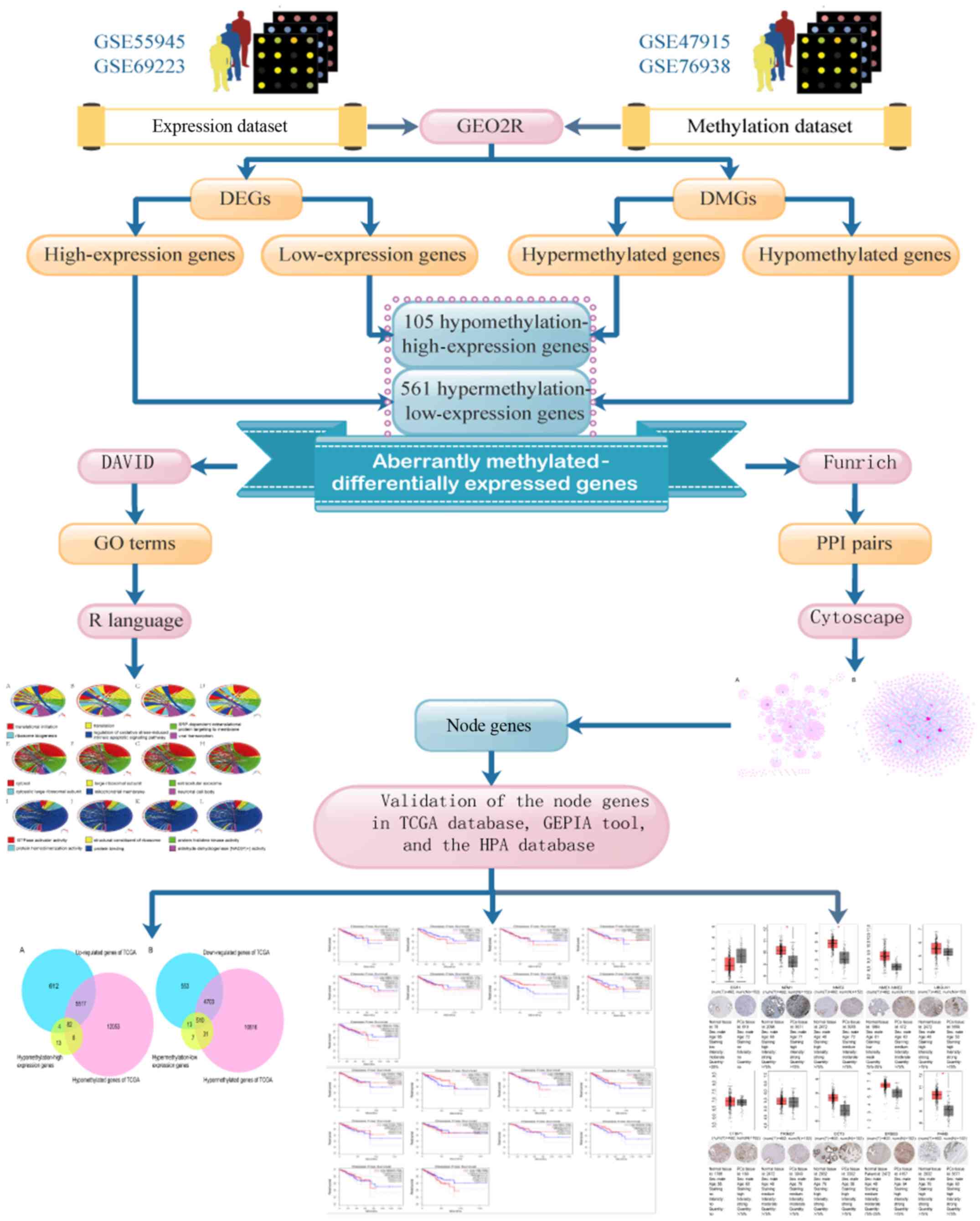
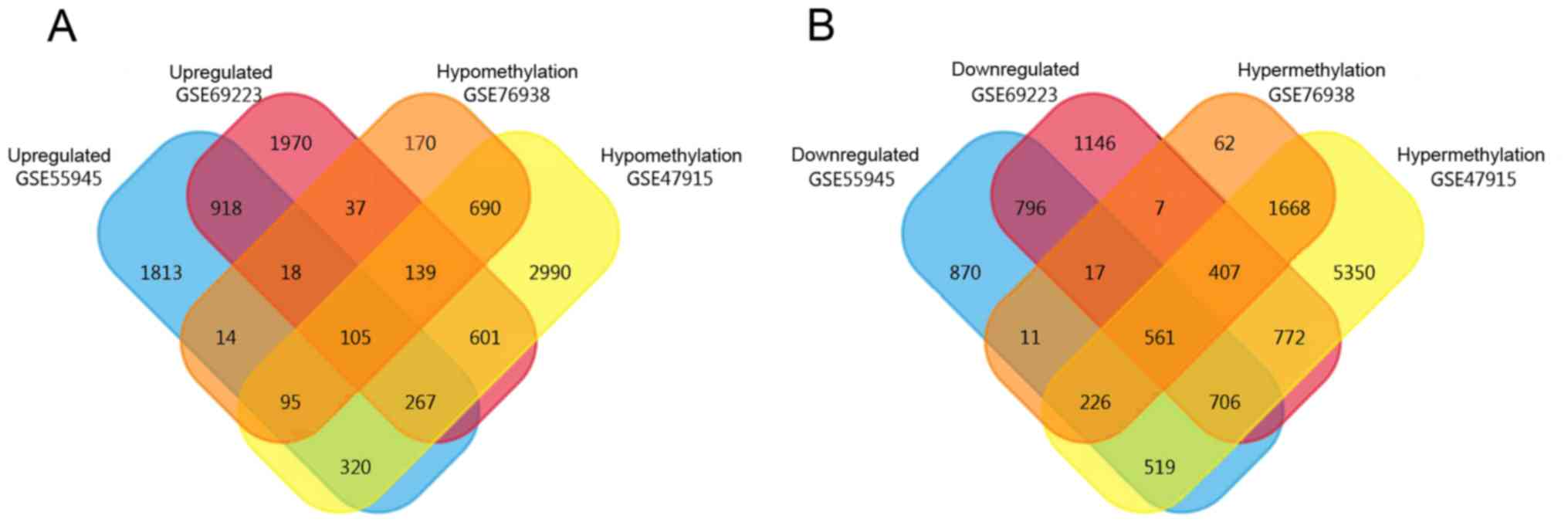
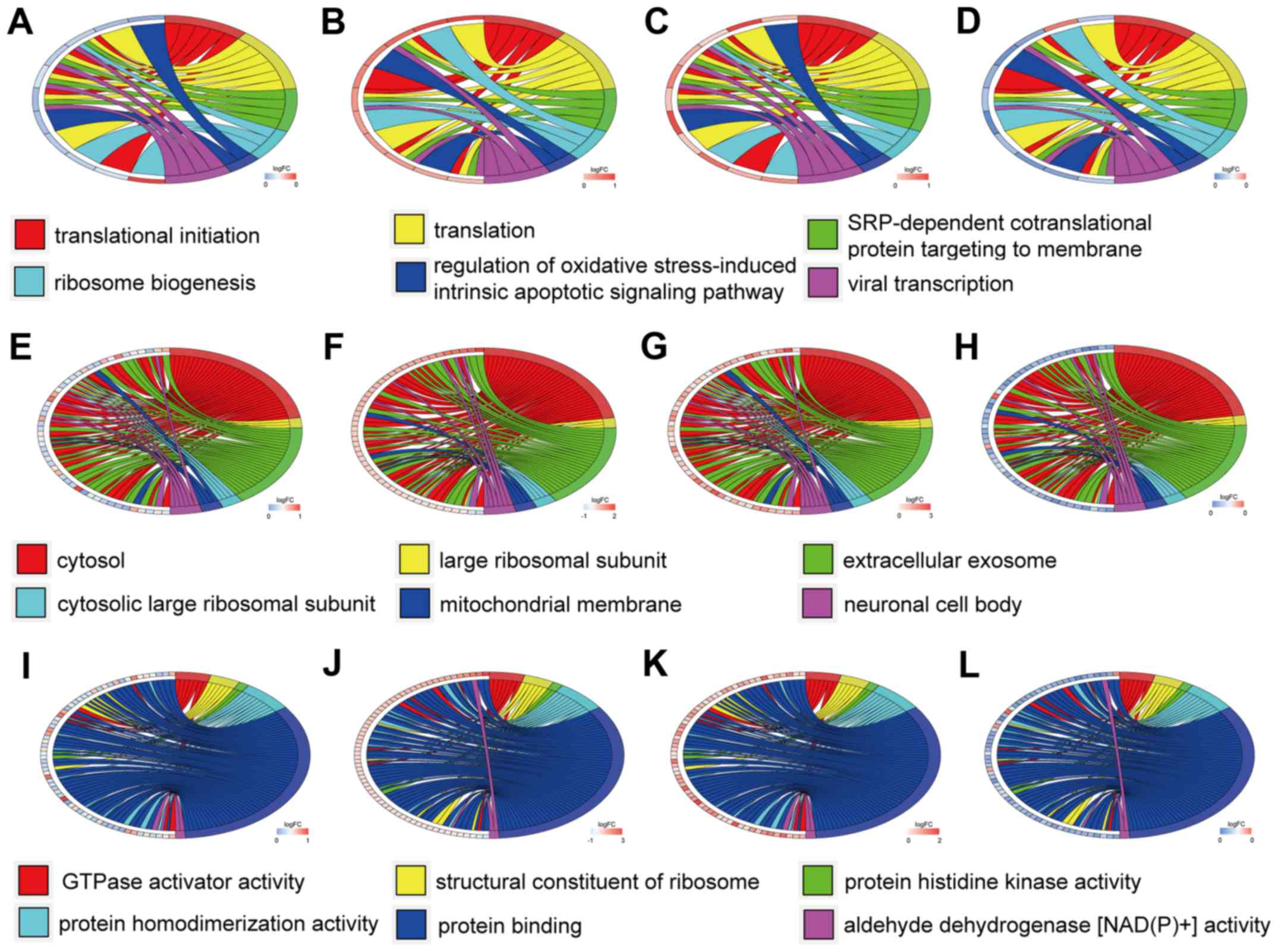
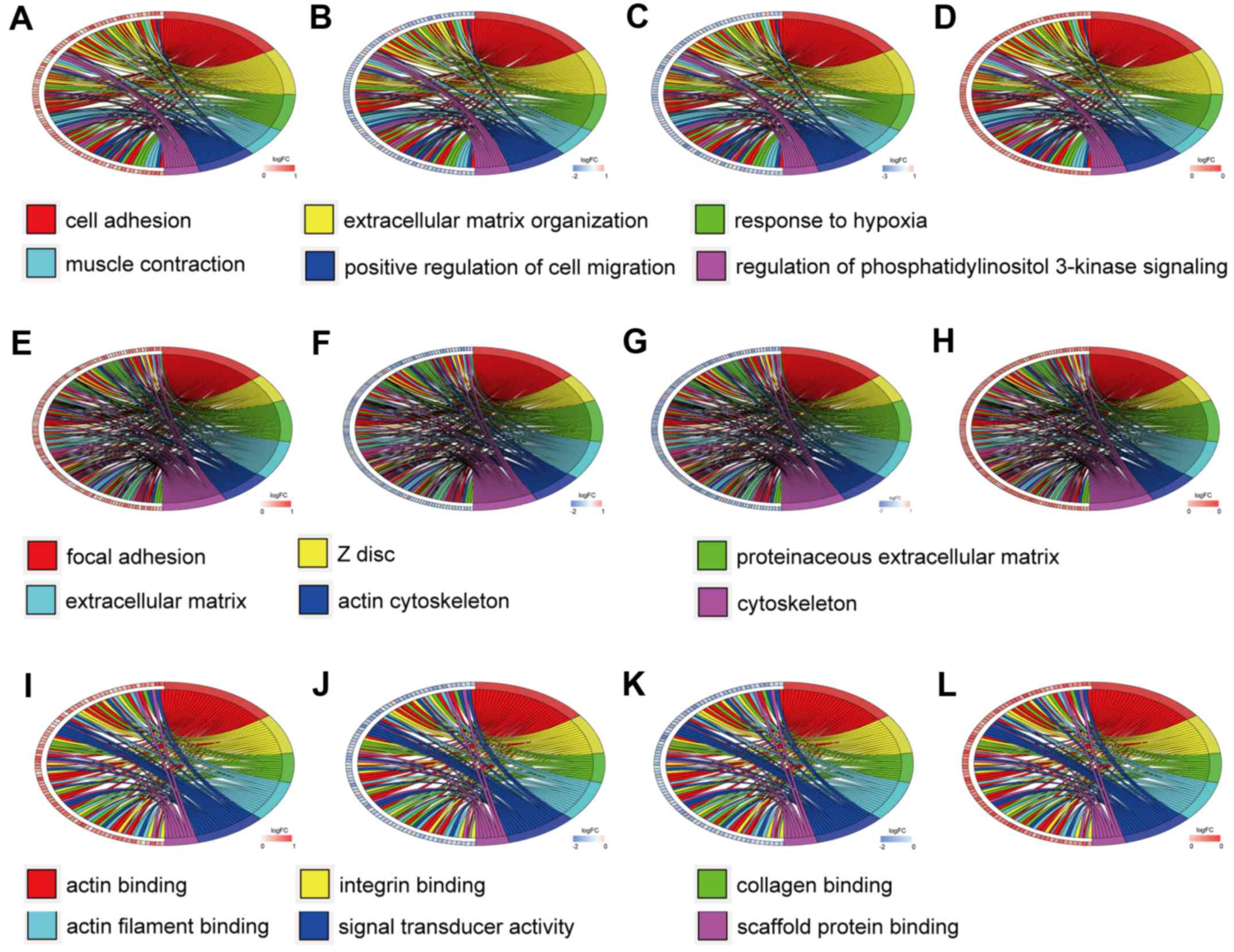
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Feinberg AP, Ohlsson R and Henikoff S: The
epigenetic progenitor origin of human cancer. Nat Rev Genet.
7:21–33. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nephew KP and Huang TH: Epigenetic gene
silencing in cancer initiation and progression. Cancer Lett.
190:125–133. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nakao M: Epigenetics: Interaction of DNA
methylation and chromatin. Gene. 278:25–31. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Strahl BD and Allis CD: The language of
covalent histone modifications. Nature. 403:41–45. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
De Carvalho DD, Sharma S, You JS, Su SF,
Taberlay PC, Kelly TK, Yang X, Liang G and Jones PA: DNA
methylation screening identifies driver epigenetic events of cancer
cell survival. Cancer Cell. 21:655–667. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jones PA and Baylin SB: The fundamental
role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 3:415–428.
2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mundbjerg K, Chopra S, Alemozaffar M,
Duymich C, Lakshminarasimhan R, Nichols PW, Aron M, Siegmund KD,
Ukimura O, Aron M, et al: Identifying aggressive prostate cancer
foci using a DNA methylation classifier. Genome Biol. 18:32017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xia D, Wang D, Kim SH, Katoh H and DuBois
RN: Prostaglandin E2 promotes intestinal tumor growth via DNA
methylation. Nat Med. 18:224–226. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Iizuka N, Oka M, Yamada-Okabe H, Nishida
M, Maeda Y, Mori N, Takao T, Tamesa T, Tangoku A, Tabuchi H, et al:
Oligonucleotide microarray for prediction of early intrahepatic
recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection.
Lancet. 361:923–929. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kulasingam V and Diamandis EP: Strategies
for discovering novel cancer biomarkers through utilization of
emerging technologies. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 5:588–599. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Verma M, Khoury MJ and Ioannidis JP:
Opportunities and challenges for selected emerging technologies in
cancer epidemiology: Mitochondrial, epigenomic, metabolomic, and
telomerase profiling. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 22:189–200.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lu W and Ding Z: Identification of key
genes in prostate cancer gene expression profile by bioinformatics.
Andrologia. 51:e131692019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ye Y, Li SL and Wang SY: Construction and
analysis of mRNA, miRNA, lncRNA, and TF regulatory networks reveal
the key genes associated with prostate cancer. PLoS One.
13:e01980552018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
He Z, Tang F, Lu Z, Huang Y, Lei H, Li Z
and Zeng G: Analysis of differentially expressed genes, clinical
value and biological pathways in prostate cancer. Am J Transl Res.
10:1444–1456. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P,
Evangelista C, Kim IF, Tomashevsky M, Marshall KA, Phillippy KH,
Sherman PM, Holko M, et al: NCBI GEO: Archive for functional
genomics data sets-update. Nucleic Acids Res. 41 (Database
Issue):D991–D995. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pathan M, Keerthikumar S, Ang CS, Gangoda
L, Quek CY, Williamson NA, Mouradov D, Sieber OM, Simpson RJ, Salim
A, et al: FunRich: An open access standalone functional enrichment
and interaction network analysis tool. Proteomics. 15:2597–2601.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lin P, He RQ, Dang YW, Wen DY, Ma J, He Y,
Chen G and Yang H: An autophagy-related gene expression signature
for survival prediction in multiple cohorts of hepatocellular
carcinoma patients. Oncotarget. 9:17368–17395. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Morris JH, Wu A, Yamashita RA,
Marchler-Bauer A and Ferrin TE: cddApp: A Cytoscape app for
accessing the NCBI conserved domain database. Bioinformatics.
31:134–136. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Galligan JJ and Petersen DR: The human
protein disulfide isomerase gene family. Hum Genomics. 6:62012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pajunen L, Jones TA, Goddard A, Sheer D,
Solomon E, Pihlajaniemi T and Kivirikko KI: Regional assignment of
the human gene coding for a multifunctional polypeptide (P4HB)
acting as the beta-subunit of prolyl 4-hydroxylase and the enzyme
protein disulfide isomerase to 17q25. Cytogenet Cell Genet.
56:165–168. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Goplen D, Wang J, Enger PØ, Tysnes BB,
Terzis AJ, Laerum OD and Bjerkvig R: Protein disulfide isomerase
expression is related to the invasive properties of malignant
glioma. Cancer Res. 66:9895–9902. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xia W, Zhuang J, Wang G, Ni J, Wang J and
Ye Y: P4HB promotes HCC tumorigenesis through downregulation of
GRP78 and subsequent upregulation of epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. Oncotarget. 8:8512–8521. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li Y and Tollefsbol TO: Impact on DNA
methylation in cancer prevention and therapy by bioactive dietary
components. Curr Med Chem. 17:2141–2151. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ehrlich M: DNA methylation in cancer: Too
much, but also too little. Oncogene. 21:5400–5413. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Davis CD and Uthus EO: DNA methylation,
cancer susceptibility, and nutrient interactions. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 229:988–995. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Toyota M, Itoh F and Imai K: DNA
methylation and gastrointestinal malignancies: Functional
consequences and clinical implications. J Gastroenterol.
35:727–734. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bjurlin MA and Taneja SS: Prostate cancer.
Urol Clin North Am. 44:xv–xvi. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ruggero D: Translational control in cancer
etiology. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 5(pii):
a0123362013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chu J, Cargnello M, Topisirovic I and
Pelletier J: Translation initiation factors: Reprogramming protein
synthesis in cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 26:918–933. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ray S, Johnston R, Campbell DC, Nugent S,
McDade SS, Waugh D and Panov KI: Androgens and estrogens stimulate
ribosome biogenesis in prostate and breast cancer cells in receptor
dependent manner. Gene. 526:46–53. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Derenzini M, Montanaro L and Trerè D:
Ribosome biogenesis and cancer. Acta Histochem. 119:190–197. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yajnik V, Paulding C, Sordella R,
McClatchey AI, Saito M, Wahrer DC, Reynolds P, Bell DW, Lake R, van
den Heuvel S, et al: DOCK4, a GTPase activator, is disrupted during
tumorigenesis. Cell. 112:673–684. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Toy W, Weir H, Razavi P, Lawson M,
Goeppert AU, Mazzola AM, Smith A, Wilson J, Morrow C, Wong WL, et
al: Activating ESR1 mutations differentially affect the efficacy of
ER antagonists. Cancer Discov. 7:277–287. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Box JK, Paquet N, Adams MN, Boucher D,
Bolderson E, O'Byrne KJ and Richard DJ: Nucleophosmin: From
structure and function to disease development. BMC Mol Biol.
17:192016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Destouches D, Sader M, Terry S, Marchand
C, Maillé P, Soyeux P, Carpentier G, Semprez F, Céraline J, Allory
Y, et al: Implication of NPM1 phosphorylation and preclinical
evaluation of the nucleoprotein antagonist N6L in prostate cancer.
Oncotarget. 7:69397–69411. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fan X, Wen L, Li Y, Lou L, Liu W and Zhang
J: The expression profile and prognostic value of APE/Ref-1 and
NPM1 in high-grade serous ovarian adenocarcinoma. APMIS.
125:857–862. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Thakur RK, Yadav VK, Kumar A, Singh A, Pal
K, Hoeppner L, Saha D, Purohit G, Basundra R, Kar A, et al:
Non-metastatic 2 (NME2)-mediated suppression of lung cancer
metastasis involves transcriptional regulation of key cell adhesion
factor vinculin. Nucleic Acids Res. 42:11589–11600. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gu Y, Xu W, Nie D, Zhang D, Dai J, Zhao X,
Zhang M, Wang Z, Chen Z and Qiao Z: Nicotine induces Nme2-mediated
apoptosis in mouse testes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 472:573–579.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bao J, Jiang X, Zhu X, Dai G, Dou R, Liu
X, Sheng H, Liang Z and Yu H: Clinical significance of ubiquilin 1
in gastric cancer. Medicine. 97:e97012018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shah PP, Lockwood WW, Saurabh K, Kurlawala
Z, Shannon SP, Waigel S, Zacharias W and Beverly LJ: Ubiquilin1
represses migration and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of
human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncogene. 34:1709–1717.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Porretti J, Dalton GN, Massillo C, Scalise
GD, Farré PL, Elble R, Gerez EN, Accialini P, Cabanillas AM,
Gardner K, et al: CLCA2 epigenetic regulation by CTBP1, HDACs,
ZEB1, EP300 and miR-196b-5p impacts prostate cancer cell adhesion
and EMT in metabolic syndrome disease. Int J Cancer. 143:897–906.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Phelps RA, Chidester S, Dehghanizadeh S,
Phelps J, Sandoval IT, Rai K, Broadbent T, Sarkar S, Burt RW and
Jones DA: A two-step model for colon adenoma initiation and
progression caused by APC loss. Cell. 137:623–634. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Blevins MA, Huang M and Zhao R: The role
of CtBP1 in oncogenic processes and its potential as a therapeutic
target. Mol Cancer Ther. 16:981–990. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ma Y, Wei Z, Bast RC Jr, Wang Z, Li Y, Gao
M, Liu Y and Wang X, Guo C, Zhang L and Wang X: Downregulation of
TRIM27 expression inhibits the proliferation of ovarian cancer
cells in vitro and in vivo. Lab Invest. 96:37–48. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Shaikhibrahim Z, Lindstrot A, Ochsenfahrt
J, Fuchs K and Wernert N: Epigenetics-related genes in prostate
cancer: Expression profile in prostate cancer tissues,
androgen-sensitive and -insensitive cell lines. Int J Mol Med.
31:21–25. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Wei Y, Wu J, Zhang P,
Shen S, Saiyin H, Wumaier R, Yang X, Wang C and Yu L: Molecular
chaperone CCT3 supports proper mitotic progression and cell
proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett.
372:101–109. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Xiong Y, Wu S, Du Q, Wang A and Wang Z:
Integrated analysis of gene expression and genomic aberration data
in osteosarcoma (OS). Cancer Gene Ther. 22:524–529. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Cui X, Hu ZP, Li Z, Gao PJ and Zhu JY:
Overexpression of chaperonin containing TCP1, subunit 3 predicts
poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol.
21:8588–8604. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Jaiswal BS, Kljavin NM, Stawiski EW, Chan
E, Parikh C, Durinck S, Chaudhuri S, Pujara K, Guillory J, Edgar
KA, et al: Oncogenic ERBB3 mutations in human cancers. Cancer Cell.
23:603–617. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Koumakpayi IH, Le Page C, Delvoye N, Saad
F and Mes-Masson AM: Macropinocytosis inhibitors and Arf6 regulate
ErbB3 nuclear localization in prostate cancer cells. Mol Carcinog.
50:901–912. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhou Y, Yang J, Zhang Q, Xu Q, Lu L, Wang
J and Xia W: P4HB knockdown induces human HT29 colon cancer cell
apoptosis through the generation of reactive oxygen species and
inactivation of STAT3 signaling. Mol Med Rep. 19:231–237.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Le Bras GF, Taubenslag KJ and Andl CD: The
regulation of cell-cell adhesion during epithelial-mesenchymal
transition, motility and tumor progression. Cell Adh Migr.
6:365–373. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Gilkes DM, Semenza GL and Wirtz D: Hypoxia
and the extracellular matrix: Drivers of tumour metastasis. Nat Rev
Cancer. 14:430–439. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Jacquemet G, Hamidi H and Ivaska J:
Filopodia in cell adhesion, 3D migration and cancer cell invasion.
Curr Opin Cell Biol. 36:23–31. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Liu X, Xu Y, Zhou Q, Chen M, Zhang Y,
Liang H, Zhao J, Zhong W and Wang M: PI3K in cancer: Its structure,
activation modes and role in shaping tumor microenvironment. Future
Oncol. 14:665–674. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Haffner MC, Esopi DM, Chaux A, Gürel M,
Ghosh S, Vaghasia AM, Tsai H, Kim K, Castagna N, Lam H, et al: AIM1
is an actin-binding protein that suppresses cell migration and
micrometastatic dissemination. Nat Commun. 8:1422017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Vanaja DK, Grossmann ME, Cheville JC, Gazi
MH, Gong A, Zhang JS, Ajtai K, Burghardt TP and Young CY: PDLIM4,
an actin binding protein, suppresses prostate cancer cell growth.
Cancer Invest. 27:264–272. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Ramovs V, Te Molder L and Sonnenberg A:
The opposing roles of laminin-binding integrins in cancer. Matrix
Biol. 57-58:213–243. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Desgrosellier JS and Cheresh DA: Integrins
in cancer: Biological implications and therapeutic opportunities.
Nat Rev Cancer. 10:9–22. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Jia D, Augert A, Kim DW, Eastwood E, Wu N,
Ibrahim AH, Kim KB, Dunn CT, Pillai SPS, Gazdar AF, et al: Crebbp
loss drives small cell lung cancer and increases sensitivity to
HDAC inhibition. Cancer Discov. 8:1422–1437. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Shaikhibrahim Z, Lindstrot A, Buettner R
and Wernert N: Analysis of laser-microdissected prostate cancer
tissues reveals potential tumor markers. Int J Mol Med. 28:605–611.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Hu J, Tian J, Zhu S, Sun L, Yu J, Tian H,
Dong Q, Luo Q, Jiang N, Niu Y and Shang Z: Sox5 contributes to
prostate cancer metastasis and is a master regulator of
TGF-β-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition through controlling
Twist1 expression. Br J Cancer. 118:88–97. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Kohonen-Corish MR, Sigglekow ND, Susanto
J, Chapuis PH, Bokey EL, Dent OF, Chan C, Lin BP, Seng TJ, Laird
PW, et al: Promoter methylation of the mutated in colorectal cancer
gene is a frequent early event in colorectal cancer. Oncogene.
26:4435–4441. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Lang SH, Hyde C, Reid IN, Hitchcock IS,
Hart CA, Bryden AA, Villette JM, Stower MJ and Maitland NJ:
Enhanced expression of vimentin in motile prostate cell lines and
in poorly differentiated and metastatic prostate carcinoma.
Prostate. 52:253–263. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Jung S, Yi L, Kim J, Jeong D, Oh T, Kim
CH, Kim CJ, Shin J, An S and Lee MS: The role of vimentin as a
methylation biomarker for early diagnosis of cervical cancer. Mol
Cells. 31:405–411. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Kang AR, An HT, Ko J and Kang S: Ataxin-1
regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cervical cancer
cells. Oncotarget. 8:18248–18259. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Li L, Yang G, Ebara S, Satoh T, Nasu Y,
Timme TL, Ren C, Wang J, Tahir SA and Thompson TC: Caveolin-1
mediates testosterone-stimulated survival/clonal growth and
promotes metastatic activities in prostate cancer cells. Cancer
Res. 61:4386–4392. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Tahir SA, Yang G, Goltsov AA, Watanabe M,
Tabata K, Addai J, Fattah el MA, Kadmon D and Thompson TC: Tumor
cell-secreted caveolin-1 has proangiogenic activities in prostate
cancer. Cancer Res. 68:731–739. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Cui J, Rohr LR, Swanson G, Speights VO,
Maxwell T and Brothman AR: Hypermethylation of the caveolin-1 gene
promoter in prostate cancer. Prostate. 46:249–256. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Sun GG, Lu YF, Zhang J and Hu WN: Filamin
A regulates MMP-9 expression and suppresses prostate cancer cell
migration and invasion. Tumour Biol. 35:3819–3826. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Jung JU, Ravi S, Lee DW, McFadden K,
Kamradt ML, Toussaint LG and Sitcheran R: NIK/MAP3K14 regulates
mitochondrial dynamics and trafficking to promote cell invasion.
Curr Biol. 26:3288–3302. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Hagiwara K, Ito H, Murate T, Miyata Y,
Ohashi H and Nagai H: PROX1 overexpression inhibits protein kinase
C beta II transcription through promoter DNA methylation. Genes
Chromosomes Cancer. 51:1024–1036. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Surdez D, Benetkiewicz M, Perrin V, Han
ZY, Pierron G, Ballet S, Lamoureux F, Rédini F, Decouvelaere AV,
Daudigeos-Dubus E, et al: Targeting the EWSR1-FLI1 oncogene-induced
protein kinase PKC-β abolishes ewing sarcoma growth. Cancer Res.
72:4494–4503. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Kahl P, Gullotti L, Heukamp LC, Wolf S,
Friedrichs N, Vorreuther R, Solleder G, Bastian PJ, Ellinger J,
Metzger E, et al: Androgen receptor coactivators lysine-specific
histone demethylase 1 and four and a half LIM domain protein 2
predict risk of prostate cancer recurrence. Cancer Res.
66:11341–11347. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Rui YN, Xu Z, Chen Z and Zhang S: The
GST-BHMT assay reveals a distinct mechanism underlying proteasome
inhibition-induced macroautophagy in mammalian cells. Autophagy.
11:812–832. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Ouyang L, Shi Z, Zhao S, Wang FT, Zhou TT,
Liu B and Bao JK: Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: A
review of apoptosis, autophagy and programmed necrosis. Cell
Prolif. 45:487–498. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|