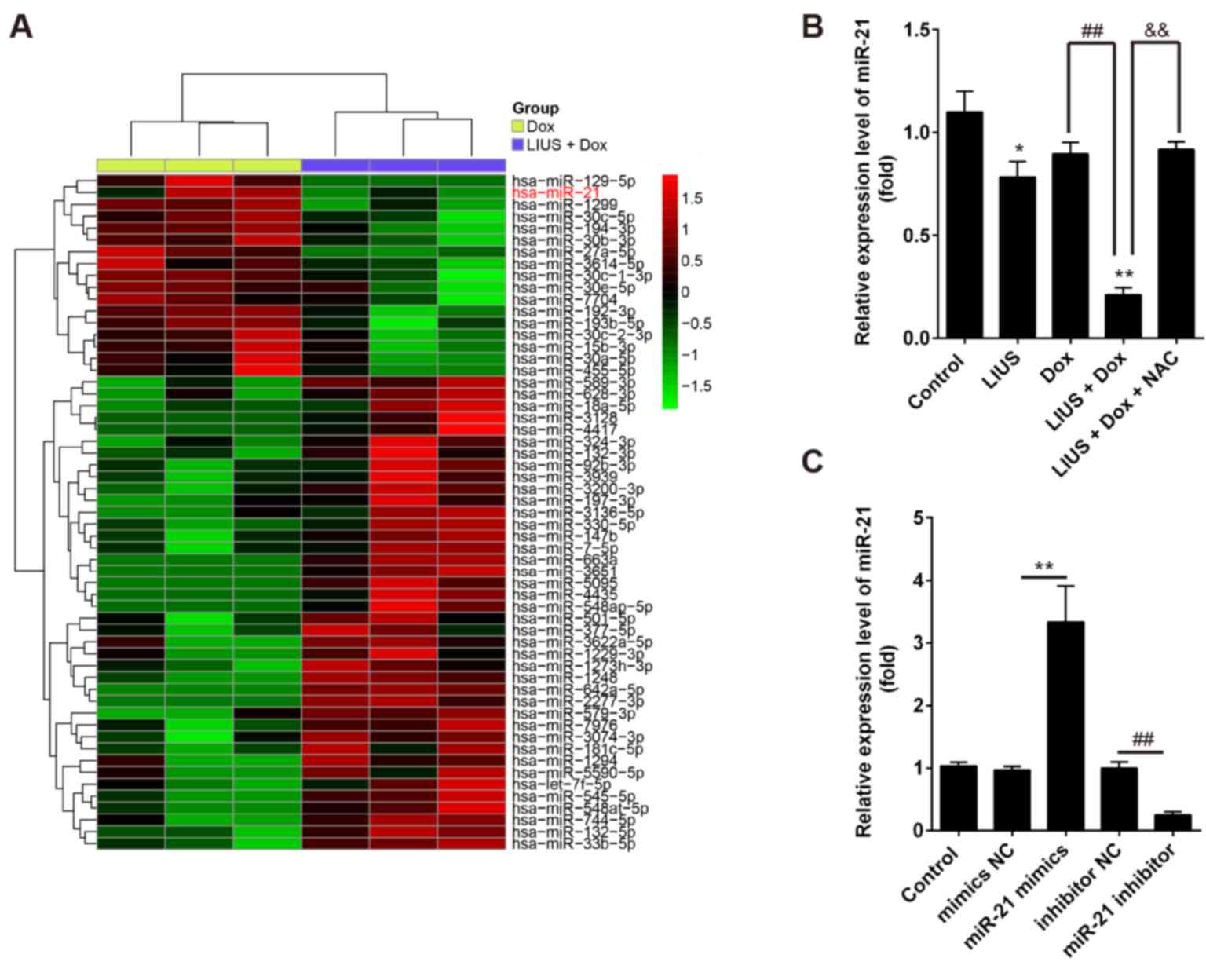
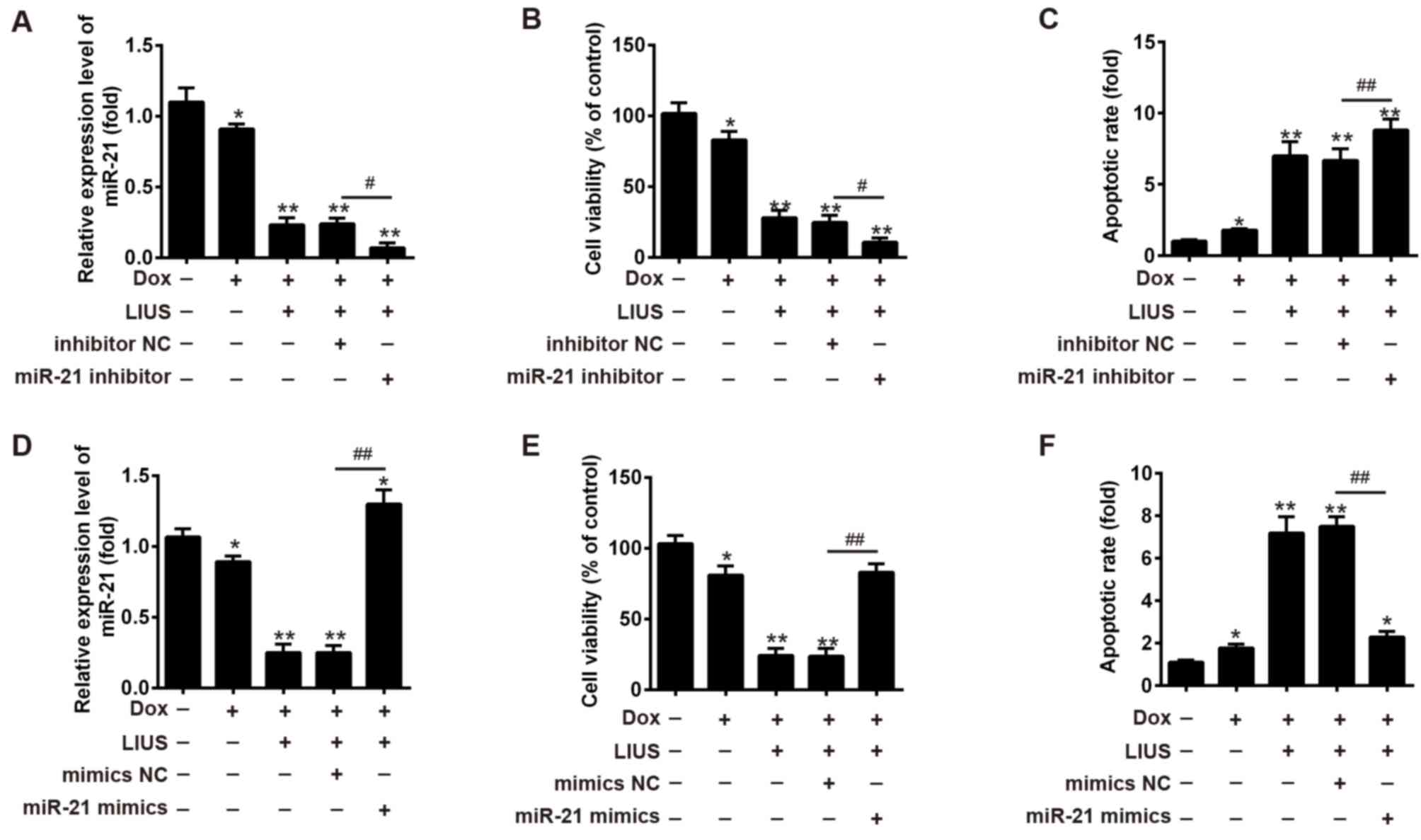
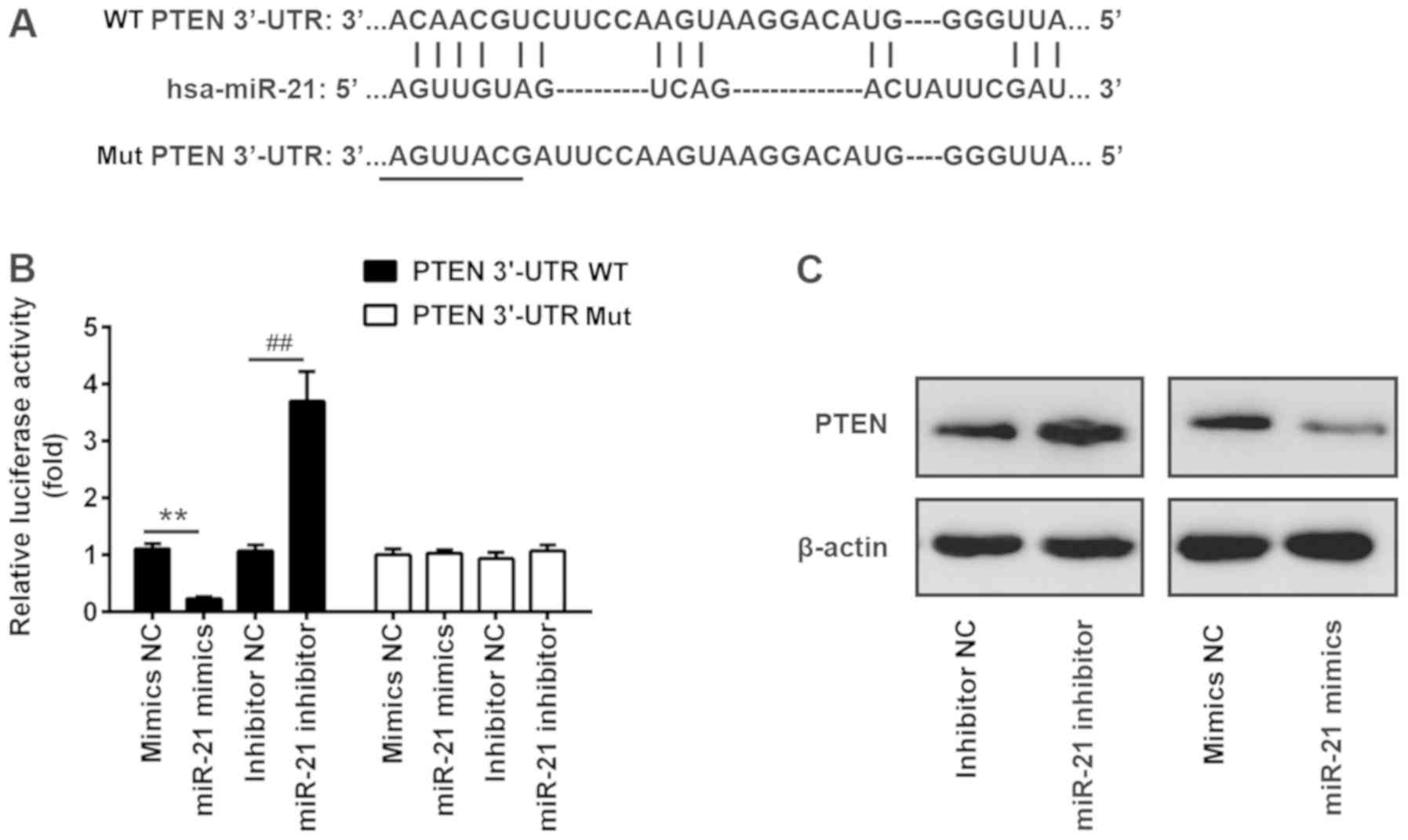
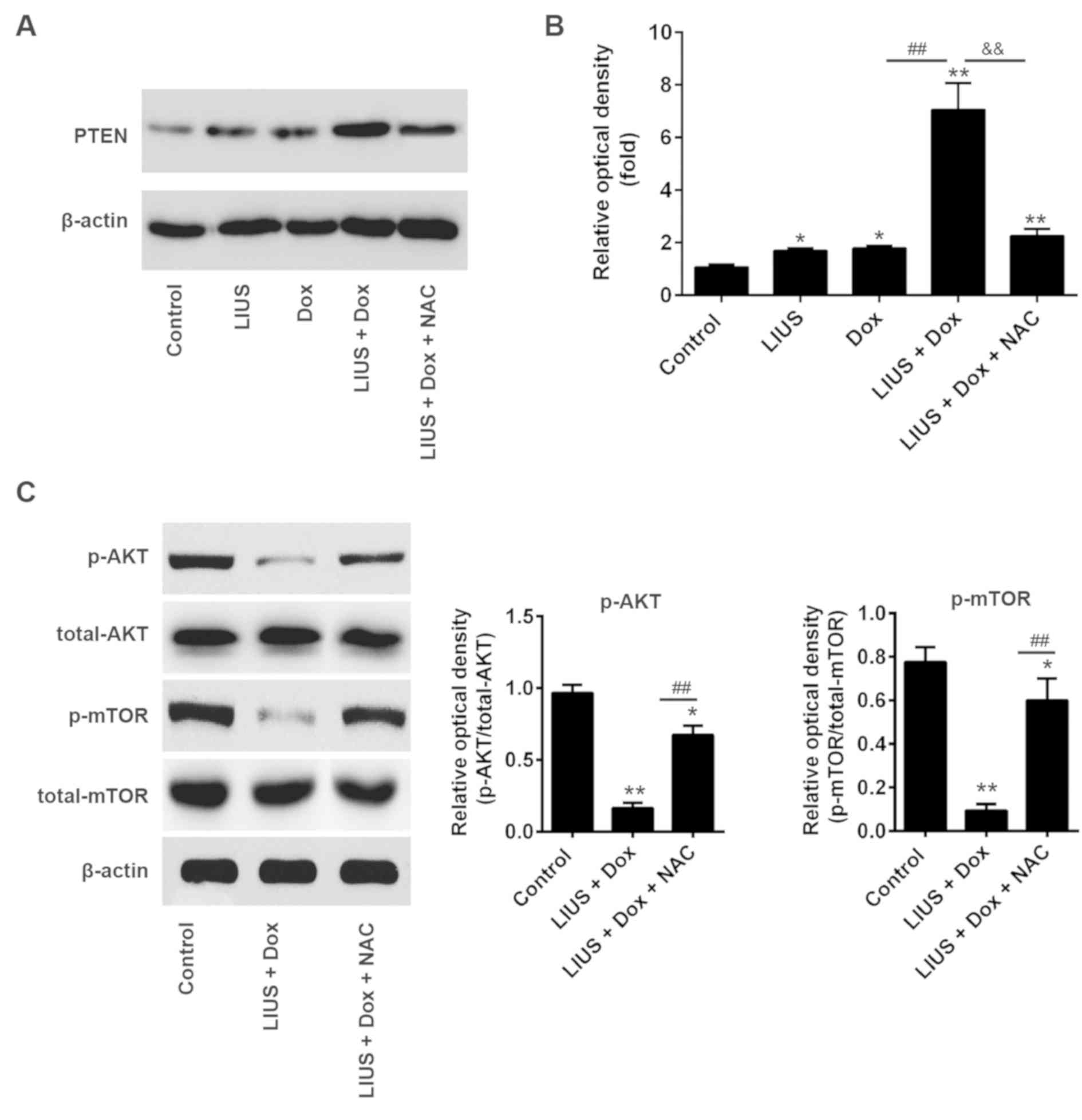
|
1
|
Yii AC, Tan GL, Tan KL, Lapperre TS and
Koh MS: Fixed airways obstruction among patients with severe
asthma: Findings from the Singapore general hospital-severe asthma
phenotype study. BMC Pulm Med. 14:1912014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lurje G, Lesurtel M and Clavien PA:
Multimodal treatment strategies in patients undergoing surgery for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis. 31:112–117. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
de Lope CR, Tremosini S, Forner A, Reig M
and Bruix J: Management of HCC. J Hepatol. 56 Suppl 1:S75–S87.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Giordano S and Columbano A: Met as a
therapeutic target in HCC: Facts and hopes. J Hepatol. 60:442–452.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu L, Chen H, Wang M, Zhao Y, Cai G, Qi X
and Han G: Combination therapy of sorafenib and TACE for
unresectable HCC: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One.
9:e911242014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nishida N, Kitano M, Sakurai T and Kudo M:
Molecular mechanism and prediction of sorafenib chemoresistance in
human hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis. 33:771–779. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Momparler RL, Karon M, Siegel SE and Avila
F: Effect of adriamycin on DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis in
cell-free systems and intact cells. Cancer Res. 36:2891–2895.
1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rivankar S: An overview of doxorubicin
formulations in cancer therapy. J Cancer Res Ther. 10:853–858.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu T, Zhang J, Chen W, Pan S, Zhi X, Wen
L, Zhou Y, Chen BW, Qiu J, Zhang Y, et al: ARK5 promotes
doxorubicin resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma via
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Lett. 377:140–148. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pan JX, Wang F and Ye LY:
Doxorubicin-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition through SEMA
4A in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
479:610–614. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhou Y, Liang C, Xue F, Chen W, Zhi X,
Feng X, Bai X and Liang T: Salinomycin decreases doxorubicin
resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting the
β-catenin/TCF complex association via FOXO3a activation.
Oncotarget. 6:10350–10365. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wood AK and Sehgal CM: A review of
low-intensity ultrasound for cancer therapy. Ultrasound Med Biol.
41:905–928. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lv Y, Fang M, Zheng J, Yang B, Li H,
Xiuzigao Z, Song W, Chen Y and Cao W: Low-intensity ultrasound
combined with 5-aminolevulinic acid administration in the treatment
of human tongue squamous carcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem.
30:321–333. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fan H, Li H, Liu G, Cong W, Zhao H, Cao W
and Zheng J: Doxorubicin combined with low intensity ultrasound
suppresses the growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma in culture
and in xenografts. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 36:1632017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lan J, Huang Z, Han J, Shao J and Huang C:
Redox regulation of microRNAs in cancer. Cancer Lett. 418:250–259.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xiao Y, Yan W, Lu L, Wang Y, Lu W, Cao Y
and Cai W: p38/p53/miR-200a-3p feedback loop promotes oxidative
stress-mediated liver cell death. Cell Cycle. 14:1548–1558. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang H, Li TW, Zhou Y, Peng H, Liu T,
Zandi E, Martínez-Chantar ML, Mato JM and Lu SC: Activation of a
novel c-Myc-miR27-prohibitin 1 circuitry in cholestatic liver
injury inhibits glutathione synthesis in mice. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 22:259–274. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jin F, Wang Y, Li M, Zhu Y, Liang H, Wang
C, Wang F, Zhang CY, Zen K and Li L: MiR-26 enhances
chemosensitivity and promotes apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma
cells through inhibiting autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 8:e25402017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang C, Liu X, Qiang H, Li K, Wang J,
Chen D and Zhuang Y: Inhibitory effects of rosa roxburghii tratt
juice on in vitro oxidative modification of low density lipoprotein
and on the macrophage growth and cellular cholesteryl ester
accumulation induced by oxidized low density lipoprotein. Clin Chim
Acta. 313:37–43. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hu Z, Lv G, Li Y, Li E, Li H, Zhou Q, Yang
B and Cao W: Enhancement of anti-tumor effects of 5-fluorouracil on
hepatocellular carcinoma by low-intensity ultrasound. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 35:712016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pfeffer SR, Yang CH and Pfeffer LM: The
role of miR-21 in cancer. Drug Dev Res. 76:270–277. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
He C, Dong X, Zhai B, Jiang X, Dong D, Li
B, Jiang H, Xu S and Sun X: MiR-21 mediates sorafenib resistance of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting autophagy via the
PTEN/Akt pathway. Oncotarget. 6:28867–28881. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li ZB, Li ZZ, Li L, Chu HT and Jia M:
MiR-21 and miR-183 can simultaneously target SOCS6 and modulate
growth and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 19:3208–3217. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang CS, Yu W, Cui H, Wang YJ, Zhang L,
Han F and Huang T: Increased expression of miR-21 predicts poor
prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:7234–7238. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lim HJ, Crowe P and Yang JL: Current
clinical regulation of PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR signalling in treatment
of human cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 141:671–689. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Leslie NR and Downes CP: PTEN function:
How normal cells control it and tumour cells lose it. Biochem J.
382:1–11. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yu HG, Ai YW, Yu LL, Zhou XD, Liu J, Li
JH, Xu XM, Liu S, Chen J, Liu F, et al: Phosphoinositide
3-kinase/Akt pathway plays an important role in chemoresistance of
gastric cancer cells against etoposide and doxorubicin induced cell
death. Int J Cancer. 122:433–443. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang SM, Huang C, Li XF, Yu MZ, He Y and
Li J: miR-21 confers cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells
by regulating PTEN. Toxicology. 306:162–168. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kirstein MM and Vogel A: The pathogenesis
of hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis. 32:545–553. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rich NE, Yopp AC and Singal AG: Medical
management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Oncol Pract. 13:356–364.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Reig M, Darnell A, Forner A, Rimola J,
Ayuso C and Bruix J: Systemic therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma:
The issue of treatment stage migration and registration of
progression using the BCLC-refined RECIST. Semin Liver Dis.
34:444–455. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pan ST, Li ZL, He ZX, Qiu JX and Zhou SF:
Molecular mechanisms for tumour resistance to chemotherapy. Clin
Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 43:723–737. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lohitesh K, Chowdhury R and Mukherjee S:
Resistance a major hindrance to chemotherapy in hepatocellular
carcinoma: An insight. Cancer Cell Int. 18:442018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Draper DO: Facts and misfits in ultrasound
therapy: Steps to improve your treatment outcomes. Eur J Phys
Rehabil Med. 50:209–216. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wu F: High intensity focused ultrasound: A
noninvasive therapy for locally advanced pancreatic cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:16480–16488. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xia B, Zou Y, Xu Z and Lv Y: Gene
expression profiling analysis of the effects of low-intensity
pulsed ultrasound on induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural
crest stem cells. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 64:927–937. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Duco W, Grosso V, Zaccari D and Soltermann
AT: Generation of ROS mediated by mechanical waves (ultrasound) and
its possible applications. Methods. 109:141–148. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jang HJ, Lee JY, Lee DH, Kim WH and Hwang
JH: Current and future clinical applications of high-intensity
focused ultrasound (HIFU) for pancreatic cancer. Gut Liver. 4 Suppl
1:S57–S61. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shi J, Chen Z, Wang B, Wang L, Lu T and
Zhang Z: Reactive oxygen species-manipulated drug release from a
smart envelope-type mesoporous titanium nanovehicle for tumor
sonodynamic-chemotherapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 7:28554–28565.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ma X, Conklin DJ, Li F, Dai Z, Hua X, Li
Y, Xu-Monette ZY, Young KH, Xiong W, Wysoczynski M, et al: The
oncogenic microRNA miR-21 promotes regulated necrosis in mice. Nat
Commun. 6:71512015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Melnik BC: MiR-21: An environmental driver
of malignant melanoma? J Transl Med. 13:2022015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sekar D, Krishnan R, Thirugnanasambantham
K, Rajasekaran B, Islam VI and Sekar P: Significance of microRNA 21
in gastric cancer. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 40:538–545.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Worby CA and Dixon JE: Pten. Annu Rev
Biochem. 83:641–669. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|