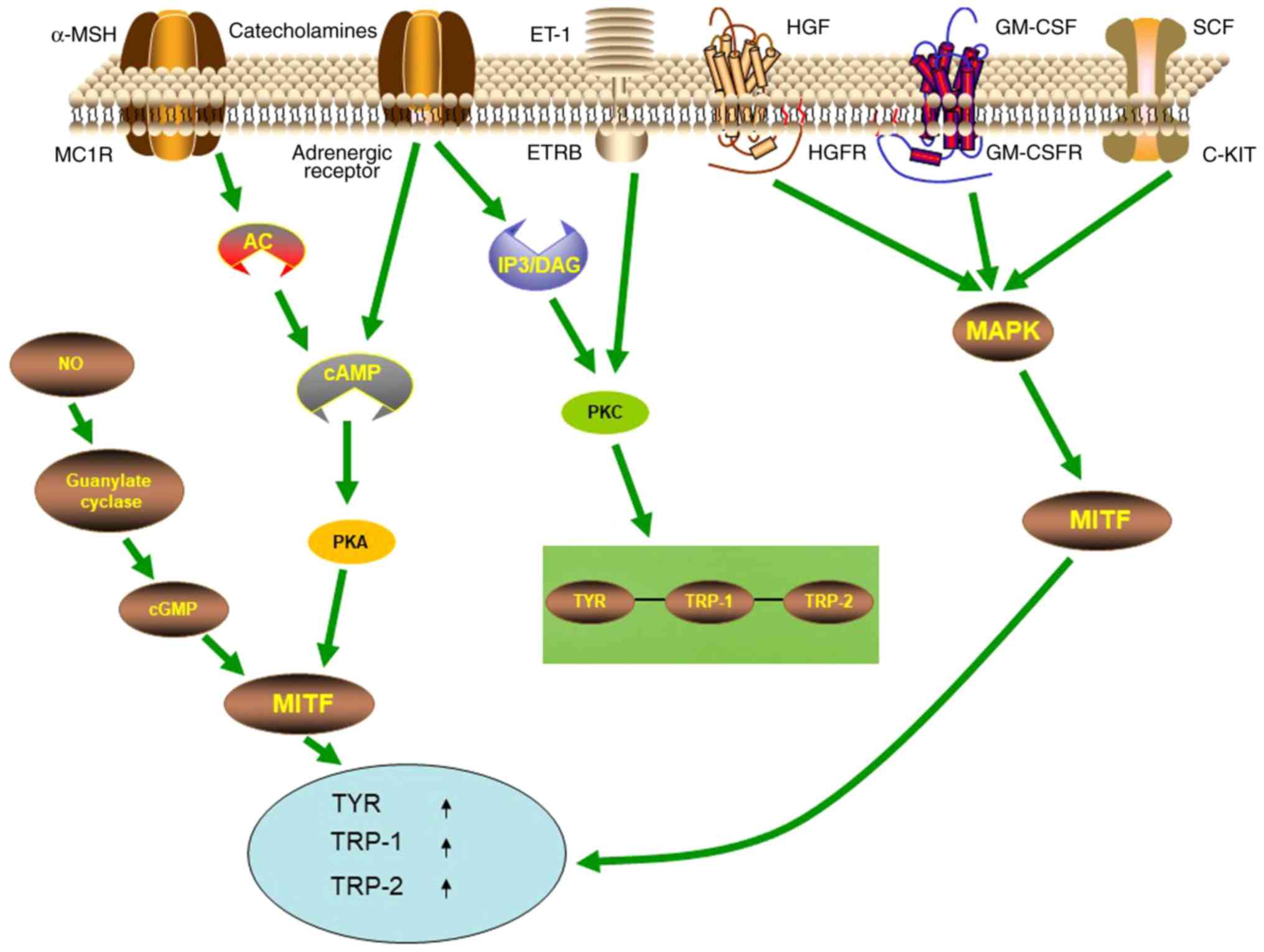
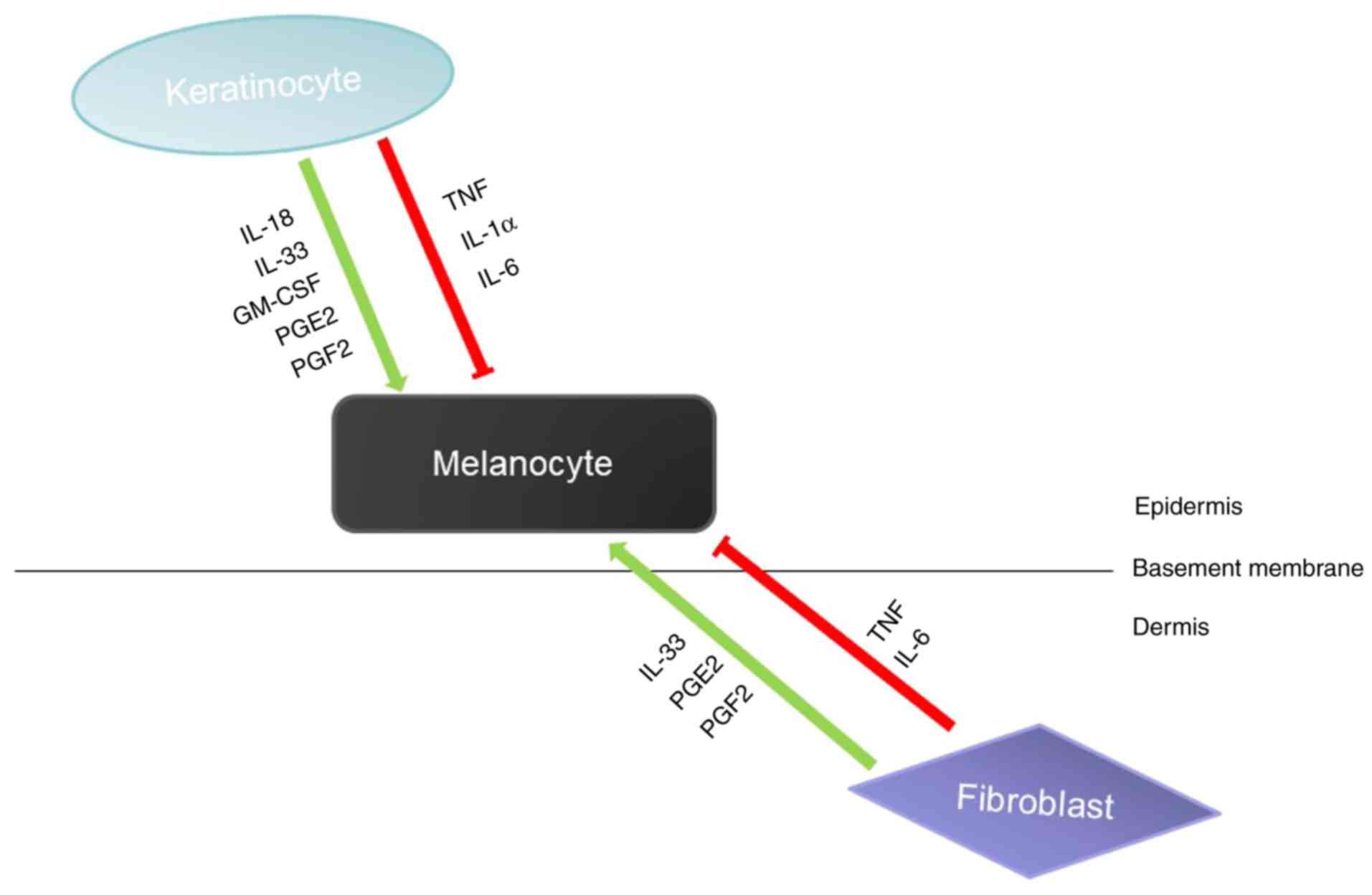
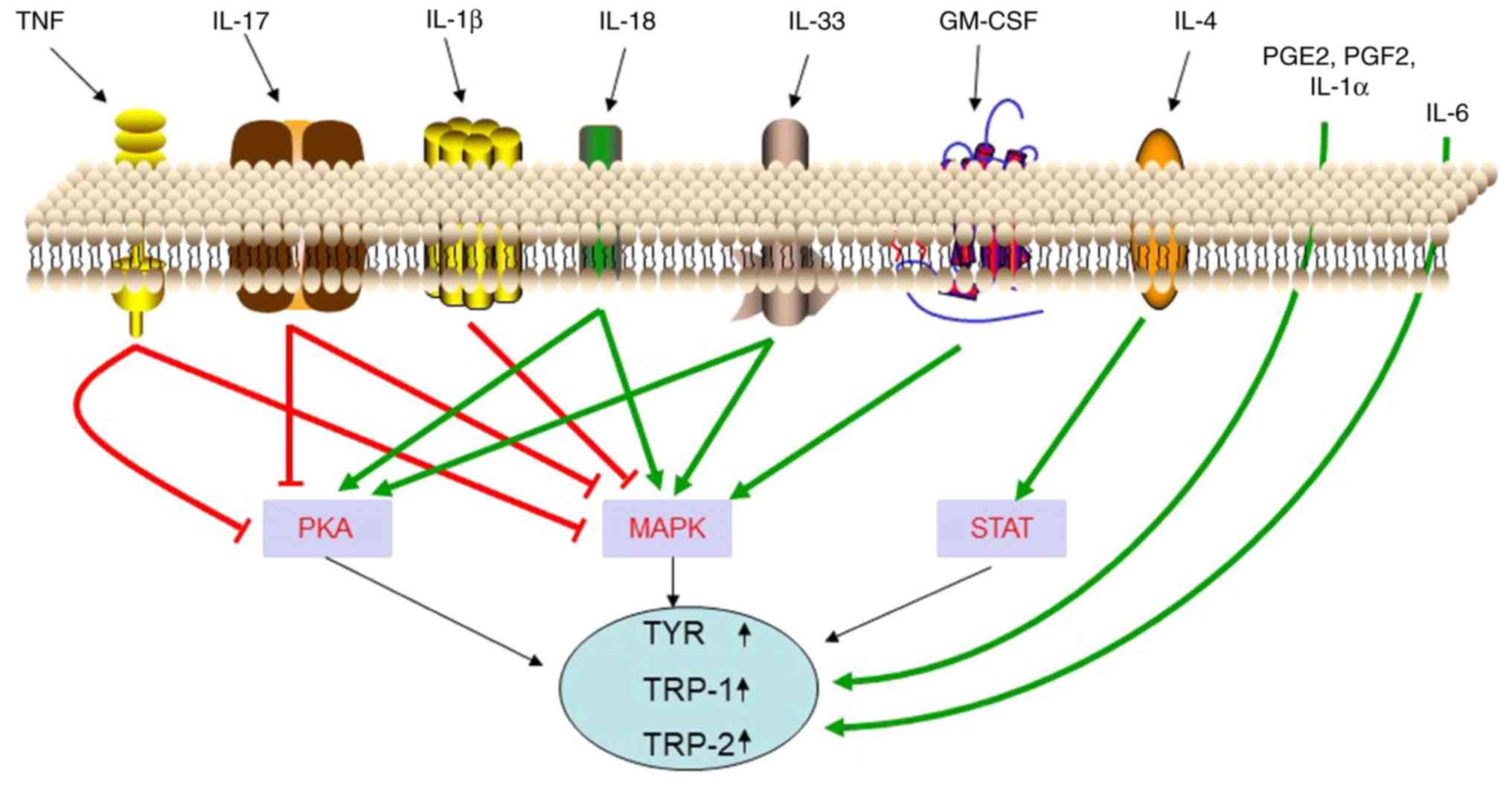
|
1
|
Gröne A: Keratinocytes and cytokines. Vet
Immunol Immunopathol. 88:1–12. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Skobowiat C, Dowdy JC, Sayre RM, Tuckey RC
and Slominski A: Cutaneous hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis
homolog: Regulation by ultraviolet radiation. Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab. 301:E484–E493. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Weiss E, Mamelak AJ, La Morgia S, Wang B,
Feliciani C, Tulli A and Sauder DN: The role of interleukin 10 in
the pathogenesis and potential treatment of skin diseases. J Am
Acad Dermatol. 50:657–678. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Martin SF: Contact dermatitis: From
pathomechanisms to immunotoxicology. Exp Dermatol. 21:382–389.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Miller LS and Cho JS: Immunity against
Staphylococcus aureus cutaneous infections. Nat Rev Immunol.
11:505–518. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Behrends U, Peter RU, Hintermeier-Knabe R,
Eissner G, Holler E, Bornkamm GW, Caughman SW and Degitz K:
Ionizing radiation induces human intercellular adhesion molecule-1
in vitro. J Invest Dermatol. 103:726–730. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fuchs J and Kern H: Modulation of
UV-light-induced skin inflammation by D-alpha-tocopherol and
L-ascorbic acid: A clinical study using solar simulated radiation.
Free Radic Biol Med. 25:1006–1012. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Basler K and Brandner JM: Tight junctions
in skin inflammation. Pflugers Arch. 469:3–14. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Grine L, Dejager L, Libert C and
Vandenbroucke RE: An inflammatory triangle in psoriasis: TNF, type
I IFNs and IL-17. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 26:25–33. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang CQF, Akalu YT, Suarez-Farinas M,
Gonzalez J, Mitsui H, Lowes MA, Orlow SJ, Manga P and Krueger JG:
IL-17 and TNF synergistically modulate cytokine expression while
suppressing melanogenesis: Potential relevance to psoriasis. J
Invest Dermatol. 133:2741–2752. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Slominski A, Tobin DJ, Shibahara S and
Wortsman J: Melanin pigmentation in mammalian skin and its hormonal
regulation. Physiol Rev. 84:1155–1228. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Swope VB, Abdel-Malek Z, Kassem LM and
Nordlund JJ: Interleukins 1 alpha and 6 and tumor necrosis
factor-alpha are paracrine inhibitors of human melanocyte
proliferation and melanogenesis. J Invest Dermatol. 96:180–185.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Choi H, Choi H, Han J, Jin SH, Park JY,
Shin DW, Lee TR, Kim K, Lee AY and Noh M: IL-4 inhibits the
melanogenesis of normal human melanocytes through the JAK2-STAT6
signaling pathway. J Invest Dermatol. 133:528–536. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou J, Song J, Ping F and Shang J:
Enhancement of the p38 MAPK and PKA signaling pathways is
associated with the pro-melanogenic activity of Interleukin 33 in
primary melanocytes. J Dermatol Sci. 73:110–116. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tsatmali M, Ancans J and Thody AJ:
Melanocyte function and its control by melanocortin peptides. J
Histochem Cytochem. 50:125–133. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Costin GE and Hearing VJ: Human skin
pigmentation: Melanocytes modulate skin color in response to
stress. FASEB J. 21:976–994. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Videira IF, Moura DF and Magina S:
Mechanisms regulating melanogenesis. An Bras Dermatol. 88:76–83.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yamaguchi Y, Brenner M and Hearing VJ: The
regulation of skin pigmentation. J Biol Chem. 282:27557–27561.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Seong ZK, Lee SY, Poudel A, Oh SR and Lee
HK: Constituents of cryptotaenia japonica inhibit melanogenesis via
CREB- and MAPK-associated signaling pathways in murine B16 melanoma
cells. Molecules. 21(pii): E12962016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Campos PM, Prudente AS, Horinouchi CD,
Cechinel-Filho V, Fávero GM, Cabrini DA and Otuki MF: Inhibitory
effect of GB-2a (I3-naringenin-II8-eriodictyol) on melanogenesis. J
Ethnopharmacol. 174:224–229. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tsao YT, Huang YF, Kuo CY, Lin YC, Chiang
WC, Wang WK, Hsu CW and Lee CH: Hinokitiol inhibits melanogenesis
via AKT/mTOR signaling in B16F10 mouse melanoma cells. Int J Mol
Sci. 17:2482016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hirobe T: Role of keratinocyte-derived
factors involved in regulating the proliferation and
differentiation of mammalian epidermal melanocytes. Pigment Cell
Res. 18:2–12. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Schallreuter KU, Kothari S, Chavan B and
Spencer JD: Regulation of melanogenesis-controversies and new
concepts. Exp Dermatol. 17:395–404. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lin JY and Fisher DE: Melanocyte biology
and skin pigmentation. Nature. 445:843–850. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Park HY, Kosmadaki M, Yaar M and Gilchrest
BA: Cellular mechanisms regulating human melanogenesis. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 66:1493–1506. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schiaffino MV: Signaling pathways in
melanosome biogenesis and pathology. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
42:1094–1104. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yuan XH and Jin ZH: Paracrine regulation
of melanogenesis. Br J Dermatol. 178:632–639. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Swope VB and Abdel-Malek ZA: MC1R: Front
and center in the bright side of dark eumelanin and DNA repair. Int
J Mol Sci. 19(pii): E26672018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Grando SA, Pittelkow MR and Schallreuter
KU: Adrenergic and cholinergic control in the biology of epidermis:
Physiological and clinical significance. J Invest Dermatol.
126:1948–1965. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bonaventure J, Domingues MJ and Larue L:
Cellular and molecular mechanisms controlling the migration of
melanocytes and melanoma cells. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res.
26:316–325. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Besmer P, Murphy JE, George PC, Qiu FH,
Bergold PJ, Lederman L, Snyder HW Jr, Brodeur D, Zuckerman EE and
Hardy WD: A new acute transforming feline retrovirus and
relationship of its oncogene v-kit with the protein kinase gene
family. Nature. 320:415–421. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yarden Y, Kuang WJ, Yang-Feng T, Coussens
L, Munemitsu S, Dull TJ, Chen E, Schlessinger J, Francke U and
Ullrich A: Human proto-oncogene c-kit: A new cell surface receptor
tyrosine kinase for an unidentified ligand. EMBO J. 6:3341–3351.
1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dorsky RI, Raible DW and Moon RT: Direct
regulation of nacre, a zebrafish MITF homolog required for pigment
cell formation, by the Wnt pathway. Genes Dev. 14:158–162.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Flaherty KT, Hodi FS and Fisher DE: From
genes to drugs: Targeted strategies for melanoma. Nat Rev Cancer.
12:349–361. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Widlund HR, Horstmann MA, Price ER, Cui J,
Lessnick SL, Wu M, He X and Fisher DE: Beta-catenin-induced
melanoma growth requires the downstream target
Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor. J Cell Biol.
158:1079–1087. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jung E, Lee J, Huh S, Lee J, Kim YS, Kim G
and Park D: Phloridzin-induced melanogenesis is mediated by the
cAMP signaling pathway. Food Chem Toxicol. 47:2436–2440. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Satomi H, Wang B, Fujisawa H and Otsuka F:
Interferon-beta from melanoma cells suppresses the proliferations
of melanoma cells in an autocrine manner. Cytokine. 18:108–115.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mattei S, Colombo MP, Melani C, Silvani A,
Parmiani G and Herlyn M: Expression of cytokine/growth factors and
their receptors in human melanoma and melanocytes. Int J Cancer.
56:853–857. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mosmann TR and Sad S: The expanding
universe of T-cell subsets: Th1, Th2 and more. Immunol Today.
17:138–146. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
O'Garra A: Cytokines induce the
development of functionally heterogeneous T helper cell subsets.
Immunity. 8:275–283. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Reiner SL and Seder RA: Dealing from the
evolutionary pawnshop: How lymphocytes make decisions. Immunity.
11:1–10. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bennicelli JL and Guerry D VI: Production
of multiple cytokines by cultured human melanomas. Exp Dermatol.
2:186–190. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhou J, Shang J, Song J and Ping F:
Interleukin-18 augments growth ability of primary human melanocytes
by PTEN inactivation through the AKT/NF-κB pathway. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 45:308–316. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yun W and Li C: JNK pathway is required
for TNCB-induced IL-18 expression in murine keratinocytes. Toxicol
In Vitro. 24:1064–1069. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wittmann M, Macdonald A and Renne J: IL-18
and skin inflammation. Autoimmun Rev. 9:45–48. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhou J, Ling J, Wang Y, Shang J and Ping
F: Cross-talk between interferon-gamma and interleukin-18 in
melanogenesis. J Photochem Photobiol B. 163:133–143. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ali S, Huber M, Kollewe C, Bischoff SC,
Falk W and Martin MU: IL-1 receptor accessory protein is essential
for IL-33-induced activation of T lymphocytes and mast cells. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:18660–18665. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Allakhverdi Z, Smith DE, Comeau MR and
Delespesse G: Cutting edge: The ST2 ligand IL-33 potently activates
and drives maturation of human mast cells. J Immunol.
179:2051–2054. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Moulin D, Donze O, Talabot-Ayer D, Mezin
F, Palmer G and Gabay C: Interleukin (IL)-33 induces the release of
pro-inflammatory mediators by mast cells. Cytokine. 40:216–225.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Theoharides TC, Zhang B, Kempuraj D, Tagen
M, Vasiadi M, Angelidou A, Alysandratos KD, Kalogeromitros D, Asadi
S, Stavrianeas N, et al: IL-33 augments substance P-induced VEGF
secretion from human mast cells and is increased in psoriatic skin.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:4448–4453. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Pushparaj PN, Tay HK, H'ng SC, Pitman N,
Xu D, McKenzie A, Liew FY and Melendez AJ: The cytokine
interleukin-33 mediates anaphylactic shock. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:9773–9778. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kurowska-Stolarska M, Stolarski B, Kewin
P, Murphy G, Corrigan CJ, Ying S, Pitman N, Mirchandani A, Rana B,
van Rooijen N, et al: IL-33 amplifies the polarization of
alternatively activated macrophages that contribute to airway
inflammation. J Immunol. 183:6469–6477. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ohno T, Oboki K, Kajiwara N, Morii E,
Aozasa K, Flavell RA, Okumura K, Saito H and Nakae S: Caspase-1,
caspase-8, and calpain are dispensable for IL-33 release by
macrophages. J Immunol. 183:7890–7897. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Schmieder A, Multhoff G and Radons J:
Interleukin-33 acts as a pro-inflammatory cytokine and modulates
its receptor gene expression in highly metastatic human pancreatic
carcinoma cells. Cytokine. 60:514–521. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hueber AJ, Alves-Filho JC, Asquith DL,
Michels C, Millar NL, Reilly JH, Graham GJ, Liew FY, Miller AM and
McInnes IB: IL-33 induces skin inflammation with mast cell and
neutrophil activation. Eur J Immunol. 41:2229–2237. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Schmitz J, Owyang A, Oldham E, Song Y,
Murphy E, McClanahan TK, Zurawski G, Moshrefi M, Qin J, Li X, et
al: IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1
receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated
cytokines. Immunity. 23:479–490. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Suzukawa M, Iikura M, Koketsu R, Nagase H,
Tamura C, Komiya A, Nakae S, Matsushima K, Ohta K, Yamamoto K and
Yamaguchi M: An IL-1 cytokine member, IL-33, induces human basophil
activation via its ST2 receptor. J Immunol. 181:5981–5989. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Rank MA, Kobayashi T, Kozaki H, Bartemes
KR, Squillace DL and Kita H: IL-33-activated dendritic cells induce
an atypical TH2-type response. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
123:1047–1054. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Arend WP, Palmer G and Gabay C: IL-1,
IL-18, and IL-33 families of cytokines. Immunol Rev. 223:20–38.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Byrne SN, Beaugie C, O'Sullivan C,
Leighton S and Halliday GM: The immune-modulating cytokine and
endogenous Alarmin interleukin-33 is upregulated in skin exposed to
inflammatory UVB radiation. Am J Pathol. 179:211–222. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wu XG, Hong WS and Xu A: GM-CSF: A
possible prognostic serum biomarker of vitiligo patients'
considered for transplantation treatment with cultured autologous
melanocytes: A pilot study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol.
30:1409–1411. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Scott G, Leopardi S, Printup S, Malhi N,
Seiberg M and Lapoint R: Proteinase-activated receptor-2 stimulates
prostaglandin production in keratinocytes: Analysis of
prostaglandin receptors on human melanocytes and effects of PGE2
and PGF2alpha on melanocyte dendricity. J Invest Dermatol.
122:1214–1224. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Scott G, Jacobs S, Leopardi S, Anthony FA,
Learn D, Malaviya R and Pentland A: Effects of PGF2alpha on human
melanocytes and regulation of the FP receptor by ultraviolet
radiation. Exp Cell Res. 304:407–416. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Ma HJ, Ma HY, Yang Y, Li PC, Zi SX, Jia CY
and Chen R: a-Melanocyte stimulating hormone (MSH) and
prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) drive melanosome transfer by promoting
filopodia delivery and shedding spheroid granules: Evidences from
atomic force microscopy observation. J Dermatol Sci. 76:222–230.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Bach EA, Aguet M and Schreiber RD: The IFN
gamma receptor: A paradigm for cytokine receptor signaling. Annu
Rev Immunol. 15:563–591. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Carnaud C, Lee D, Donnars O, Park SH,
Beavis A, Koezuka Y and Bendelac A: Cutting edge: Cross-talk
between cells of the innate immune system: NKT cells rapidly
activate NK cells. J Immunol. 163:4647–4650. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Frucht DM, Fukao T, Bogdan C, Schindler H,
O'Shea JJ and Koyasu S: IFN-gamma production by antigen-presenting
cells: Mechanisms emerge. Trends Immunol. 22:556–560. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Flaishon L, Hershkoviz R, Lantner F, Lider
O, Alon R, Levo Y, Flavell RA and Shachar I: Autocrine secretion of
interferon gamma negatively regulates homing of immature B cells. J
Exp Med. 192:1381–1388. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Harris JE, Harris TH, Weninger W, Wherry
EJ, Hunter CA and Turka LA: A mouse model of vitiligo with focused
epidermal depigmentation requires IFN-γ for autoreactive
CD8+ T-cell accumulation in the skin. J Invest Dermatol.
132:1869–1876. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Gregg RK, Nichols L, Chen Y, Lu B and
Engelhard VH: Mechanisms of spatial and temporal development of
autoimmune vitiligo in tyrosinase-specific TCR transgenic mice. J
Immunol. 184:1909–1917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Yang L, Wei Y, Sun Y, Shi W, Yang J, Zhu L
and Li M: Interferon-gamma inhibits melanogenesis and induces
apoptosis in melanocytes: A pivotal role of CD8+ cytotoxic T
lymphocytes in vitiligo. Acta Derm Venereol. 95:664–670. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Natarajan VT, Ganju P, Singh A, Vijayan V,
Kirty K, Yadav S, Puntambekar S, Bajaj S, Dani PP, Kar HK, et al:
IFN-γ signaling maintains skin pigmentation homeostasis through
regulation of melanosome maturation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:2301–2306. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Kristensen M, Chu CQ, Eedy DJ, Feldmann M,
Brennan FM and Breathnach SM: Localization of tumour necrosis
factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and its receptors in normal and psoriatic
skin: Epidermal cells express the 55-kD but not the 75-kD TNF
receptor. Clin Exp Immunol. 94:354–362. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Kholmanskikh O, van Baren N, Brasseur F,
Ottaviani S, Vanacker J, Arts N, van der Bruggen P, Coulie P and De
Plaen E: Interleukins 1alpha and 1beta secreted by some melanoma
cell lines strongly reduce expression of MITF-M and melanocyte
differentiation antigens. Int J Cancer. 127:1625–1636. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Martin MU and Wesche H: Summary and
comparison of the signaling mechanisms of the Toll/interleukin-1
receptor family. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1592:265–280. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Tang A and Gilchrest B: Regulation of
keratinocyte growth factor gene expression in human skin
fibroblasts. J Dermatol Sci. 11:41–50. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Grewe M, Gyufko K, Budnik A, Ruzicka T,
Olaizola-Horn S, Berneburg M and Krutmann J: Interleukin-1
receptors type I and type II are differentially regulated in human
keratinocytes by ultraviolet B radiation. J Invest Dermatol.
107:865–870. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Kondo S, Sauder DN, Kono T, Galley KA and
McKenzie RC: Differential modulation of interleukin-1 alpha (IL-1
alpha) and interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta) in human epidermal
keratinocytes by UVB. Exp Dermatol. 3:29–39. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Chen N, Hu Y, Li WH, Eisinger M, Seiberg M
and Lin CB: The role of keratinocyte growth factor in
melanogenesis: A possible mechanism for the initiation of solar
lentigines. Exp Dermatol. 19:865–872. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Sims J, March C, Cosman D, Widmer MB,
MacDonald HR, McMahan CJ, Grubin CE, Wignall JM, Jackson JL, Call
SM, et al: cDNA expression cloning of the IL-1 receptor, a member
of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Science. 241:585–589. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Barata LT, Ying S, Meng Q, Barkans J,
Rajakulasingam K, Durham SR and Kay AB: IL-4- and IL-5-positive T
lymphocytes, eosinophils, and mast cells in allergen-induced
late-phase cutaneous reactions in atopic subjects. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 101:222–230. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Min B, Prout M, Hu-Li J, Zhu J, Jankovic
D, Morgan ES, Urban JF Jr, Dvorak AM, Finkelman FD, LeGros G and
Paul WE: Basophils produce IL-4 and accumulate in tissues after
infection with a Th2-inducing parasite. J Exp Med. 200:507–517.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Imran M, Laddha N, Dwivedi M, Mansuri MS,
Singh J, Rani R, Gokhale RS, Sharma VK, Marfatia YS and Begum R:
Interleukin-4 genetic variants correlate with its transcript and
protein levels in patients with vitiligo. Br J Dermatol.
167:314–323. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Salgame P, Abrams JS, Clayberger C,
Goldstein H, Convit J, Modlin RL and Bloom BR: Differing lymphokine
profiles of functional subsets of human CD4 and CD8 T cell clones.
Science. 254:279–282. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Basak PY, Adiloglu AK, Ceyhan AM, Tas T
and Akkaya VB: The role of helper and regulatory T cells in the
pathogenesis of vitiligo. J Am Acad Dermatol. 60:256–260. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Nouri-Koupaee A, Mansouri P, Jahanbini H,
Sanati MH and Jadali Z: Differential expression of mRNA for T-bet
and GATA-3 transcription factors in peripheral blood mononuclear
cells of patients with vitiligo. Clin Exp Dermatol. 40:735–740.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Hirano T, Ishihara K and Hibi M: Roles of
STAT3 in mediating the cell growth, differentiation and survival
signals relayed through the IL-6 family of cytokine receptors.
Oncogene. 19:2548–2556. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Speeckaert R, Lambert J, Grine L, Van Gele
M, De Schepper S and van Geel N: The many faces of interleukin-17
in inflammatory skin diseases. Br J Dermatol. 175:892–901. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Volpe E, Servant N, Zollinger R, Bogiatzi
SI, Hupé P, Barillot E and Soumelis V: A critical function for
transforming growth factor-beta, interleukin 23 and proinflammatory
cytokines in driving and modulating human T(H)-17 responses. Nat
Immunol. 9:650–657. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Kang WH, Yoon KH, Lee ES, Kim J, Lee KB,
Yim H, Sohn S and Im S: Melasma: Histopathological characteristics
in 56 Korean patients. Br J Dermatol. 146:228–237. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Nakajima M, Shinoda I, Fukuwatari Y and
Hayasawa H: Arbutin increases the pigmentation of cultured human
melanocytes through mechanisms other than the induction of
tyrosinase activity. Pigment Cell Res. 11:12–17. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Palumbo A, d'Ischia M, Misuraca G and
Prota G: Mechanism of inhibition of melanogenesis by hydroquinone.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1073:85–90. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Smith CJ, O'Hare KB and Allen JC:
Selective cytotoxicity of hydroquinone for melanocyte-derived cells
is mediated by tyrosinase activity but independent of melanin
content. Pigment Cell Res. 1:386–389. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Wang X and Zhang Y: Resveratrol alleviates
LPS-induced injury in human keratinocyte cell line HaCaT by
up-regulation of miR-17. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 501:106–112.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Kim ES, Chang H, Choi H, Shin JH, Park SJ,
Jo YK, Choi ES, Baek SY, Kim BG, Chang JW, et al: Autophagy induced
by resveratrol suppresses a-MSH-induced melanogenesis. Exp
Dermatol. 23:204–206. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Salzes C, Abadie S, Seneschal J, Whitton
M, Meurant JM, Jouary T, Ballanger F, Boralevi F, Taieb A, Taieb C
and Ezzedine K: The vitiligo impact patient scale (VIPs):
Development and validation of a vitiligo burden assessment tool. J
Invest Dermatol. 136:52–58. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Moretti S, Spallanzani A, Amato L,
Hautmann G, Gallerani I, Fabiani M and Fabbri P: New insights into
the pathogenesis of vitiligo: Imbalance of epidermal cytokines at
sites of lesions. Pigment Cell Res. 15:87–92. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Moretti S, Fabbri P, Baroni G, Berti S,
Bani D, Berti E, Nassini R, Lotti T and Massi D: Keratinocyte
dysfunction in vitiligo epidermis: Cytokine microenvironment and
correlation to keratinocyte apoptosis. Histol Histopathol.
24:849–857. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Kim NH, Jeon S, Lee HJ and Lee AY:
Impaired PI3K/Akt activation-mediated NF-kappaB inactivation under
elevated TNF-alpha is more vulnerable to apoptosis in vitiliginous
keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 127:2612–2617. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Barygina V, Becatti M, Lotti T, Moretti S,
Taddei N and Fiorillo C: Treatment with low-dose cytokines reduces
oxidative-mediated injury in perilesional keratinocytes from
vitiligo skin. J Dermatol Sci. 79:163–170. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Debbaneh MG, Levin E, Sanchez Rodriguez R,
Leon A, Koo J and Rosenblum MD: Plaque-based sub-blistering
dosimetry: Reaching PASI-75 after two treatments with 308-nm
excimer laser in a generalized psoriasis patient. J Dermatolog
Treat. 26:45–48. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Grimes P, Morris R, Avaniss-Aghajani E,
Soriano T, Meraz M and Metzger A: Topical tacrolimus therapy for
vitiligo: Therapeutic responses and skin messenger RNA expression
of proinflammatory cytokines. J Am Acad Dermatol. 51:52–61. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Sakuma S, Higashi Y, Sato N, Sasakawa T,
Sengoku T, Ohkubo Y, Amaya T and Goto T: Tacrolimus suppressed the
production of cytokines involved in atopic dermatitis by direct
stimulation of human PBMC system. (Comparison with steroids). Int
Immunopharmacol. 1:1219–1226. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Birol A, Kisa U, Kurtipek GS, Kara F,
Kocak M, Erkek E and Caglayan O: Increased tumor necrosis factor
alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin 1 alpha (IL1-alpha) levels in the
lesional skin of patients with nonsegmental vitiligo. Int J
Dermatol. 45:992–993. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Alghamdi K and Khurrum H: Methotrexate for
the treatment of generalized vitiligo. Saudi Pharm J. 21:423–424.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Grimes PE, Hamzavi I, Lebwohl M, Ortonne
JP and Lim HW: The efficacy of afamelanotide and narrowband UV-B
phototherapy for repigmentation of vitiligo. JAMA Dermatol.
149:68–73. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|