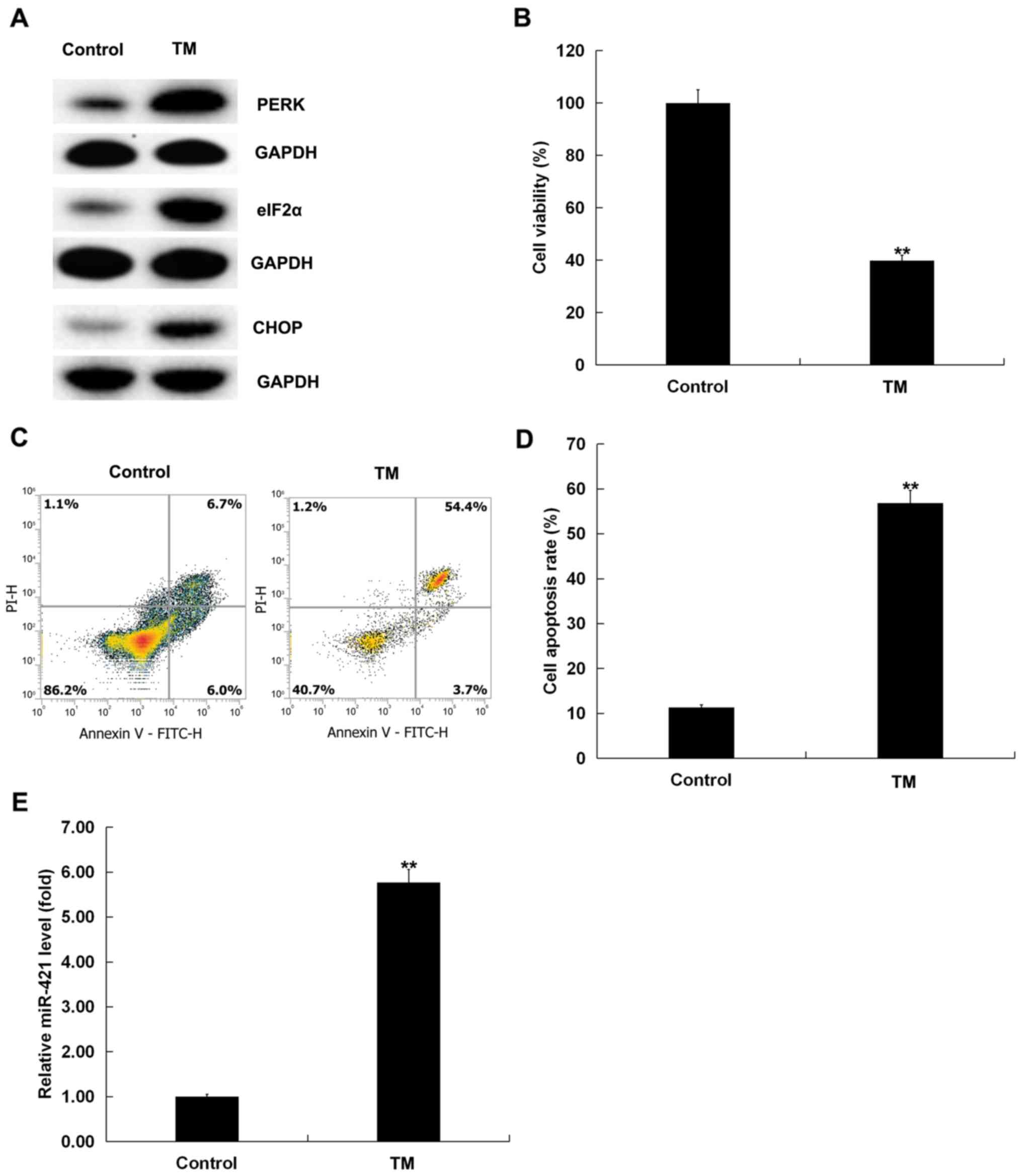
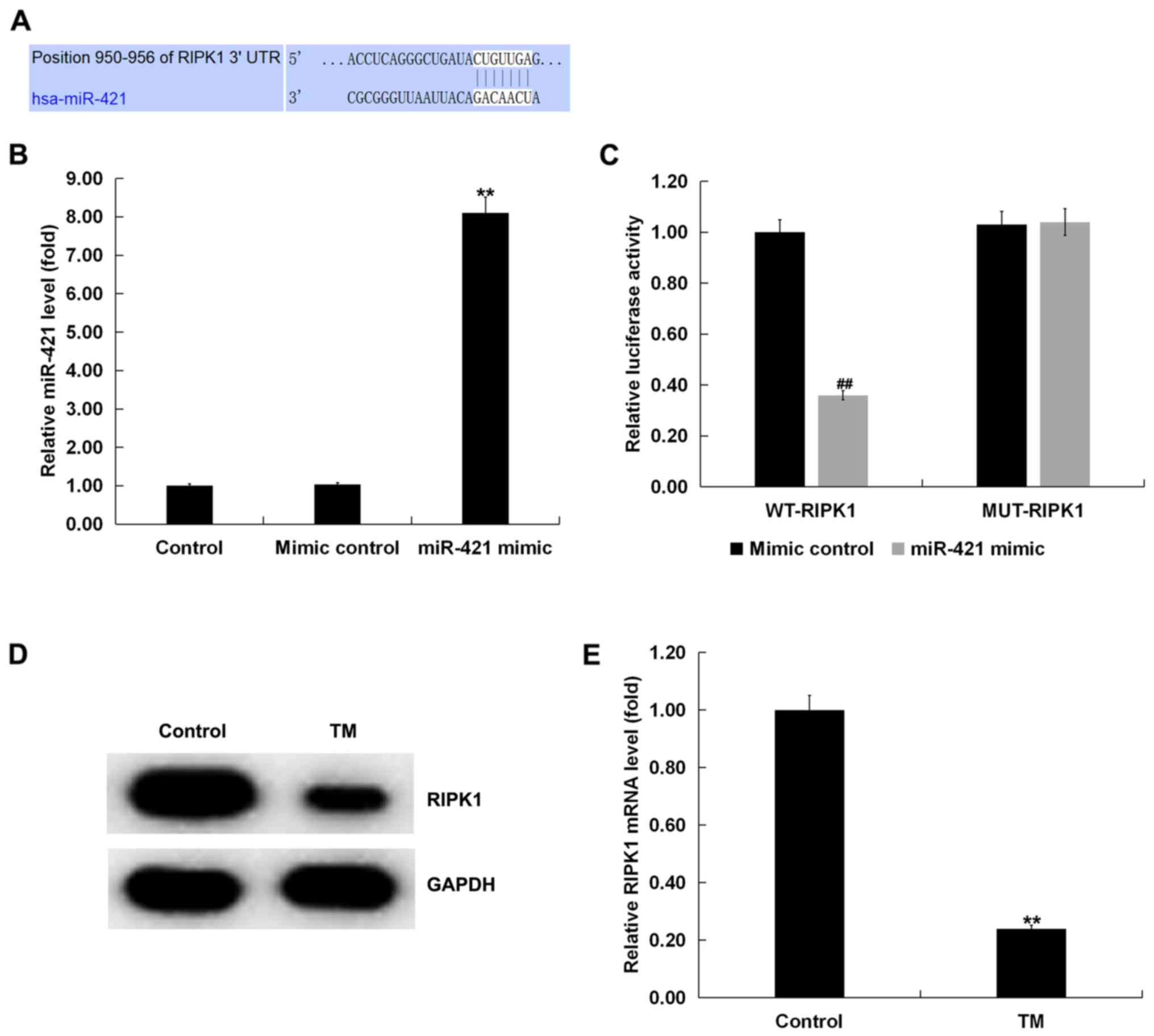
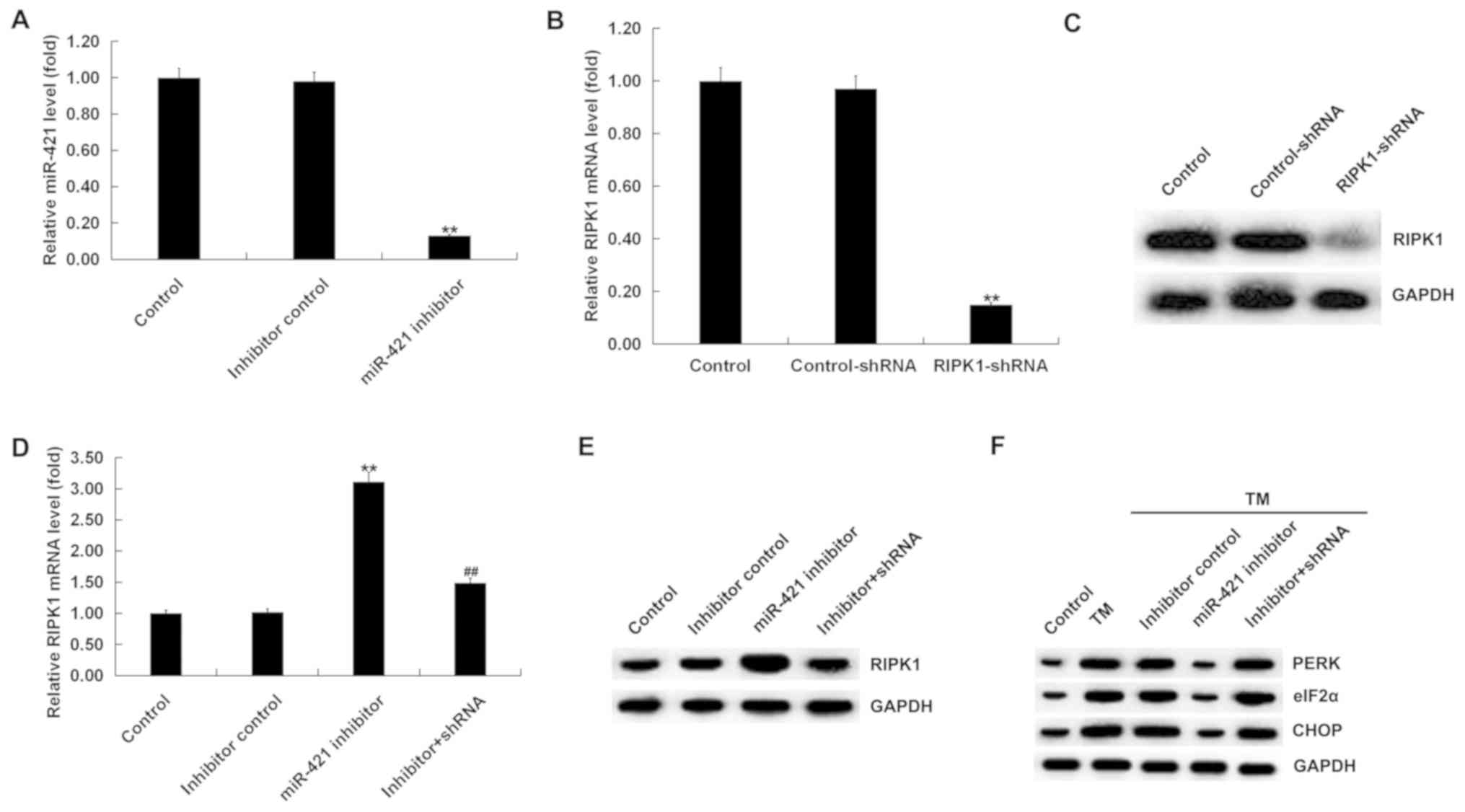
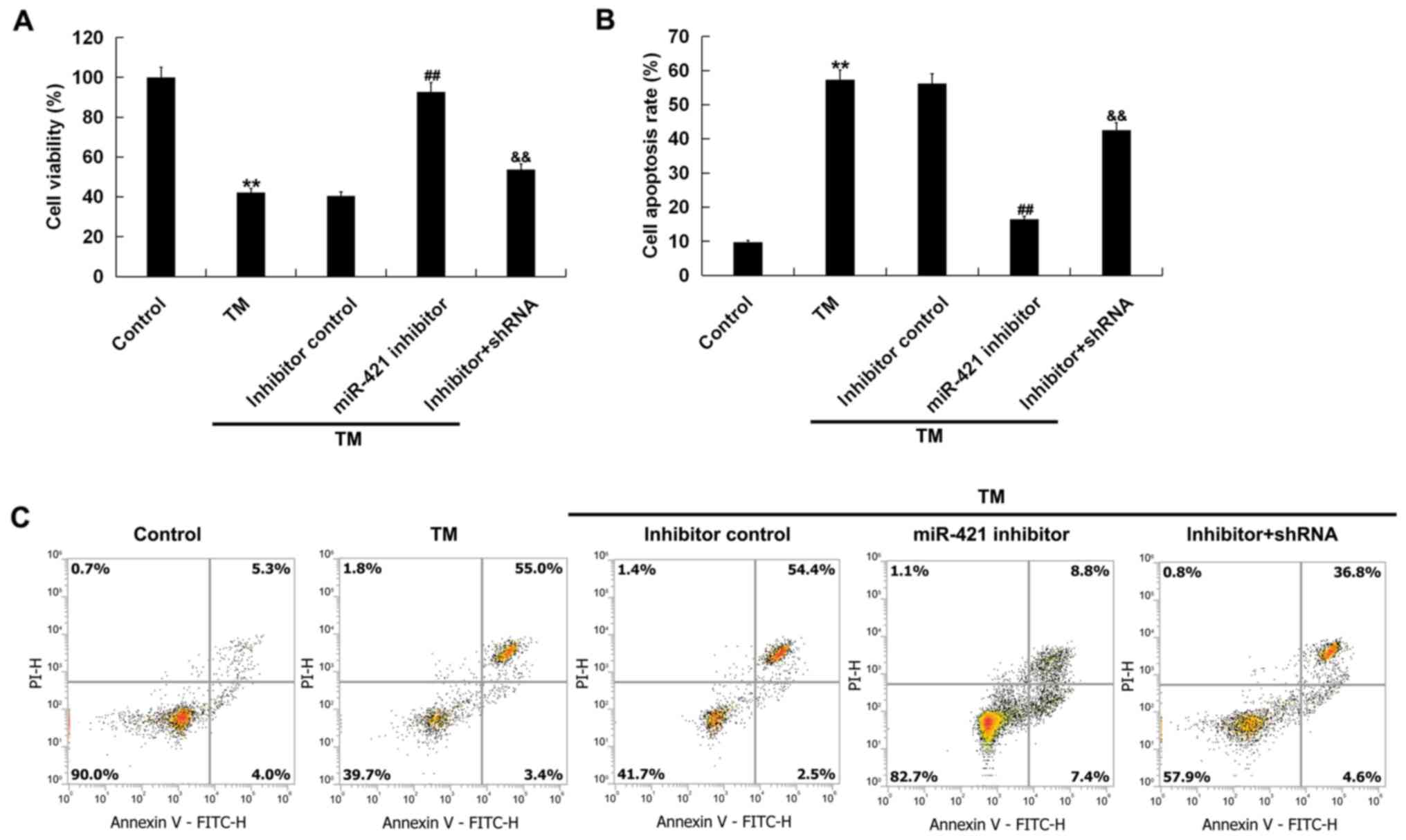
|
1
|
Ezzedine K, Eleftheriadou V, Whitton M and
van Geel N: Vitiligo. Lancet. 386:74–84. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jain A, Mal J, Mehndiratta V, Chander R
and Patra SK: Study of oxidative stress in vitiligo. Indian J Clin
Biochem. 26:78–81. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Silverberg JI and Silverberg NB:
Association between vitiligo extent and distribution and
quality-of-life impairment. JAMA Dermatol. 149:159–164. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Karelson M, Silm H and Kingo K: Quality of
life and emotional state in vitiligo in an Estonian sample:
Comparison with psoriasis and healthy controls. Acta Derm Venereol.
93:446–450. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jin Y, Birlea SA, Fain PR, Gowan K,
Riccardi SL, Holland PJ, Mailloux CM, Sufit AJ, Hutton SM,
Amadi-Myers A, et al: Variant of TYR and autoimmunity
susceptibility loci in generalized vitiligo. New Engl J Med.
362:1686–1697. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Alghamdi KM, Khurrum H, Taieb A and
Ezzedine K: Treatment of generalized vitiligo with anti-TNF-α
agents. J Drugs Dermatol. 11:534–539. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Manga P, Elbuluk N and Orlow SJ: Recent
advances in understanding vitiligo. F1000Res. 5(pii): F1000 Faculty
Rev. 22342016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Eleftheriadou V, Whitton ME, Gawkrodger
DJ, Batchelor J, Corne J, Lamb B, Ersser S, Ravenscroft J and
Thomas KS: Future research into the treatment of vitiligo: Where
should our priorities lie? Results of the vitiligo priority setting
partnership. Br J Dermatol. 164:530–536. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Luan Q, Jin L, Jiang CC, Tay KH, Lai F,
Liu XY, Liu YL, Guo ST, Li CY, Yan XG, et al: RIPK1 regulates
survival of human melanoma cells upon endoplasmic reticulum stress
through autophagy. Autophagy. 11:975–994. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Šahmatova L, Tankov S, Prans E, Aab A,
Hermann H, Reemann P, Pihlap M, Karelson M, Abram K, Kisand K, et
al: MicroRNA-155 is dysregulated in the skin of patients with
vitiligo and inhibits melanogenesis-associated genes in melanocytes
and keratinocytes. Acta Derm Venereol. 96:742–747. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bijkerk R, de Bruin RG, van Solingen C,
van Gils JM, Duijs JM, van der Veer EP, Rabelink TJ, Humphreys BD
and van Zonneveld AJ: Silencing of microRNA-132 reduces renal
fibrosis by selectively inhibiting myofibroblast proliferation.
Kidney Int. 89:1268–1280. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zu Y, Yang Y, Zhu J, Bo X, Hou S, Zhang B,
Qiu J and Zheng J: MiR-146a suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma by
downregulating TRAF6. Am J Cancer Res. 6:2502–2513. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li Q, Zhang X, Li N, Liu Q and Chen D:
miR-30b inhibits cancer cell growth, migration, and invasion by
targeting homeobox A1 in esophageal cancer. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 485:506–512. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tian W, Wang G, Liu Y, Huang Z, Zhang C,
Ning K, Yu C, Shen Y, Wang M, Li Y, et al: The miR-599 promotes
non-small cell lung cancer cell invasion via SATB2. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 485:35–40. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hao J, Zhang S, Zhou Y, Liu C, Hu X and
Shao C: MicroRNA 421 suppresses DPC4/Smad4 in pancreatic cancer.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 406:552–557. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu JH, Yao YL, Gu T, Wang ZY, Pu XY, Sun
WW, Zhang X, Jiang YB and Wang JJ: MiR-421 regulates apoptosis of
BGC-823 gastric cancer cells by targeting caspase-3. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 15:5463–5468. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pasparakis M and Vandenabeele P:
Necroptosis and its role in inflammation. Nature. 517:311–320.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schneider AT, Gautheron J, Feoktistova M,
Roderburg C, Loosen SH, Roy S, Benz F, Schemmer P, Büchler MW,
Nachbur U, et al: RIPK1 Suppresses a TRAF2-dependent pathway to
liver cancer. Cancer Cell. 31:94–109. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Saeed WK and Jun DW: Necroptosis: An
emerging type of cell death in liver diseases. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:12526–12532. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shan B, Pan H, Najafov A and Yuan J:
Necroptosis in development and diseases. Genes Dev. 32:327–340.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cao C and Wan Y: Parameters of protection
against ultraviolet radiation-induced skin cell damage. J Cell
Physiol. 220:277–284. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cao C, Huang X, Han Y, Wan Y, Birnbaumer
L, Feng GS, Marshall J, Jiang M and Chu WM: Galpha(i1) and
Galpha(i3) are required for epidermal growth factor-mediated
activation of the Akt-mTORC1 pathway. Sci Signal. 2:ra172009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cao C, Lu S, Jiang Q, Wang WJ, Song X,
Kivlin R, Wallin B, Bagdasarian A, Tamakloe T, Chu WM, et al: EGFR
activation confers protections against UV-induced apoptosis in
cultured mouse skin dendritic cells. Cell Signal. 20:1830–1838.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cheng LB, Cheng L, Bi HE, Zhang ZQ, Yao J,
Zhou XZ and Jiang Q: Alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone protects
retinal pigment epithelium cells from oxidative stress through
activation of melanocortin 1 receptor-Akt-mTOR signaling. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 443:447–452. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kadekaro AL, Kavanagh R, Kanto H, Terzieva
S, Hauser J, Kobayashi N, Schwemberger S, Cornelius J, Babcock G,
Shertzer HG, et al: Alpha-Melanocortin and endothelin-1 activate
antiapoptotic pathways and reduce DNA damage in human melanocytes.
Cancer Res. 65:4292–4299. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wan J, Lin F, Zhang W, Xu A, DeGiorgis J,
Lu H and Wan Y: Novel approaches to vitiligo treatment via
modulation of mTOR and NF-κB pathways in human skin melanocytes.
Int J Biol Sci. 13:391–400. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Le Poole IC, Das PK, van den Wijngaard RM,
Bos JD and Westerhof W: Review of the etiopathomechanism of
vitiligo: A convergence theory. Exp Dermatol. 2:145–153. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gawkrodger DJ, Ormerod AD, Shaw L,
Mauri-Sole I, Whitton ME, Watts MJ, Anstey AV, Ingham J and Young
K: Vitiligo: Concise evidence based guidelines on diagnosis and
management. Postgrad Med J. 86:466–471. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gianfaldoni S, Wollina U, Tirant M,
Tchernev G, Lotti J, Satolli F, Rovesti M, França K and Lotti T:
Herbal compounds for the treatment of vitiligo: A review. Open
Access Maced J Med Sci. 6:203–207. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lotti T, Wollina U, Tchernev G, Valle Y,
Lotti J, França K, Satolli F, Rovesti M, Tirant M, Lozev I, et al:
An innovative therapeutic protocol for Vitiligo: Experience with
the use of fraxel herbium laser, topical latanoprost and successive
irradiation with UVA-1 Laser. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 6:49–51.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mehrgou A and Akouchekian M: Therapeutic
impacts of microRNAs in breast cancer by their roles in regulating
processes involved in this disease. J Res Med Sci. 22:1302017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Spiegelman VS and Elcheva IA: Metabo-miR:
miR-211 regulates mitochondrial energy metabolism in vitiligo. J
Invest Dermatol. 137:1828–1830, 137. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shi Q, Zhang W, Guo S, Jian Z, Li S, Li K,
Ge R, Dai W, Wang G, Gao T and Li C: Oxidative stress-induced
overexpression of miR-25: The mechanism underlying the degeneration
of melanocytes in vitiligo. Cell Death Differ. 23:496–508. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li Y, Li W, Zhang JG, Li HY and Li YM:
Downregulation of tumor suppressor menin by miR-421 promotes
proliferation and migration of neuroblastoma. Tumour Biol.
35:10011–10017. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tan H, Qi J, Fan BY, Zhang J, Su FF and
Wang HT: MicroRNA-24-3p attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
injury by suppressing RIPK1 expression in mice. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 51:46–62. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Walter P and Ron D: The unfolded protein
response: From stress pathway to homeostaticregulation. Science.
334:1081–1086. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li Y, Zhang Y, Fu H, Huang H, Lu Q, Qin H,
Wu Y, Huang H, Mao G, Wei Z and Liao P: Hes1 knockdown exacerbates
ischemic stroke following tMCAO by increasing ER stress-dependent
apoptosis via the PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP signaling pathway. Neurosci
Bull. Jul 15–2019.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Umeda J, Sano S, Kogawa K, Motoyama N,
Yoshikawa K, Itami S, Kondoh G, Watanabe T and Takeda J: In vivo
cooperation between Bcl-xL and the phosphoinositide 3-kinase-Akt
signalingpathway for the protection of epidermal keratinocytes from
apoptosis. FASEB J. 17:610–620. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yue L, Ailin W, Jinwei Z, Leng L, Jianan
W, Li L, Haiming C, Ling H and Chuanjian L: PSORI-CM02 ameliorates
psoriasis in vivo and in vitro by inducing autophagy via inhibition
of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Phytomedicine. 64:1530542019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Arshad Z, Rezapour-Firouzi S, Mohammadian
M and Ebrahimifar: The sources of essential fatty acids for
allergic and cancer patients; a connection with insight into
mammalian target of rapamycin: A narrative review. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 19:2391–2401. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Shin JM, Kim MY, Sohn KC, Jung SY, Lee HE,
Lim JW, Kim S, Lee YH, Im M, Seo YJ, et al: Nrf2 negatively
regulates melanogenesis by modulating PI3K/Akt signaling. PLoS One.
9:e960352014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Larribere L, Khaled M, Tartare-Deckert S,
Busca R, Luciano F, Bille K, Valony G, Eychene A, Auberger P,
Ortonne JP, et al: PI3K mediates protection against TRAIL-induced
apoptosis in primary human melanocytes. Cell Death Differ.
11:1084–1091. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|