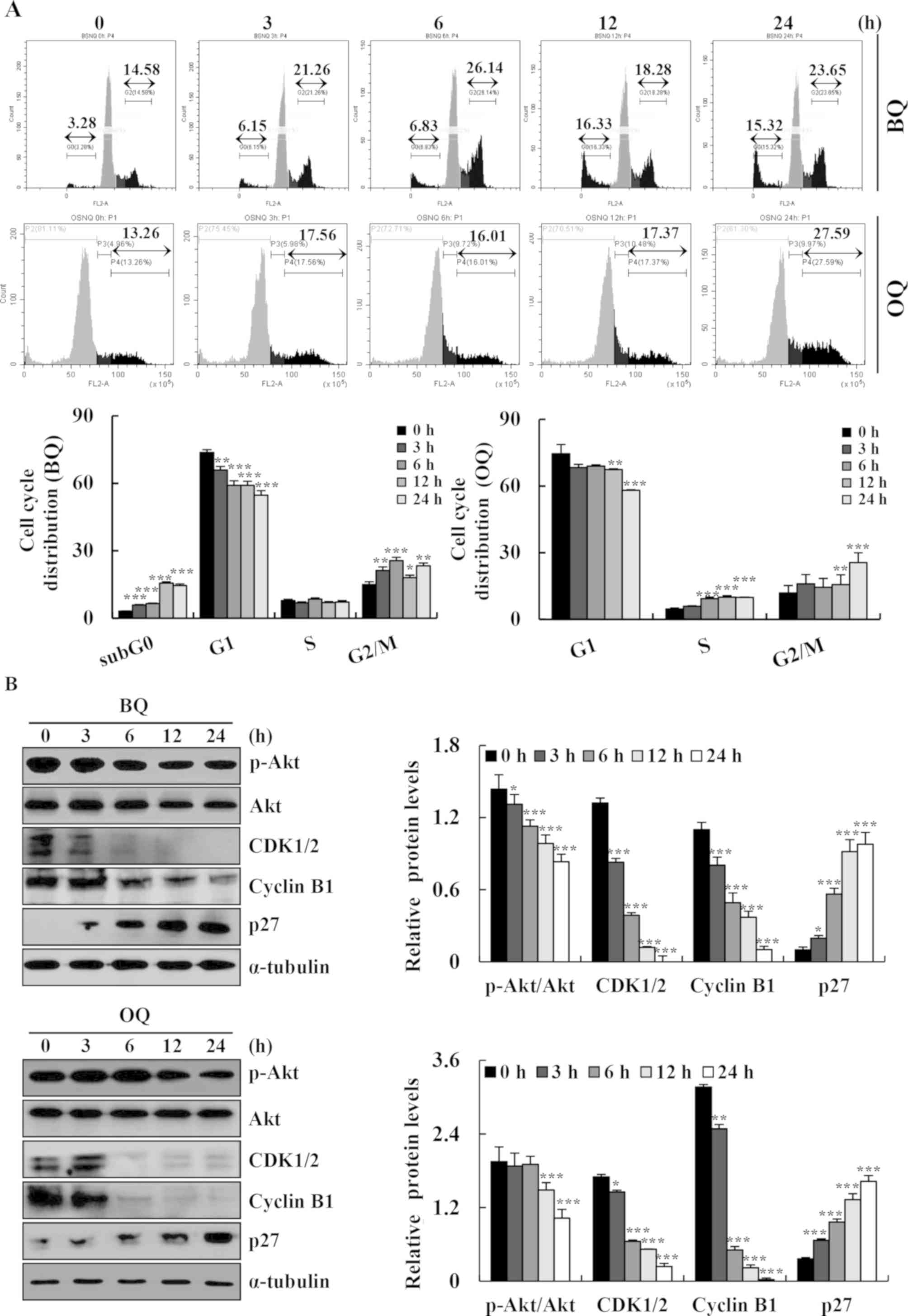
|
1
|
Jou E and Rajdev L: Current and emerging
therapies in unresectable and recurrent gastric cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:4812–4823. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Lee SY and Oh SC: Changing strategies for
target therapy in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol.
3:1179–1189. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Han G, Gong H, Wang Y, Guo S and Liu K:
AMPK/mTOR-mediated inhibition of surviving partly contributes to
metformin-induced apoptosis in human gastric cancer cell. Cancer
Biol Ther. 16:77–87. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang C, Chen Z, Zhou X, Xu W, Wang G,
Tang X, Luo L, Tu J, Zhu Y, Hu W, et al: Cantharidin induces
G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis in human gastric cancer
SGC-7901 and BGC-823 cells. Oncol Lett. 6:2721–2726. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Sinha K, Das J, Pal PB and Sil PC:
Oxidative stress: The mitochondria-dependent and
mitochondria-independent pathways of apoptosis. Arch Toxicol.
87:1157–1180. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Woo SM, Choi YK, Kim AJ, Cho SG and Ko SG:
p53 causes butein-mediated apoptosis of chronic myeloid leukemia
cells. Mol Med Rep. 13:1091–1096. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lan Q, Li S, Lai W, Xu H, Zhang Y, Zeng Y,
Lan W and Chu Z: Methyl sartortuoate inhibits colon cancer cell
growth by inducing apoptosis and G2/M-phase arrest. Int J Mol Sci.
16:19401–194118. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee H, Lee H, Chin H, Kim K and Lee D:
ERBB3 knockdown induces cell cycle arrest and activation of Bak and
Bax-dependent apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Oncotarget.
5:5138–5152. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang L, Zhou Y, Li Y, Zhou J, Wu Y, Cui Y,
Yang G and Hong Y: Mutations of p53 and KRAS activate NF-κB to
promote chemoresistance and tumorigenesis via dysregulation of cell
cycle and suppression of apoptosis in lung cancer cells. Cancer
Lett. 357:520–526. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kumar K, Sabarwal A and Singh RP: Mancozeb
selectively induces mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis in human
gastric carcinoma cells through ROS generation. Mitochondrion. Jun
11–2018.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Duan F, Yu Y, Guan R, Xu Z, Liang H and
Hong L: Vitamin K2 induces mitochondria-related apoptosis in human
bladder cancer cells via ROS and JNK/p38 MAPK signal pathways. PLoS
One. 11:e01618862016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cheng HB, Bo Y, Shen WX, Ren XG, Tan JN,
Jia ZR and Xu CL: Longikaurin E induces apoptosis of pancreatic
cancer cells via modulation of the p38 and PI3K/AKT pathways by
ROS. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 388:623–634. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rajamanickam V, Zhu H, Feng C, Chen X,
Zheng H, Xu X, Zhang Q, Zou P, He G, Dai X, et al: Novel allylated
monocarbonyl analogs of curcumin induce mitotic arrest and
apoptosis by reactive oxygen species-mediated endoplasmic reticulum
stress and inhibition of STAT3. Oncotarget. 8:101112–101129. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang Q, Dong J, Cui J, Huang G, Meng Q
and Li S: Cytotoxicity of Synthesized 1,4-Naphthoquinone Oxime
derivatives on selected human cancer cell lines. Chem Pharm Bull
(Tokyo). 66:612–619. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ghosh SK, Ganta A and Spanjaard RA:
Discovery and cellular stress pathway analysis of
1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives with novel, highly potent
broad-spectrum anticancer activity. J Biomed Sci. 25:122018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Farias MS, Pich CT, Kviecinski MR, Bucker
NC, Felipe KB, Da Silva FO, Günther TM, Correia JF, Ríos D, Benites
J, et al: Substituted 3-acyl-2-2-phenylamino-1,4-naphthoquinones
intercalate into DNA and cause genotoxicity through the increased
generation of reactive oxygen species culminating in cell death.
Mol Med Rep. 10:405–410. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ollinger K and Brunmark A: Effect of
hydroxy substituentposition on 1,4-naphthoquinone toxicity to rat
hepatocyt. J Biol Chem. 266:21496–22150. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ball MD, Bartlett MS, Shaw M, Smith JW,
Nasr M and Meshnick SR: Activities and conformational fitting of
1,4-Naphthoquinone Derivatives and other cyclic 1,4-Diones tested
in vitro against Pneumocystis carinii. Antimicrob Agents
Chemother. 45:1473–1479. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Suhara Y, Watanabe M, Motoyoshi S,
Nakagawa K, Wada A, Takeda K, Takahashi K, Tokiwa H and Okano T:
Synthesis of new vitamin K analogues as steroid and xenobiotic
receptor (SXR) agonists: Insights into the biological role of the
side chain part of vitamin K. J Med Chem. 54:4918–4922. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Abiko Y, Shinkai Y, Unoki T, Hirose R,
Uehara T and Kumagai Y: Polysulfide Na2S4
regulates the activation of PTEN/Akt/CREB signaling and
cytotoxicity mediated by 1,4-naphthoquinone through formation of
sulfur adducts. Sci Rep. 7:48142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bezkorovaynyj AO, Zyn AR, Harasym NM, Len
JT, Figurka OM and Figurka DI: Loach embryos prooxidant-antioxidant
status under the influence of amide derivatives of
1,4-naphthoquinone. Ukr Biochem J. 88:46–53. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Oh B, Figtree G, Costa D, Eade T, Hruby G,
Lim S, Elfiky A, Martine N, Rosenthal D, Clarke S and Back M:
Oxidative stress in prostate cancer patients: A systematic review
of case control studies. Prostate Int. 4:71–87. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang L, Zheng YX, Deng HZ, Liang L and
Peng J: Aloperine induces G2/M phase cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis in HCT116 human colon cancer cells. Int J Mol Med.
33:1613–1620. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ma WD, Zou YP, Wang P, Yao XH, Sun Y, Duan
MH, Fu YJ and Yu B: Chimaphilin induces apoptosis in human breast
cancer MCF-7 cells through a ROS-mediated mitochondrial pathway.
Food Chem Toxicol. 70:1–8. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ong JY, Yong PV, Lim YM and Ho AS:
2-Methoxy-1, 4-naphthoquinone (MNQ) induces apoptosis of A549 lung
adenocarcinoma cells via oxidation-triggered JNK and p38 MAPK
signaling pathways. Life Sci. 135:158–164. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Eldhose B, Gunawan M, Rahman M, Latha MS
and Notario V: Plumbagin reduces human colon cancer cell survival
by inducing cell cycle arrest and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis.
Int J Oncol. 45:1913–1920. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang YL, Zhang R, Xu HL, Yu XF, Qu SC and
Sui DY: 20(S)-protopanaxadiol triggers mitochondrial-mediated
apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells via inhibiting
the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Am J Chin Med. 41:1137–1152. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Laux I and Nel A: Evidence that oxidative
stress-induced apoptosis by menadione involves Fas-dependent and
Fas-independent pathways. Clin Immunol. 101:335–344. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
McKallip RJ, Lombard C, Sun J and
Ramakrishnan R: Plumbagin-induced apoptosis in lymphocytes is
mediated through increased reactive oxygen species production,
upregulation of Fas, and activation of the caspase cascade. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 247:41–52. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tian R, Li Y and Gao M: Shikonin causes
cell-cycle arrest and induces apoptosis by regulating the
EGFR-NF-κB signalling pathway in human epidermoid carcinoma A431
cells. Biosci Rep. 35(pii): e001892015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xu N, Lao Y, Zhang Y and Gillespie DA:
Akt: A double-edged sword in cell proliferation and genome
stability. J Oncol. 2012:9517242012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shan ZL, Zhong L, Xiao CL, Gan LG, Xu T,
Song H, Yang R, Li L and Liu BZ: Shikonin suppresses proliferation
and induces apoptosis in human leukemia NB4 cells through
modulation of MAPKs and c-Myc. Mol Med Rep. 16:3055–3060. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang J, Zhang JN, Chen WL, Wang GS, Mao Q,
Li SQ, Xiong WH, Lin YY, Ge JW, Li XX, et al: Effects of AQP5 gene
silencing on proliferation, migration and apoptosis of human glioma
cells through regulating EGFR/ERK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway.
Oncotarget. 8:38444–38455. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tan BB, Zhang MM, Li Y, Zhao Q, Fan LQ,
Liu Y and Wang D: Inhibition of Vav3 gene can promote apoptosis of
human gastric cancer cell line MGC803 by regulating ERK pathway.
Tumour Biol. 37:7823–7833. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yuan Z, Guo W, Yang J, Li L, Wang M, Lei
Y, Wan Y, Zhao X, Luo N, Cheng P, et al: PNAS-4, an Early DNA
damage response gene, induces S phase arrest and apoptosis by
activating checkpoint kinases in lung cancer cells. J Biol Chem.
290:14927–14944. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cao Y, Yin X, Jia Y, Liu B, Wu S and Shang
M: Plumbagin, a natural naphthoquinone, inhibits the growth of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells through inactivation of
STAT3. Int J Mol Med. 42:1569–1576. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhong WF, Wang XH, Pan B, Li F, Kuang L
and Su ZX: Eupatilin induces human renal cancer cell apoptosis via
ROS-mediated MAPK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. Oncol Lett.
12:2894–2899. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Verrax J, Delvaux M, Beghein N, Taper H,
Gallez B and Buc Calderon P: Enhancement of quinone redox cycling
by ascorbate induces a caspase-3 independent cell death in human
leukaemia cells. An in vitro comparative study. Free Radic Res.
39:649–657. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Prachayasittikul V, Pingaew R,
Worachartcheewan A, Nantasenamat C, Prachayasittikul S, Ruchirawat
S and Prachayasittikul V: Synthesis, anticancer activity and QSAR
study of 1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives. Eur J Med Chem.
84:247–263. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|