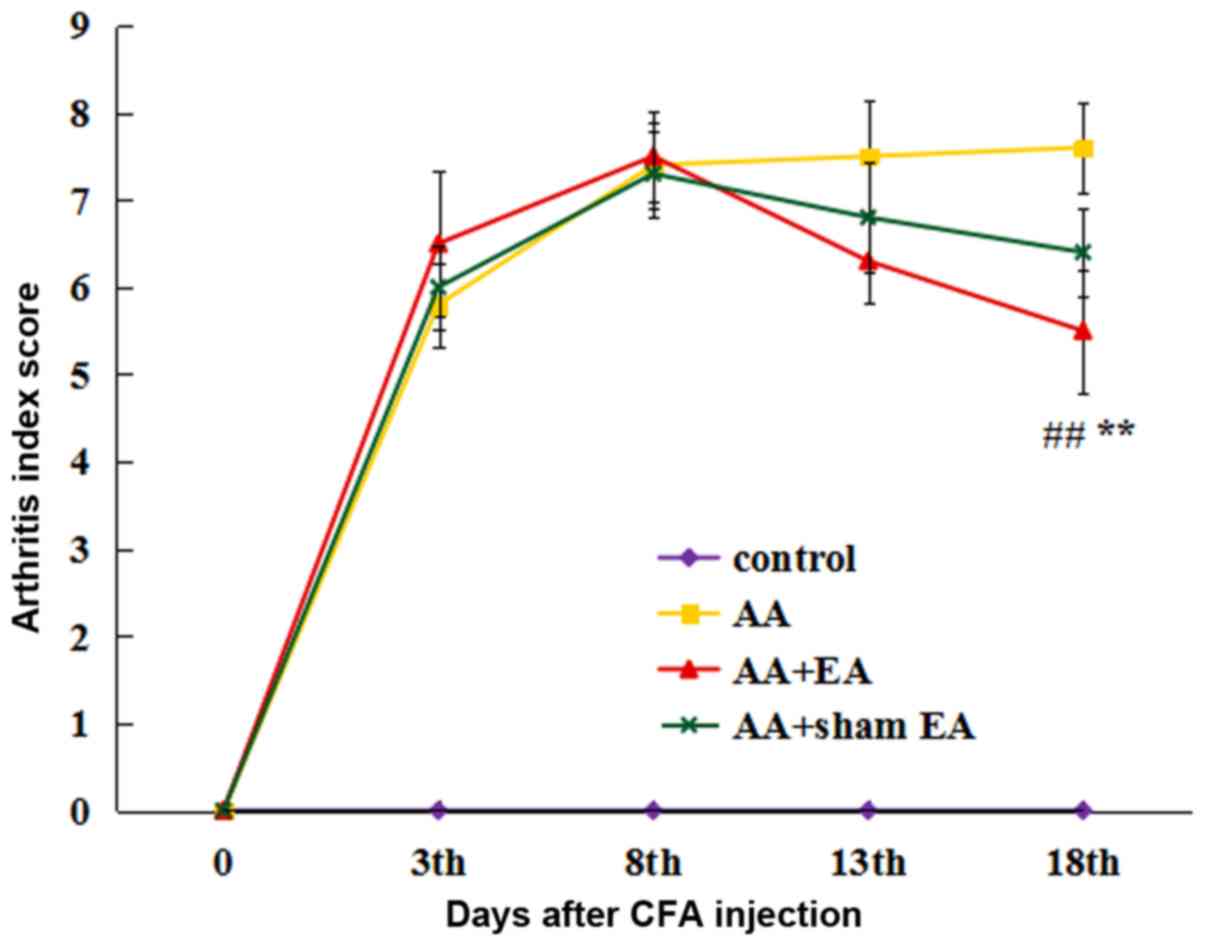
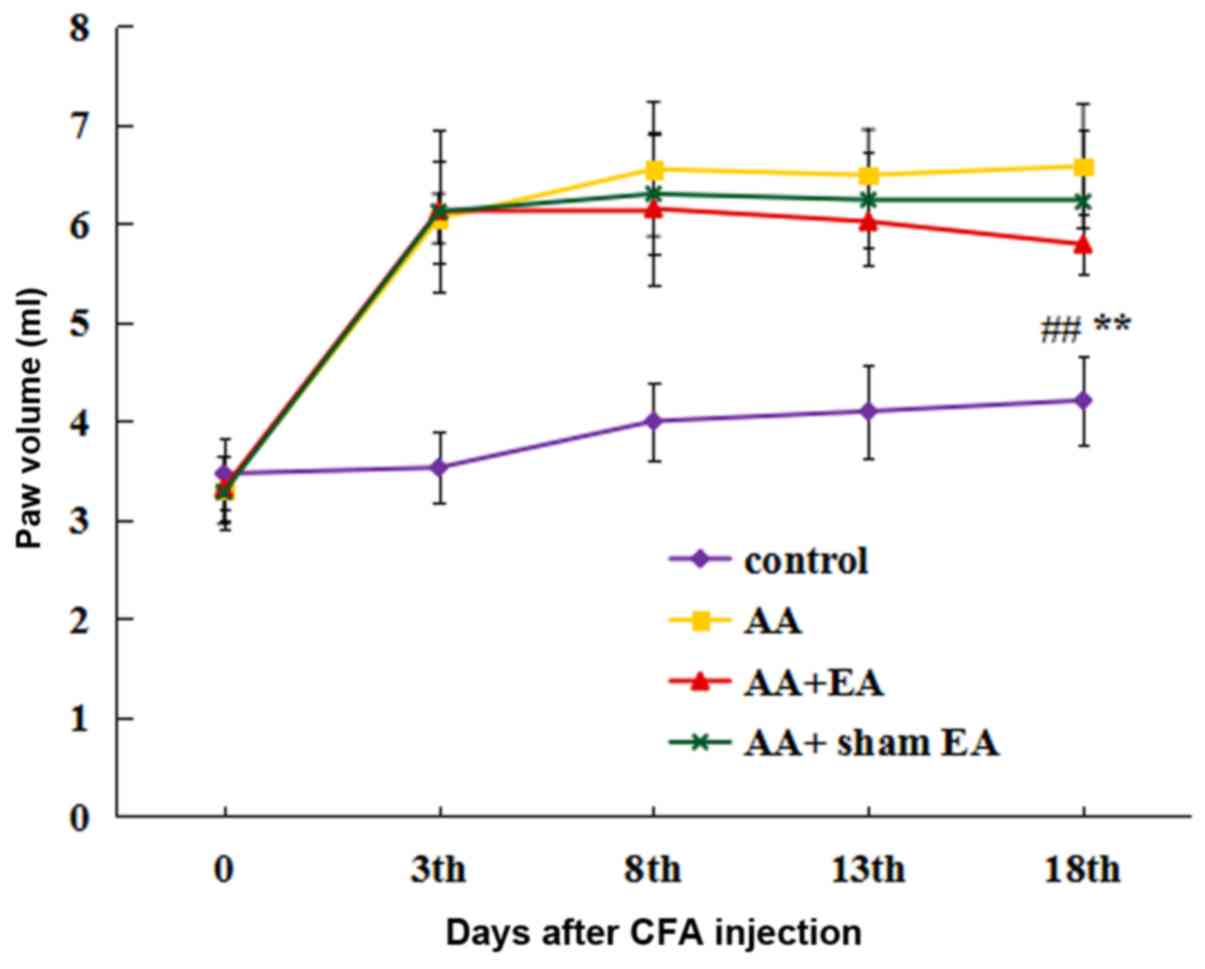
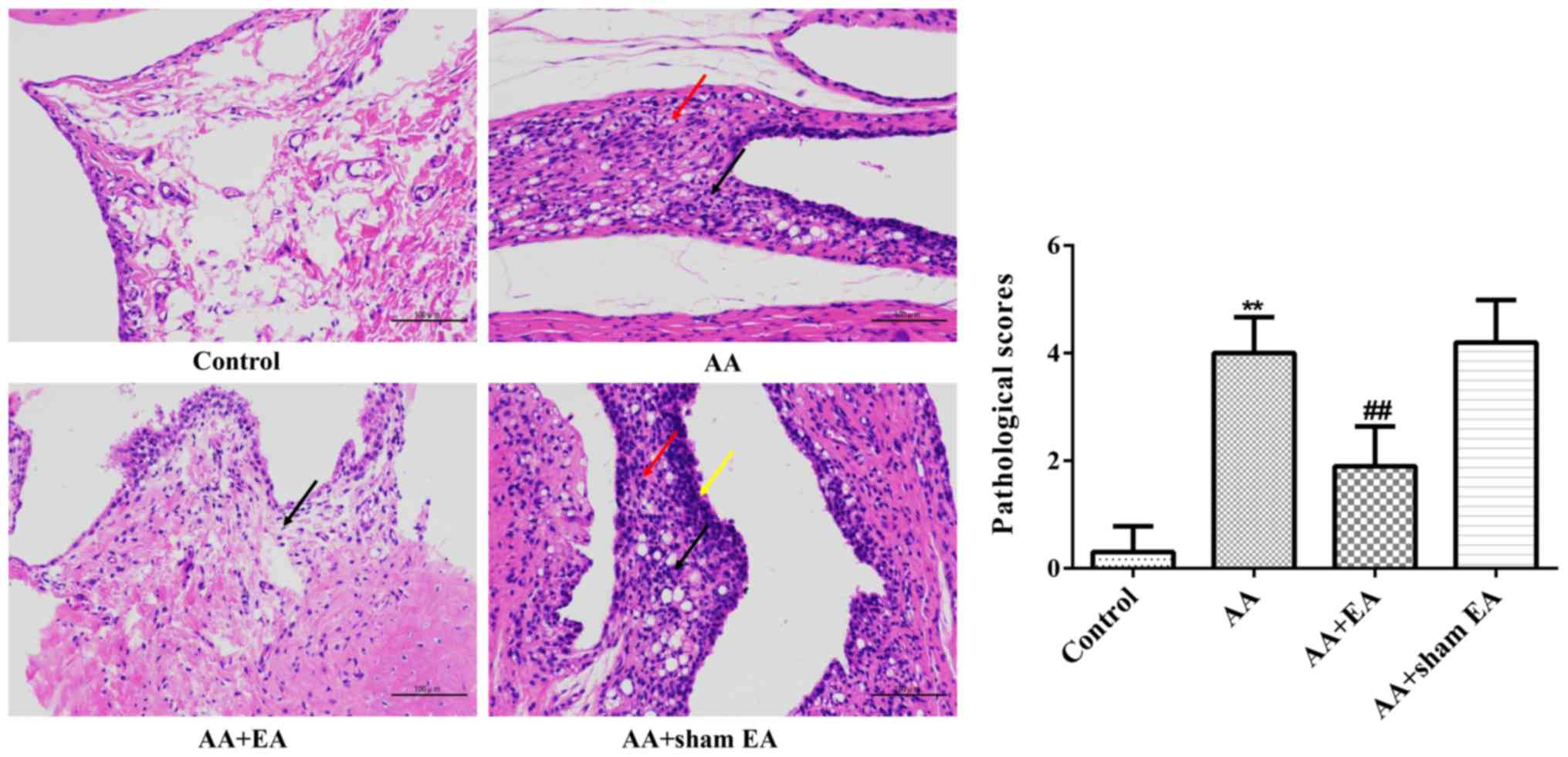
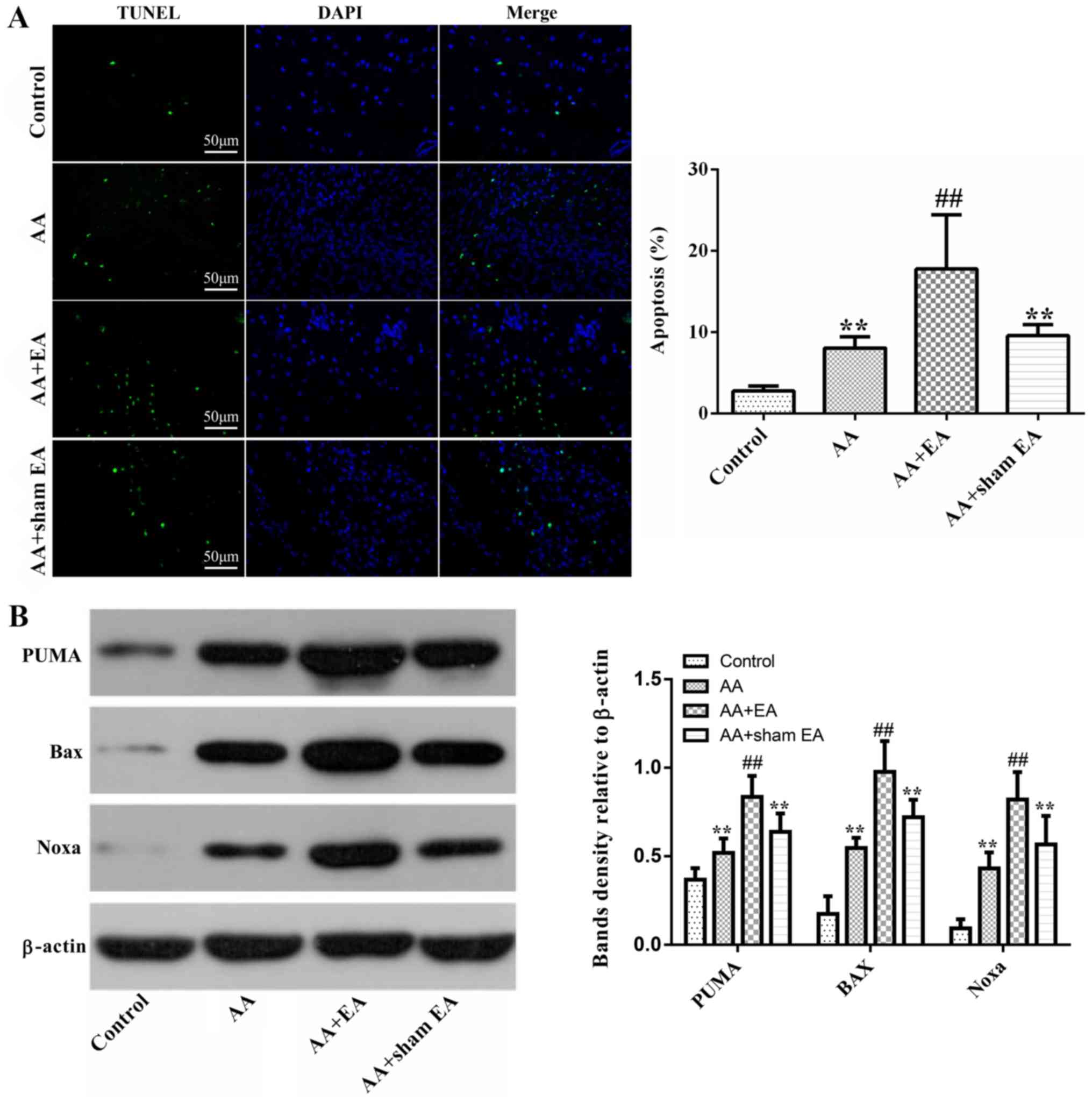
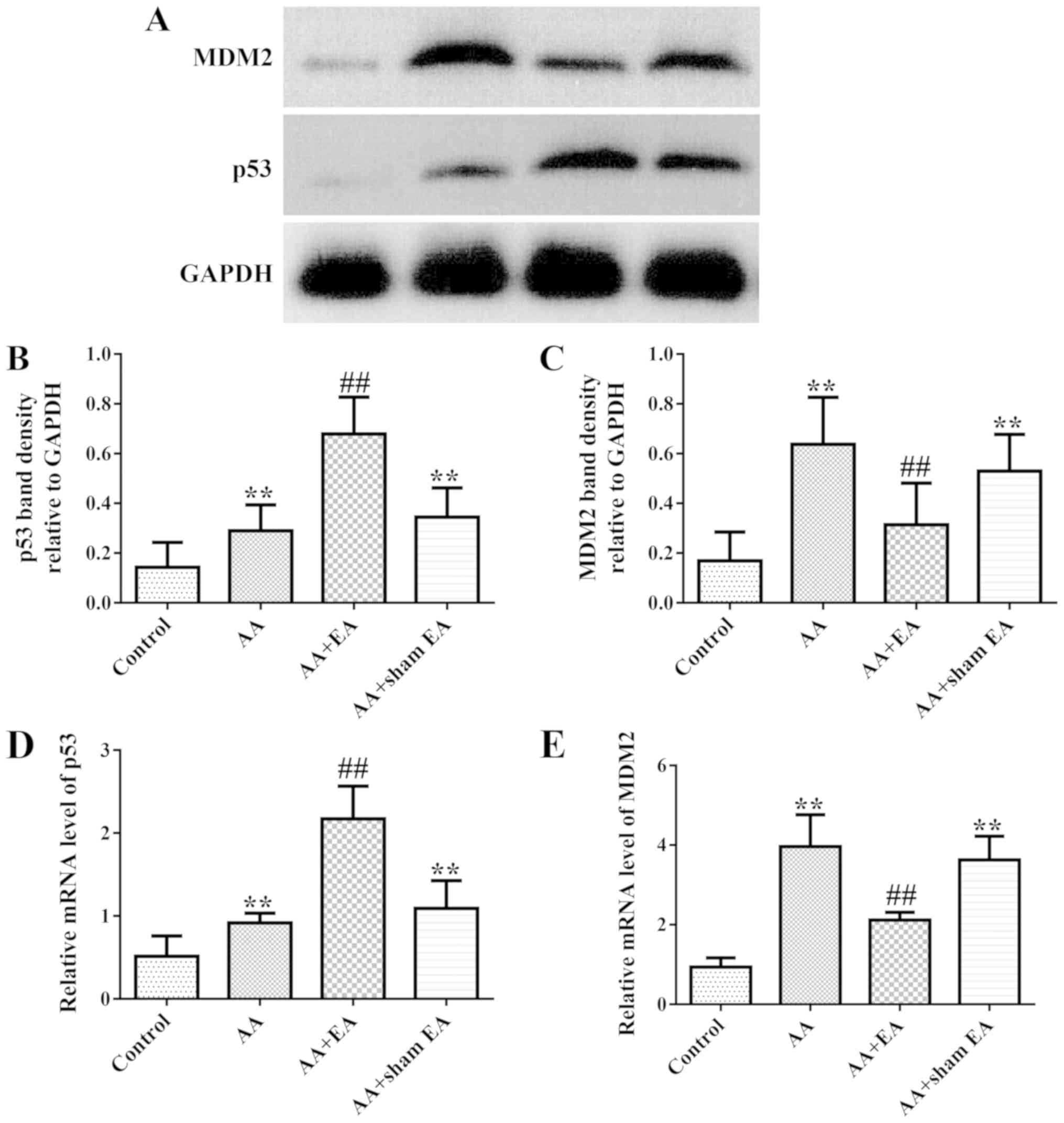
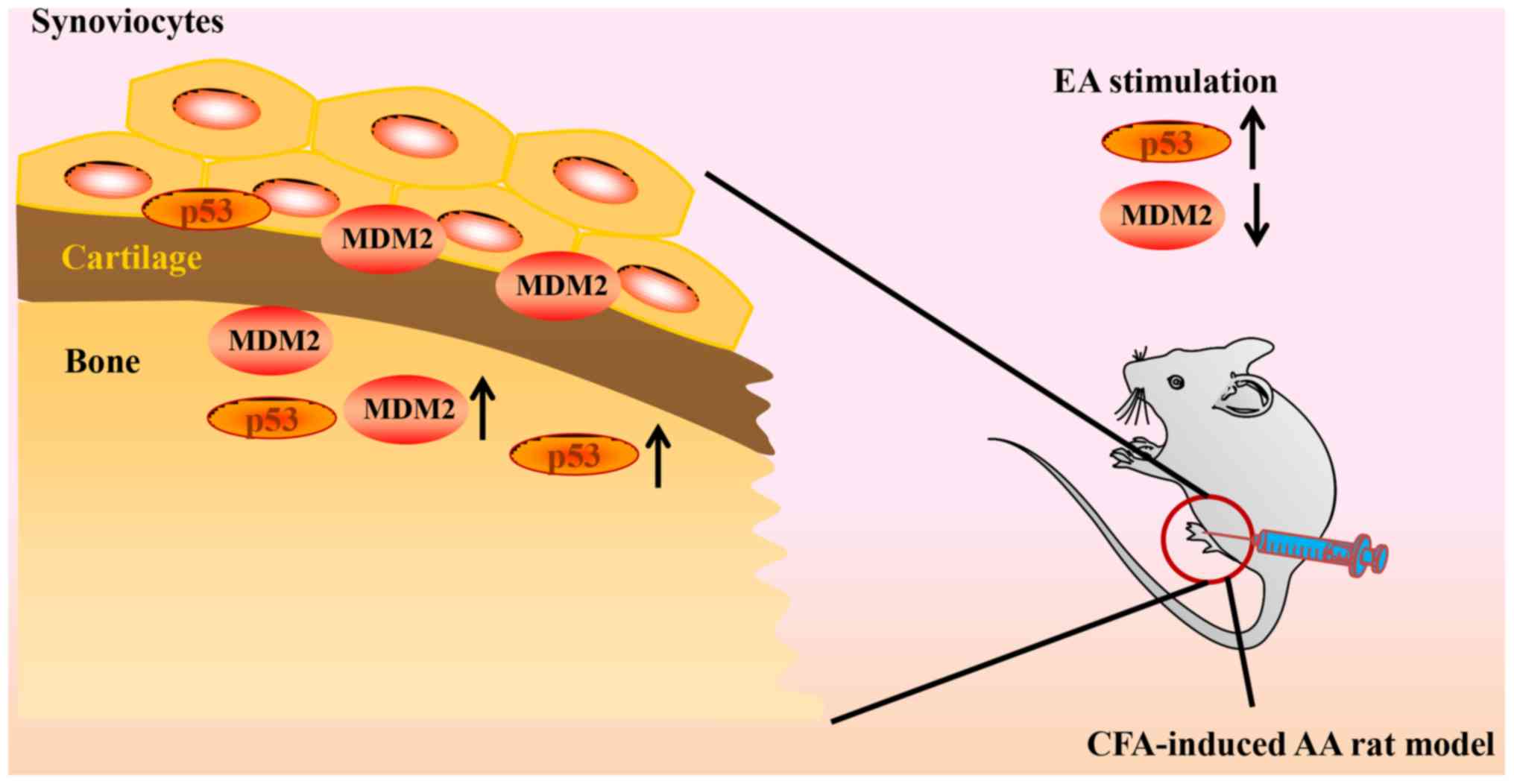
|
1
|
Firestein GS: Evolving concepts of
rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 423:356–361. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Matsui T, Nakata N, Nagai S, Nakatani A,
Takahashi M, Momose T, Ohtomo K and Koyasu S: Inflammatory
cytokines and hypoxia contribute to 18F-FDG uptake by cells
involved in pannus formation in rheumatoid arthritis. J Nucl Med.
50:920–926. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bartok B and Firestein GS: Fibroblast-like
synoviocytes: Key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol
Rev. 233:233–255. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ma J, Wang X, Lv T, Liu J, Ren Y, Zhang J
and Zhang Y: Effects of fhrelin on the apoptosis of rheumatoid
arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocyte MH7A cells. Biol Pharm Bull.
42:158–163. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mahoney JA and Rosen A: Apoptosis and
autoimmunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 17:583–588. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chou CT, Yang JS and Lee MR: Apoptosis in
rheumatoid arthritis-expression of Fas, Fas-L, p53, and Bcl-2 in
rheumatoid synovial tissues. J Pathol. 193:110–116. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hou YN and Guo LH: Role of synovial
fibroblasts in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Chin J
Cell Biol. 31:157e1622009.
|
|
8
|
Li R, Cai L, Tang WJ, Lei C, Hu CM and Yu
F: Apoptotic effect of geniposide on fibroblast-like synoviocytes
in rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis via inhibiting ERK signal
pathway in vitro. Inflflammation. 39:30–38. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Aupperle KR, Boyle DL, Hendrix M, Seftor
EA, Zvaifler NJ, Barbosa M and Firestein GS: Regulation of
synoviocyte proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion by the p53 tumor
suppressor gene. Am J Pathol. 152:1091–1098. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tak PP, Zvaifler NJ, Green DR and
Firestein GS: Rheumatoid arthritis and p53: How oxidative stress,
might alter the course of inflammatory diseases. Immunol Today.
21:78–82. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yamanishi Y, Boyle DL, Rosengren S, Green
DR, Zvaifler NJ and Firestein GS: Regional analysis of p53
mutations in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
99:10025–10030. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Doroshevskaya AY, Kondratovskii PM,
Dubikov AI and Eliseikina MG: Apoptosis regulator proteins: Basis
for the development of innovation strategies for the treatment of
rheumatoid arthritis in patients of different age. Bull Exp Biol
Med. 156:377–380. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nakano K and Vousden KH: PUMA, a novel
proapoptotic gene, is induced by p53. Mol Cell. 7:683–694. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Villunger A, Michalak EM, Coultas L,
Müllauer F, Böck G, Ausserlechner MJ, Adams JM and Strasser A: p53-
and drug-induced apoptotic responses mediated by BH3-only proteins
puma and Noxa. Science. 302:1036–1038. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Thomasova D, Mulay SR, Bruns H and Anders
HJ: p53-Independent roles of MDM2 in NF-κB signaling: Implications
for cancer therapy, wound healing, and autoimmune diseases.
Neoplasia. 14:1097–1101. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang L, Luo J, Wen H, Zhang T, Zuo X and
Li X: MDM2 promotes rheumatoid arthritis via activation of MAPK and
NF-κB. Int Immunopharmacol. 30:69–73. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cory S and Adams JM: The Bcl2 family:
Regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:647–656. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bouvard V, Zaitchouk T, Vacher M, Duthu A,
Canivet M, Choisy-Rossi C, Nieruchalski M and May E: Tissue and
cell-specific expression of the p53-target genes: Bax, Fas, MDM2
and Waf1/p21, before and following ionising irradiation in mice.
Oncogene. 19:649–660. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ohtsuka T, Ryu H, Minamishima YA, Macip S,
Sagara J, Nakayama KI, Aaronson SA and Lee SW: ASC is a Bax adaptor
and regulates the p53-Bax mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Nat Cell
Biol. 6:121–128. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Itoh K, Hase H, Kojima H, Saotome K,
Nishioka K and Kobata T: Central role of mitochondria and p53 in
Fas-mediated apoptosis of rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 43:277–285. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tak PP, Klapwijk MS, Broersen SF, van de
Geest DA, Overbeek M and Firestein GS: Apoptosis and 53 expression
in rat adjuvant arthritis. Arthritis Res. 2:229–235. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li Y, He N, Shen L and Liu M: Apoptotic
effect of Aralia echinocaulis extract on fibroblast-like
synoviocytes in rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis via inhibiting
the Akt/Hif-1α signaling pathway in vitro. J Pharmacol Sci.
139:340–345. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cha HS, Rosengren S, Boyle DL and
Firestein GS: PUMA regulation and proapoptotic effects in
fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 54:587–592. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mazumder S, Choudhary GS, Al-Harbi S and
Almasan A: Mcl-1 phosphorylation defines ABT-737 resistance that
can be overcome by increased NOXA expression in leukemic B cells.
Cancer Res. 72:3069–3079. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Idrus E, Nakashima T, Wang L, Hayashi M,
Okamoto K, Kodama T, Tanaka N, Taniguchi T and Takayanagi H: The
role of the BH3-only protein Noxa in bone homeostasis. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 410:620–625. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cottier KE, Fogle EM, Fox DA and Ahmed S:
Noxa in rheumatic diseases: Present understanding and future
impact. Rheumatology (Oxford). 53:1539–1546. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
He G, Wu Z, Wang Q, et al: Therapeutic
observation of electroacupuncture plus electromagnetic therapy for
rheumatoid arthritis. Shanghai J Acupuncture Moxibustion.
33:247–250. 2014.(In Chinese).
|
|
28
|
Ouyang BS, Gao J, Che JL, Zhang Y, Li J,
Yang HZ, Hu TY, Yang M, Wu YJ and Ji LL: Effect of
Electro-acupuncture on tumor necrosis Factor-α and vascular
endothelial growth factor in peripheral blood and Joint synovia of
patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Chin J Integr Med. 17:505–509.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chou PC and Chu HY: Clinical efficacy of
acupuncture on rheumatoid arthritis and associated mechanisms: A
systemic review. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2018:85969182018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
He TF, Yang WJ, Zhang SH, Zhang CY, Li LB
and Chen YF: Electroacupuncture inhibits inflammation reaction by
upregulating vasoactive intestinal peptide in rats with
adjuvant-induced arthritis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2011:1–8. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhu J, Chen XY, Li LB, Yu XT, Zhou Y, Yang
WJ, Liu Z, Zhao N, Fu C, Zhang SH and Chen YF: Electroacupuncture
attenuates collagen-induced arthritis in rats through vasoactive
intestinal peptide signalling-dependent re-establishment of the
regulatory T cell/T-helper 17 cell balance. Acupunct Med.
33:305–311. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dong ZQ, Zhu J, Lu DZ, Chen Q and Xu YL:
Effect of electroacupuncture in ‘Zusanli’ and ‘Kunlun’ acupoints on
TLR4 signaling pathway of adjuvant arthritis rats. Am J Ther.
25:e314–e319. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen L, Wu Q, Yang M, Deng S, Bai L, Chen
L and Liang L: Research review of the action mechanism of
acupuncture based on cell apoptosis. Shanghai J Acupuncture
Moxibustion. 35:1143–1146. 2016.(In Chinese).
|
|
34
|
Liu J, Zhang Y, Sun J, Xu S and Zhang X:
Effect of acupuncture on the p53 Protein expression of mice with
Alzheimer's disease. Chin J Integrated Traditional Western Med.
33:1367–1371. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
35
|
Park JY, Choi H, Baek S, Jang J, Lee A,
Jeon S, Kim J and Park HJ: p53 signalling mediates
acupuncture-induced neuroprotection in Parkinson's disease. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 460:772–779. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
An N, Xu T, Sun Q and Zhang H: Research on
effect of electroacupuncture on MDM2 expression in hypoxic-ischemic
encephalopathy rat model. Chin Arch Traditional Chin Med.
34:289–292. 2016.(In Chinese).
|
|
37
|
Shi WY, Yan J, Chang XR, Lou BD, Li JX,
Huang J, Lin H, Wang C and Zhang W: Observation of
electroacupuncture intervention on cell apoptosis and Bax and Bcl-2
expression in cerebral and myocardial tissues in cerebral ischemia
rats based on ‘heart-brain correlation’ theory. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu.
44:107–112. 2019.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhu Y and Zeng Y: Electroacupuncture
protected pyramidal cells in hippocampal CA1 region of vascular
dementia rats by inhibiting the expression of P53 and Noxa. CNS
Neurosci Ther. 17:599–604. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shalev M: APHIS, FDA, and NIH issue
memorandum of understanding on laboratory animal welfare. Lab Anim
(NY). 15:132006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Li P, Xie G, Song S, Huang P, Wu Y, Wang
Q, Chang Y, Zhang Y, Zhou A, Liu L, et al: Clinical manifestations
and the main evaluation method on adjuvant-induced arthritis model
in rats. Chin J Immunol. 28:453–457. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
41
|
Ai X, Hou Y, Wang X, Wang X, Liang Y, Zhu
Z, Wang P, Zeng Y, Li X, Lai X, et al: Amelioration of dry eye
syndrome in db/db mice with diabetes mellitus by treatment with
Tibetan Medicine Formula Jikan mingmu drops. J Ethnopharmacol.
241:1119922019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hou Y, Wang X, Chen X, Zhang J, Ai X,
Liang Y, Yu Y, Zhang Y, Meng X, Kuang T and Hu Y: Establishment and
evaluation of a simulated high-altitude hypoxic brain injury model
in SD rats. Mol Med Rep. 19:2758–2766. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang X, Hou Y, Li Q, Li X, Wang W, Ai X,
Kuang T, Chen X, Zhang Y, Zhang J, et al: Rhodiola crenulata
attenuates apoptosis and mitochondrial energy metabolism disorder
in rats with hypobaric hypoxia-induced brain injury by regulating
the HIF-1α/microRNA 210/ISCU1/2(COX10) signaling pathway. J
Ethnopharmacol. 241:1118012019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhu J, Su CG, Chen YZ, Hao XY and Jiang
JZ: Electroacupuncture on ST36 and GB39 acupoints inhibits synovial
angiogenesis via downregulating HIF-1α/VEGF expression in a rat
model of adjuvant arthritis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2019:57419312019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Müller-Ladner U and Pap T: Pathogenesis of
RA: More than just immune cells. Z Rheumatol. 64:396–401. 2005.(In
German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Bottini N and Firestein GS: Duality of
fibroblast-like synoviocytes in RA: Passive responders and
imprinted aggressors. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 9:24–33. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Baier A, Meineckel I, Gay S and Pap T:
Apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 15:274–279.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Peng C, Luo L, Hu L, Wu Z, Cai R, Hao F,
Hu W and Hong J: Study on the effect of moxibustion in treating
rhreumatoid arthritis rats and its mechanism. J Acupuncture Tuina
Sci. 10:336–341. 2012.(In Chinese). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Zhang C, Cai R and Tang Z: Influences of
moxibustion on inflammatory factors and synoviocytes in rats with
rheumatoid arthritis. J Beijing Univ Traditional Chin Med.
37:190–194. 2014.(In Chinese).
|
|
51
|
Chen L, Wu QF, Yang MX, et al: Research
review of the action mechanism of acupuncture based on cell
apoptosis. Shanghai J Acupuncture Moxibustion. 35:1143–1146.
2016.(In Chinese).
|
|
52
|
Gao W, Deng Q, Bai S and Tong L:
Establishment and characteristic analysis of fibroblast-like
synoviocytes in rats with adjuvant arthritis. Chin Pharmacol
Bulletin. 12:1693–1698. 2015.
|
|
53
|
Meng Q, Du X, Wang H, Gu H, Zhan J and
Zhou Z: Astragalus polysaccharides inhibits cell growth and
pro-inflammatory response in IL-1β-stimulated fibroblast-like
synoviocytes by enhancement of autophagy via PI3K/AKT/mTOR
inhibition. Apoptosis. 22:1138–1146. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Dekkers JS, Schoones JW, Huizinga TW, Toes
RE and van der Helm-van Mil AH: Possibilities for preventive
treatment in rheumatoid arthritis? Lessons from experimental animal
models of arthritis: A systematic literature review and
meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 76:458–467. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Taşçi Bozbaş G, Yilmaz M, Paşaoğlu E,
Gürer G, Ivgin R and Demirci B: Effect of ozone in Freund's
complete adjuvant-induced arthritis. Arch Rheumatol. 33:137–142.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Smolen JS, Aletaha D and McInnes IB:
Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 388:2023–2038. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ren XY, Liu QX and Wang HY: p53 and cell
death. Chin J Bioch Mol Biol. 34:588–594. 2018.
|
|
58
|
Zhen D, Zhao F and Song H: Progress of
polysaccharides regulating p53 signal network. Chin J Cell Biol.
39:1234–1242. 2017.
|
|
59
|
Peng L, Liu J, Xie X, et al: The research
progress of p53 regulating the balance of tumor and aging. Chem
Life. 37:515–520. 2017.(In Chinese).
|
|
60
|
Zhu J, Chen X, Li L, Zhou Y, Bing X and
Chen Y: Experimental study on vasoactive intestinal peptide
mediated by electroacupuncture for the treatment of
collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Shanghai J Traditional Chin
Med. 49:72–76. 2015.(In Chinese).
|
|
61
|
Lassus P, Bertrand C, Zugasti O, Chambon
JP, Soussi T, Mathieu-Mahul D and Hibner U: Anti-apoptotic activity
of p53 maps to the COOH-terminal domain and is retained in a highly
oncogenic natural mutant. Oncogene. 18:4699–4709. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Nakajima T, Aono H, Hasunuma T, Yamamoto
K, Shirai T, Hirohata K and Nishioka K: Apoptosis and functional
Fas antigen in rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes. Arthritis Rheum.
38:485–491. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Firestein GS, Yeo M and Zvaifler NJ:
Apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. J Clin Invest.
96:1631–1638. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Kobayashi T, Okamoto K, Kobata T, Hasunuma
T and Nishioka K: Apomodulation as a novel therapeutic concept for
the regulation of apoptosis in rheumatoid synoviocytes. Curr Opin
Rheumatol. 11:188–193. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Yao Q, Wang S, Glorioso JC, Evans CH,
Robbins PD, Ghivizzani SC and Oligino TJ: Gene transfer of p53 to
arthritic joints stimulates synovial apoptosis and inhibits
inflammation. Mol Ther. 3:901–910. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Tang B, You X, Zhao L, Zhang T, Zhang L,
Zhang X and Tang F: The effect of p53 expression in fibroblast-like
synoviocytes on CD4+ T lymphocytes in patients with
rheumatoid arthritis. Chin J Rheumatol. 13:587–591. 2009.(In
Chinese).
|
|
67
|
Vassilev LT, Vu BT, Graves B, Carvajal D,
Podlaski F, Filipovic Z, Kong N, Kammlott U, Lukacs C, Klein C, et
al: In vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule
antagonists of MDM2. Science. 303:844–848. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Yang E, Zha J, Jockel J, Boise LH,
Thompson CB and Korsmeyer SJ: Bad, a heterodimeric partner for
Bcl-XL and Bcl-2, displaces Bax and promotes cell death. Cell.
80:285–291. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Oda E, Ohki R, Murasawa H, Nemoto J,
Shibue T, Yamashita T, Tokino T, Taniguchi T and Tanaka N: Noxa, a
BH3-only member of the Bcl-2 family and candidate mediator of
p53induced apoptosis. Science. 288:1053–1058. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Liu FT, Newland AC and Jia L: Bax
conformational change is a crucial step for PUMA-mediated apoptosis
in human leukemia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 310:956–962. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Seca S, Patrício M, Kirch S, Franconi G,
Cabrita AS and Greten HJ: Effectiveness of acupuncture on pain,
functional disability, and quality of life in rheumatoid arthritis
of the hand: Results of a double-blind randomized clinical trial. J
Altern Complement Med. 25:86–97. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Liu Z, Liu Y, Xu H, He L, Chen Y, Fu L, Li
N, Lu Y, Su T, Sun J, et al: Effect of electroacupuncture on
urinary leakage among women with stress urinary incontinence: A
randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 317:2493–2501. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Liu Z, Yan S, Wu J, He L, Li N, Dong G,
Fang J, Fu W, Fu L, Sun J, et al: Acupuncture for chronic severe
functional constipation: A randomized trial. Ann Intern Med.
165:761–769. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Song JG, Li HH, Cao YF, Lv X, Zhang P, Li
YS, Zheng YJ, Li Q, Yin PH, Song SL, et al: Electroacupuncture
improves survival in rats with lethal endotoxemia via the autonomic
nervous system. Anesthesiology. 116:406–414. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|