|
1
|
Ropper AE and Ropper AH: Acute spinal cord
compression. N Eng J Med. 376:1358–1369. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Furlan JC, Sakakibara BM, Miller WC and
Krassioukov AV: Global incidence and prevalence of traumatic spinal
cord injury. Can J Neurol Sci. 40:456–464. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jain NB, Ayers GD, Peterson EN, Harris MB,
Morse L, O'Connor KC and Garshick E: Traumatic spinal cord injury
in the United States, 1993–2012. JAMA. 313:2236–2243. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Miller LE and Herbert WG: Health and
economic benefits of physical activity for patients with spinal
cord injury. Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 8:551–558. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hurlbert RJ, Hadley MN, Walters BC, Aarabi
B, Dhall SS, Gelb DE, Rozzelle CJ, Ryken TC and Theodore N:
Pharmacological therapy for acute spinal cord injury. Neurosurgery.
72 Suppl 2:S93–S105. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Herzer KR, Chen Y, Heinemann AW and
González-Fernández M: Association between time to rehabilitation
and outcomes after traumatic spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med
Rehabil. 97:1620–1627.e4. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Anwar MA, Al Shehabi TS and Eid AH:
Inflammogenesis of secondary spinal cord injury. Front Cell
Neurosci. 10:982016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huang JH, Yin XM, Xu Y, Xu CC, Lin X, Ye
FB, Cao Y and Lin FY: Systemic administration of exosomes released
from mesenchymal stromal cells attenuates apoptosis, inflammation,
and promotes angiogenesis after spinal cord injury in rats. J
Neurotrauma. 34:3388–3396. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xun C, Mamat M, Guo H, Mamati P, Sheng J,
Zhang J, Xu T, Liang W, Cao R and Sheng W: Tocotrienol alleviates
inflammation and oxidative stress in a rat model of spinal cord
injury via suppression of transforming growth factor-β. Exp Ther
Med. 14:431–438. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
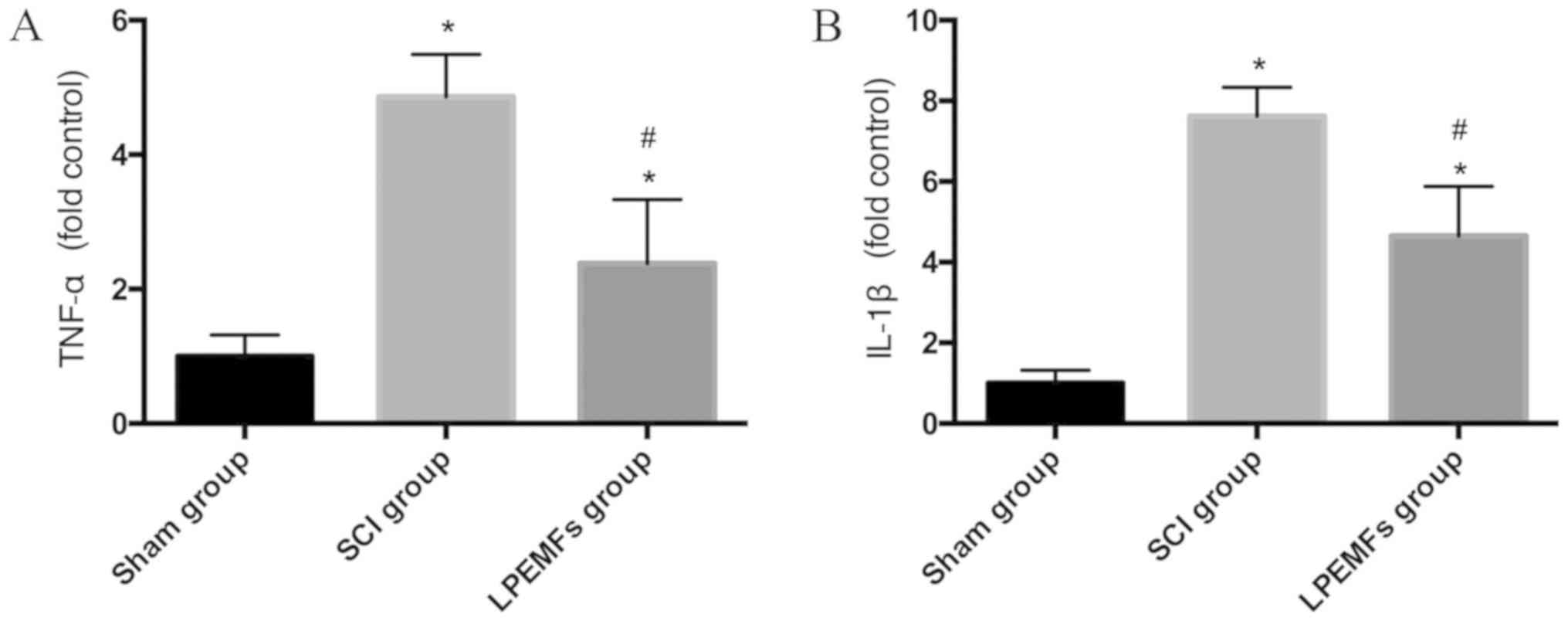
Zou J, Chen Y, Qian J and Yang H: Effect
of a low-frequency pulsed electromagnetic field on expression and
secretion of IL-1β and TNF-α in nucleus pulposus cells. J Int Med
Res. 45:462–470. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ehnert S, Fentz AK, Schreiner A, Birk J,
Wilbrand B, Ziegler P, Reumann MK, Wang H, Falldorf K and Nussler
AK: Extremely low frequency pulsed electromagnetic fields cause
antioxidative defense mechanisms in human osteoblasts via induction
of •O2 and H2O2. Sci Rep.
7:145442017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Urnukhsaikhan E, Mishig-Ochir T, Kim SC,
Park JK and Seo YK: Neuroprotective effect of low frequency-pulsed
electromagnetic fields in ischemic stroke. Appl Biochem Biotechnol.
181:1360–1371. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Capelli E, Torrisi F, Venturini L, Granato
M, Fassina L, Lupo GF and Ricevuti G: Low-frequency pulsed
electromagnetic field is able to modulate miRNAs in an experimental
cell model of Alzheimer's disease. J Healthc Eng 2017.
25302702017.
|
|
14
|
Dey S, Bose S, Kumar S, Rathore R, Mathur
R and Jain S: Extremely low frequency magnetic field protects
injured spinal cord from the microglia- and iron-induced tissue
damage. Electromagn Biol Med. 36:330–340. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
NIH (National Institutes of Health U.S.A):
Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. The National
Academies Press; Washington, DC: pp. 2462011
|
|
16
|
Zhou H, Li X, Wu Q, Li F, Fu Z, Liu C,
Liang Z, Chu T, Wang T, Lu L, et al: shRNA against PTEN promotes
neurite outgrowth of cortical neurons and functional recovery in
spinal cord contusion rats. Regen Med. 10:411–429. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
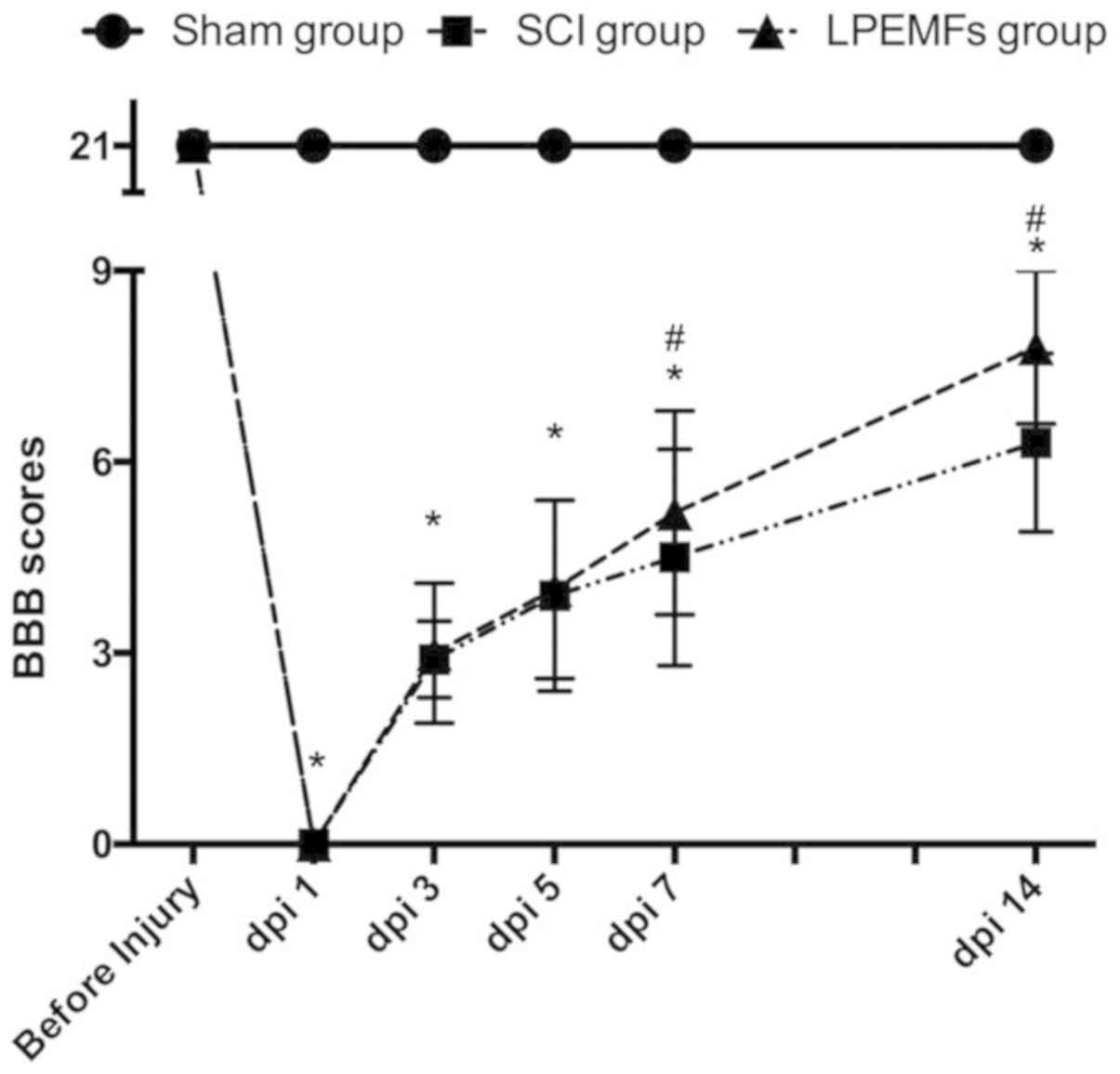
Basso DM, Beattie MS and Bresnahan JC: A
sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field
testing in rats. J Neurotrauma. 12:1–21. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wei ZJ, Zhou XH, Fan BY, Lin W, Ren YM and
Feng SQ: Proteomic and bioinformatic analyses of spinal cord
injury-induced skeletal muscle atrophy in rats. Mol Med Rep.
14:165–174. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
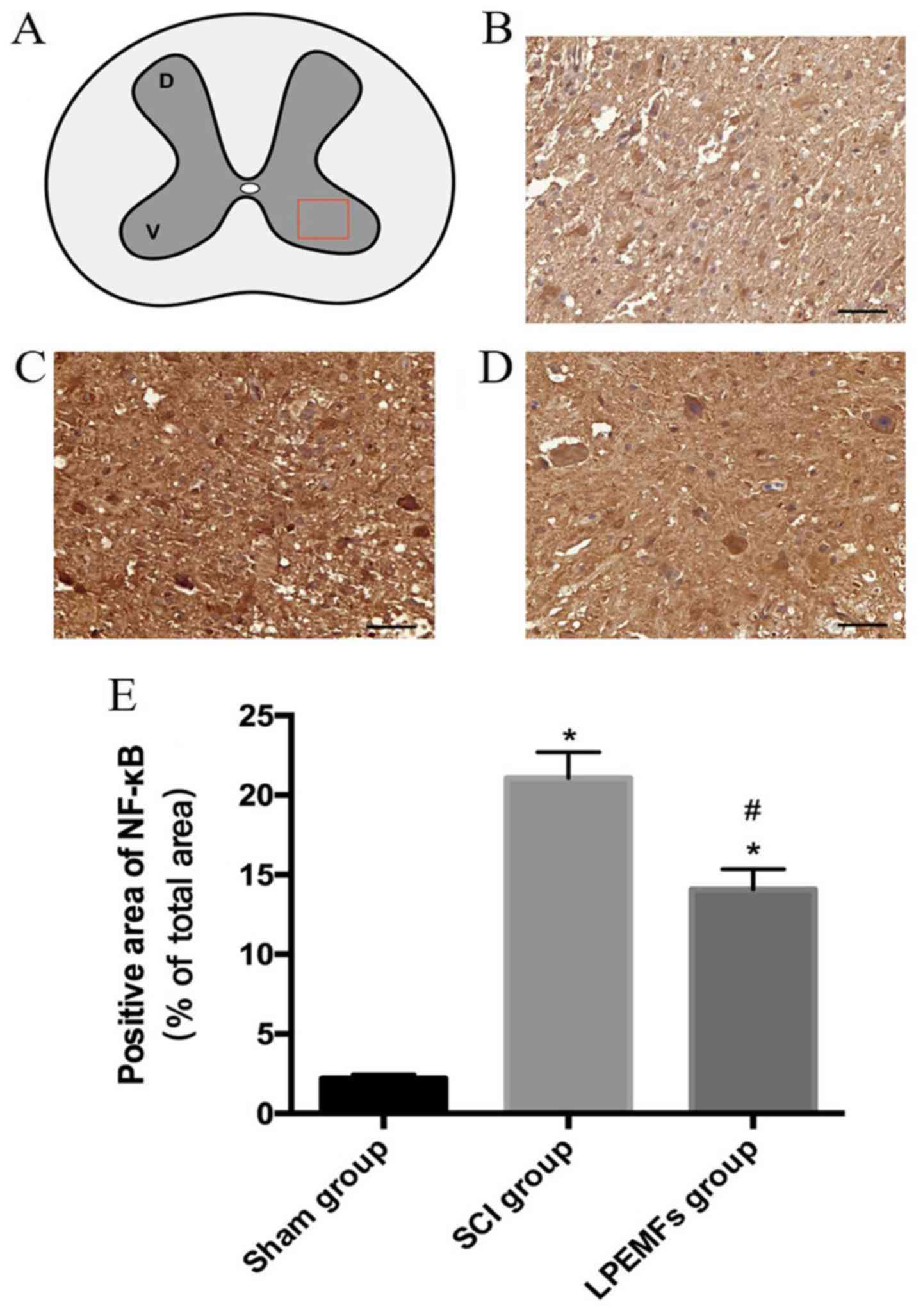
Xu L, Botchway BOA, Zhang S, Zhou J and
Liu X: Inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway by resveratrol
improves spinal cord injury. Front Neurosci. 12:6902018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ferroni L, Tocco I, De Pieri A, Menarin M,
Fermi E, Piattelli A, Gardin C and Zavan B: Pulsed magnetic therapy
increases osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells only
if they are pre-committed. Life Sci. 152:44–51. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ottani V, De Pasquale V, Govoni P, Franchi
M, Zaniol P and Ruggeri A: Effects of pulsed
extremely-low-frequency magnetic fields on skin wounds in the rat.
Bioelectromagnetics. 9:53–62. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jorgensen WA, Frome BM and Wallach C:
Electrochemical therapy of pelvic pain: Effects of pulsed
electromagnetic fields (PEMF) on tissue trauma. Eur J Surg Suppl.
83–86. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kavand H, Haghighipour N, Zeynali B,
Seyedjafari E and Abdemami B: Extremely low frequency
electromagnetic field in mesenchymal stem cells gene regulation:
Chondrogenic markers evaluation. Artif Organs. 40:929–937. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Feng SQ, Zhou XF, Rush RA and Ferguson IA:
Graft of pre-injured sural nerve promotes regeneration of
corticospinal tract and functional recovery in rats with chronic
spinal cord injury. Brain Res 1209. 40–48. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Feng SQ, Kong XH, Guo SF, Wang P, Li L,
Zhong JH and Zhou XF: Treatment of spinal cord injury with
co-grafts of genetically modified Schwann cells and fetal spinal
cord cell suspension in the rat. Neurotox Res. 7:169–177. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kjell J and Olson L: Rat models of spinal
cord injury: From pathology to potential therapies. Dis Model Mech.
9:1125–1137. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cavalli G and Dinarello CA: Suppression of
inflammation and acquired immunity by IL-37. Immunol Rev.
281:179–190. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ni H, Jin W, Zhu T, Wang J, Yuan B, Jiang
J, Liang W and Ma Z: Curcumin modulates TLR4/NF-κB inflammatory
signaling pathway following traumatic spinal cord injury in rats. J
Spinal Cord Med. 38:199–206. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Varani K, De Mattei M, Vincenzi F, Gessi
S, Merighi S, Pellati A, Ongaro A, Caruso A, Cadossi R and Borea
PA: Characterization of adenosine receptors in bovine chondrocytes
and fibroblast-like synoviocytes exposed to low frequency low
energy pulsed electromagnetic fields. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
16:292–304. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Vincenzi F, Targa M, Corciulo C, Gessi S,
Merighi S, Setti S, Cadossi R, Goldring MB, Borea PA and Varani K:
Pulsed electromagnetic fields increased the anti-inflammatory
effect of A2A and A3 adenosine receptors in
human T/C-28a2 chondrocytes and hFOB 1.19 osteoblasts. PLoS One.
8:e655612013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ongaro A, Varani K, Masieri FF, Pellati A,
Massari L, Cadossi R, Vincenzi F, Borea PA, Fini M, Caruso A and De
Mattei M: Electromagnetic fields (EMFs) and adenosine receptors
modulate prostaglandin E(2) and cytokine release in human
osteoarthritic synovial fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 227:2461–2469.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Visavadiya NP, Patel SP, VanRooyen JL,
Sullivan PG and Rabchevsky AG: Cellular and subcellular oxidative
stress parameters following severe spinal cord injury. Redox Biol.
8:59–67. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang Y, Bazhin AV, Werner J and
Karakhanova S: Reactive oxygen species in the immune system. Int
Rev Immunol. 32:249–270. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
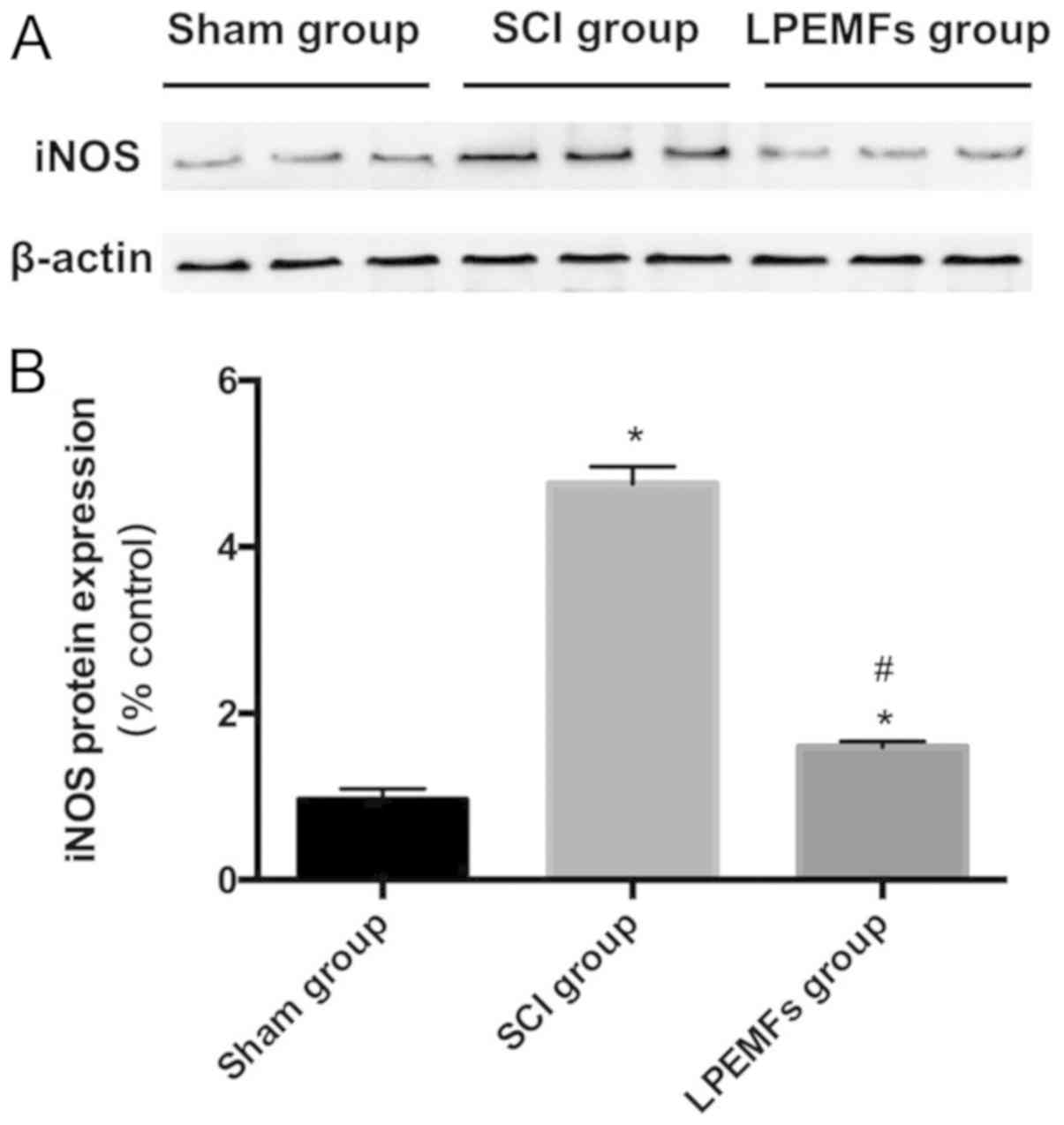
Sheng W, Zong Y, Mohammad A, Ajit D, Cui
J, Han D, Hamilton JL, Simonyi A, Sun AY, Gu Z, et al:
Pro-inflammatory cytokines and lipopolysaccharide induce changes in
cell morphology, and upregulation of ERK1/2, iNOS and
sPLA2-IIA expression in astrocytes and microglia. J
Neuroinflammation. 8:1212011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang Q, Chen Q, Ding Q, Yang Q, Peng Y, Lu
Y, Deng J and Xiong L: Sevoflurane postconditioning attenuates
spinal cord reperfusion injury through free radicals-mediated
up-regulation of antioxidant enzymes in rabbits. J Surg Res.
169:292–300. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vincenzi F, Ravani A, Pasquini S, Merighi
S, Gessi S, Setti S, Cadossi R, Borea PA and Varani K: Pulsed
electromagnetic field exposure reduces Hypoxia and inflammation
damage in neuron-like and microglial cells. J Cell Physiol.
232:1200–1208. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jacquier-Sarlin MR, Fuller K, Dinh-Xuan
AT, Richard MJ and Polla BS: Protective effects of hsp70 in
inflammation. Experientia. 50:1031–1038. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sevin M, Girodon F, Garrido C and de
Thonel A: HSP90 and HSP70: Implication in inflammation processes
and therapeutic approaches for myeloproliferative neoplasms.
Mediators Inflamm 2015. 9702422015.
|
|
39
|
Shabbir A, Bianchetti E, Cargonja R,
Petrovic A, Mladinic M, Pilipović K and Nistri A: Role of HSP70 in
motoneuron survival after excitotoxic stress in a rat spinal cord
injury model in vitro. Eur J Neurosci. 42:3054–3065. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|