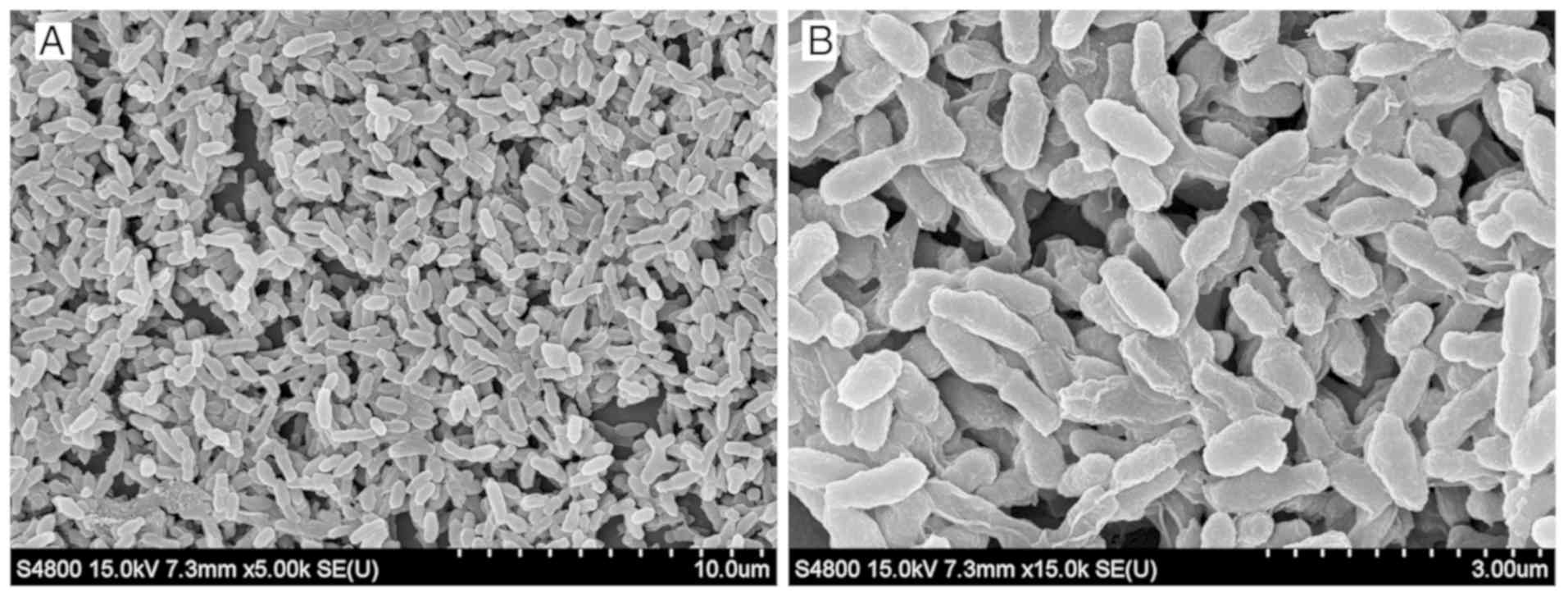
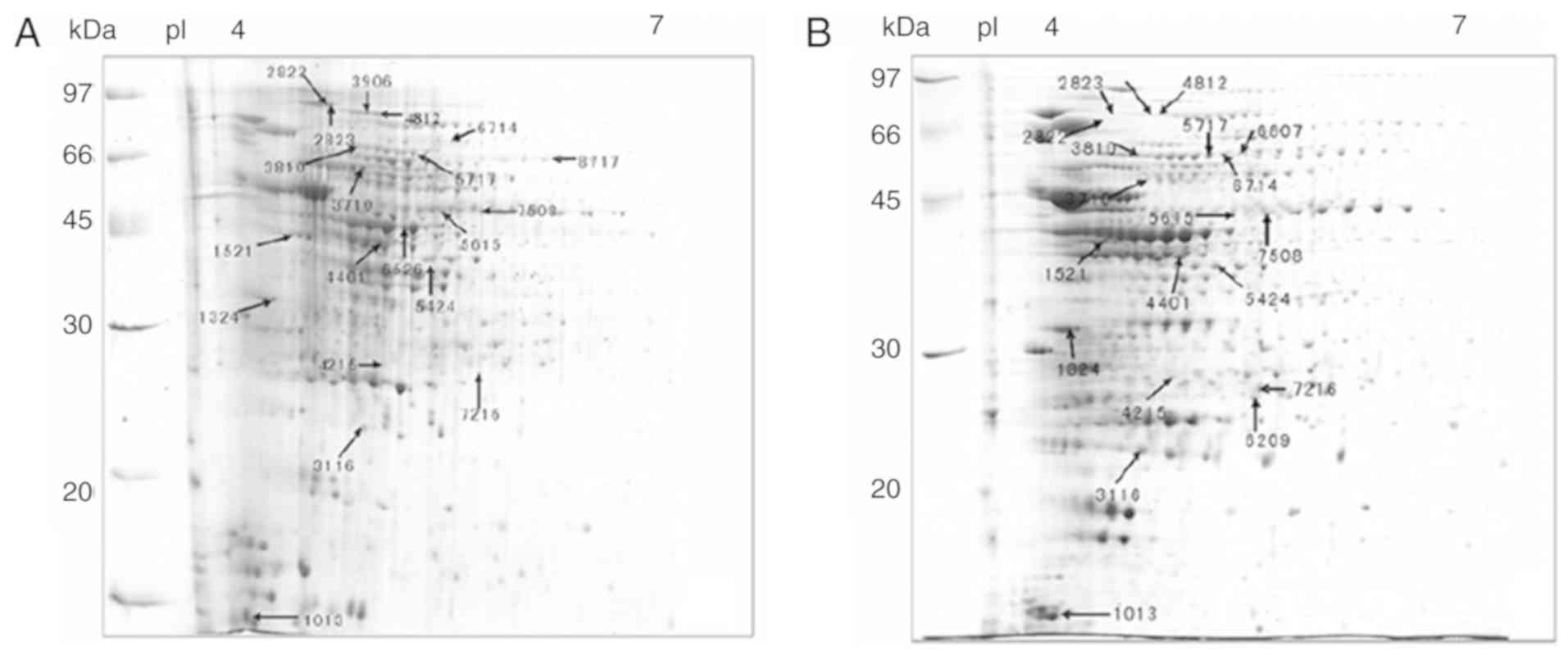
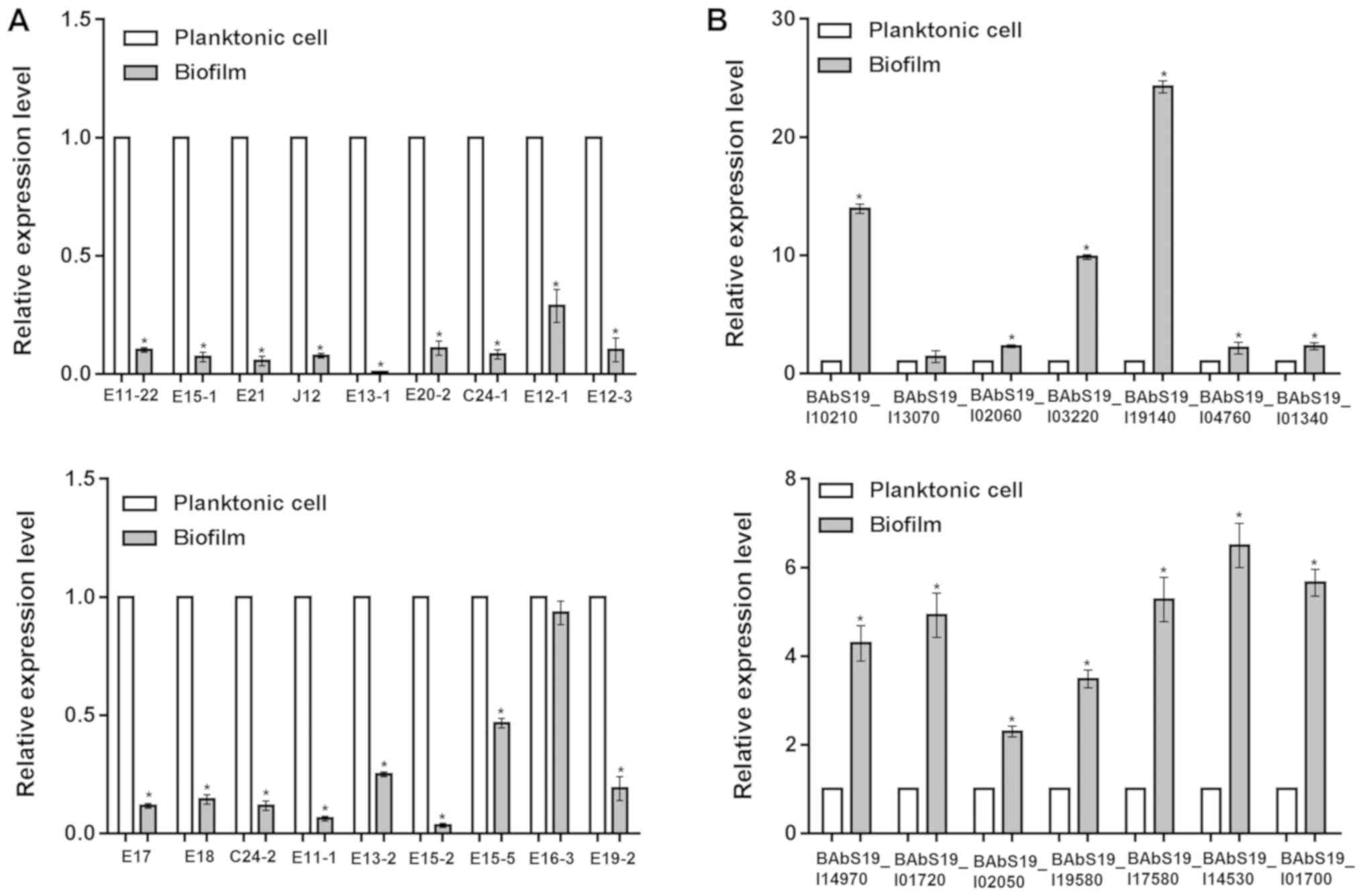
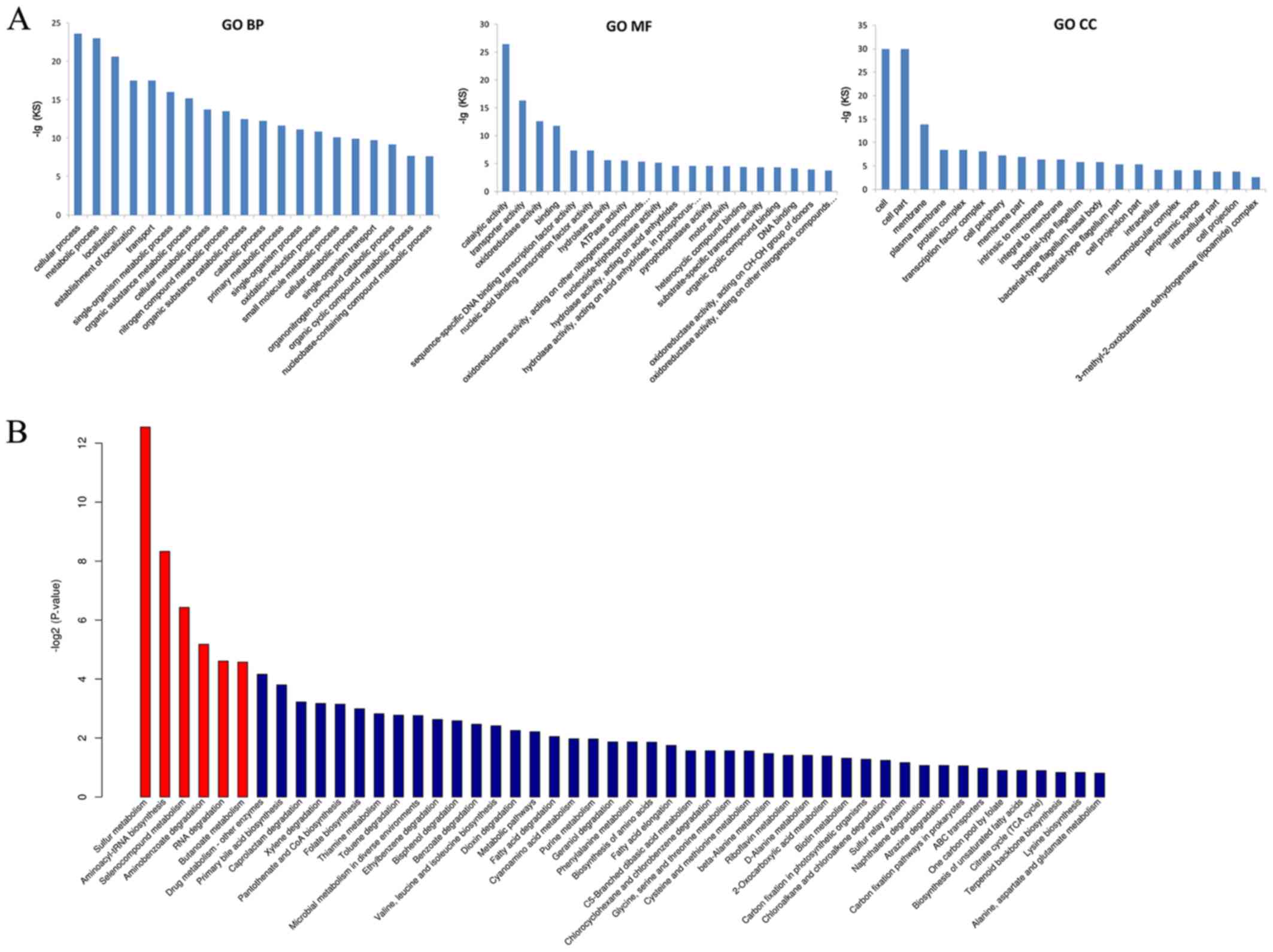
|
1
|
Byndloss MX and Tsolis RM: Brucella spp.
virulence factors and immunity. Annu Rev Anim Biosci. 4:111–127.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hasanjani Roushan MR and Ebrahimpour S:
Human brucellosis: An overview. Caspian J Intern Med. 6:46–47.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Atluri VL, Xavier MN, de Jong MF, den
Hartigh AB and Tsolis RM: Interactions of the human pathogenic
Brucella species with their hosts. Annu Rev Microbiol. 65:523–541.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Halling SM, Peterson-Burch BD, Bricker BJ,
Zuerner RL, Qing Z, Li LL, Kapur V, Alt DP and Olsen SC: Completion
of the genome sequence of Brucella abortus and comparison to
the highly similar genomes of Brucella melitensis and
Brucella suis. J Bacteriol. 187:2715–2726. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Doganay G and Doganay M: Brucella as a
potential agent of bioterrorism. Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov.
8:27–33. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dang H and Lovell CR: Microbial surface
colonization and biofilm development in marine environments.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 80:91–138. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu H, Moser C, Wang HZ, Høiby N and Song
ZJ: Strategies for combating bacterial biofilm infections. Int J
Oral Sci. 7:1–7. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Burmølle M, Thomsen TR, Fazli M, Dige I,
Christensen L, Homøe P, Tvede M, Nyvad B, Tolker-Nielsen T, Givskov
M, et al: Biofilms in chronic infections a matter of opportunity
monospecies biofilms in multispecies infections. FEMS Immunol Med
Microbiol. 59:324–336. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Parsek MR and Singh PK: Bacterial
biofilms: An emerging link to disease pathogenesis. Annu Rev
Microbiol. 57:677–701. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang Y, Yi L, Wu Z, Shao J, Liu G, Fan H,
Zhang W and Lu C: Comparative proteomic analysis of streptococcus
suis biofilms and planktonic cells that identified biofilm
infection-related immunogenic proteins. PLoS One. 7:e333712012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kumon H, Ono N, Iida M and Nickel JC:
Combination effect of fosfomycin and ofloxacin against Pseudomonas
aeruginosa growing in a biofilm. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
39:1038–1044. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wilson M: Susceptibility of oral bacterial
biofilms to antimicrobial agents. J Med Microbiol. 44:79–87. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang L, Li Y, Wang L, Zhu M, Zhu X, Qian C
and Li W: Responses of biofilm microorganisms from moving bed
biofilm reactor to antibiotics exposure: Protective role of
extracellular polymeric substances. Bioresour Technol. 254:268–277.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Flury D, Behrend H, Sendi P, von Kietzell
M and Strahm C: Brucella melitensis prosthetic joint
infection. J Bone Jt Infect. 2:136–142. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Almirón MA, Roset MS and Sanjuan N: The
aggregation of Brucella abortus occurs under microaerobic
conditions and promotes desiccation tolerance and biofilm
formation. Open Microbiol J. 7:87–91. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Conde-Álvarez R, Arce-Gorvel V, Iriarte M,
Manček-Keber M, Barquero-Calvo E, Palacios-Chaves L, Chacón-Díaz C,
Chaves-Olarte E, Martirosyan A, von Bargen K, et al: The
lipopolysaccharide core of Brucella abortus acts as a shield
against innate immunity recognition. PLoS Pathog. 8:e10026752012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Spera JM, Ugalde JE, Mucci J, Comerci DJ
and Ugalde RA: A B lymphocyte mitogen is a Brucella abortus
virulence factor required for persistent infection. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 103:16514–16519. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Manterola L, Guzmán-Verri C, Chaves-Olarte
E, Barquero-Calvo E, de Miguel MJ, Moriyón I, Grilló MJ, López-Goñi
I and Moreno E: BvrR/BvrS-controlled outer membrane proteins Omp3a
and Omp3b are not essential for Brucella abortus virulence.
Infect Immun. 75:4867–4874. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Harro JM, Peters BM, O'May GA, Archer N,
Kerns P, Prabhakara R and Shirtliff ME: Vaccine development in
Staphylococcus aureus: Taking the biofilm phenotype into
consideration. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 59:306–323. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yi L, Wang Y, Ma Z, Zhang H, Li Y, Zheng
JX, Yang YC, Fan HJ and Lu CP: Biofilm formation of Streptococcus
equi ssp. zooepidemicus and comparative proteomic analysis of
biofilm and planktonic cells. Curr Microbiol. 69:227–233. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang L, Wang S and Li W: RSeQC: Quality
control of RNA-seq experiments. Bioinformatics. 28:2184–2185. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Trapnell C, Pachter L and Salzberg SL:
TopHat: Discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics.
25:1105–1111. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L, Pertea G,
Kim D, Kelley DR, Pimentel H, Salzberg SL, Rinn JL and Pachter L:
Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq
experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat Protoc. 7:562–578. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene
Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang Y, Yi L, Zhang Z, Fan H, Cheng X and
Lu C: Biofilm formation, host-cell adherence, and virulence genes
regulation of Streptococcus suis in response to autoinducer-2
signaling. Curr Microbiol. 68:575–580. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Steinberg D: Studying plaque biofilms on
various dental surfaces. Handbook of bacterial adhesion Springer.
353–370. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Costerton JW, Stewart PS and Greenberg E:
Bacterial biofilms: A common cause of persistent infections.
Science. 284:1318–1322. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
De Angelis M, Siragusa S, Campanella D, Di
Cagno R and Gobbetti M: Comparative proteomic analysis of biofilm
and planktonic cells of Lactobacillus plantarum DB200. Proteomics.
15:2244–2257. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ning J, Gao X, Xiao M, et al: Comparative
proteomic analysis between biofilm-forming cells and planktonic
cells of swine Brodetella bronchiseptica. J Agric
Biotechnol. 26:159–166. 2018.[In Chinese].
|
|
32
|
Romero-Lastra P, Sánchez MC, Ribeiro-Vidal
H, Llama-Palacios A, Figuero E, Herrera D and Sanz M: Comparative
gene expression analysis of Porphyromonas gingivalis ATCC
33277 in planktonic and biofilms states. PLoS One. 12:e01746692017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Charlebois A, Jacques M and Archambault M:
Comparative transcriptomic analysis of Clostridium perfringens
biofilms and planktonic cells. Avian Pathol. 45:593–601. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Furano AV: Content of elongation factor Tu
in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 72:4780–4784.
1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Harding SV, Sarkar-Tyson M, Smither SJ,
Atkins TP, Oyston PC, Brown KA, Liu Y, Wait R and Titball RW: The
identification of surface proteins of Burkholderia pseudomallei.
Vaccine. 25:2664–2672. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kunert A, Losse J, Gruszin C, Hühn M,
Kaendler K, Mikkat S, Volke D, Hoffmann R, Jokiranta TS, Seeberger
H, et al: Immune evasion of the human pathogen Pseudomonas
aeruginosa: Elongation factor Tuf is a factor H and plasminogen
binding protein. J Immunol. 179:2979–2988. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Barel M, Hovanessian AG, Meibom K, Briand
JP, Dupuis M and Charbit A: A novel receptor-ligand pathway for
entry of Francisella tularensis in monocyte-like THP-1 cells:
Interaction between surface nucleolin and bacterial elongation
factor Tu. BMC Microbiol. 8:1452008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Foulston L, Elsholz AK, DeFrancesco AS and
Losick R: The extracellular matrix of Staphylococcus aureus
biofilms comprises cytoplasmic proteins that associate with the
cell surface in response to decreasing pH. MBio. 5:e01667–e01614.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Entelis N, Brandina I, Kamenski P,
Krasheninnikov IA, Martin RP and Tarassov I: A glycolytic enzyme,
enolase, is recruited as a cofactor of tRNA targeting toward
mitochondria in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev. 20:1609–1620.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Pancholi V: Multifunctional a-enolase: Its
role in diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci. 58:902–920. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sriram G, Martinez JA, McCabe ER, Liao JC
and Dipple KM: Single-gene disorders: What role could moonlighting
enzymes play? Am J Hum Genet. 76:911–924. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kolberg J, Aase A, Bergmann S, Herstad TK,
Rødal G, Frank R, Rohde M and Hammerschmidt S: Streptococcus
pneumoniae enolase is important for plasminogen binding despite low
abundance of enolase protein on the bacterial cell surface.
Microbiology. 152:1307–1317. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pancholi V and Fischetti VA:
alpha-enolase, a novel strong plasmin(ogen) binding protein on the
surface of pathogenic streptococci. J Biol Chem. 273:14503–14515.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Silva RC, Padovan AC, Pimenta DC, Ferreira
RC, da Silva CV and Briones MR: Extracellular enolase of Candida
albicans is involved in colonization of mammalian intestinal
epithelium. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 4:662014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Han X, Ding C, Chen H, Hu Q and Yu S:
Enzymatic and biological characteristics of enolase in Brucella
abortus A19. Mol Biol Rep. 39:2705–2711. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sieńczyk J, Skłodowska A, Grudniak A and
Wolska KI: Influence of DnaK and DnaJ chaperones on Escherichia
coli membrane lipid composition. Pol J Microbiol. 53:121–123.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
McCarty JS and Walker GC: DnaK mutants
defective in ATPase activity are defective in negative regulation
of the heat shock response: Expression of mutant DnaK proteins
results in filamentation. J Bacteriol. 176:764–780. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Grudniak AM, Włodkowska J and Wolska KI:
Chaperone DnaJ influences the formation of biofilm by Escherichia
coli. Pol J Microbiol. 64:279–283. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Dwyer MA and Hellinga HW: Periplasmic
binding proteins: A versatile superfamily for protein engineering.
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 14:495–504. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Inui M, Nakata K, Roh JH, Zahn K and
Yukawa H: Molecular and functional characterization of the
Rhodopseudomonas palustris no. 7 phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase
gene. J Bacteriol. 181:2689–2696. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Li Z, Chen Y, Liu D, Zhao N, Cheng H, Ren
H, Guo T, Niu H, Zhuang W, Wu J and Ying H: Involvement of
glycolysis/gluconeogenesis and signaling regulatory pathways in
Saccharomyces cerevisiae biofilms during fermentation. Front
Microbiol. 6:1392015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Viadas C, Rodríguez MC, Sangari FJ, Gorvel
JP, García-Lobo JM and López-Goñi I: Transcriptome analysis of the
Brucella abortus BvrR/BvrS two-component regulatory system.
PLoS One. 5:e102162010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Liu P, Wood D and Nester EW:
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase is an acid-induced, chromosomally
encoded virulence factor in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol.
187:6039–6045. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Higgins C, Hyde S, Mimmack M, Gileadi U,
Gill D and Gallagher M: Binding protein-dependent transport
systems. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 22:571–592. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Stirling D, Hulton C, Waddell L, Park SF,
Stewart GS, Booth IR and Higgins CF: Molecular characterization of
the proU loci of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli
encoding osmoregulated glycine betaine transport systems. Mol
Microbiol. 3:1025–1038. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|