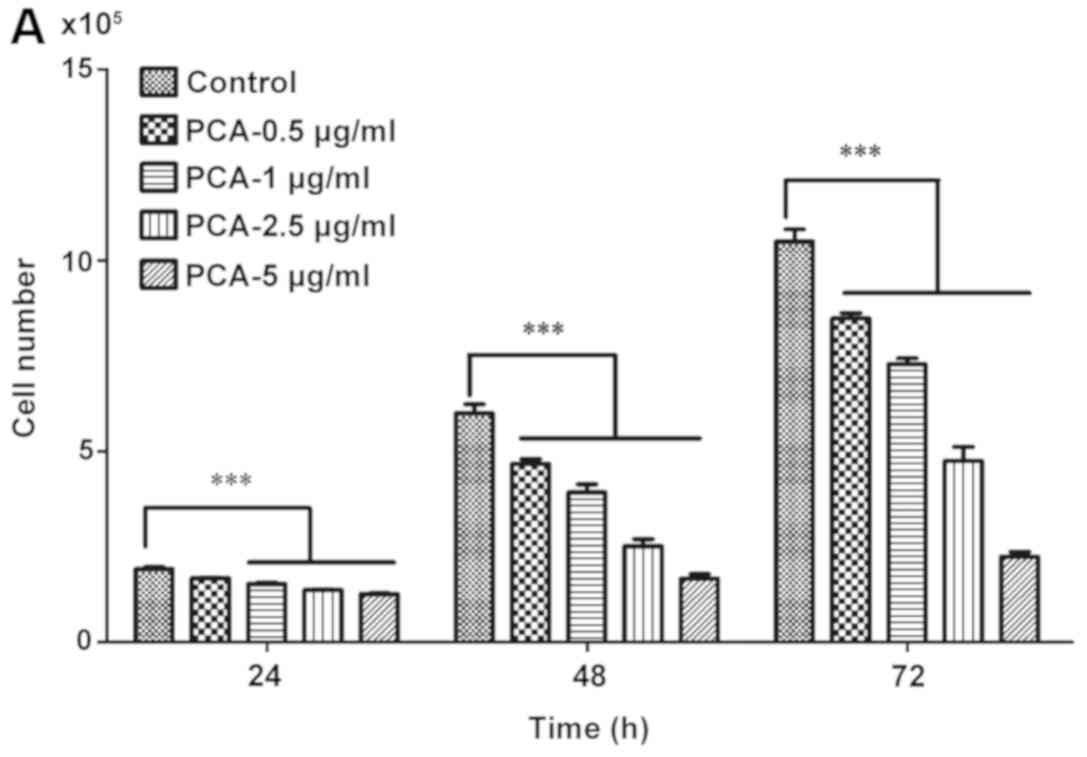
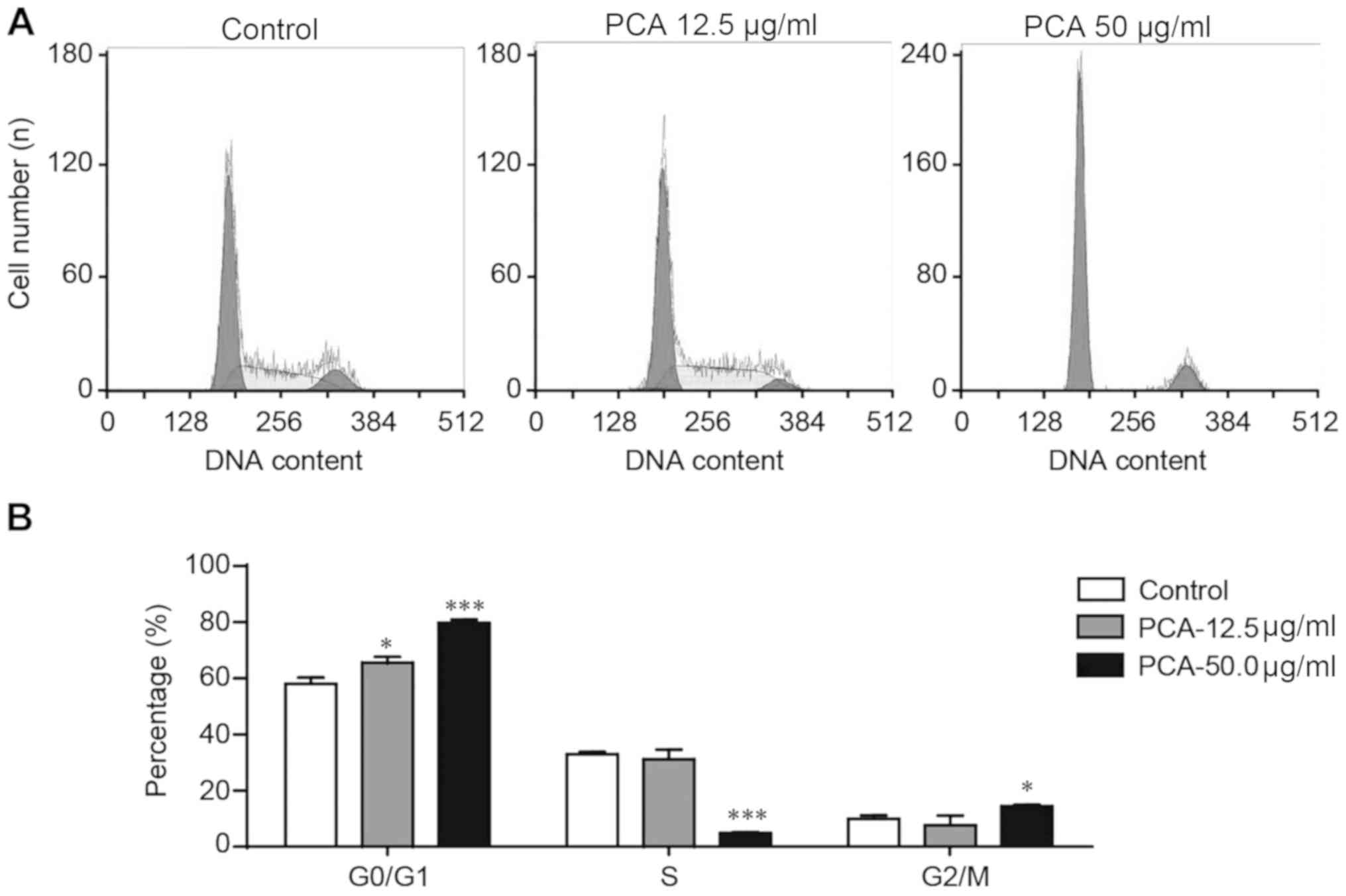
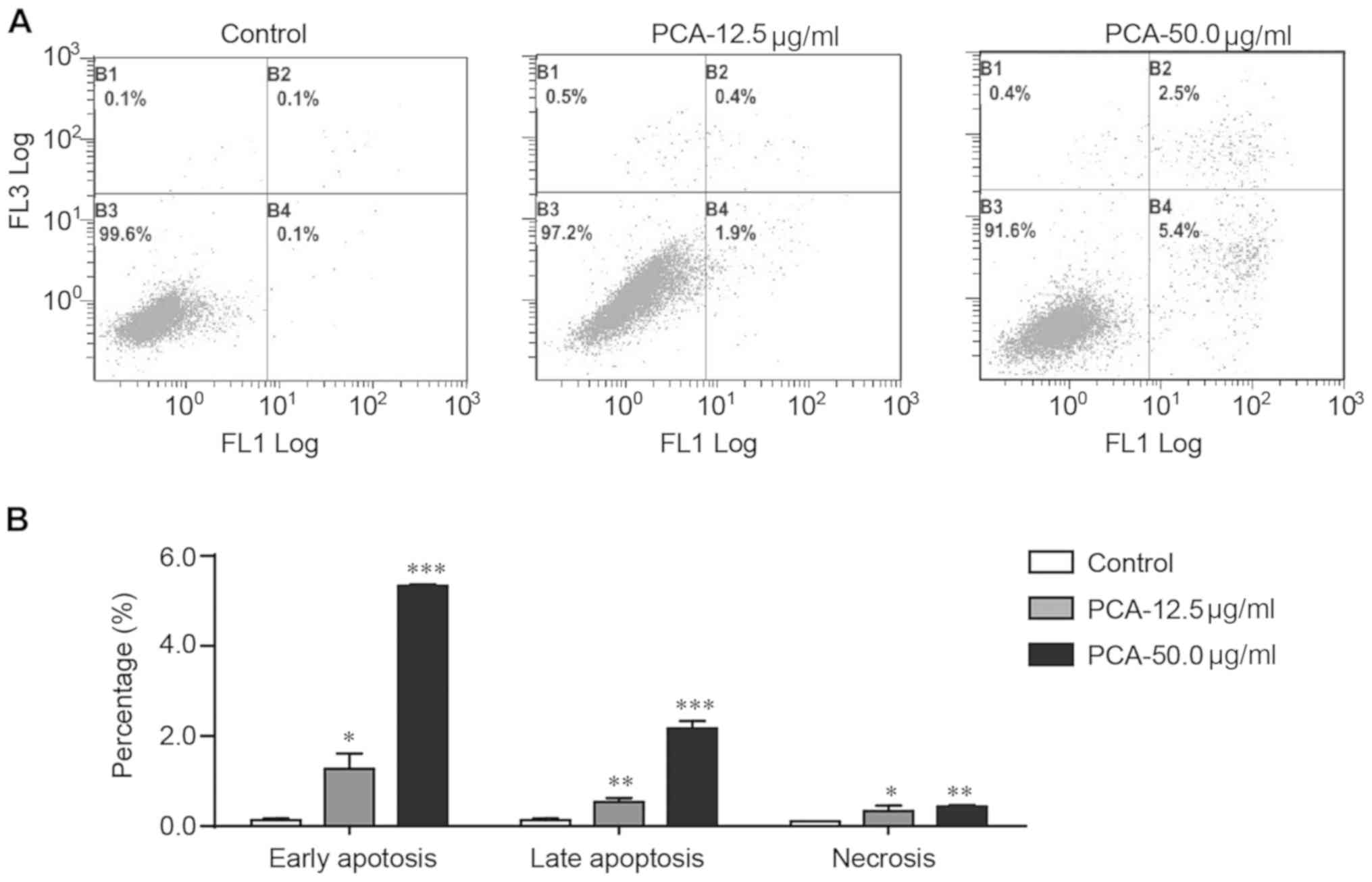
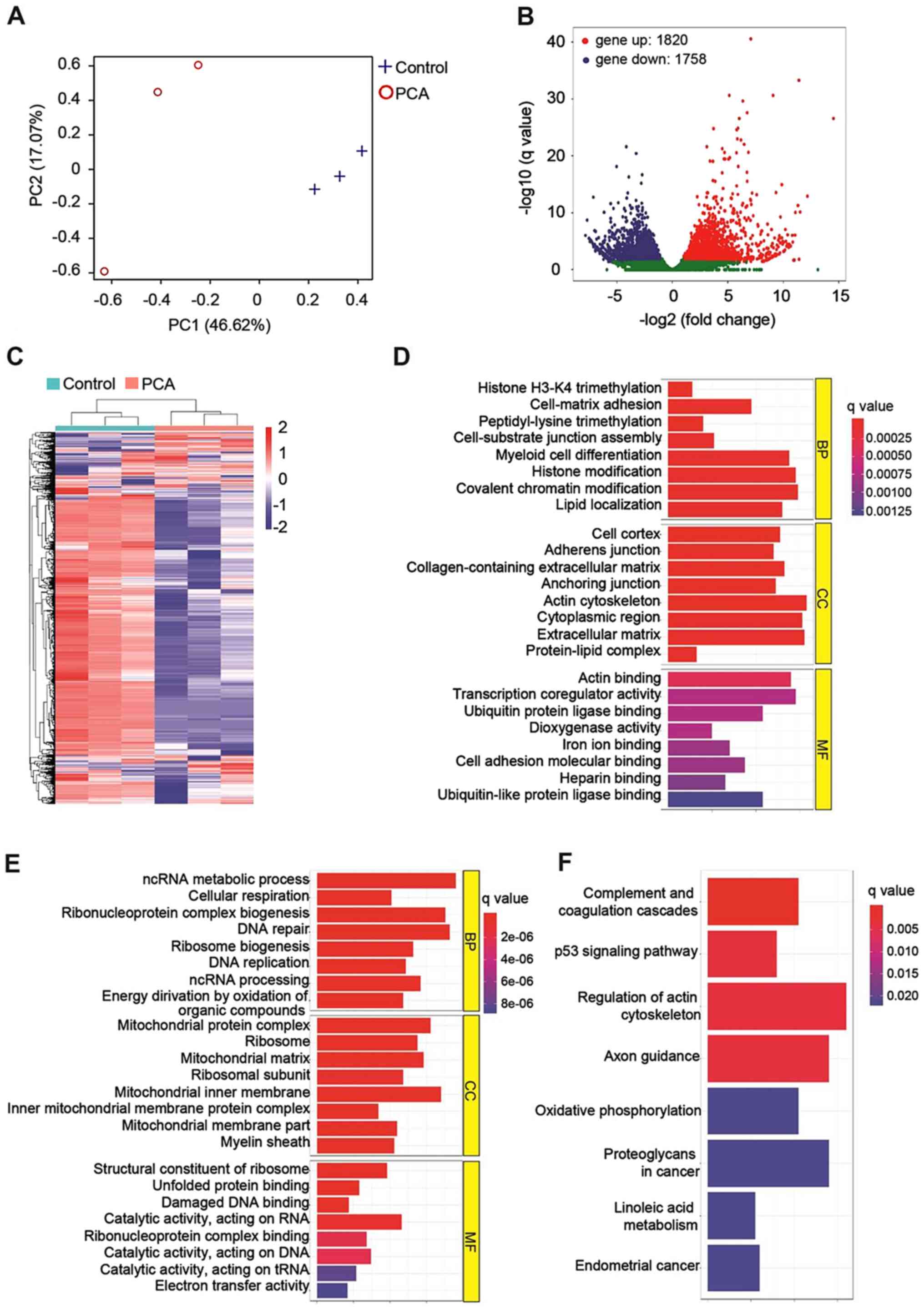
|
1
|
Savoia P, Fava P, Casoni F and Cremona O:
Targeting the ERK signaling pathway in melanoma. Int J Mol Sci.
20:E14832019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mishra H, Mishra PK, Ekielski A, Jaggi M,
Iqbal Z and Talegaonkar S: Melanoma treatment: From conventional to
nanotechnology. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 144:2283–2302. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Weinstock MA, Lott JP, Wang Q, Titus LJ,
Onega T, Nelson HD, Pearson L, Piepkorn M, Barnhill RL, Elmore JG
and Tosteson ANA: Skin biopsy utilization and melanoma incidence
among Medicare beneficiaries. Br J Dermatol. 176:949–954. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Barbieri A, Quagliariello V, Del Vecchio
V, Falco M, Luciano A, Amruthraj NJ, Nasti G, Ottaiano A, Berretta
M, Iaffaioli RV and Arra C: Anticancer and anti-inflammatory
properties of ganoderma lucidum extract effects on melanoma and
triple-negative breast cancer treatment. Nutrients. 9:E2102017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Albuquerque KRS, Pacheco NM, Del Rosario
Loyo Casao T, de Melo F, Novaes RD and Goncalves RV: Applicability
of plant extracts in preclinical studies of melanoma: A systematic
review. Mediators Inflamm. 2018:67979242018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Momtaz S, Niaz K, Maqbool F, Abdollahi M,
Rastrelli L and Nabavi SM: STAT3 targeting by polyphenols: Novel
therapeutic strategy for melanoma. Biofactors. 43:347–370. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen X, Chang L, Qu Y, Liang J, Jin W and
Xia X: Tea polyphenols inhibit the proliferation, migration, and
invasion of melanoma cells through the down-regulation of TLR4. Int
J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 32:3946320177395312018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gao JW, Yamane T, Maita H, Ishikawa S,
Iguchi-Ariga SM, Pu XP and Ariga H: DJ-1-Mediated protective effect
of protocatechuic aldehyde against oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y
cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 115:36–44. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang L, Ji Y, Kang Z, Lv C and Jiang W:
Protocatechuic aldehyde ameliorates experimental pulmonary fibrosis
by modulating HMGB1/RAGE pathway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
283:50–56. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim KJ, Kim MA and Jung JH: Antitumor and
antioxidant activity of protocatechualdehyde produced from
Streptomyces lincolnensis M-20. Arch Pharm Res.
31:1572–1577. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhong S, Li YG, Ji DF, Lin TB and Lv ZQ:
Protocatechualdehyde induces S-phase arrest and apoptosis by
stimulating the p27(KIP1)-cyclin A/D1-CDK2 and mitochondrial
apoptotic pathways in HT-29 cells. Molecules. 21:E9342016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee BH, Yoon SH, Kim YS, Kim SK, Moon BJ
and Bae YS: Apoptotic cell death through inhibition of protein
kinase CKII activity by 3,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde purified from
Xanthium strumarium. Nat Prod Res. 22:1441–1450. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim D, Langmead B and Salzberg SL: HISAT:
A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Methods.
12:357–360. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Love MI, Huber W and Anders S: Moderated
estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with
DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15:5502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Young MD, Wakefield MJ, Smyth GK and
Oshlack A: Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: Accounting for
selection bias. Genome Biol. 11:R142010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
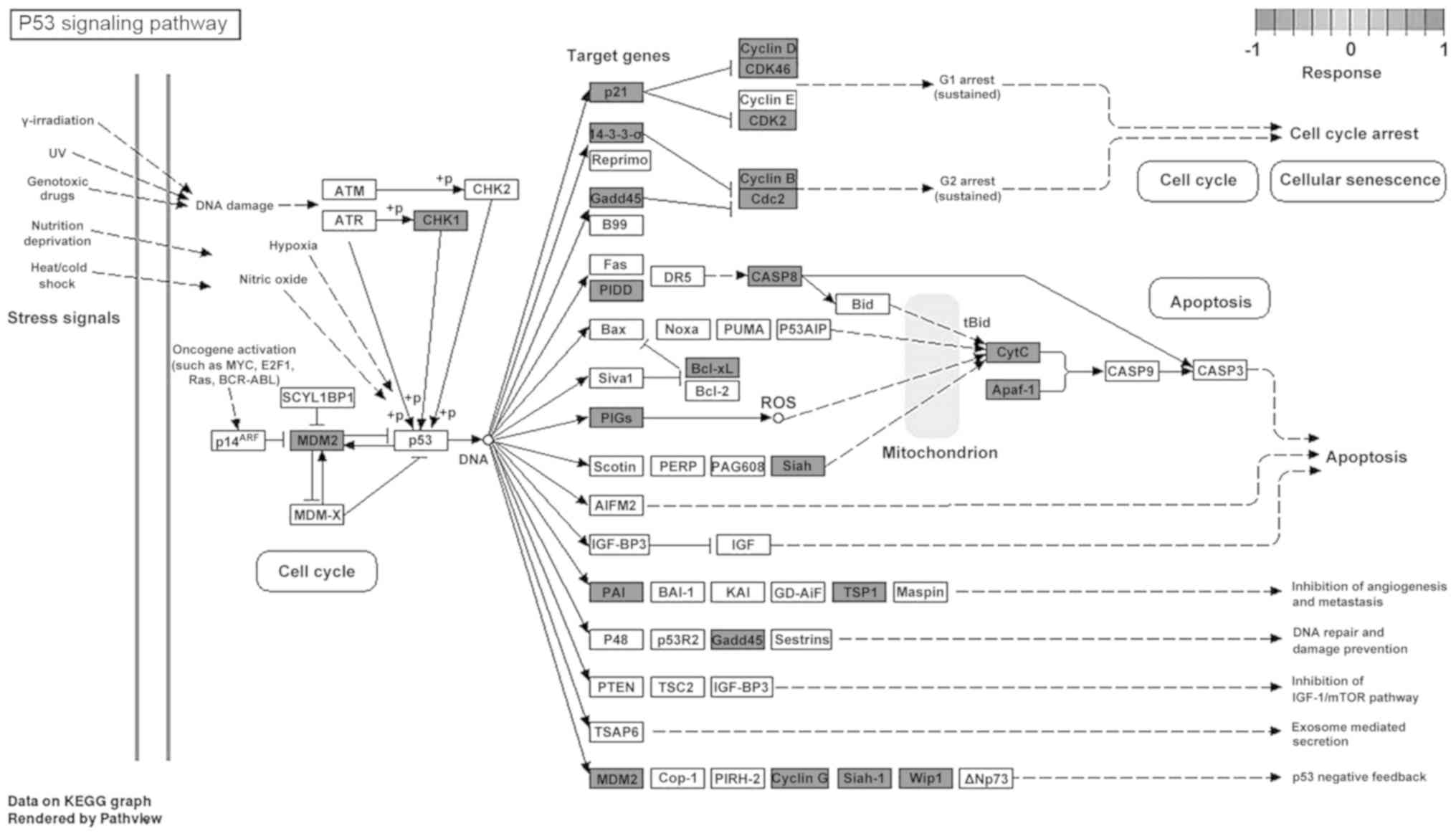
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mao X, Cai T, Olyarchuk JG and Wei L:
Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the
KEGG Orthology (KO) as a controlled vocabulary. Bioinformatics.
21:3787–3793. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
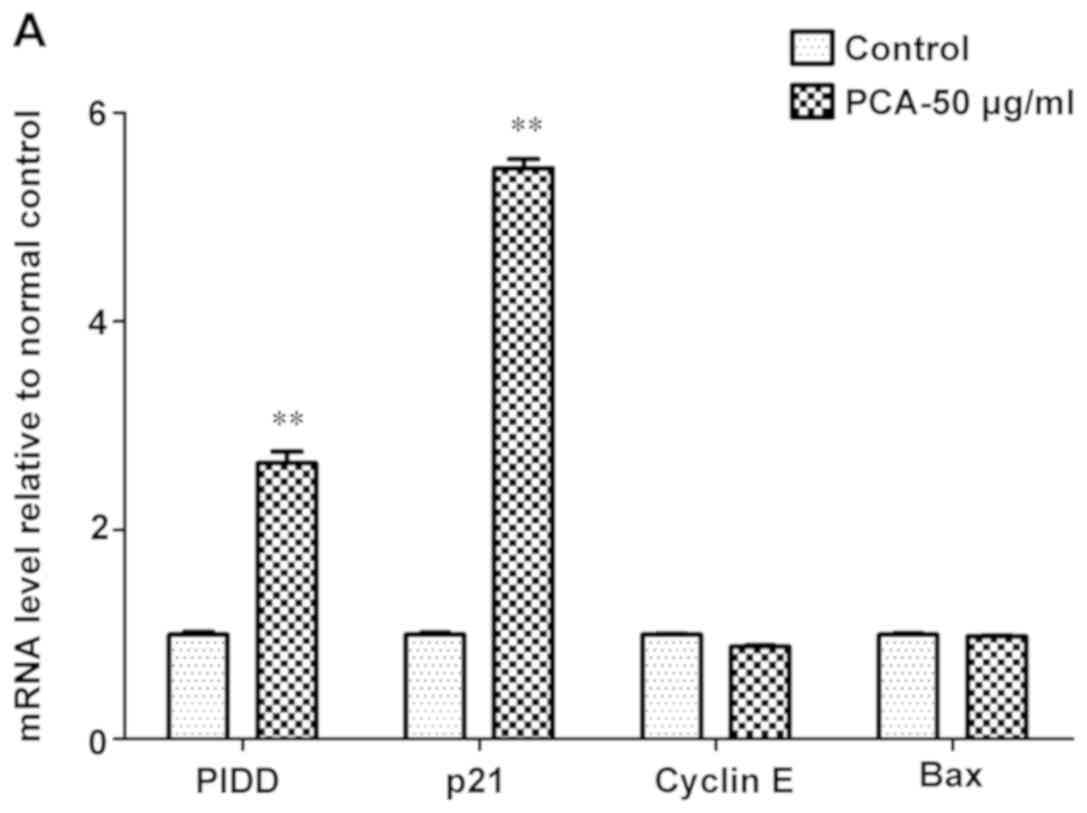
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Luo W and Brouwer C: Pathview: An
R/Bioconductor package for pathway-based data integration and
visualization. Bioinformatics. 29:1830–1831. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Harvey AL, Edrada-Ebel R and Quinn RJ: The
re-emergence of natural products for drug discovery in the genomics
era. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 14:111–129. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
DiMarco-Crook C and Xiao H: Diet-based
strategies for cancer chemoprevention: The role of combination
regimens using dietary bioactive components. Annu Rev Food Sci
Technol. 6:505–526. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bahramsoltani R, Ebrahimi F, Farzaei MH,
Baratpourmoghaddam A, Ahmadi P, Rostamiasrabadi P, Rasouli
Amirabadi AH and Rahimi R: Dietary polyphenols for atherosclerosis:
A comprehensive review and future perspectives. Crit Rev Food Sci
Nutr. 59:114–132. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rothwell JA, Knaze V and Zamora-Ros R:
Polyphenols: Dietary assessment and role in the prevention of
cancers. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 20:512–521.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Moussa RS, Park KC, Kovacevic Z and
Richardson DR: Ironing out the role of the cyclin-dependent kinase
inhibitor, p21 in cancer: Novel iron chelating agents to target p21
expression and activity. Free Radic Biol Med. 133:276–294. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Harper JW, Adami GR, Wei N, Keyomarsi K
and Elledge SJ: The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent
inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 75:805–816. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ogryzko VV, Wong P and Howard BH: WAF1
retards S-phase progression primarily by inhibition of
cyclin-dependent kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 17:4877–4882. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Newton K, Wickliffe KE, Dugger DL,
Maltzman A, Roose-Girma M, Dohse M, Kőműves L, Webster JD and Dixit
VM: Cleavage of RIPK1 by caspase-8 is crucial for limiting
apoptosis and necroptosis. Nature. 574:428–431. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Garcia PB and Attardi LD: Illuminating p53
function in cancer with genetically engineered mouse models. Semin
Cell Dev Biol. 27:74–85. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hennessy EJ: Selective inhibitors of Bcl-2
and Bcl-xL: Balancing antitumor activity with on-target toxicity.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 26:2105–2114. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|