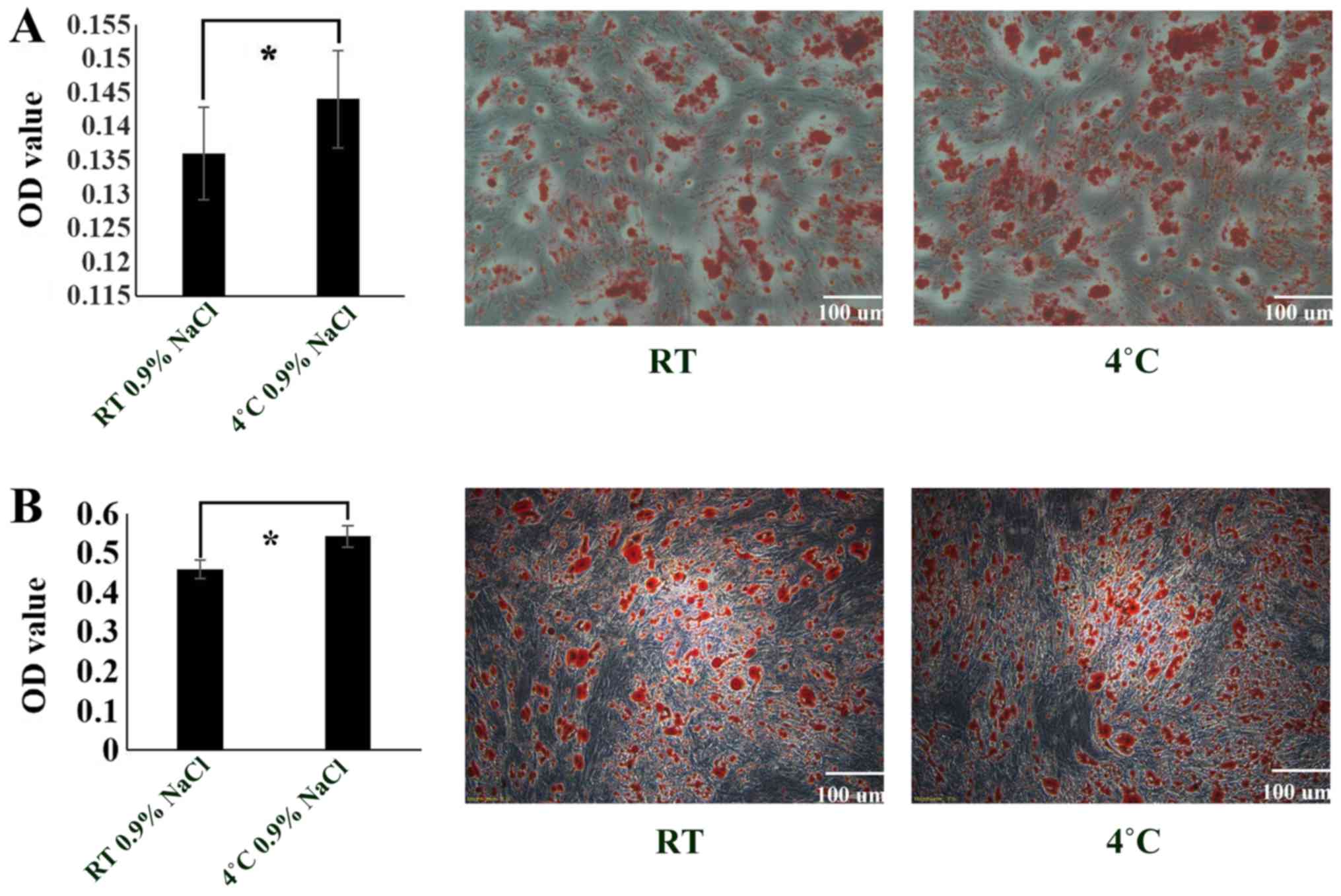
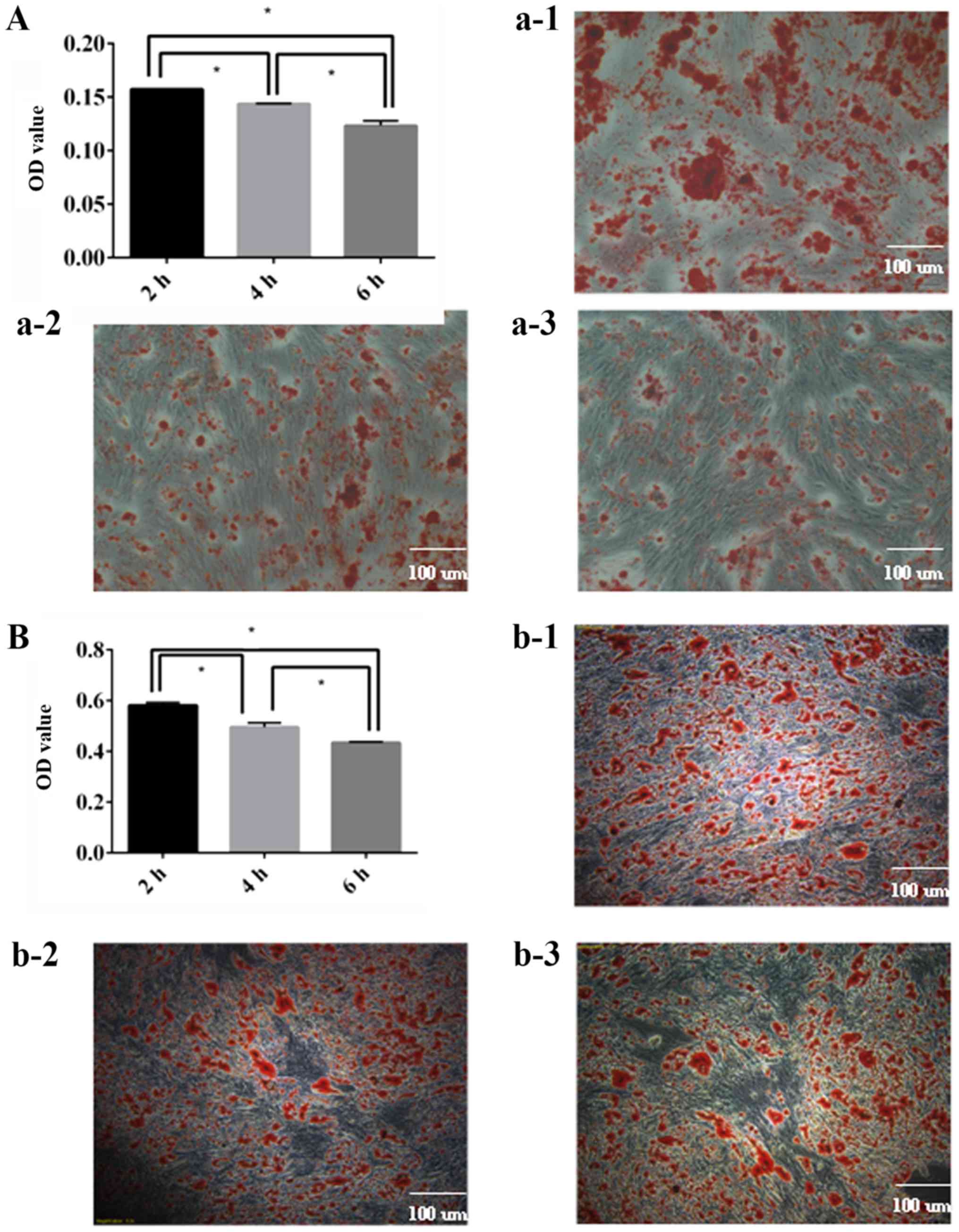
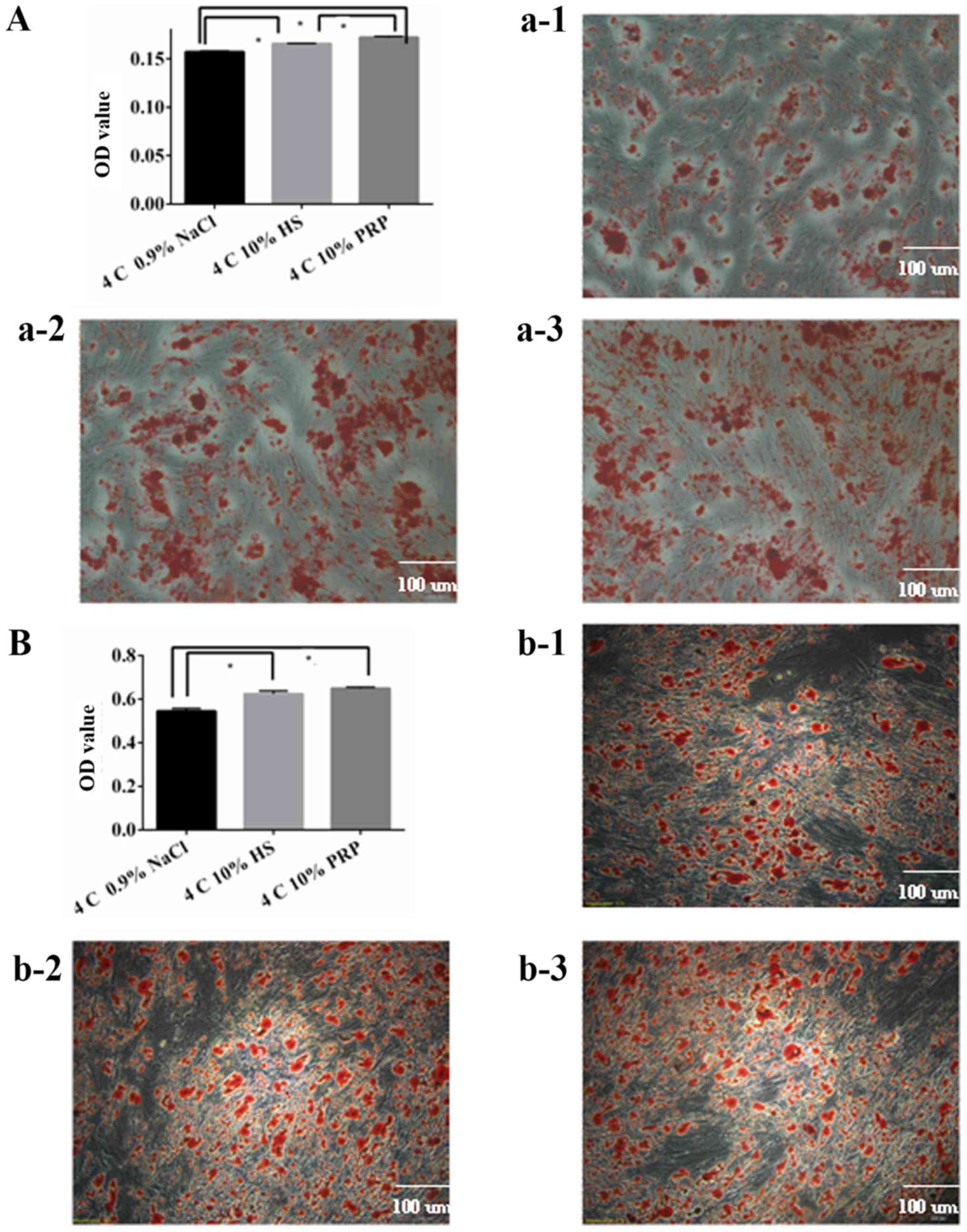
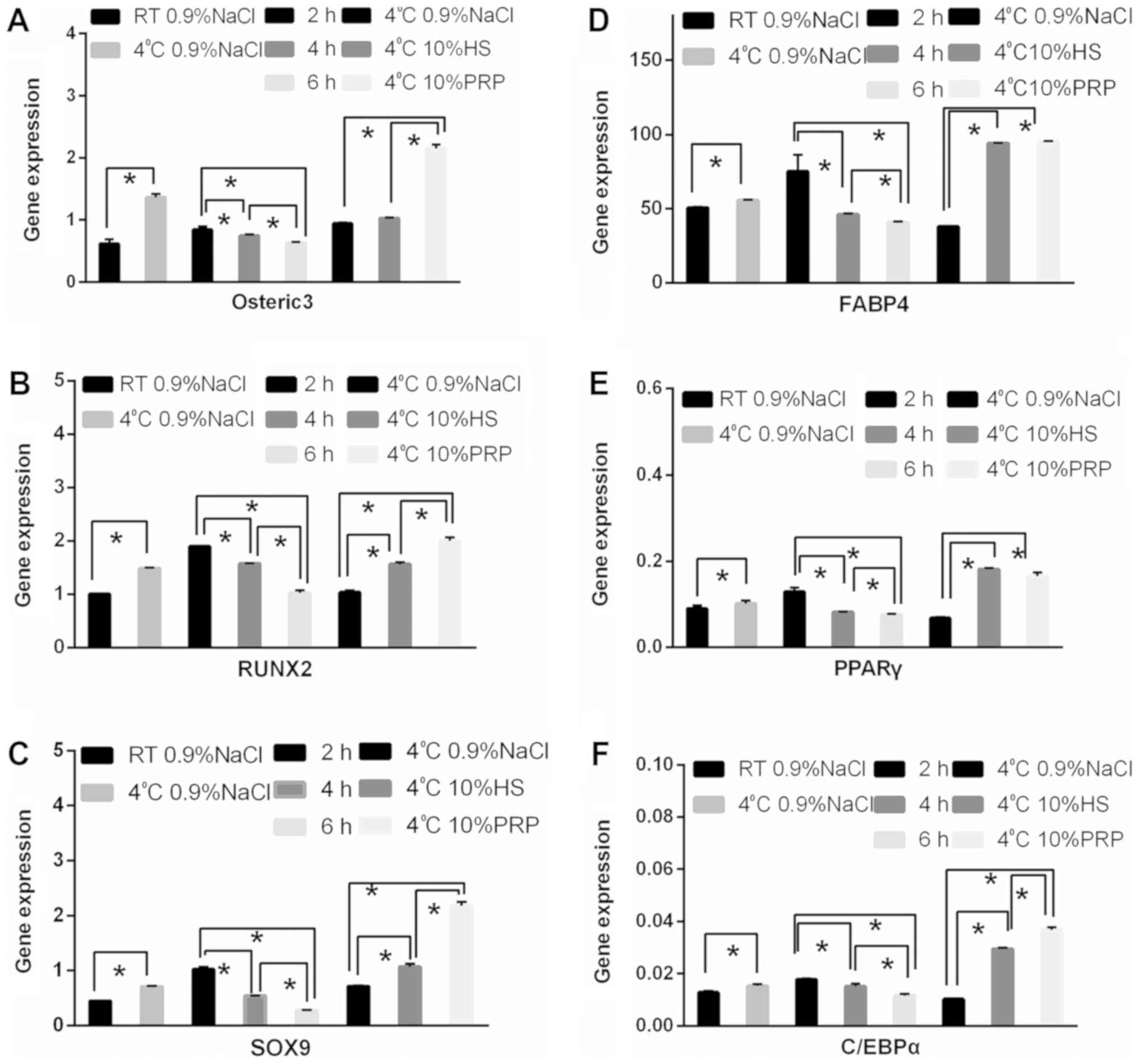
|
1
|
Gimble JM, Katz AJ and Bunnell BA:
Adipose-derived stem cell for regenerative medicine. Circ Res.
100:1249–1260. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bora P and Majumdar AS: Adipose
tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction in regenerative medicine:
A brief review on biology and translation. Stem Cell Res Ther.
8:1452017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gimble JM: Adipose tissue-derived
therapeutics. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 3:705–713. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Baer PC and Geiger H: Adipose-derived
mesenchymal stromal/stem cell: Tissue localization,
characterization, and heterogeneity. Stem Cells Int 2012.
8126932012.
|
|
5
|
Qiu X, Fandel TM, Ferretti L, Albersen M,
Orabi H, Zhang H, Lin G, Lin CS, Schroeder T and Lue TF: Both
immediate and delayed intracavernous injection of autologous
adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction enhances recovery of
erectile function in a rat model of cavernous nerve injury. Eur
Urol. 62:720–727. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lin G, Garcia M, Ning H, Banie L, Guo YL,
Lue TF and Lin CS: Defining stem and progenitor cell within adipose
tissue. Stem Cells Dev. 17:1053–1063. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tobita M, Orbay H and Mizuno H:
Adipose-derived stem cell: Current findings and future
perspectives. Discov Med. 11:160–170. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gonda K, Shigeura T, Sato T, Matsumoto D,
Suga H, Inoue K, Aoi N, Kato H, Sato K, Murase S, et al: Preserved
proliferative capacity and multipotency of human adipose-derived
stem cell after long-term cryopreservation. Plast Reconstr Surg.
121:401–410. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gonzalez-Fernandez ML, Perez-Castrillo S,
Ordas-Fernandez P, Lopez-Gonzalez ME, Colaco B and Villar-Suarez V:
Study on viability and chondrogenic differentiation of
cryopreserved adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cell for
future use in regenerative medicine. Cryobiology. 71:256–263. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Matsumoto D, Shigeura T, Sato K, Inoue K,
Suga H, Kato H, Aoi N, Murase S, Gonda K and Yoshimura K:
Influences of preservation at various temperatures on liposuction
aspirates. Plast Reconstr Surg. 120:1510–1517. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Saragusty J and Arav A: Current progress
in oocyte and embryo cryopreservation by slow freezing and
vitrification. Reproduction. 141:1–19. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Saragusty J, Gacitua H, Rozenboim I and
Arav A: Protective effects of iodixanol during bovine sperm
cryopreservation. Theriogenology. 71:1425–1432. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bunnell BA, Flaat M, Gagliardi C, Patel B
and Ripoll C: Adipose-derived stem cell: Isolation, expansion and
differentiation. Methods. 45:115–120. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang F, Ren H, Shao X, Zhuang C, Chen Y
and Qi N: Preservation media, durations and cell concentrations of
short-term storage affect key features of human adipose-derived
mesenchymal stem cells for therapeutic application. PeerJ.
5:e33012017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Higman MA, Port JD, Beauchamp NJ Jr and
Chen AR: Reversible leukoencephalopathy associated with re-infusion
of DMSO preserved stem cell. Bone Marrow Transplant. 26:797–800.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu Y, Zhou Y, Feng H, Ma GE and Ni Y:
Injectable tissue-engineered bone composed of human adipose-derived
stromal cell and platelet-rich plasma. Biomaterials. 29:3338–3345.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shafaei H, Esmaeili A, Mardani M, Razavi
S, Hashemibeni B, Nasr-Esfahani MH, Shiran MB and Esfandiari E:
Effects of human placental serum on proliferation and morphology of
human adipose tissue-derived stem cell. Bone Marrow Transplant.
46:1464–1471. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jalowiec JM, D'Este M, Bara JJ, Denom J,
Menzel U, Alini M, Verrier S and Herrmann M: An in vitro
investigation of platelet-rich plasma-gel as a cell and growth
factor delivery vehicle for tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part C
Methods. 22:49–58. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Weibrich G, Kleis WK, Hafner G and Hitzler
WE: Growth factor levels in platelet-rich plasma and correlations
with donor age, sex, and platelet count. J Craniomaxillofac Surg.
30:97–102. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Freymann U, Degrassi L, Kruger JP,
Metzlaff S, Endres M and Petersen W: Effect of serum and
platelet-rich plasma on human early or advanced degenerative
meniscus cells. Connect Tissue Res. 58:509–519. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bura A, Planat-Benard V, Bourin P,
Silvestre JS, Gross F, Grolleau JL, Saint-Lebese B, Peyrafitte JA,
Fleury S, Gadelorge M, et al: Phase I trial: The use of autologous
cultured adipose-derived stroma/stem cell to treat patients with
non-revascularizable critical limb ischemia. Cytotherapy.
16:245–257. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Guo X, Li S, Ji Q, Lian R and Chen J:
Enhanced viability and neural differential potential in poor
post-thaw hADSCs by agarose multi-well dishes and spheroid culture.
Hum Cell. 28:175–189. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gu H, Guo F, Zhou X, Gong L, Zhang Y, Zhai
W, Chen L, Cen L, Yin S, Chang J and Cui L: The stimulation of
osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cell by
ionic products from akermanite dissolution via activation of the
ERK pathway. Biomaterials. 32:7023–7033. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang J, Ye Y, Tian H, Yang S, Jin X, Tong
W and Zhang Y: In vitro osteogenesis of human adipose-derived stem
cell by coculture with human umbilical vein endothelial cell.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 412:143–149. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Visweswaran M, Schiefer L, Arfuso F,
Dilley RJ, Newsholme P and Dharmarajan A: Wnt antagonist secreted
frizzled-related protein 4 upregulates adipogenic differentiation
in human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell. PLoS One.
10:e1180052015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Li HX, Luo X, Liu RX, Yang YJ and Yang GS:
Roles of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in adipogenic differentiation
potential of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 291:116–124. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Samuel S, Ahmad RE, Ramasamy TS,
Karunanithi P, Naveen SV, Murali MR, Abbas AA and Kamarul T:
Platelet-rich concentrate in serum free medium enhances osteogenic
differentiation of bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stromal
cell. PeerJ. 4:e23472016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bunnell BA, Estes BT, Guilak F and Gimble
JM: Differentiation of adipose stem cell. Methods Mol Biol.
456:155–171. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang X, Spandidos A, Wang H and Seed B:
PrimerBank: A PCR primer database for quantitative gene expression
analysis, 2012 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:D1144–D1149. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Frese L, Dijkman PE and Hoerstrup SP:
Adipose tissue-derived stem cells in regenerative medicine.
Transfus Med Hemother. 43:268–274. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Martínez-González I, Cruz MJ, Moreno R,
Morell F, Muñoz X and Aran JM: Human mesenchymal stem cell resolve
airway inflammation, hyperreactivity, and histopathology in a mouse
model of occupational asthma. Stem Cells Dev. 23:2352–2363. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Won CH, Yoo HG, Kwon OS, Sung MY, Kang YJ,
Chung JH, Park BS, Sung JH, Kim WS and Kim KH: Hair growth
promoting effects of adipose tissue-derived stem cell. J Dermatol
Sci. 57:134–137. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hernández-Bule ML, Martínez-Botas J,
Trillo MÁ, Paíno CL and Úbeda A: Antiadipogenic effects of
subthermal electric stimulation at 448 kHz on differentiating human
mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Med Rep. 13:3895–3903. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rumiński S, Ostrowska B, Jaroszewicz J,
Skirecki T, Włodarski K, Święszkowski W and Lewandowska-Szumieł M:
Three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone-based scaffolds provide
an advantageous environment for osteogenic differentiation of human
adipose-derived stem cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 12:e473–e485.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Benazzo F, Botta L, Scaffino MF, Caliogna
L, Marullo M, Fusi S and Gastaldi G: Trabecular titanium can induce
in vitro osteogenic differentiation of human adipose derived stem
cells without osteogenic factors. J Biomed Mater Res A.
102:2061–2071. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rada T, Reis RL and Gomes ME: Distinct
stem cells subpopulations isolated from human adipose tissue
exhibit different chondrogenic and osteogenic differentiation
potential. Stem Cell Rev. 7:64–76. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Smyth DC, Takenaka S, Yeung C and Richards
CD: Oncostatin M regulates osteogenic differentiation of murine
adipose-derived mesenchymal progenitor cells through a
PKCdelta-dependent mechanism. Cell Tissue Res. 360:309–319. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Regassa A, Suh M, Datar J, Chen C and Kim
WK: Fatty acids have different adipogenic differentiation
potentials in stromal vascular cells isolated from abdominal fat in
laying hens. Lipids. 52:513–522. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Nurden AT, Nurden P, Sanchez M, Andia I
and Anitua E: Platelets and wound healing. Front Biosci.
13:3532–3548. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Whitman DH, Berry RL and Green DM:
Platelet gel: An autologous alternative to fibrin glue with
applications in oral and maxillofacial surgery. J Oral Maxillofac
Surg. 55:1294–1299. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Alsousou J, Thompson M, Hulley P, Noble A
and Willett K: The biology of platelet-rich plasma and its
application in trauma and orthopaedic surgery: A review of the
literature. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 91:987–996. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nikolidakis D and Jansen JA: The biology
of platelet-rich plasma and its application in oral surgery:
Literature review. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 14:249–258. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Anitua E: Plasma rich in growth factors:
Preliminary results of use in the preparation of future sites for
implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 14:529–535.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Drago L, Bortolin M, Vassena C, Romanò CL,
Taschieri S and Del Fabbro M: Plasma components and platelet
activation are essential for the antimicrobial properties of
autologous platelet-rich plasma: An in vitro study. PLoS One.
9:e1078132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Margolis DJ, Kantor J, Santanna J, Strom
BL and Berlin JA: Effectiveness of platelet releasate for the
treatment of diabetic neuropathic foot ulcers. Diabetes Care.
24:483–488. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Josh F, Kobe K, Tobita M, Tanaka R, Suzuki
K, Ono K, Hyakusoku H and Mizuno H: Accelerated and safe
proliferation of human adipose-derived stem cell in medium
supplemented with human serum. J Nippon Med Sch. 79:444–452. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Adkins JN, Varnum SM, Auberry KJ, Moore
RJ, Angell NH, Smith RD, Springer DL and Pounds JG: Toward a human
blood serum proteome: Analysis by multidimensional separation
coupled with mass spectrometry. Mol Cell Proteomics. 1:947–955.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kobayashi T, Watanabe H, Yanagawa T,
Tsutsumi S, Kayakabe M, Shinozaki T, Higuchi H and Takagishi K:
Motility and growth of human bone-marrow mesenchymal stem cell
during ex vivo expansion in autologous serum. J Bone Joint Surg Br.
87:1426–1433. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|