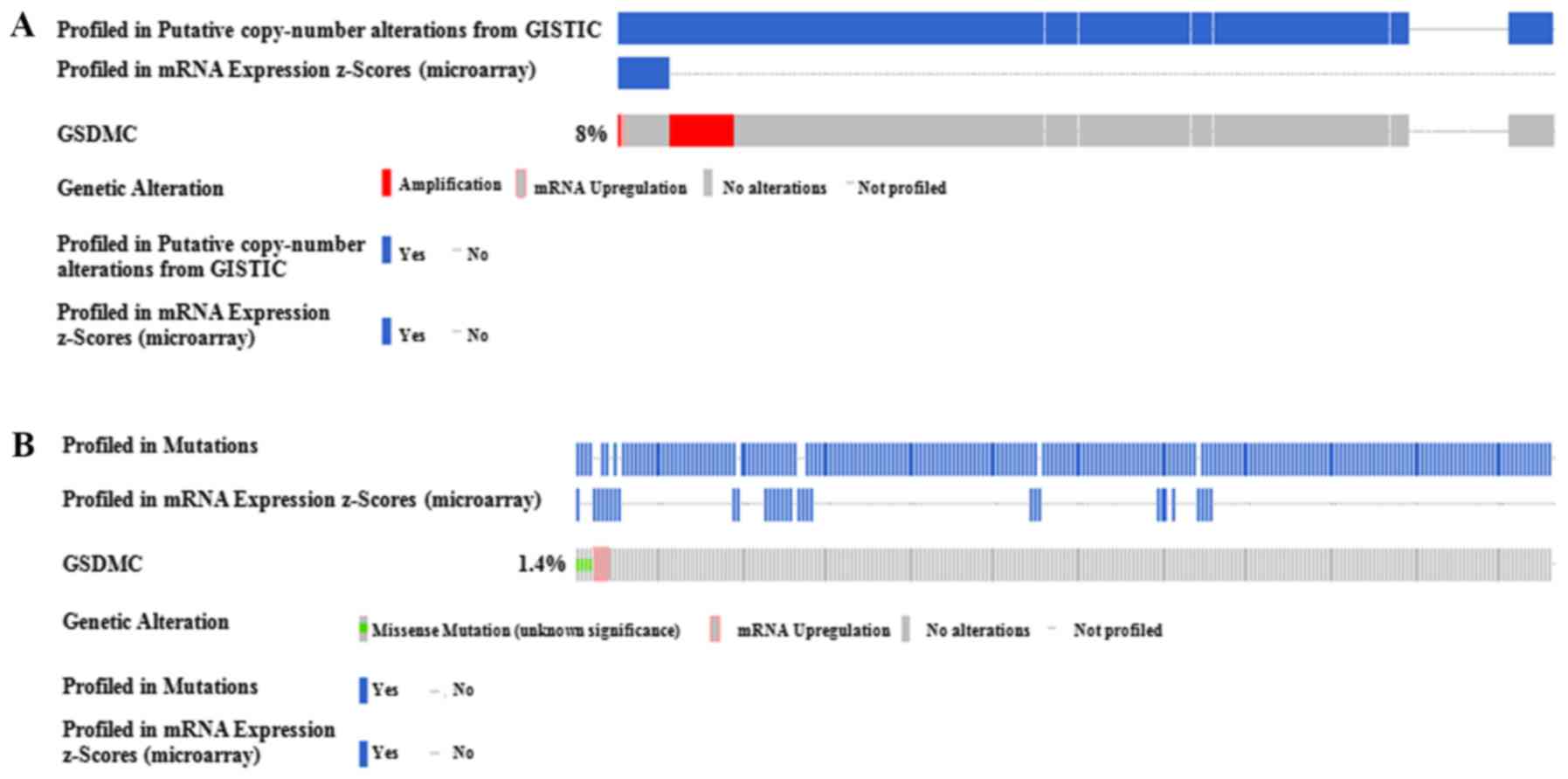
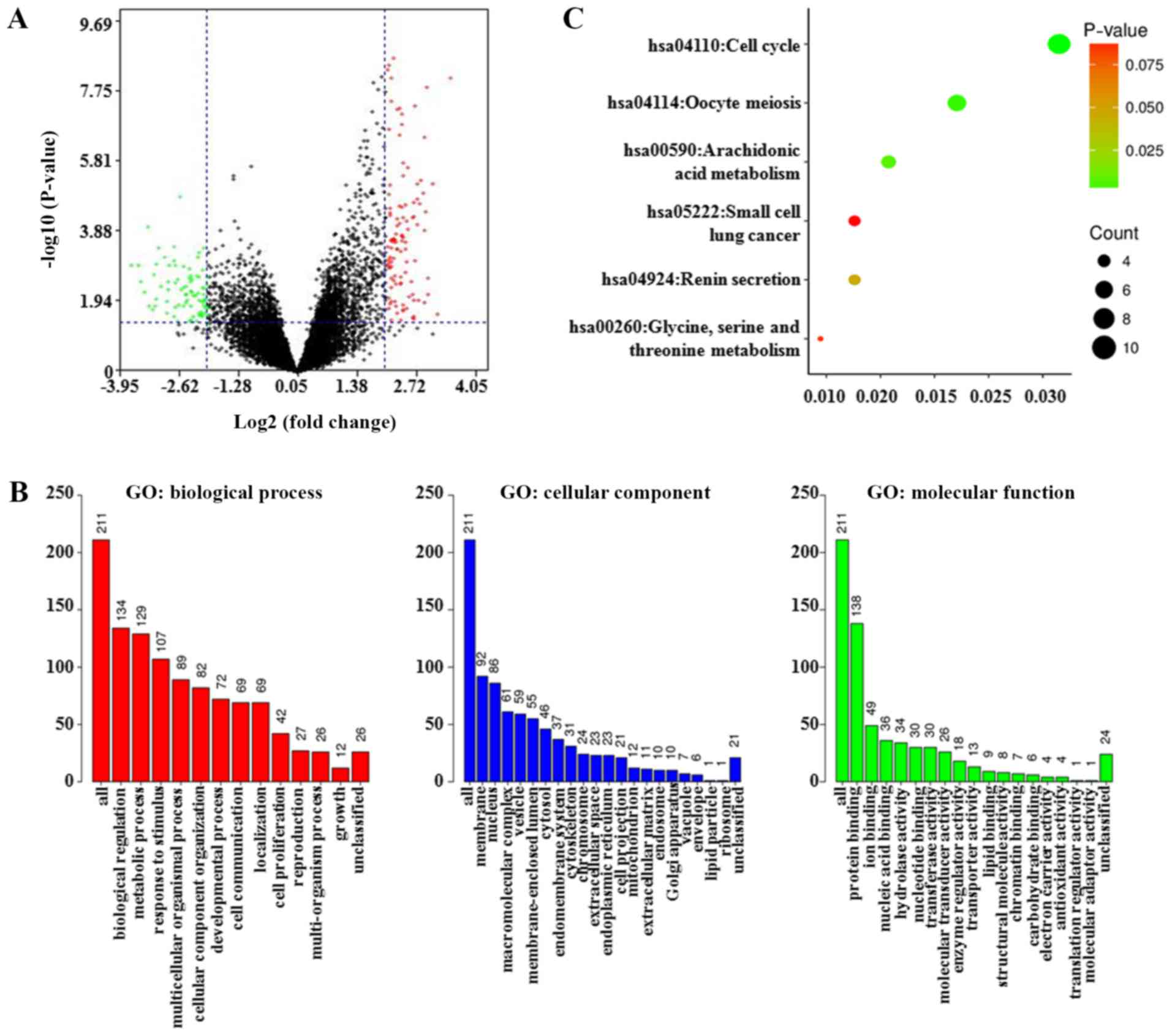
|
1
|
Miller KD, Siegel RL, Lin CC, Mariotto AB,
Kramer JL, Rowland JH, Stein KD, Alteri R and Jemal A: Cancer
treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin.
66:271–289. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yan Y, Su W, Zeng S, Qian L, Chen X, Wei
J, Chen N, Gong Z and Xu Z: Effect and mechanism of tanshinone I on
the radiosensitivity of lung cancer cells. Mol Pharm. 15:4843–4853.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jordan EJ, Kim HR, Arcila ME, Barron D,
Chakravarty D, Gao J, Chang MT, Ni A, Kundra R, Jonsson P, et al:
Prospective comprehensive molecular characterization of lung
adenocarcinomas for efficient patient matching to approved and
emerging therapies. Cancer Discov. 7:596–609. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kovacs SB and Miao EA: Gasdermins:
Effectors of pyroptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 27:673–684. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shi J, Gao W and Shao F: Pyroptosis:
Gasdermin-mediated programmed necrotic cell death. Trends Biochem
Sci. 42:245–254. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yuan YY, Xie KX, Wang SL and Yuan LW:
Inflammatory caspase-related pyroptosis: Mechanism, regulation and
therapeutic potential for inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol
Rep (Oxf). 6:167–176. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lutkowska A, Roszak A, Lianeri M, Sowinska
A, Sotiri E and Jagodzinski PP: Analysis of rs8067378 polymorphism
in the risk of uterine cervical cancer from a polish population and
its impact on gasdermin B expression. Mol Diagn Ther. 21:199–207.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Miguchi M, Hinoi T, Shimomura M, Adachi T,
Saito Y, Niitsu H, Kochi M, Sada H, Sotomaru Y, Ikenoue T, et al:
Gasdermin C is upregulated by inactivation of transforming growth
factor β receptor type II in the presence of mutated apc, promoting
colorectal cancer proliferation. PloS One. 11:e01664222016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C and
Zhang Z: GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression
profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45:W98–W102.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya
SAH, Creighton CJ, Ponce-Rodriguez I, Chakravarthi BVSK and
Varambally S: UALCAN: A portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene
expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia. 19:649–658. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rhodes DR, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Mahavisno
V, Varambally R, Yu J, Briggs BB, Barrette TR, Anstet MJ,
Kincead-Beal C, Kulkarni P, et al: Oncomine 3.0: Genes, pathways,
and networks in a collection of 18,000 cancer gene expression
profiles. Neoplasia. 9:166–180. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Barretina J, Caponigro G, Stransky N,
Venkatesan K, Margolin AA, Kim S, Wilson CJ, Lehár J, Kryukov GV,
Sonkin D, et al: The cancer cell line encyclopedia enables
predictive modelling of anticancer drug sensitivity. Nature.
483:603–607. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Uhlen M, Zhang C, Lee S, Sjöstedt E,
Fagerberg L, Bidkhori G, Benfeitas R, Arif M, Liu Z, Edfors F, et
al: A pathology atlas of the human cancer transcriptome. Science.
357:eaan25072017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G,
Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y, Jacobsen A, Sinha R, Larsson E, et al:
Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical
profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal. 6:pl12013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gyorffy B, Surowiak P, Budczies J and
Lanczky A: Online survival analysis software to assess the
prognostic value of biomarkers using transcriptomic data in
non-small-cell lung cancer. PloS One. 8:e822412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang WY, Hsu SD, Huang HY, Sun YM, Chou
CH, Weng SL and Huang HD: MethHC: A database of DNA methylation and
gene expression in human cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 43:D856–D861.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Koch A, De Meyer T, Jeschke J and Van
Criekinge W: MEXPRESS: Visualizing expression, DNA methylation and
clinical TCGA data. BMC Genomics. 16:6362015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Kir J, Liu D,
Bryant D, Guo Y, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC and Lempicki RA:
DAVID Bioinformatics Resources: Expanded annotation database and
novel algorithms to better extract biology from large gene lists.
Nucleic Acids Res. 35:W169–W175. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang J, Duncan D, Shi Z and Zhang B:
WEB-based GEne SeT analysis toolkit (WebGestalt): Update 2013.
Nucleic Acids Res. 41:W77–W83. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu Z, Yan Y, Xiao L, Dai S, Zeng S, Qian
L, Wang L, Yang X, Xiao Y and Gong Z: Radiosensitizing effect of
diosmetin on radioresistant lung cancer cells via Akt signaling
pathway. PloS One. 12:e01759772017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
You S, Li R, Park D, Xie M, Sica GL, Cao
Y, Xiao ZQ and Deng X: Disruption of STAT3 by niclosamide reverses
radioresistance of human lung cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 13:606–616.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dai S, Yan Y, Xu Z, Zeng S, Qian L, Huo L,
Li X, Sun L and Gong Z: SCD1 confers temozolomide resistance to
human glioma cells via the Akt/GSK3β/β-catenin signaling axis.
Front Pharmacol. 8:9602017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ouyang Z, Peng D and Dhakal DP: Risk
factors for hematological toxicity of chemotherapy for bone and
soft tissue sarcoma. Oncol Lett. 5:1736–1740. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tandon P, Reddy KR, O'Leary JG,
Garcia-Tsao G, Abraldes JG, Wong F, Biggins SW, Maliakkal B, Fallon
MB, Subramanian RM, et al: A Karnofsky performance status-based
score predicts death after hospital discharge in patients with
cirrhosis. Hepatology. 65:217–224. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Watabe K, Ito A, Asada H, Endo Y,
Kobayashi T, Nakamoto K, Itami S, Takao S, Shinomura Y, Aikou T, et
al: Structure, expression and chromosome mapping of MLZE, a novel
gene which is preferentially expressed in metastatic melanoma
cells. Jap J Cancer Res. 92:140–151. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Saeki N, Usui T, Aoyagi K, Kim DH, Sato M,
Mabuchi T, Yanagihara K, Ogawa K, Sakamoto H, Yoshida T and Sasaki
H: Distinctive expression and function of four GSDM family genes
(GSDMA-D) in normal and malignant upper gastrointestinal
epithelium. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 48:261–271. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Borczuk AC: Prognostic considerations of
the new world health organization classification of lung
adenocarcinoma. Eur Respir Rev. 25:364–371. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang X, Xu Z, Ren X, Chen X, Wei J, Lin W,
Li Z, Ou C, Gong Z and Yan Y: Function of low ADARB1 expression in
lung adenocarcinoma. PLoS One. 14:e02222982019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang X, Xu Z, Chen X, Ren X, Wei J, Zhou
S, Yang X, Zeng S, Qian L, Wu G, et al: A tropomyosin receptor
kinase family protein, NTRK2 is a potential predictive biomarker
for lung adenocarcinoma. PeerJ. 7:e71252019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang X, Xu ZJ, Chen X, Zeng SS, Qian L,
Wei J, Peng M, Wang X, Liu WL, Ma HY, et al: Clinical value of
preoperative methylated septin 9 in Chinese colorectal cancer
patients. World J Gastroenterol. 25:2099–2109. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen X, Xu Z, Zeng S, Wang X, Liu W, Qian
L, Wei J, Yang X, Shen Q, Gong Z and Yan Y: SIRT5 downregulation is
associated with poor prognosis in glioblastoma. Cancer Biomark.
24:449–459. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhou S, Yan Y, Chen X, Wang X, Zeng S,
Qian L, Wei J, Yang X, Zhou Y, Gong Z and Xu Z: Roles of highly
expressed PAICS in lung adenocarcinoma. Gene. 692:1–8. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Upchurch GM, Haney SL and Opavsky R:
Aberrant promoter hypomethylation in CLL: Does it matter for
disease development? Front Oncol. 6:1822016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang W, Barger CJ, Link PA,
Mhawech-Fauceglia P, Miller A, Akers SN, Odunsi K and Karpf AR: DNA
hypomethylation-mediated activation of Cancer/Testis Antigen 45
(CT45) genes is associated with disease progression and reduced
survival in epithelial ovarian cancer. Epigenetics. 10:736–748.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Milanovic M, Yu Y and Schmitt CA: The
senescence-stemness alliance-a cancer-hijacked regeneration
principle. Trends Cell Biol. 28:1049–1061. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Vymětalová L and Kryštof V: Potential
clinical uses of CDK inhibitors: Lessons from synthetic lethality
screens. Med Res Rev. 35:1156–1174. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wu M, Wang Y, Yang D, Gong Y, Rao F, Liu
R, Danna Y, Li J, Fan J, Chen J, et al: A PLK1 kinase inhibitor
enhances the chemosensitivity of cisplatin by inducing pyroptosis
in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. EBioMedicine. 41:244–255.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|