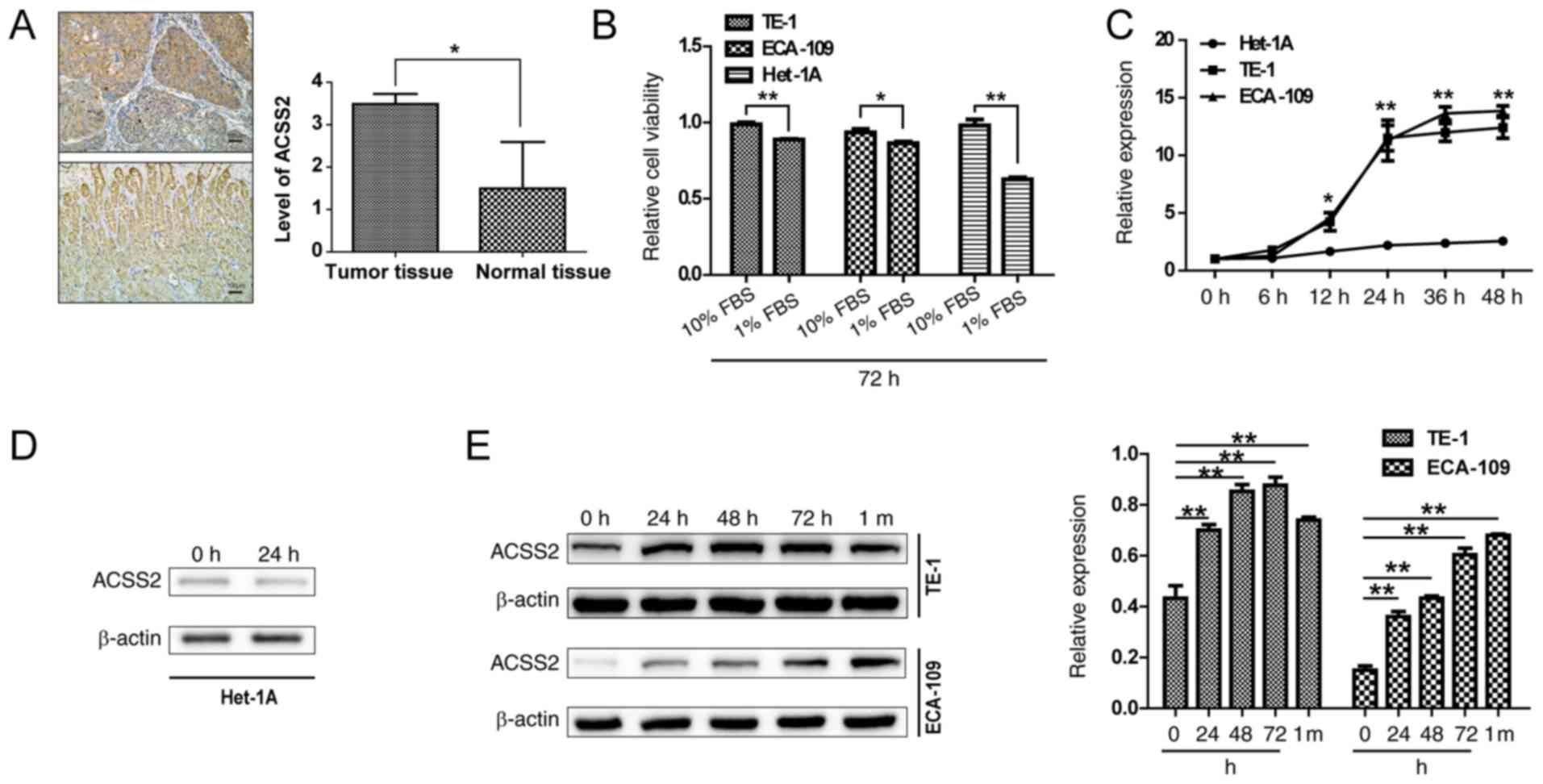
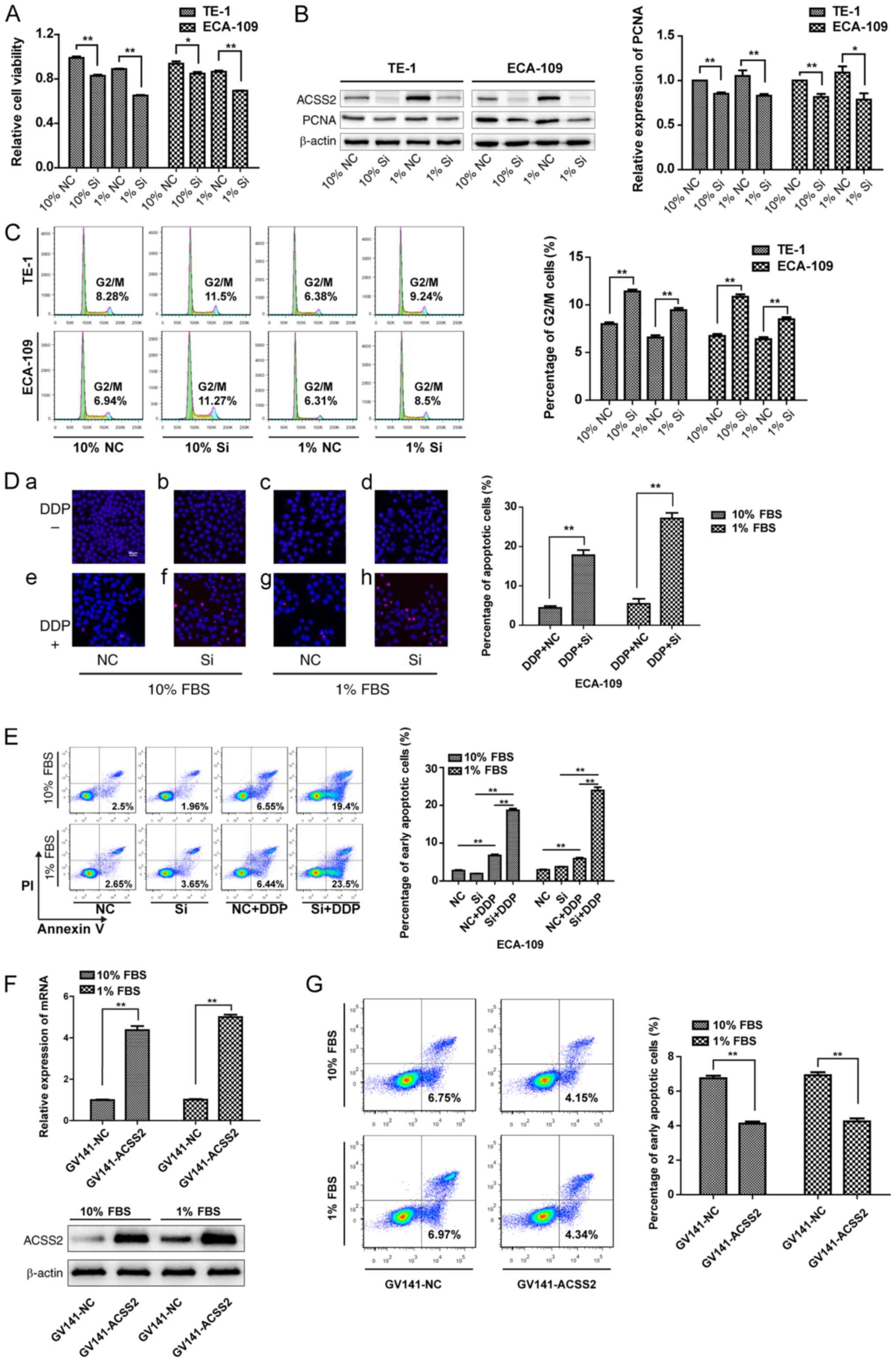
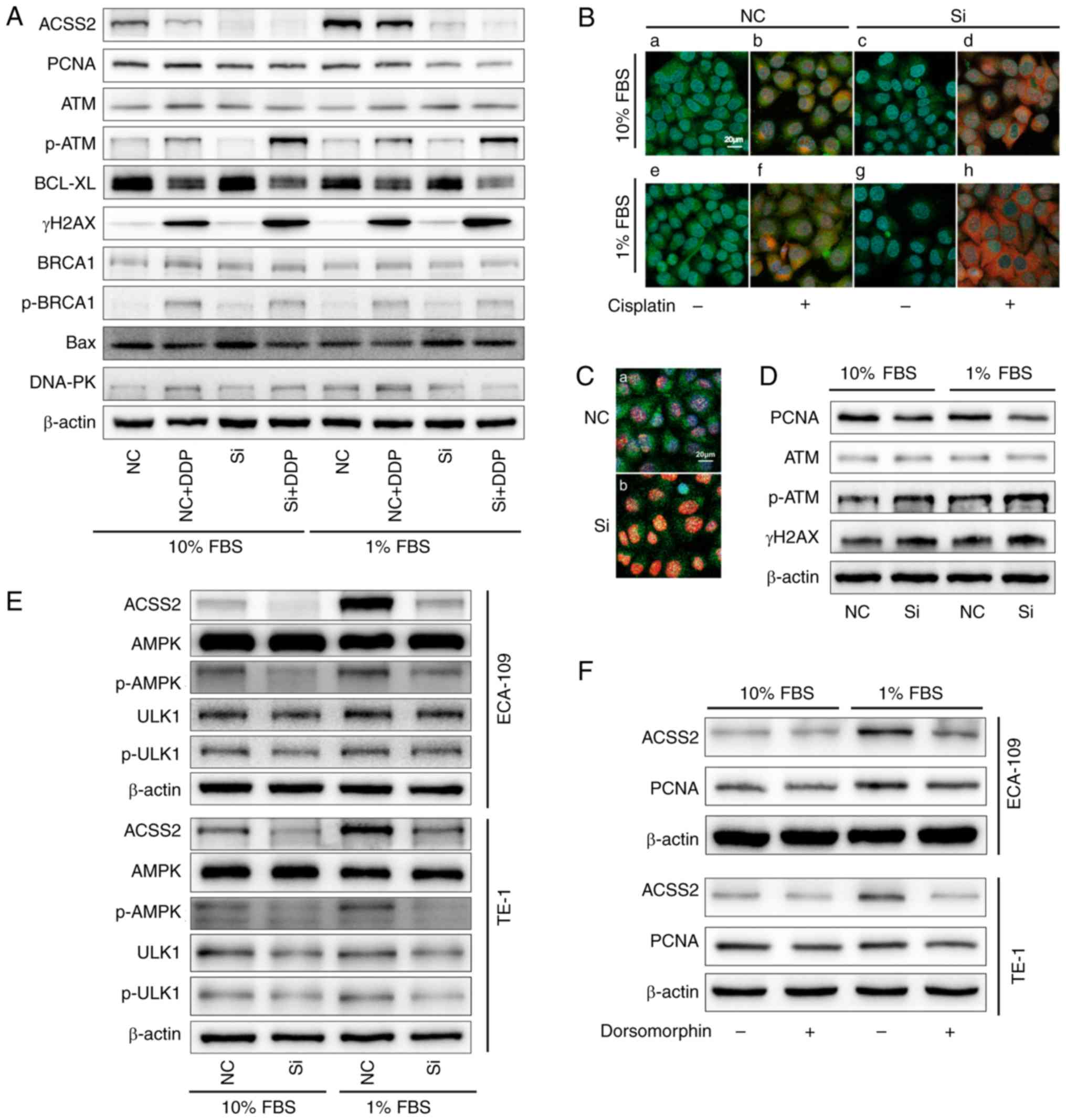
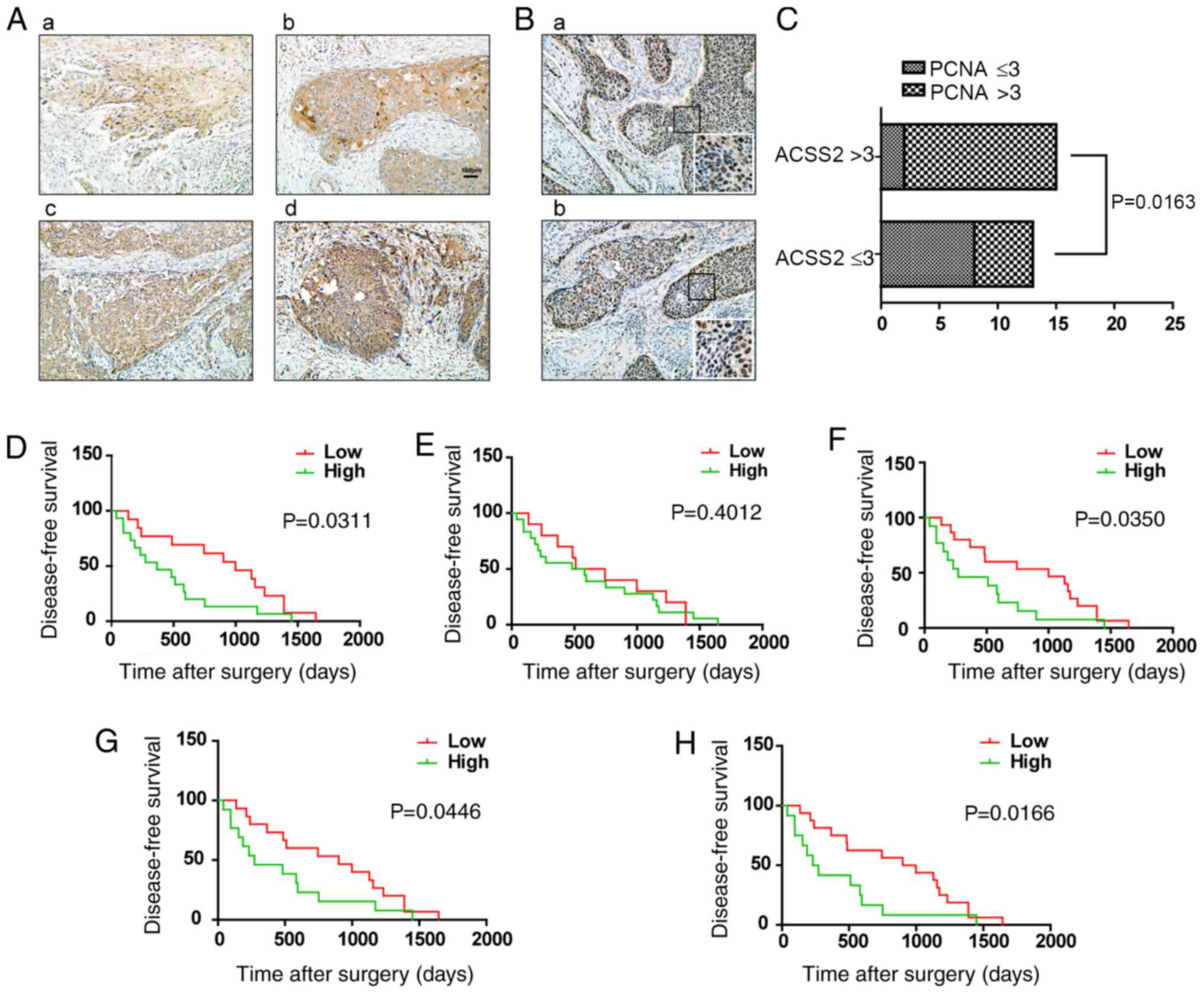
|
1
|
Choe KN and Moldovan GL: Forging ahead
through darkness: PCNA, Still the principal conductor at the
replication fork. Mol Cell. 65:380–392. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
De March M and De Biasio A: The dark side
of the ring: Role of the DNA sliding surface of PCNA. Crit Rev
Biochem Mol Biol. 52:663–673. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gu L, Lingeman R, Yakushijin F, Sun E, Cui
Q, Chao J, Hu W, Li H, Hickey RJ, Stark JM, et al: The anticancer
activity of a First-in-class Small-molecule targeting PCNA. Clin
Cancer Res. 24:6053–6065. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shiomi Y and Nishitani H: Control of
genome integrity by RFC complexes; conductors of PCNA loading onto
and unloading from chromatin during DNA Replication. Genes. 8(pii):
E522017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tan Z, Wortman M, Dillehay KL, Seibel WL,
Evelyn CR, Smith SJ, Malkas LH, Zheng Y, Lu S and Dong Z:
Small-molecule targeting of proliferating cell nuclear antigen
chromatin association inhibits tumor cell growth. Mol Pharmacol.
81:811–819. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bartová E, Suchanková J, Legartová S,
Malyšková B, Hornáček M, Skalníková M, Mašata M, Raška I and
Kozubek S: PCNA is recruited to irradiated chromatin in late
S-phase and is most pronounced in G2 phase of the cell cycle.
Protoplasma. 254:2035–2043. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Recouvreux MV and Commisso C:
Macropinocytosis: A metabolic adaptation to nutrient stress in
cancer. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 8:2612017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
White E, Mehnert JM and Chan CS:
Autophagy, metabolism, and cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 21:5037–5046.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Peck B, Ferber EC and Schulze A:
Antagonism between FOXO and MYC regulates cellular powerhouse.
Front Oncol. 3:962013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Singh D, Arora R, Kaur P, Singh B, Mannan
R and Arora S: Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor and
metabolic pathways: Possible targets of cancer. Cell Biosci.
7:622017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
El Hout M, Dos Santos L, Hamaï A and
Mehrpour M: A promising new approach to cancer therapy: Targeting
iron metabolism in cancer stem cells. Semin Cancer Biol.
53:125–138. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Conacci-Sorrell M, Ngouenet C, Anderson S,
Brabletz T and Eisenman RN: Stress-induced cleavage of Myc promotes
cancer cell survival. Genes Dev. 28:689–707. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hu G, Zhou Y, Zhu Y, Zhou L, Ling R, Wu D,
Mi L, Wang X, Dai D, Mao C and Chen D: Novel transduction of
nutrient stress to Notch pathway by RasGRP3 promotes malignant
aggressiveness in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol
Rep. 38:2975–2984. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen R, Xu M, Nagati J and Garcia JA:
Coordinate regulation of stress signaling and epigenetic events by
Acss2 and HIF-2 in cancer cells. PLoS One. 12:e01902412017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Keenan MM and Chi JT: Alternative fuels
for cancer cells. Cancer J. 21:49–55. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lakhter AJ, Hamilton J, Konger RL,
Brustovetsky N, Broxmeyer HE and Naidu SR: Glucose-independent
acetate metabolism promotes melanoma cell survival and tumor
growth. J Biol Chem. 291:21869–21879. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vysochan A, Sengupta A, Weljie AM, Alwine
JC and Yu Y: ACSS2-mediated acetyl-CoA synthesis from acetate is
necessary for human cytomegalovirus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 114:E1528–E1535. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cao TT, Lin SH, Fu L, Tang Z, Che CM,
Zhang LY, Ming XY, Liu TF, Tang XM, Tan BB, et al: Eukaryotic
translation initiation factor 5A2 promotes metabolic reprogramming
in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis. 38:94–104. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Comerford SA, Huang Z, Du X, Wang Y, Cai
L, Witkiewicz AK, Walters H, Tantawy MN, Fu A, Manning HC, et al:
Acetate dependence of tumors. Cell. 159:1591–1602. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Schug ZT, Vande Voorde J and Gottlieb E:
The metabolic fate of acetate in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
16:708–717. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang S, He J, Jia Z, Yan Z and Yang J:
Acetyl-CoA synthetase 2 enhances tumorigenesis and is indicative of
a poor prognosis for patients with renal cell carcinoma. Urol
Oncol. 36:243.e9–243.e20. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sun L, Kong Y, Cao M, Zhou H, Li H, Cui Y,
Fang F, Zhang W, Li J, Zhu X, et al: Decreased expression of
acetyl-CoA synthase 2 promotes metastasis and predicts poor
prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 108:1338–1346.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bae JM, Kim JH, Oh HJ, Park HE, Lee TH,
Cho NY and Kang GH: Downregulation of acetyl-CoA synthetase 2 is a
metabolic hallmark of tumor progression and aggressiveness in
colorectal carcinoma. Mod Pathol. 30:267–277. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee MY, Yeon A, Shahid M, Cho E, Sairam V,
Figlin R, Kim KH and Kim J: Reprogrammed lipid metabolism in
bladder cancer with cisplatin resistance. Oncotarget.
9:13231–13243. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dauer P, Nomura A, Saluja A and Banerjee
S: Microenvironment in determining chemo-resistance in pancreatic
cancer: Neighborhood matters. Pancreatology. 17:7–12. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chou CW, Wang CC, Wu CP, Lin YJ, Lee YC,
Cheng YW and Hsieh CH: Tumor cycling hypoxia induces
chemoresistance in glioblastoma multiforme by upregulating the
expression and function of ABCB1. Neuro Oncol. 14:1227–1238. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Iyama T and Wilson DM III: DNA repair
mechanisms in dividing and non-dividing cells. DNA Repair (Amst).
12:620–636. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yung MM, Ngan HY and Chan DW: Targeting
AMPK signaling in combating ovarian cancers: Opportunities and
challenges. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 48:301–317. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zeng J, Liu W, Fan YZ, He DL and Li L:
PrLZ increases prostate cancer docetaxel resistance by inhibiting
LKB1/AMPK-mediated autophagy. Theranostics. 8:109–123. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Oh TI, Lee JH, Kim S, Nam TJ, Kim YS, Kim
BM, Yim WJ and Lim JH: Fascaplysin sensitizes anti-cancer effects
of drugs targeting AKT and AMPK. Molecules. 23(pii): E422017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pan Y, Zhang F, Zhao Y, Shao D, Zheng X,
Chen Y, He K, Li J and Chen L: Berberine enhances chemosensitivity
and induces apoptosis through Dose-orchestrated AMPK signaling in
breast cancer. J Cancer. 8:1679–1689. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lam TG, Jeong YS, Kim SA and Ahn SG: New
metformin derivative HL156A prevents oral cancer progression by
inhibiting the insulin-like growth factor/AKT/mammalian target of
rapamycin pathways. Cancer Sci. 109:699–709. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pan Y, Liu L, Li S, Wang K, Ke R, Shi W,
Wang J, Yan X, Zhang Q, Wang Q, et al: Activation of AMPK inhibits
TGF-β1-induced airway smooth muscle cells proliferation and its
potential mechanisms. Sci Rep. 8:36242018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu L, Pan Y, Song Y, Su X, Ke R, Yang L,
Gao L and Li M: Activation of AMPK α2 inhibits airway smooth muscle
cells proliferation. Eur J Pharmacol. 791:235–243. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhao Y, Liu Y, Jing Z, Peng L, Jin P, Lin
Y, Zhou Y, Yang L, Ren J, Xie Q and Jin X: N-oleoylethanolamide
suppresses intimal hyperplasia after balloon injury in rats through
AMPK/PPARα pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 496:415–421. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang T, Guo P, Zhang Y, Xiong H, Yu X, Xu
S, Wang X, He D and Jin X: The antidiabetic drug metformin inhibits
the proliferation of bladder cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Int
J Mol Sci. 14:24603–24618. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Feng J, Qi B, Guo L, Chen LY, Wei XF, Liu
YZ and Zhao BS: miR-382 functions as a tumor suppressor against
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol.
23:4243–4251. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li X, Yu W, Qian X, Xia Y, Zheng Y, Lee
JH, Li W, Lyu J, Rao G, Zhang X, et al: Nucleus-translocated ACSS2
promotes gene transcription for lysosomal biogenesis and autophagy.
Mol Cell. 66:684–697.e9. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Schug ZT, Peck B, Jones DT, Zhang Q,
Grosskurth S, Alam IS, Goodwin LM, Smethurst E, Mason S, Blyth K,
et al: Acetyl-CoA synthetase 2 promotes acetate utilization and
maintains cancer cell growth under metabolic stress. Cancer Cell.
27:57–71. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang L, Cheng X, Gao Y, Bao J, Guan H, Lu
R, Yu H, Xu Q and Sun Y: Induction of ROS-independent DNA damage by
curcumin leads to G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human
papillary thyroid carcinoma BCPAP cells. Food Funct. 7:315–325.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Huang HW, Tang JY, Ou-Yang F, Wang HR,
Guan PY, Huang CY, Chen CY, Hou MF, Sheu JH and Chang HW: Sinularin
selectively kills breast cancer cells showing G2/M arrest,
apoptosis, and oxidative DNA damage. Molecules. 23(pii): E8492018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hegde M, Vartak SV, Kavitha CV, Ananda H,
Prasanna DS, Gopalakrishnan V, Choudhary B, Rangappa KS and
Raghavan SC: A benzothiazole derivative (5g) induces DNA damage and
potent G2/M arrest in cancer cells. Sci Rep. 7:25332017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Finzel A, Grybowski A, Strasen J,
Cristiano E and Loewer A: Hyperactivation of ATM upon DNA-PKcs
inhibition modulates p53 dynamics and cell fate in response to DNA
damage. Mol Biol Cell. 27:2360–2367. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tomimatsu N, Mukherjee B and Burma S:
Distinct roles of ATR and DNA-PKcs in triggering DNA damage
responses in ATM-deficient cells. EMBO Rep. 10:629–635. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shen B, He PJ and Shao CL: Norcantharidin
induced DU145 cell apoptosis through ROS-mediated mitochondrial
dysfunction and energy depletion. PLoS One. 8:e846102013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Bártová E, Malyšková B, Komůrková D,
Legartová S, Suchánková J, Krejčí J and Kozubek S: Function of
heterochromatin protein 1 during DNA repair. Protoplasma.
254:1233–1240. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Saggar JK, Yu M, Tan Q and Tannock IF: The
tumor microenvironment and strategies to improve drug distribution.
Front Oncol. 3:1542013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tan Q, Saggar JK, Yu M, Wang M and Tannock
IF: Mechanisms of drug resistance related to the microenvironment
of solid tumors and possible strategies to inhibit them. Cancer J.
21:254–262. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Rohwer N and Cramer T: Hypoxia-mediated
drug resistance: Novel insights on the functional interaction of
HIFs and cell death pathways. Drug Resist Updat. 14:191–201. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ojha R, Bhattacharyya S and Singh SK:
Autophagy in cancer stem cells: A potential link between
chemoresistance, recurrence, and metastasis. Biores Open Access.
4:97–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hua Y, Gorshkov K, Yang Y, Wang W, Zhang N
and Hughes DP: Slow down to stay alive: HER4 protects against
cellular stress and confers chemoresistance in neuroblastoma.
Cancer. 118:5140–5154. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Salaroglio IC, Panada E, Moiso E,
Buondonno I, Provero P, Rubinstein M, Kopecka J and Riganti C: PERK
induces resistance to cell death elicited by endoplasmic reticulum
stress and chemotherapy. Mol Cancer. 16:912017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Baserga R: Growth regulation of the PCNA
gene. J Cell Sci. 98:433–436. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Feng W, Guo Y, Huang J, Deng Y, Zang J and
Huen MS: TRAIP regulates replication fork recovery and progression
via PCNA. Cell Discov. 2:160162016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Fox JT, Lee KY and Myung K: Dynamic
regulation of PCNA ubiquitylation/deubiquitylation. FEBS Lett.
585:2780–2785. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Slade D: Maneuvers on PCNA rings during
DNA replication and repair. Genes (Basel). 9(pii): E4162018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Bidkhori G, Benfeitas R, Klevstig M, Zhang
C, Nielsen J, Uhlen M, Boren J and Mardinoglu A: Metabolic
network-based stratification of hepatocellular carcinoma reveals
three distinct tumor subtypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
115:E11874–E11883. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wen H, Lee S, Zhu WG, Lee OJ, Yun SJ, Kim
J and Park S: Glucose-derived acetate and ACSS2 as key players in
cisplatin resistance in bladder cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol
Cell Biol Lipids. 1864:413–421. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yao L, Guo X and Gui Y: Acetyl-CoA
synthetase 2 promotes cell migration and invasion of renal cell
carcinoma by upregulating lysosomal-associated membrane protein 1
expression. Cell Physiol Biochem. 45:984–992. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Puente C, Hendrickson RC and Jiang X:
Nutrient-regulated phosphorylation of ATG13 inhibits
starvation-induced autophagy. J Biol Chem. 291:6026–6035. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|