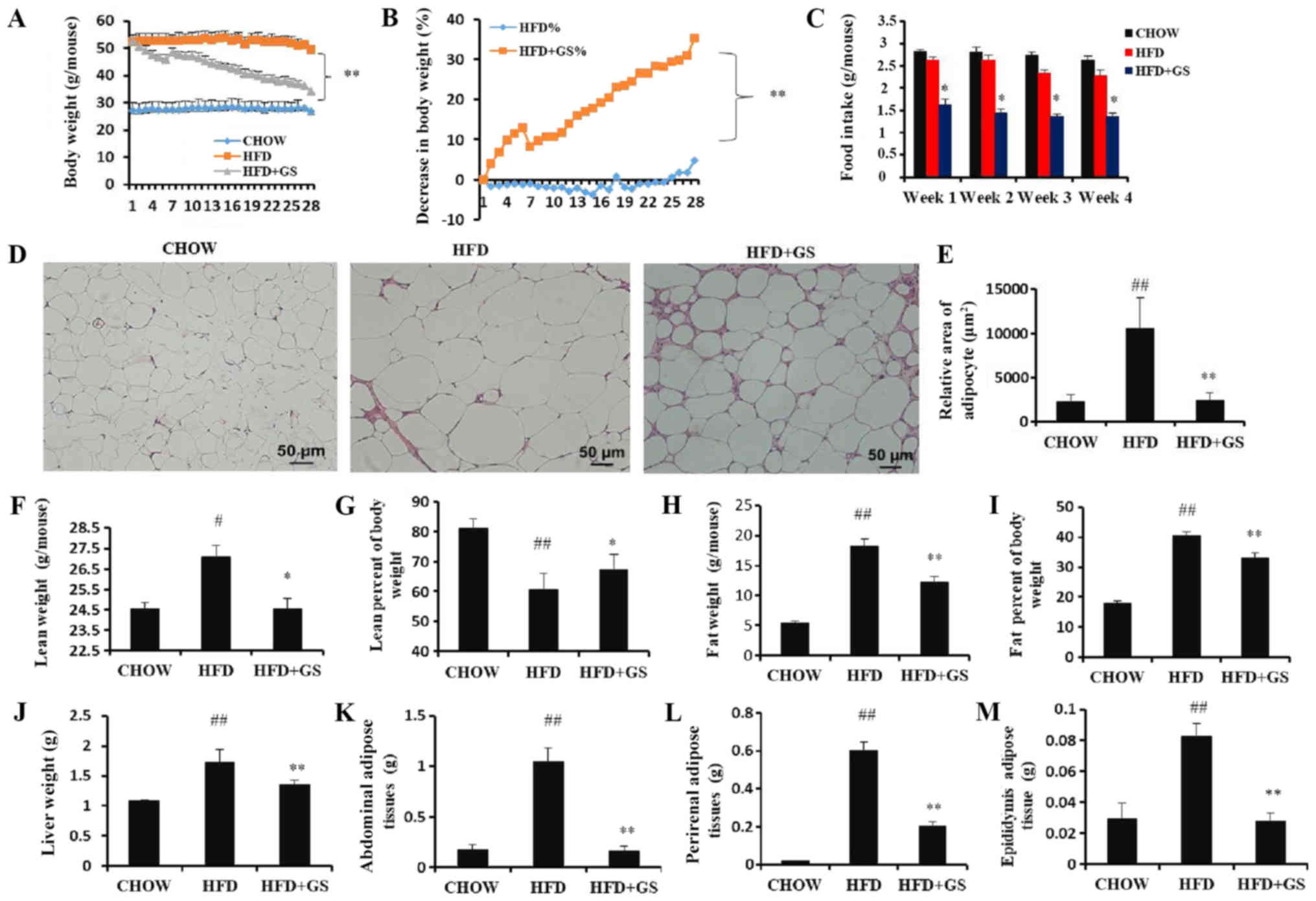
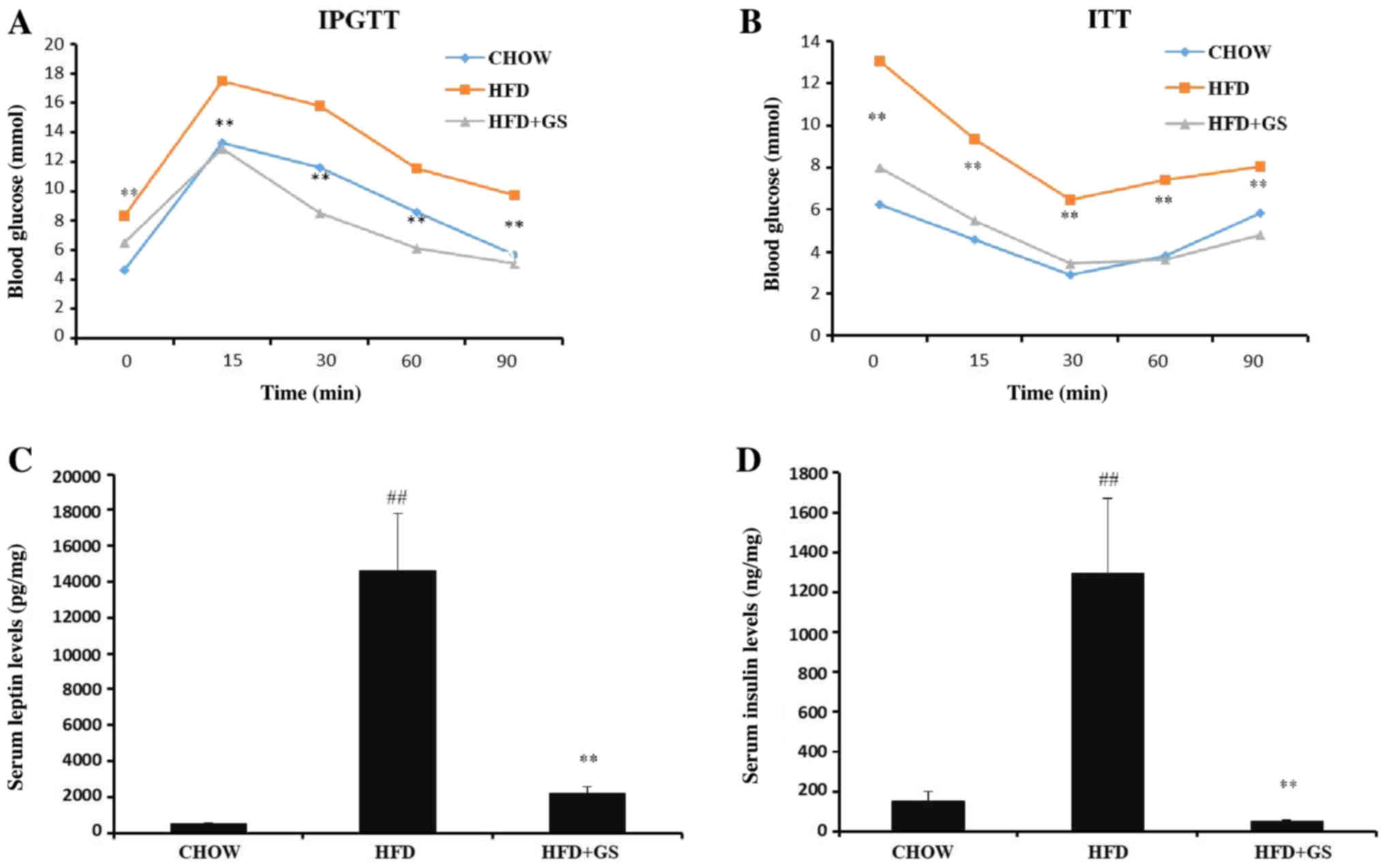
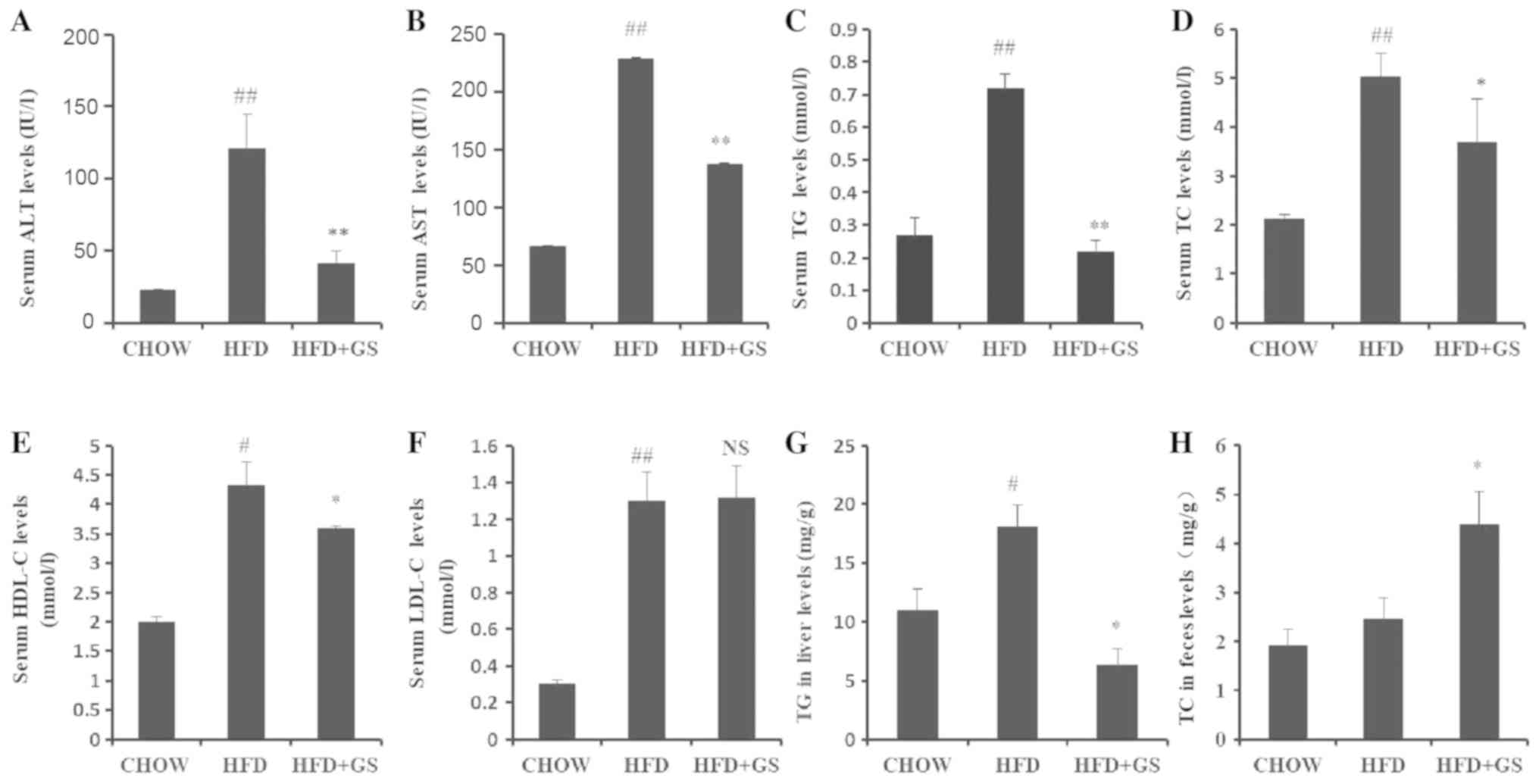
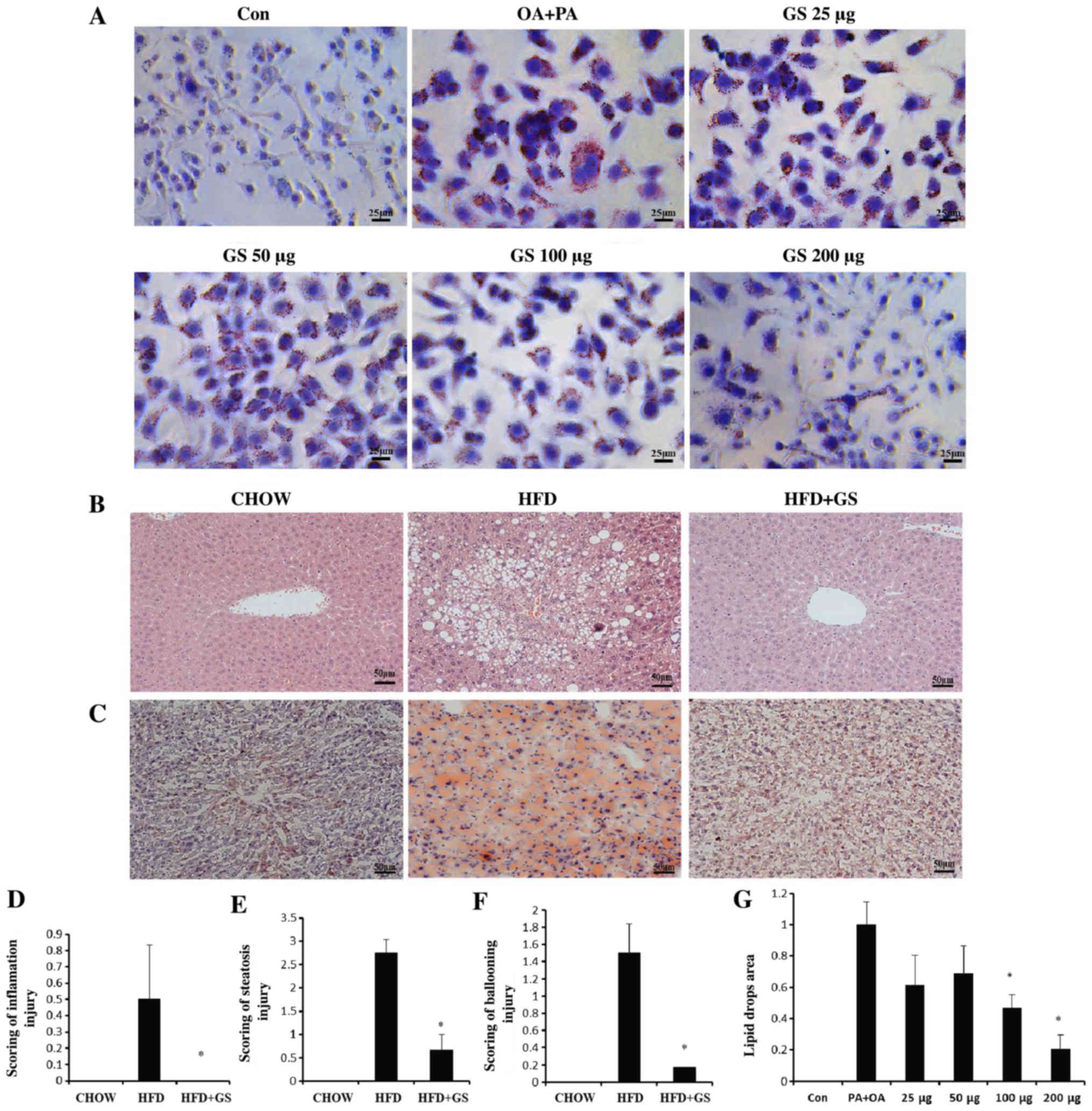
|
1
|
Kinlen D, Cody D and O'Shea D:
Complications of obesity. QJM. 111:437–443. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ahirwar R and Mondal PR: Prevalence of
obesity in India: A systematic review. Diabetes Metab Syndr.
13:318–321. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hu L, Huang X, You C, Li J, Hong K, Li P,
Wu Y, Wu Q, Wang Z, Gao R, et al: Prevalence of overweight,
obesity, abdominal obesity and obesity-related risk factors in
southern China. PLoS One. 12:e01839342017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yilmaz Y and Younossi ZM:
Obesity-associated nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Liver
Dis. 18:19–31. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fruh SM: Obesity: Risk factors,
complications, and strategies for sustainable long-term weight
management. J Am Assoc Nurse Pract. 29 (Suppl 1):S3–S14.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sáinz N, Barrenetxe J, Moreno-Aliaga MJ
and Martínez JA: Leptin resistance and diet-induced obesity:
Central and peripheral actions of leptin. Metabolism. 64:35–46.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Eseberri I, Lasa A, Miranda J, Gracia A
and Portillo MP: Potential miRNA involvement in the anti-adipogenic
effect of resveratrol and its metabolites. PLoS One.
12:e01848752017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu L, Li H, Zhou G, Lu W, Yang R, Liu H
and Yang G: DNA-binding activity of STAT3 increased in hypothalamus
of DIO mice; the reduction of STAT3 phosphorylation may facilitate
leptin signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 505:229–235. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen Y, Lu W, Jin Z, Yu J and Shi B:
Carbenoxolone ameliorates hepatic lipid metabolism and inflammation
in obese mice induced by high fat diet via regulating the
JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 74:1054982019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Habib DF, Fahmi AA, Kholousy NM, Amin AI,
Shalaby M, Ahmed MM and Shanab AMA: The role of liver in leptin
metabolism in experimental nephrotic syndrome. EXCLI J. 10:322–331.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bergmann TJ and Molinari M: Three branches
to rule them all? UPR signaling in response to chemicallyversus
misfolded proteins-induced ER stress. Biol Cell. 110:197–204. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Saito A: Physiological functions of
endoplasmic reticulum stress transducer OASIS in central nervous
system. Anat Sci Int. 89:11–20. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yilmaz E: Endoplasmic reticulum stress and
obesity. Adv Exp Med Biol. 960:261–276. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ding S, Jiang J, Zhang G, Bu Y, Zhang G
and Zhao X: Resveratrol and caloric restriction prevent hepatic
steatosis by regulating SIRT1-autophagy pathway and alleviating
endoplasmic reticulum stress in high-fat diet-fed rats. PLoS One.
12:e01835412017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kozuka C, Shimizu-Okabe C, Takayama C,
Nakano K, Morinaga H, Kinjo A, Fukuda K, Kamei A, Yasuoka A, Kondo
T, et al: Marked augmentation of PLGA nanoparticle-induced
metabolically beneficial impact of ү-oryzanol on fuel
dyshomeostasis in genetically obese-diabetic ob/ob mice. Drug
Deliv. 24:558–568. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Abenavoli L, Di Renzo L, Boccuto L,
Alwardat N, Gratteri S and De Lorenzo A: Health benefits of
Mediterranean diet in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Expert Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 12:873–881. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shin J, He M, Liu Y, Paredes S, Villanova
L, Brown K, Qiu X, Nabavi N, Mohrin M, Wojnoonski K, et al: SIRT7
represses Myc activity to suppress ER stress and prevent fatty
liver disease. Cell Rep. 5:654–665. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Henkel A and Green RM: The unfolded
protein response in fatty liver disease. Semin Liver Dis.
33:321–329. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sozio MS, Liangpunsakul S and Crabb D: The
role of lipid metabolism in the pathogenesis of alcoholic and
nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis. Semin Liver Dis. 30:378–390. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang Y, Tang C, Tian Y, Yuan H, Gao R and
Cao J: Effects of electroacupuncture combined with dietary control
on liver endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats with non-alcoholic
fatty liver disease. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 36:951–956. 2016.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li Z and Ji GE: Ginseng and obesity. J
Ginseng Res. 42:1–8. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shin BK, Kwon SW and Park JH: Chemical
diversity of ginseng saponins from Panax ginseng. J Ginseng Res.
39:287–298. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Christensen LP: Chapter 1 Ginsenosides:
Chemistry, biosynthesis, analysis, and potential health effects.
Adv Food Nutr Res. 55:1–99. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim JH: Pharmacological and medical
applications of Panax ginseng and ginsenosides: A review for use in
cardiovascular diseases. J Ginseng Res. 42:264–269. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cui ZY, Jo E, Jang HJ, Hwang HI, Lee KB,
Yoo HS, Park SJ, Jung MK, Lee YW and Jang IS: Modified ginseng
extract induces apoptosis in HepG2 cancer cells by blocking the
CXCL8-mediated Akt/Nuclear Factor-κB signaling pathway. Am J Chin
Med. 46:1645–1662. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lee JB, Yoon SJ, Lee SH, Lee MS, Jung H,
Kim TD, Yoon SR, Choi I, Kim IS, Chung SW, et al: Ginsenoside Rg3
ameliorated HFD-induced hepatic steatosis through downregulation of
STAT5-PPARү. J Endocrinol. 235:223–235. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Etou H, Sakata T, Fujimoto K, Terada K,
Yoshimatsu H, Ookuma K, Hayashi T and Arichi S: Ginsenoside-Rb1 as
a suppressor in central modulation of feeding in the rat. Nihon
Yakurigaku Zasshi. 91:9–15. 1988.(In Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hurtado-Carneiro V, Sanz C, Roncero I,
Vazquez P, Blazquez E and Alvarez E: Glucagon-Like Peptide 1
(GLP-1) can reverse AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and S6
Kinase (P70S6K) activities induced by fluctuations in glucose
levels in hypothalamic areas involved in feeding behaviour. Mol
Neurobiol. 45:348–361. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li Z and Ji GE: Ginseng and obesity. J
Ginseng Res. 42:1–8. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wu LX, Xu YY, Yang ZJ and Feng Q:
Hydroxytyrosol and olive leaf extract exert cardioprotective
effects by inhibiting GRP78 and CHOP expression. J Biomed Res.
32:371–379. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fan S, Zhang Y, Sun Q, Yu L, Li M, Zheng
B, Wu X, Yang B, Li Y and Huang C: Extract of okra lowers blood
glucose and serum lipids in high-fat diet-induced obese C57BL/6
mice. J Nutr Biochem. 25:702–709. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gao J, Bai H, Li Q, Li J, Wan F, Tian M,
Li Y, Song Y, Zhang J and Si Y: In vitro investigation of
the mechanism underlying the effect of ginsenoside on the
proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells subjected to
oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion. Int J Mol Med. 41:353–363.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Luo L, Yin L, Wang D, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Li
F, Fang J, Chen H, Fan S and Huang C: Ginkgolide B lowers body
weight and ameliorates hepatic steatosis in high-fat diet-induced
obese mice correlated with pregnane X receptor activation. RSC Adv.
7:37858–37866. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Arif A, Terenzi F, Potdar AA, Jia J, Sacks
J, China A, Halawani D, Vasu K, Li X, Brown JM, et al: EPRS is a
critical mTORC1-S6K1 effector that influences adiposity in mice.
Nature. 542:357–361. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, Behling
C, Contos MJ, Cummings OW, Ferrell LD, Liu YC, Torbenson MS,
Unalp-Arida A, et al: Design and validation of a histological
scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology.
41:1313–1321. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
la Fuente FP, Quezada L, Sepúlveda C,
Monsalves-Alvarez M, Rodríguez JM, Sacristán C, Chiong M, Llanos M,
Espinosa A and Troncoso R: Exercise regulates lipid droplet
dynamics in normal and fatty liver. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell
Biol Lipids. 1864:1585192019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gerlini R, Berti L, Darr J, Lassi M,
Brandmaier S, Fritsche L, Scheid F, Böhm A, Königsrainer A,
Grallert H, et al: Glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity define
adipocyte transcriptional programs in human obesity. Mol Metab.
18:42–50. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Coccia F, Testa M, Guarisco G, Di
Cristofano C, Silecchia G, Leonetti F, Gastaldelli A and Capoccia
D: Insulin resistance, but not insulin response, during oral
glucose tolerance test (OGTT) is associated to worse histological
outcome in obese NAFLD. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. Aug 10–2019.doi:
10.1016/j.numecd.2019.08.001 (Epub ahead of print). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rosenzweig T, Skalka N, Rozenberg K,
Elyasiyana U, Pinkusb A, Greenb B, Stanevskyb M and Drori E: Red
wine and wine pomace reduced the development of insulin resistance
and liver steatosis in HFD-fed mice. J Funct Foods. 34:379–389.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Garg N, Thakur S, McMahan CA and Adamo ML:
High fat diet induced insulin resistance and glucose intolerance
are gender-specific in IGF-1R heterozygous mice. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 413:476–480. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Loftus TM, Maggs DG and Lane MD: The
adipose tissue/central nervous system axis. Diabetologia. 40 (Suppl
3):B16–B20. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Svensson AM, Hellerstrom C and Jansson L:
Diet-induced obesity and pancreatic islet blood flow in the rat: A
preferential increase in islet blood perfusion persists after
withdrawal of the diet and normalization of body weight. J
Endocrinol. 151:507–511. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zakrzewska KE, Cusin I, Stricker-Krongrad
A, Boss O, Ricquier D, Jeanrenaud B and Rohner-Jeanrenaud F:
Induction of obesity and hyperleptinemia by central glucocorticoid
infusion in the rat. Diabetes. 48:365–370. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Strader AD, Reizes O, Woods SC, Benoit SC
and Seeley RJ: Mice lacking the syndecan-3 gene are resistant to
diet-induced obesity. J Clin Invest. 114:1354–1360. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Müller C, Gardemann A, Keilhoff G, Peter
D, Wiswedel I and Schild L: Prevention of free fatty acid-induced
lipid accumulation, oxidative stress, and cell death in primary
hepatocyte cultures by a Gynostemma pentaphyllum extract.
Phytomedicine. 19:395–401. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sheng L, Cho KW, Zhou Y, Shen H and Rui L:
Lipocalin 13 protein protects against hepatic steatosis by both
inhibiting lipogenesis and stimulating fatty acid β-oxidation. J
Biol Chem. 286:38128–38135. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gao Q, Jia Y, Yang G, Zhang X, Boddu PC,
Petersen B, Narsingam S, Zhu YJ, Thimmapaya B, Kanwar YS and Reddy
JK: PPARα-deficient ob/ob obese mice become more obese and manifest
severe hepatic steatosis due to decreased fatty acid oxidation. Am
J Pathol. 185:1396–1408. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Takagi K, Saito H and Tsuchiya M: Effect
of panax ginseng root on spontaneous movement and exercise in mice.
Jpn J Pharmacol. 24:41–48. 1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Watanabe H, Ohta H, Imamura L, Asakura W,
Matoba Y and Matsumoto K: Effect of Panax ginseng on age-related
changes in the spontaneous motor activity and dopaminergic nervous
system in the rat. Jpn J Pharmacol. 55:51–56. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lee J, Liu J, Feng X, Salazar Hernández
MA, Mucka P, Ibi D, Choi JW and Ozcan U: Withaferin A is a leptin
sensitizer with strong antidiabetic properties in mice. Nat Med.
22:1023–1032. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Xu Y, Ding J, An JN, Qu YK, Li X, Ma XP,
Zhang YM, Dai GJ and Lin N: Effect of the Interaction of Veratrum
Nigrum with Panax ginseng on estrogenic activity in vivo and in
vitro. Sci Rep. 6:269242016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zheng M, Xin Y, Li Y, Xu F, Xi X, Guo H,
Cui X, Cao H, Zhang X and Han C: Ginsenosides: A potential
neuroprotective agent. Biomed Res Int. 2018:81743452018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Riaz M, Rahman NU, Zia-Ul-Haq M, Jaffar
HZE and Manea R: Ginseng: A dietary supplement as immune-modulator
in various diseases. Trends Food Sci Technol. 83:12–30. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Kim KH, Lee D, Lee HL, Kim CE, Jung K and
Kang KS: Beneficial effects of Panax ginseng for the treatment and
prevention of neurodegenerative diseases: Past findings and future
directions. J Ginseng Res. 42:239–247. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Chen T, Li B, Qiu Y, Qiu Z and Qu P:
Functional mechanism of Ginsenosides on tumor growth and
metastasis. Saudi J Biol Sci. 25:917–922. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kim JH, Yi YS, Kim MY and Cho JY: Role of
ginsenosides, the main active components of Panax ginseng, in
inflammatory responses and diseases. J Ginseng Res. 41:435–443.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhang L, Virgous C and Si H: Ginseng and
obesity: Observations and understanding in cultured cells, animals
and humans. J Nutr Biochem. 44:1–10. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Majumdar SK, Shaw GK, O'Gorman P and
Thomson AD: The effect of naftidrofuryl on ethanol-induced liver
damage in chronic alcoholic patients. Drug Alcohol Depend.
10:135–142. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Musialik J, Suchecka W, Klimacka-Nawrot E,
Petelenz M, Hartman M and Błońska-Fajfrowska B: Taste and appetite
disorders of chronic hepatitis C patients. Eur J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 24:1400–1405. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kim HG, Jang SS, Lee JS, Kim HS and Son
CG: Panax ginseng Meyer prevents radiation-induced liver injury via
modulation of oxidative stress and apoptosis. J Ginseng Res.
41:159–168. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Niranjana Murthy H, Dandin VS and Yoeup
Paek K: Hepatoprotective activity of ginsenosides from Panax
ginseng adventitious roots against carbon tetrachloride treated
hepatic injury in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 158:442–446. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Chen W, Balland E and Cowley MA:
Hypothalamic insulin resistance in obesity: Effects on glucose
homeostasis. Neuroendocrinology. 104:364–381. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Hofmann A, Peitzsch M, Brunssen C, Mittag
J, Jannasch A, Frenzel A, Brown N, Weldon SM, Eisenhofer G,
Bornstein SR and Morawietz H: Elevated steroid hormone production
in the db/db mouse model of obesity and type 2 diabetes. Horm Metab
Res. 49:43–49. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Chen HJ and Liu J: Actein ameliorates
hepatic steatosis and fibrosis in high fat diet-induced NAFLD by
regulation of insulin and leptin resistant. Biomed Pharmacother.
97:1386–1396. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Crujeiras AB, Carreira MC, Cabia B,
Andrade S, Amil M and Casanueva FF: Leptin resistance in obesity:
An epigenetic landscape. Life Sci. 140:57–63. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Adam CL and Findlay PA: Decreased
blood-brain leptin transfer in an ovine model of obesity and weight
loss: Resolving the cause of leptin resistance. Int J Obes (Lond).
34:980–988. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Myers MG Jr, Leibel RL, Seeley RJ and
Schwartz MW: Obesity and leptin resistance: Distinguishing cause
from effect. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 21:643–651. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Ibars M, Ardid-Ruiz A, Suárez M, Muguerza
B, Bladé C and Aragonès G: Proanthocyanidins potentiate
hypothalamic leptin/STAT3 signalling and Pomc gene expression in
rats with diet-induced obesity signalling. Int J Obes (Lond).
41:129–136. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Contreras C, Fondevila MF and López M:
Hypothalamic GRP78, a new target against obesity? Adipocyte.
7:63–66. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Raptis L, Arulanandam R, Geletu M and
Turkson J: The R(h)oads to Stat3: Stat3 activation by the Rho
GTPases. Exp Cell Res. 317:1787–1795. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Koga S, Kojima A, Ishikawa C, Kuwabara S,
Arai K and Yoshiyama Y: Effects of diet-induced obesity and
voluntary exercise in a tauopathy mouse model: Implications of
persistent hyperleptinemia and enhanced astrocytic leptin receptor
expression. Neurobiol Dis. 71:180–192. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Liu J, Lee J, Salazar Hernandez MA,
Mazitschek R and Ozcan U: Treatment of Obesity with Celastrol.
Cell. 161:999–1011. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Sahin-Efe A, Polyzos SA, Dincer F,
Zaichenko L, McGovern R, Schneider B and Mantzoros CS:
Intracellular leptin signaling following effective weight loss.
Metabolism. 64:888–895. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Scarpace PJ, Matheny M and Shek EW:
Impaired leptin signal transduction with age-related obesity.
Neuropharmacology. 39:1872–1879. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Scarpace PJ and Tümer N: Peripheral and
hypothalamic leptin resistance with age-related obesity. Physiol
Behav. 74:721–727. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Scarpace PJ, Matheny M and Tümer N:
Hypothalamic leptin resistance is associated with impaired leptin
signal transduction in aged obese rats. Neuroscience.
104:1111–1117. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Oakes SA and Papa FR: The role of
endoplasmic reticulum stress in human pathology. Annu Rev Pathol.
10:173–194. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Schwarz DS and Blower MD: The endoplasmic
reticulum: Structure, function and response to cellular signaling.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:79–94. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Ye Z, Liu G, Guo J and Su Z: Hypothalamic
endoplasmic reticulum stress as a key mediator of obesity-induced
leptin resistance. Obes Rev. 19:770–785. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Tsuchiya Y, Saito M and Kohno K:
Pathogenic mechanism of diabetes development due to dysfunction of
unfolded protein response. Yakugaku Zasshi. 136:817–825. 2016.(In
Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Joe Y, Kim S, Kim HJ, Park J, Chen Y, Park
HJ, Jekal SJ, Ryter SW, Kim UH and Chung HT: FGF21 induced by
carbon monoxide mediates metabolic homeostasisviathe PERK/ATF4
pathway. FASEB J. 32:2630–2643. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Cai M, Wang H, Li JJ, Zhang YL, Xin L, Li
F and Lou SJ: The signaling mechanisms of hippocampal endoplasmic
reticulum stress affecting neuronal plasticity-related protein
levels in high fat diet-induced obese rats and the regulation of
aerobic exercise. Brain Behav Immun. 57:347–359. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Wang D, Lao L, Pang X, Qiao Q, Pang L,
Feng Z, Bai F, Sun X, Lin X and Wei J: Asiatic acid from Potentilla
chinensis alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver by regulating
endoplasmic reticulum stress and lipid metabolism. Int
Immunopharmacol. 65:256–267. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Fujii J, Homma T, Kobayashi S and Seo HG:
Mutual interaction between oxidative stress and endoplasmic
reticulum stress in the pathogenesis of diseases specifically
focusing on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Biol Chem.
9:1–15. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|