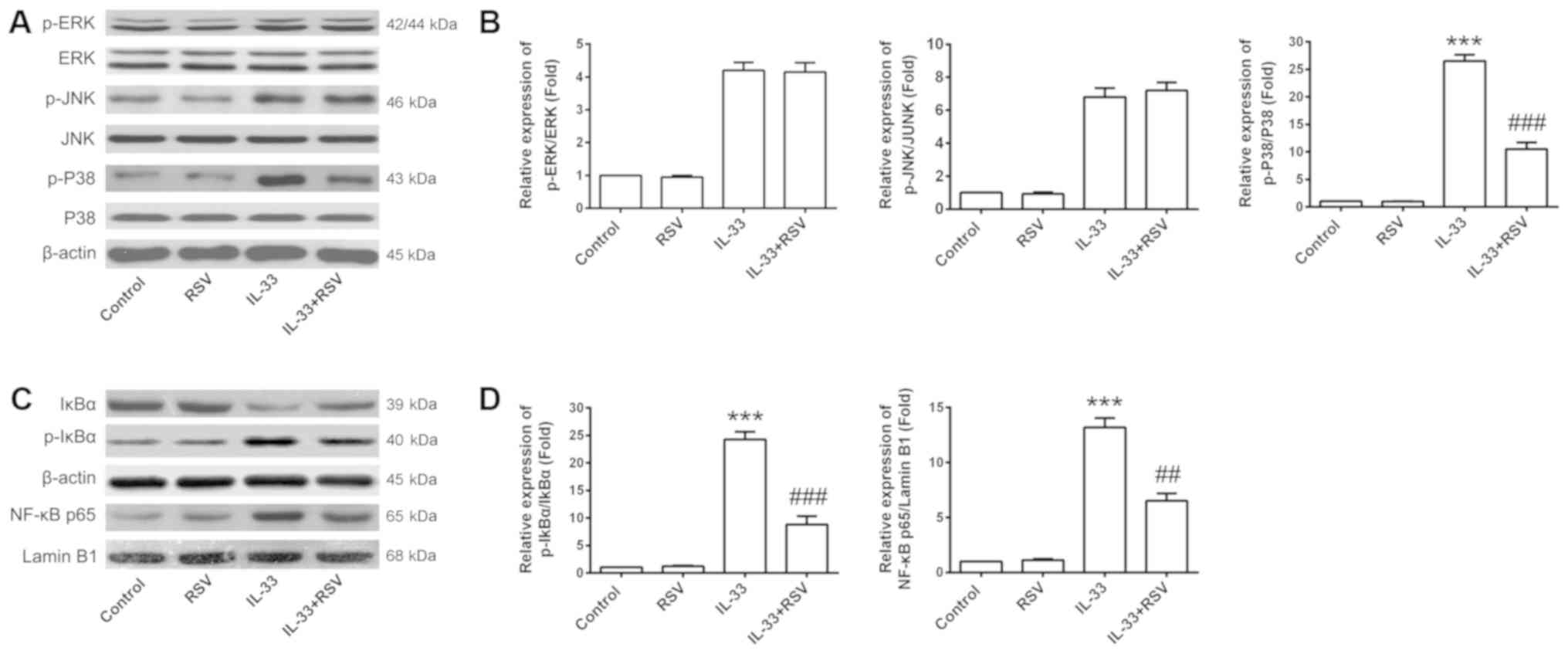
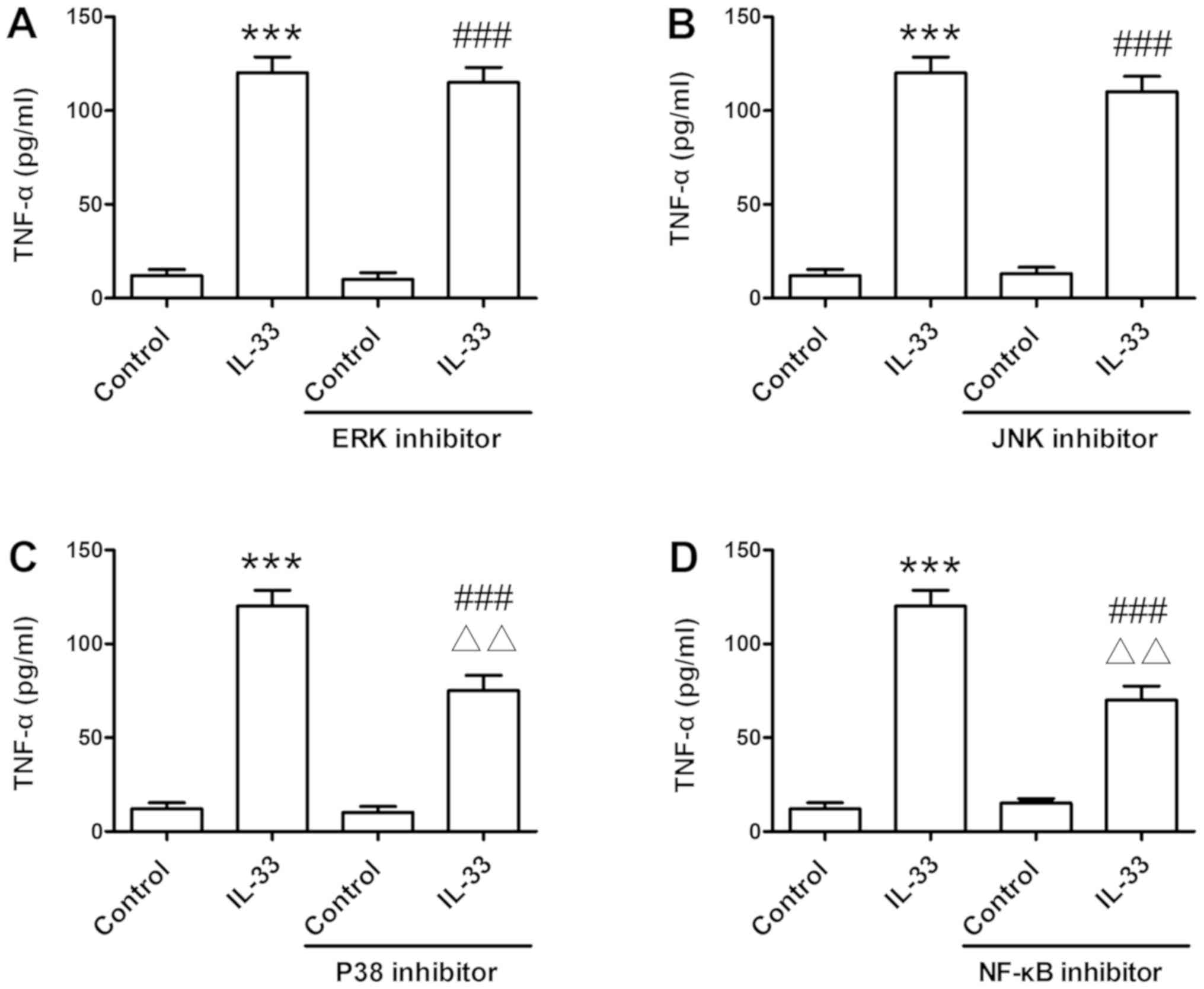
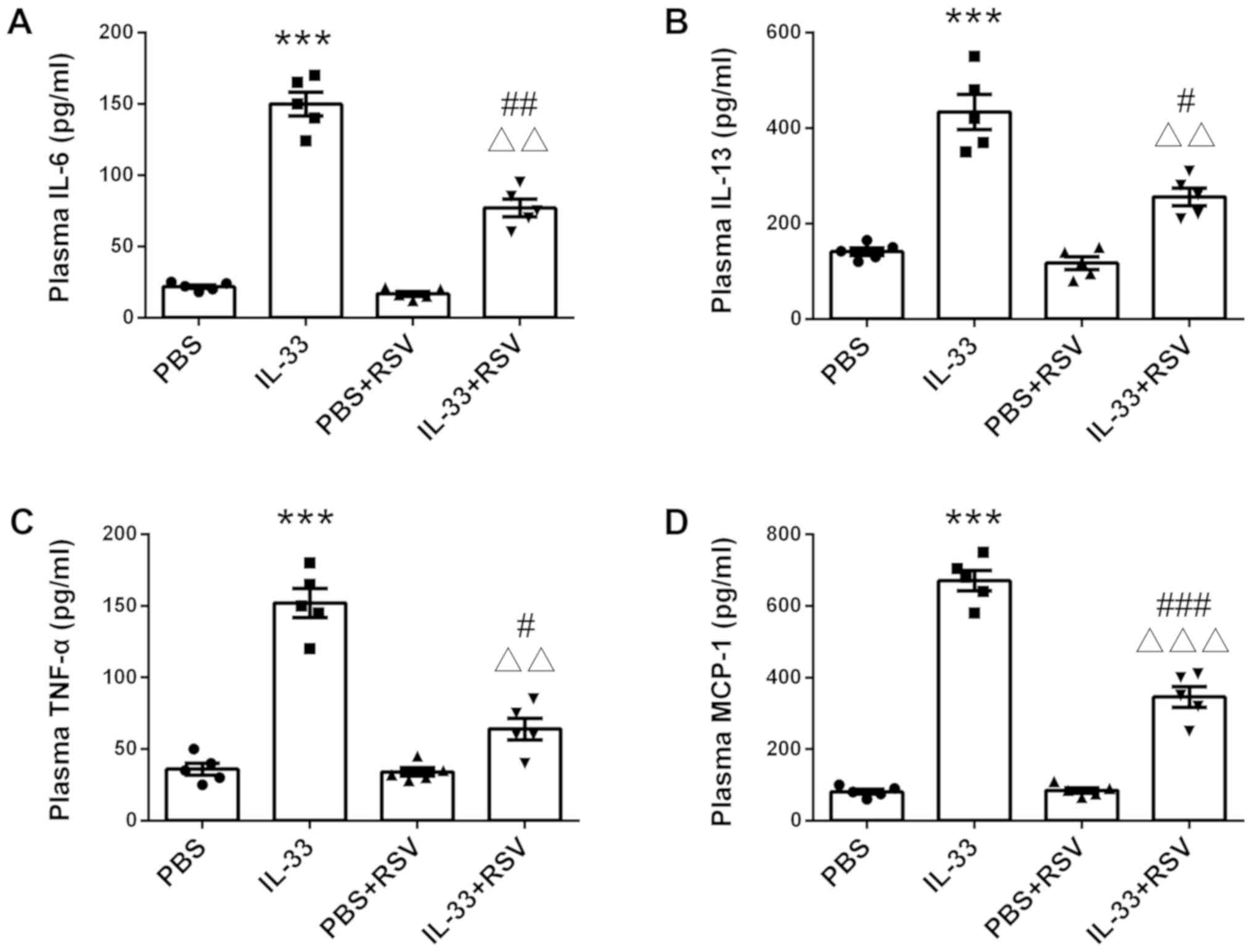
|
1
|
Singh VK, Mehrotra S and Agarwal SS: The
paradigm of Th1 and Th2 cytokines: Its relevance to autoimmunity
and allergy. Immunol Res. 20:147–161. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liew FY, Pitman NI and McInnes IB:
Disease-associated functions of IL-33: The new kid in the IL-1
family. Nat Rev Immunol. 10:103–110. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Préfontaine D, Lajoie-Kadoch S, Foley S,
Audusseau S, Olivenstein R, Halayko AJ, Lemière C, Martin JG and
Hamid Q: Increased expression of IL-33 in severe asthma: Evidence
of expression by airway smooth muscle cells. J Immunol.
183:5094–5103. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hayakawa H, Hayakawa M, Kume A and
Tominaga S: Soluble ST2 blocks interleukin-33 signaling in allergic
airway inflammation. J Biol Chem. 282:26369–26380. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
De Salvo C, Wang XM, Pastorelli L,
Mattioli B, Omenetti S, Buela KA, Chowdhry S, Garg RR, Goodman WA,
Rodriguez-Palacios A, et al: IL-33 drives eosinophil infiltration
and pathogenic type 2 helper T-cell immune responses leading to
chronic experimental ileitis. Am J Pathol. 186:885–898. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Imaeda H, Andoh A, Aomatsu T, Uchiyama K,
Bamba S, Tsujikawa T, Naito Y and Fujiyama Y: Interleukin-33
suppresses Notch ligand expression and prevents goblet cell
depletion in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. Int J Mol Med.
28:573–578. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Russi AE, Ebel ME, Yang Y and Brown MA:
Male-specific IL-33 expression regulates sex-dimorphic EAE
susceptibility. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 115:E1520–E1529. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Palmer G and Gabay C: Interleukin-33
biology with potential insights into human diseases. Nat Rev
Rheumatol. 7:321–329. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Balato A, Lembo S, Mattii M, Schiattarella
M, Marino R, De Paulis A, Balato N and Ayala F: IL-33 is secreted
by psoriatic keratinocytes and induces pro-inflammatory cytokines
via keratinocyte and mast cell activation. Exp Dermatol.
21:892–894. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li W, Yin N, Tao W, Wang Q, Fan H and Wang
Z: Berberine suppresses IL-33-induced inflammatory responses in
mast cells by inactivating NF-κB and p38 signaling. Int
Immunopharmacol. 66:82–90. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Silver MR, Margulis A, Wood N, Goldman SJ,
Kasaian M and Chaudhary D: IL-33 synergizes with IgE-dependent and
IgE-independent agents to promote mast cell and basophil
activation. Inflamm Res. 59:207–218. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cayrol C and Girard JP: Interleukin-33
(IL-33): A nuclear cytokine from the IL-1 family. Immunol Rev.
281:154–168. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Takatori H, Makita S, Ito T, Matsuki A and
Nakajima H: Regulatory mechanisms of IL-33-ST2-mediated allergic
inflammation. Front Immunol. 9:20042018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
He X, Wang L, Szklarz G, Bi Y and Ma Q:
Resveratrol inhibits paraquat-induced oxidative stress and
fibrogenic response by activating the nuclear factor erythroid
2-related factor 2 pathway. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 342:81–90. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Baolin L, Inami Y, Tanaka H, Inagaki N,
Iinuma M and Nagai H: Resveratrol inhibits the release of mediators
from bone marrow-derived mouse mast cells in vitro. Planta Med.
70:305–359. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Han SY, Bae JY, Park SH, Kim YH, Park JH
and Kang YH: Resveratrol inhibits IgE-mediated basophilic mast cell
degranulation and passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in mice. J Nutr.
143:632–639. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pan J, Xu T, Xu F, Zhang Y, Liu Z, Chen W,
Fu W, Dai Y, Zhao Y, Feng J and Liang G: Development of
resveratrol-curcumin hybrids as potential therapeutic agents for
inflammatory lung diseases. Eur J Med Chem. 125:478–491. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Thangam EB, Jemima EA, Singh H, Baig MS,
Khan M, Mathias CB, Church MK and Saluja R: The role of histamine
and histamine receptors in mast cell-mediated allergy and
inflammation: The hunt for new therapeutic targets. Front Immunol.
9:18732018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sibilano R, Frossi B and Pucillo CE: Mast
cell activation: A complex interplay of positive and negative
signaling pathways. Eur J Immunol. 44:2558–2566. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kitaura J, Song J, Tsai M, Asai K,
Maeda-Yamamoto M, Mocsai A, Kawakami Y, Liu FT, Lowell CA, Barisas
BG, et al: Evidence that IgE molecules mediate a spectrum of
effects on mast cell survival and activation via aggregation of the
FcepsilonRI. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:12911–12916. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hsu CL, Neilsen CV and Bryce PJ: IL-33 is
produced by mast cells and regulates IgE-dependent inflammation.
PLoS One. 5:e119442010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Katwa P, Wang X, Urankar RN, Podila R,
Hilderbrand SC, Fick RB, Rao AM, Ke PC, Wingard CJ and Brown JM: A
carbon nanotube toxicity paradigm driven by mast cells and the
IL-33/ST2 axis. Small. 8:2904–2912. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Caslin HL, McLeod JJA, Spence AJ, Qayum
AA, Kolawole EM, Taruselli MT, Paranjape A, Elford HL and Ryan JJ:
Didox (3,4-dihydroxybenzohydroxamic acid) suppresses IL-33-induced
cytokine production in primary mouse mast cells. Cell Immunol.
319:10–16. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Milovanovic M, Volarevic V, Radosavljevic
G, Jovanovic I, Pejnovic N, Arsenijevic N and Lukic ML: IL-33/ST2
axis in inflammation and immunopathology. Immunol Res. 52:89–99.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bandara G, Beaven MA, Olivera A, Gilfillan
AM and Metcalfe DD: Activated mast cells synthesize and release
soluble ST2-a decoy receptor for IL-33. Eur J Immunol.
45:3034–3044. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Velez TE, Bryce PJ and Hulse KE: Mast cell
interactions and crosstalk in regulating allergic inflammation.
Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 18:302018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zoltowska AM, Lei Y, Fuchs B, Rask C,
Adner M and Nilsson GP: The interleukin-33 receptor ST2 is
important for the development of peripheral airway
hyperresponsiveness and inflammation in a house dust mite mouse
model of asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 46:479–490. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Saglani S, Lui S, Ullmann N, Campbell GA,
Sherburn RT, Mathie SA, Denney L, Bossley CJ, Oates T, Walker SA,
et al: IL-33 promotes airway remodeling in pediatric patients with
severe steroid-resistant asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
132:676–685. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim EK and Choi EJ: Compromised MAPK
signaling in human diseases: An update. Arch Toxicol. 89:867–882.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee M, Kim S, Kwon OK, Oh SR, Lee HK and
Ahn K: Anti-inflammatory and anti-asthmatic effects of resveratrol,
a polyphenolic stilbene, in a mouse model of allergic asthma. Int
Immunopharmacol. 9:418–424. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ahmad SF, Ansari MA, Nadeem A, Bakheet SA,
Alzahrani MZ, Alshammari MA, Alanazi WA, Alasmari AF and Attia SM:
Resveratrol attenuates pro-inflammatory cytokines and activation of
JAK1-STAT3 in BTBR T+ Itpr3tf/J autistic mice. Eur J Pharmacol.
829:70–78. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhou ZX, Mou SF, Chen XQ, Gong LL and Ge
WS: Anti-inflammatory activity of resveratrol prevents inflammation
by inhibiting NF-κB in animal models of acute pharyngitis. Mol Med
Rep. 17:1269–1274. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Byun EB, Sung NY, Park JN, Yang MS, Park
SH and Byun EH: Gamma-irradiated resveratrol negatively regulates
LPS-induced MAPK and NF-κB signaling through TLR4 in macrophages.
Int Immunopharmacol. 25:249–259. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang G, Hu Z, Fu Q, Song X, Cui Q, Jia R,
Zou Y, He C, Li L and Yin Z: Resveratrol mitigates
lipopolysaccharide-mediated acute inflammation in rats by
inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κBp65/MAPKs signaling cascade. Sci Rep.
7:450062017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kauppinen A, Suuronen T, Ojala J,
Kaarniranta K and Salminen A: Antagonistic crosstalk between NF-κB
and SIRT1 in the regulation of inflammation and metabolic
disorders. Cell Signal. 25:1939–1948. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu Z, Jiang C, Zhang J, Liu B and Du Q:
Resveratrol inhibits inflammation and ameliorates insulin resistant
endothelial dysfunction via regulation of AMP-activated protein
kinase and sirtuin 1 activities. J Diabetes. 8:324–335. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Han SY, Choi YJ, Kang MK, Park JH and Kang
YH: Resveratrol suppresses cytokine production linked to FcεRI-MAPK
activation in IgE-antigen complex-exposed basophilic mast cells and
mice. Am J Chin Med. 43:1605–1623. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hossen MJ, Cho JY and Kim D: PDK1 in NF-κB
signaling is a target of Xanthium strumarium methanolic
extract-mediated anti-inflammatory activities. J Ethnopharmacol.
190:251–260. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Aich J, Mabalirajan U, Ahmad T, Khanna K,
Rehman R, Agrawal A and Ghosh B: Resveratrol attenuates
experimental allergic asthma in mice by restoring inositol
polyphosphate 4 phosphatase (INPP4A). Int Immunopharmacol.
14:438–443. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lee HY, Kim IK, Yoon HK, Kwon SS, Rhee CK
and Lee SY: Inhibitory effects of resveratrol on airway remodeling
by transforming growth factor-β/Smad signaling pathway in chronic
asthma model. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 9:25–34. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|