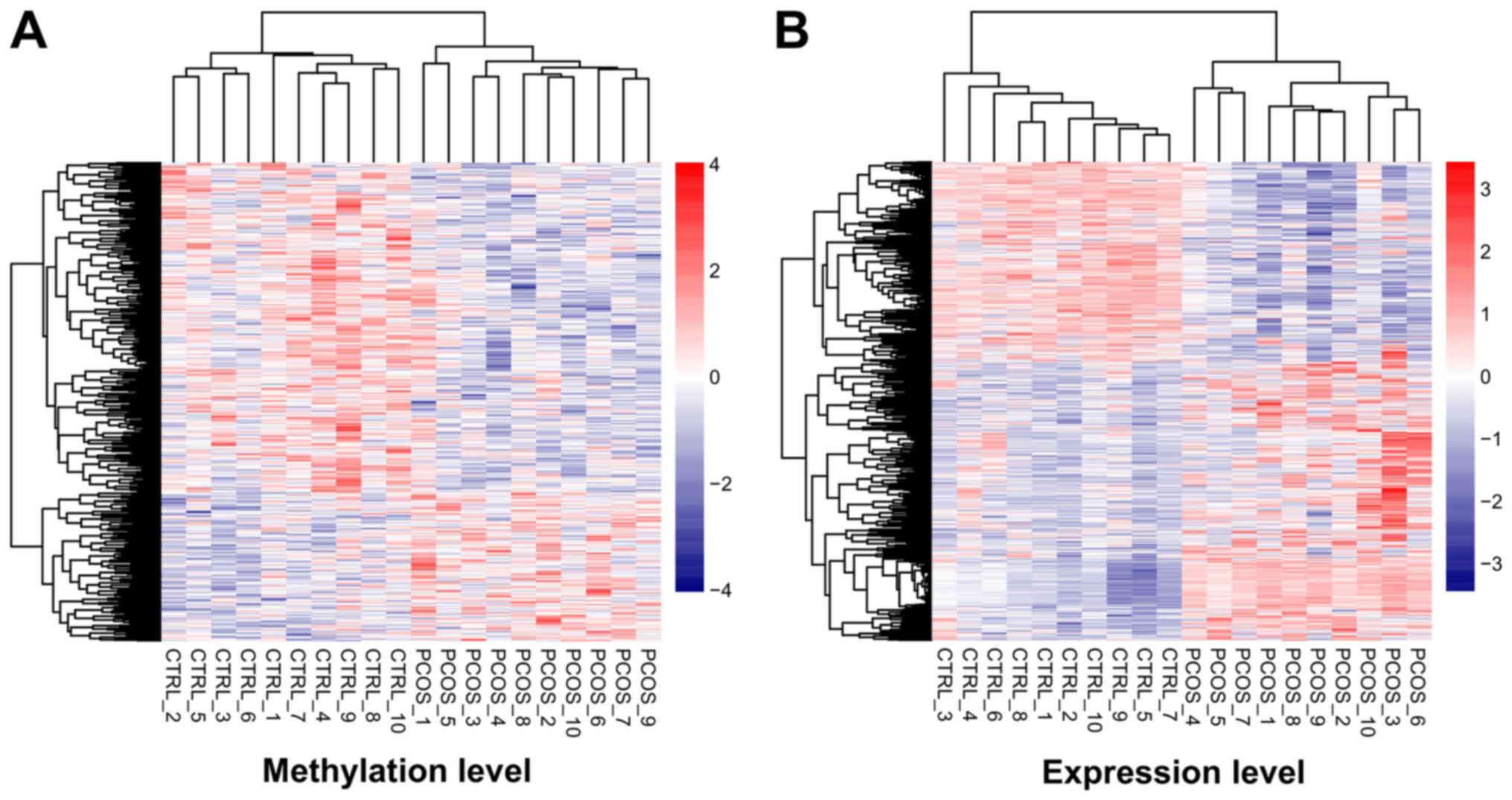
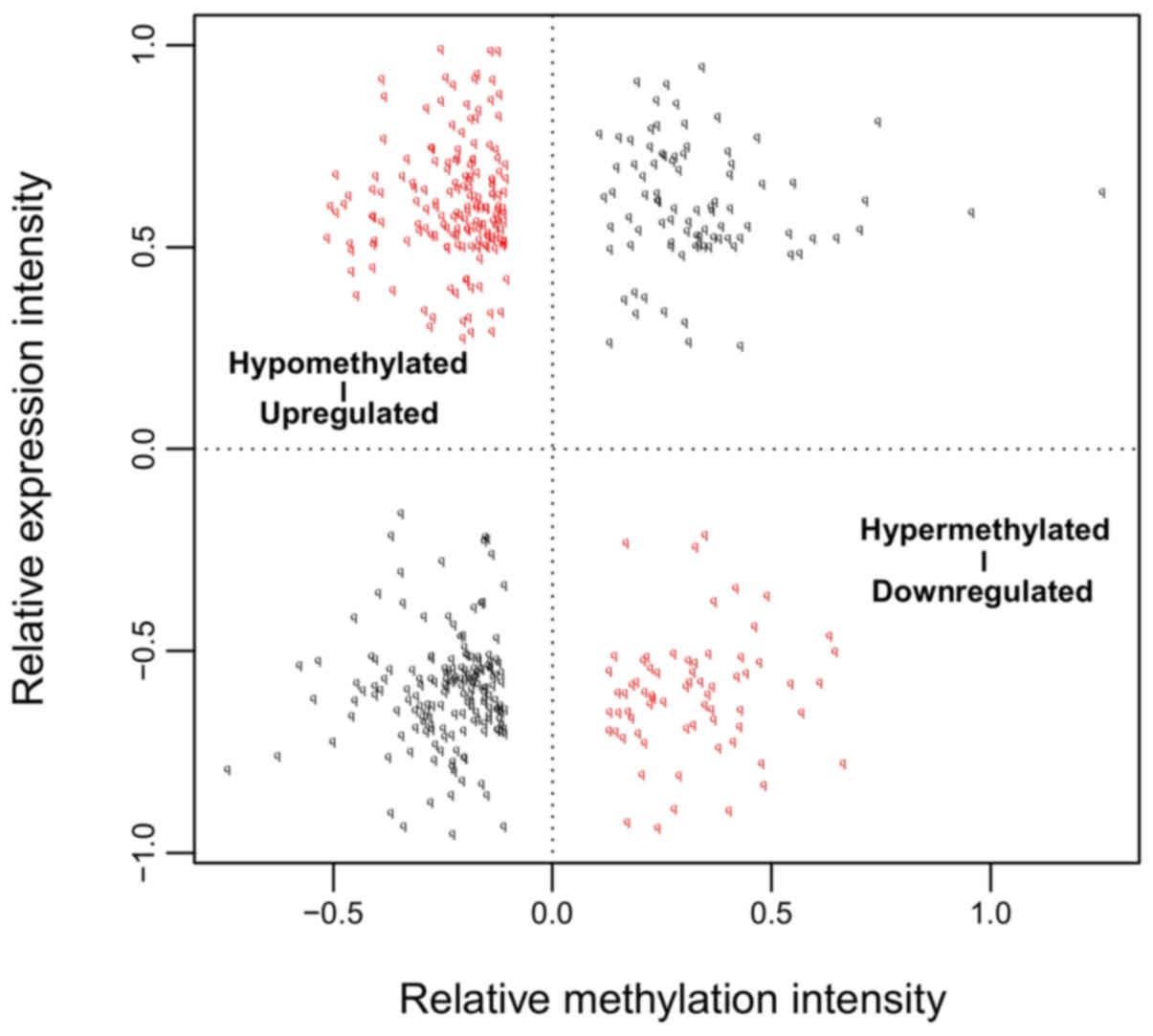
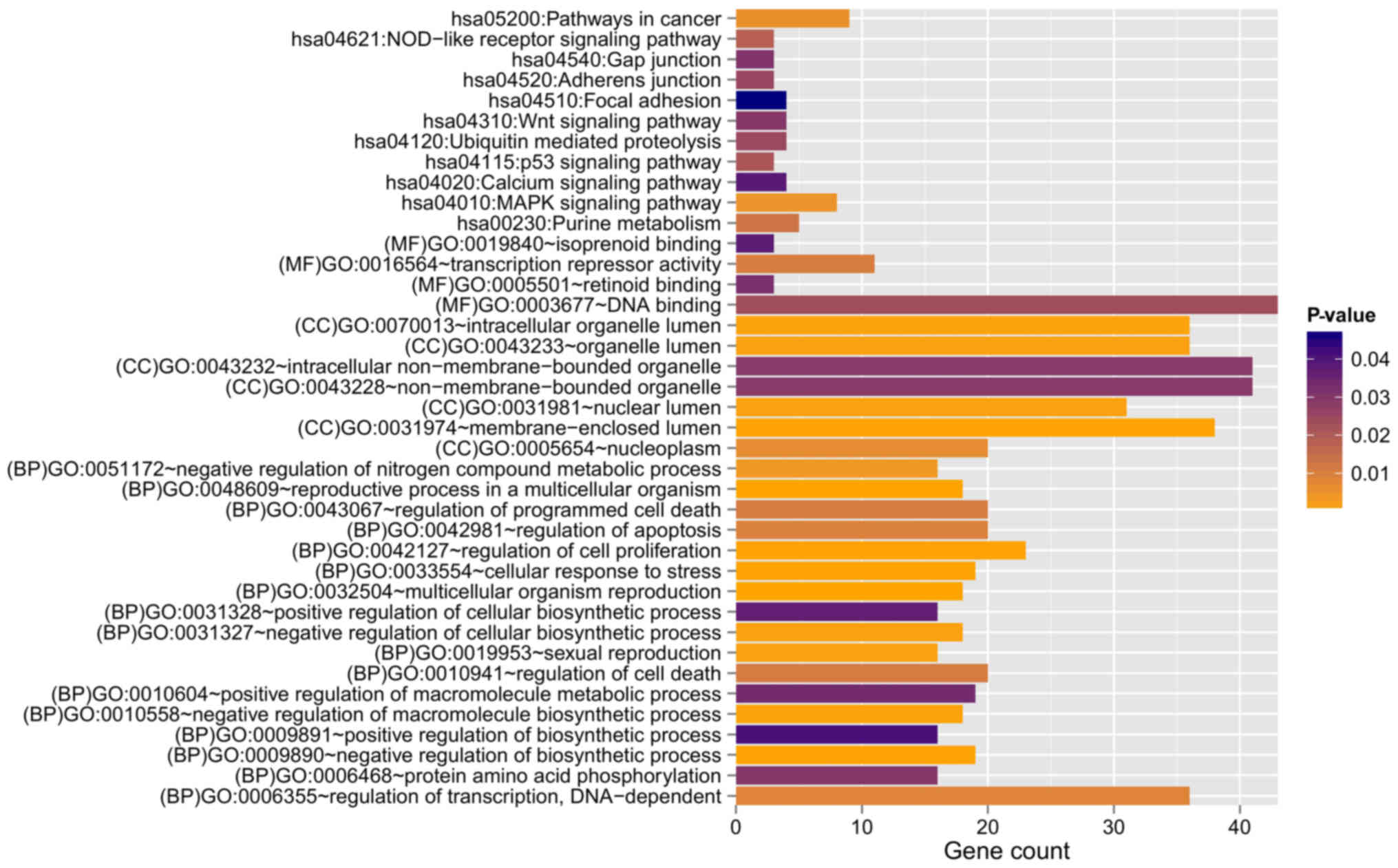
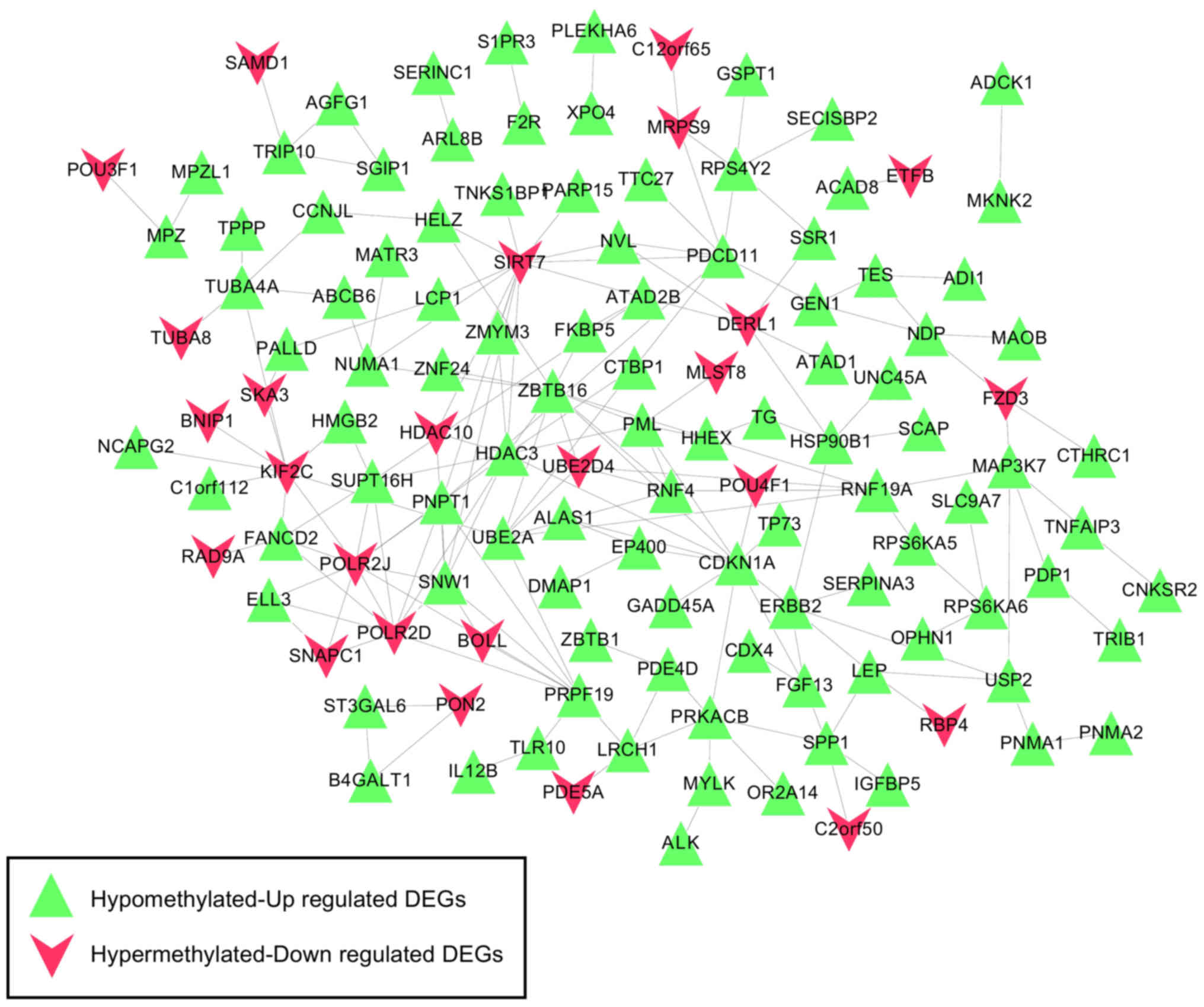
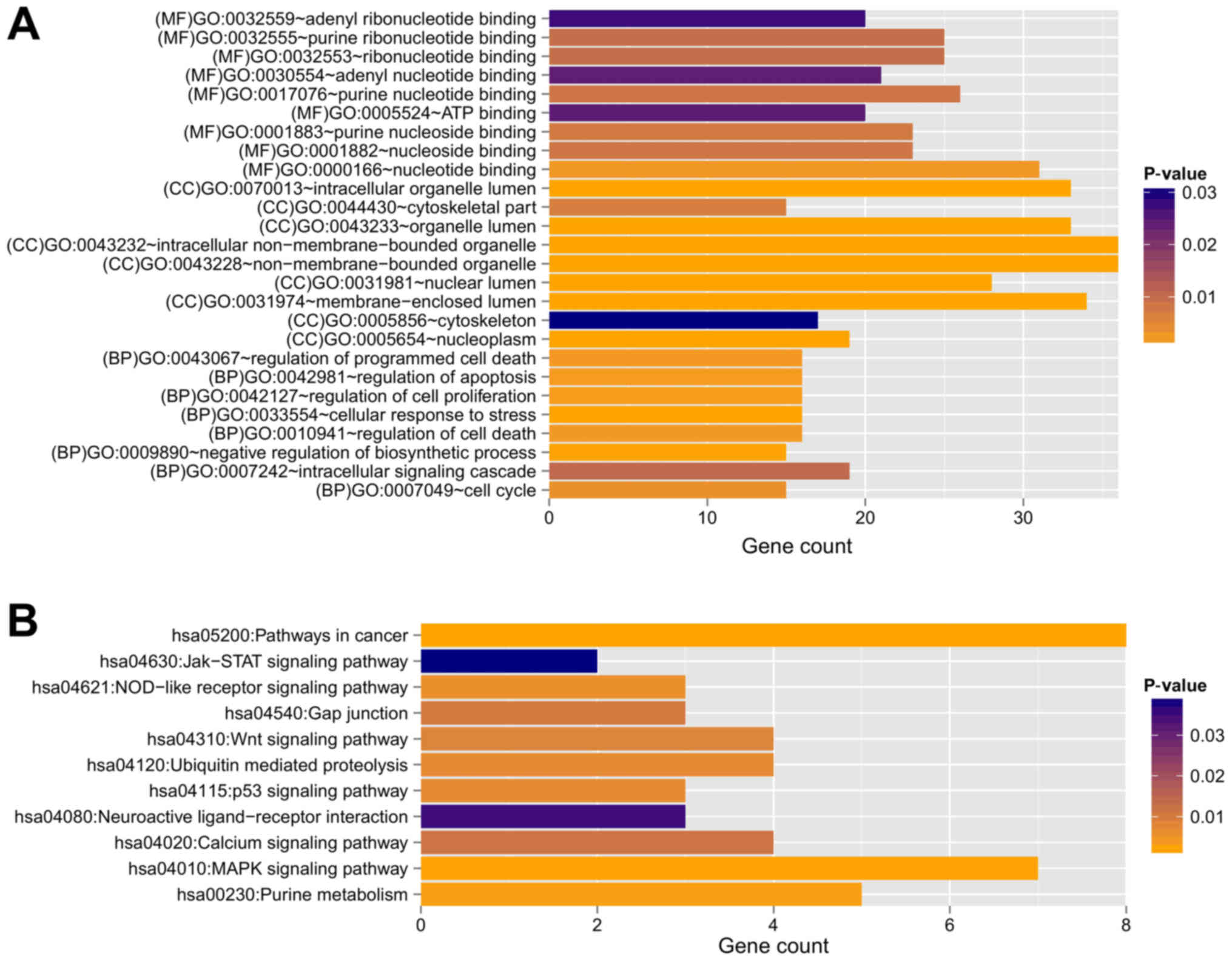
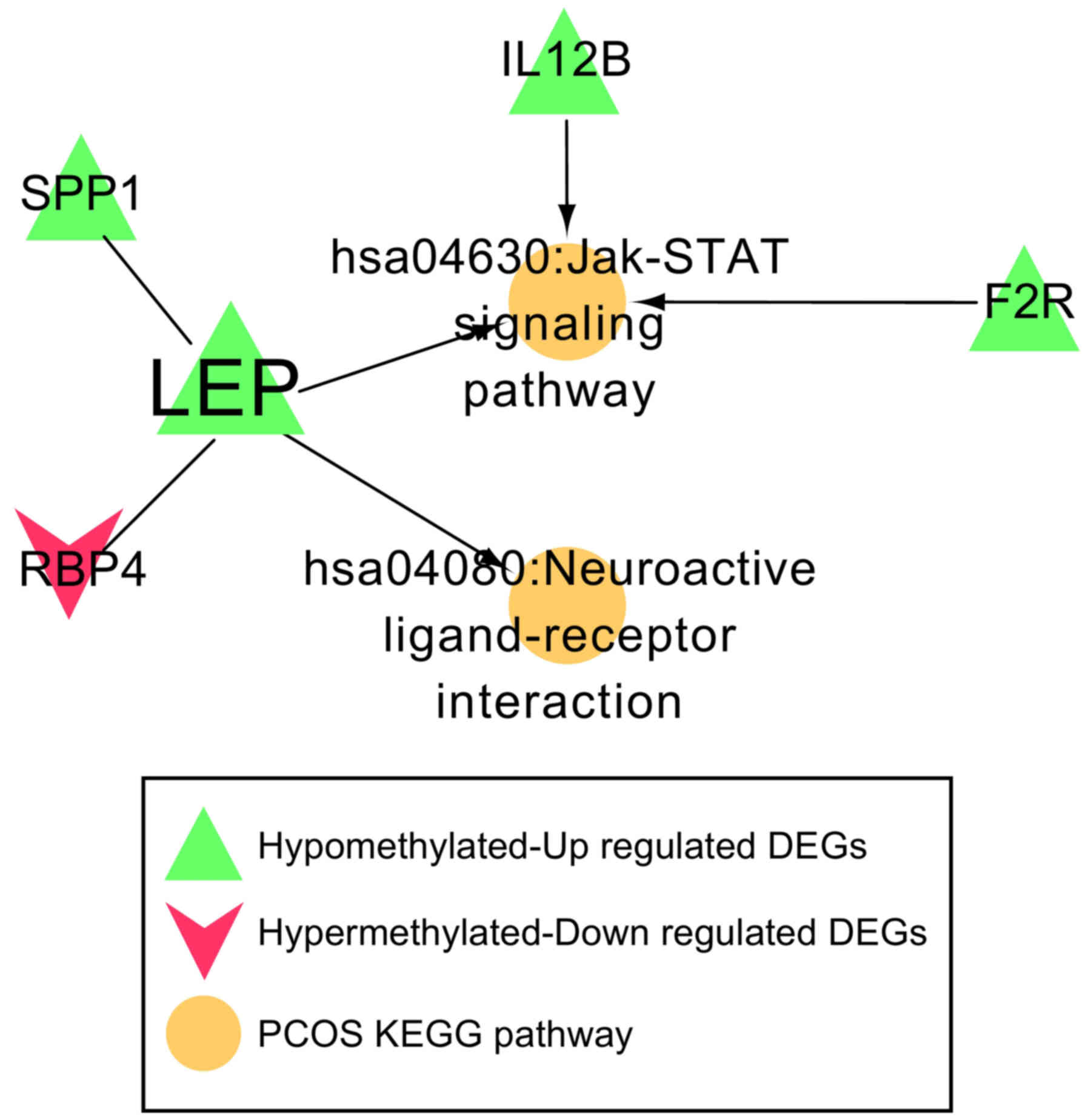
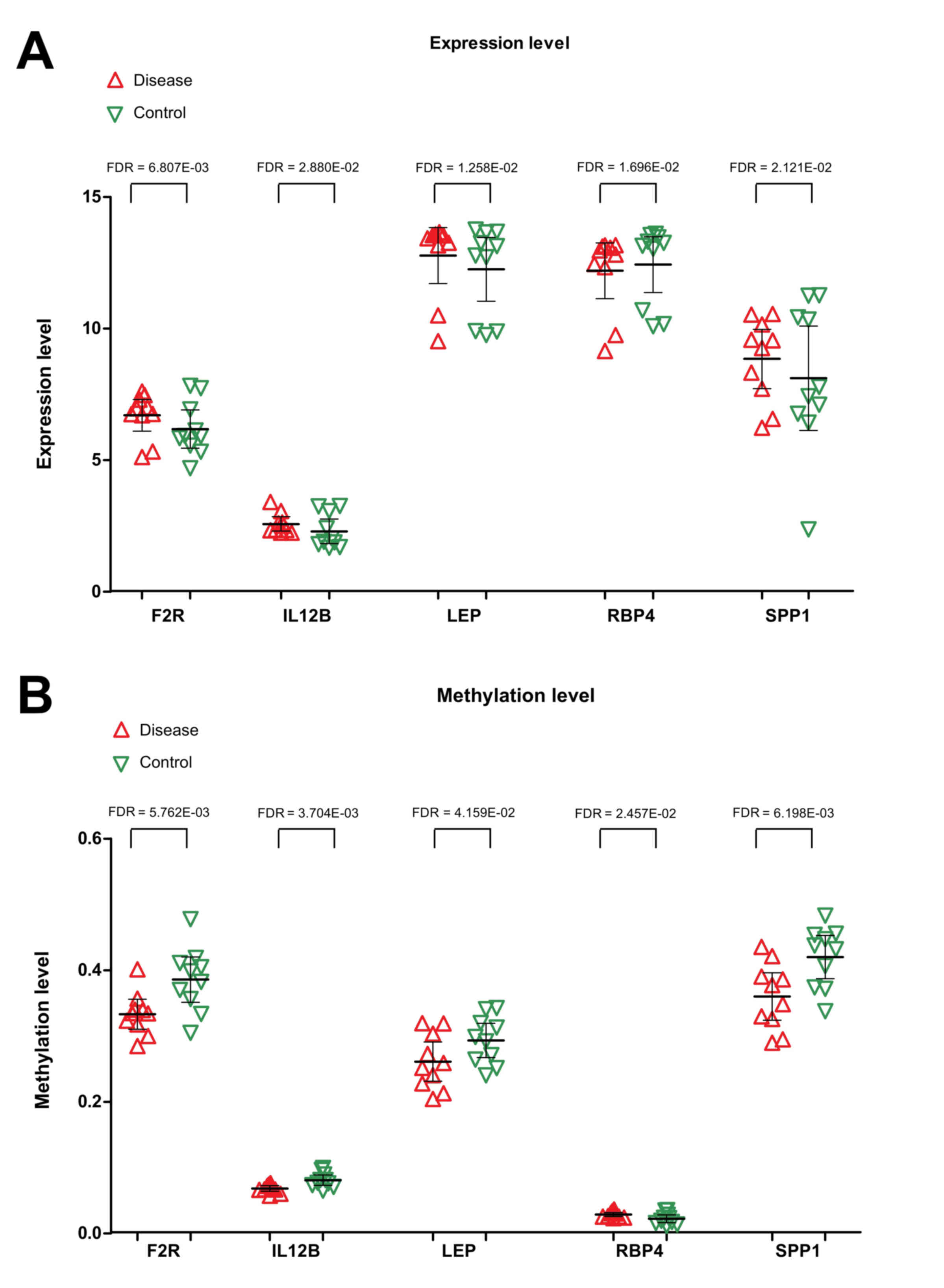
|
1
|
Azziz R, Carmina E, Chen Z, Dunaif A,
Laven JS, Legro RS, Lizneva D, Natterson-Horowtiz B, Teede HJ and
Yildiz BO: Polycystic ovary syndrome. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
2:160582016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Neven ACH, Laven J, Teede HJ and Boyle JA:
A summary on polycystic ovary syndrome: Diagnostic criteria,
prevalence, clinical manifestations, and management according to
the latest international guidelines. Semin Reprod Med. 36:5–12.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Strauss JF, Modi BP and McAllister JM: The
genetics of polycystic ovary syndrome: From genome-wide association
to molecular mechanisms. Reproductive Medicine for Clinical
Practice. Springer; pp. 25–33. 2018, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zhong Z, Li F, Li Y, Qin S, Wen C, Fu Y
and Xiao Q: Inhibition of microRNA-19b promotes ovarian granulosa
cell proliferation by targeting IGF-1 in polycystic ovary syndrome.
Mol Med Rep. 17:4889–4898. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Barber T and Franks S: Genetic and
environmental factors in the etiology of polycystic ovary syndrome.
The Ovary. Elsevier; pp. 437–459. 2019, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Guo F, Li X, Liang D, Li T, Zhu P, Guo H,
Wu X, Wen L, Gu TP, Hu B, et al: Active and passive demethylation
of male and female pronuclear DNA in the mammalian zygote. Cell
Stem Cell. 15:447–459. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wijaya AD, Febri RR, Hestiantoro A and
Asmarinah: DNA methylation analysis of anti-mullerian hormone gene
in ovarian granulosa cells in PCOS patients. J Phys Conf Ser.
1073:0320772018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Xu N, Azziz R and Goodarzi MO: Epigenetics
in polycystic ovary syndrome: A pilot study of global DNA
methylation. Fertil Steril. 94:781–783.e1. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shen HR, Qiu LH, Zhang ZQ, Qin YY, Cao C
and Di W: Genome-wide methylated DNA immunoprecipitation analysis
of patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. PLoS One. 8:e648012013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xu J, Xiao B, Peng Z, Wang L, Du L, Niu W
and Sun Y: Comprehensive analysis of genome-wide DNA methylation
across human polycystic ovary syndrome ovary granulosa cell.
Oncotarget. 7:27899–27909. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang XX, Wei JZ, Jiao J, Jiang SY, Yu DH
and Li D: Genome-wide DNA methylation and gene expression patterns
provide insight into polycystic ovary syndrome development.
Oncotarget. 5:6603–6610. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Parkinson H, Sarkans U, Kolesnikov N,
Abeygunawardena N, Burdett T, Dylag M, Emam I, Farne A, Hastings E,
Holloway E, et al: ArrayExpress update-an archive of microarray and
high-throughput sequencing-based functional genomics experiments.
Nucleic Acids Res. 39:D1002–D1004. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: Limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rao Y, Lee Y, Jarjoura D, Ruppert AS, Liu
CG, Hsu JC and Hagan JP: A comparison of normalization techniques
for microRNA microarray data. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol.
7:Article222008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Smyth GK: Limma: Linear models for
microarray data. Bioinformatics and computational biology solutions
using R and Bioconductor. Springer; pp. 397–420. 2005, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. J Royal Stat Soc Series B. 57:289–300. 1995.
|
|
17
|
Uchino H, Ito M, Kazumata K, Hama Y,
Hamauchi S, Terasaka S, Sasaki H and Houkin K: Circulating miRNome
profiling in moyamoya disease-discordant monozygotic twins and
endothelial microRNA expression analysis using iPS cell line. BMC
Med Genomics. 11:722018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang L, Cao C, Ma Q, Zeng Q, Wang H, Cheng
Z, Zhu G, Qi J, Ma H, Nian H and Wang Y: RNA-seq analyses of
multiple meristems of soybean: Novel and alternative transcripts,
evolutionary and functional implications. BMC Plant Biol.
14:1692014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Deza MM and Deza E: Encyclopedia of
Distances. Encyclopedia of Distances. Springer; Berlin, Heidelberg:
2009, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive
functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:1–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Szklarczyk D, Morris JH, Cook H, Kuhn M,
Wyder S, Simonovic M, Santos A, Doncheva NT, Roth A, Bork P, et al:
The STRING database in 2017: Quality-controlled protein-protein
association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res.
45:D362–D368. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Davis AP, Murphy CG, Johnson R, Lay JM,
Lennon-Hopkins K, Saraceni-Richards C, Sciaky D, King BL,
Rosenstein MC, Wiegers TC and Mattingly CJ: The comparative
toxicogenomics database: Update 2013. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:D1104–D1114. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Azziz R: PCOS in 2015: New insights into
the genetics of polycystic ovary syndrome. Nat Rev Endocrinol.
12:74–75. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Margetic S, Gazzola C, Pegg GG and Hill
RA: Leptin: A review of its peripheral actions and interactions.
Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 26:1407–1433. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nomair AM, Aref NK, Rizwan F, Ezzo OH and
Hassan N: Serum leptin level in obese women with polycystic ovary
syndrome and its relation to insulin resistance. Asian Pac J
Reproduction. 3:288–294. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Marciniak A and Starczewski A: The role of
leptin in polycystic ovary syndrome. Pol Merkur Lekarski.
25:390–393. 2008.(In Polish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zheng SH, Du DF and Li XL: Leptin levels
in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A systematic review and a
meta-analysis. Reprod Sci. 24:656–670. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Flier JS: Leptin expression and action:
New experimental paradigms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:4242–4245.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ghilardi N and Skoda RC: The leptin
receptor activates janus kinase 2 and signals for proliferation in
a factor-dependent cell line. Mol Endocrinol. 11:393–399. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kloek C, Haq AK, Dunn SL, Lavery HJ, Banks
AS and Myers MG Jr: Regulation of Jak kinases by intracellular
leptin receptor sequences. J Biol Chem. 277:41547–41555. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Maliqueo M, Sundström Poromaa I, Vanky E,
Fornes R, Benrick A, Åkerud H, Stridsklev S, Labrie F, Jansson T
and Stener-Victorin E: Placental STAT3 signaling is activated in
women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Hum Reprod. 30:692–700. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen MJ, Yang WS, Chen CL, Wu MY, Yang YS
and Ho HN: The relationship between anti-Müllerian hormone,
androgen and insulin resistance on the number of antral follicles
in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Hum Reprod. 23:952–957.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Maliqueo M, Clementi M, Gabler F, Johnson
MC, Palomino A, Sir-Petermann T and Vega M: Expression of steroid
receptors and proteins related to apoptosis in endometria of women
with polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil Steril. 80 (Suppl
2):S812–S819. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Du Y, Wang J, Lyu B, Yan G and Sun H:
Impaired granulosa cells promote self-damage by regulating the
generation of macrophage in polycystic ovary syndrome. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 9:10992–11002. 2016.
|
|
37
|
Das M, Djahanbakhch O, Hacihanefioglu B,
Saridogan E, Ikram M, Ghali L, Raveendran M and Storey A: Granulosa
cell survival and proliferation are altered in polycystic ovary
syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 93:881–887. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fu X, He Y, Wang X, Peng D, Chen X, Li X
and Wan Q: MicroRNA-16 promotes ovarian granulosa cell
proliferation and suppresses apoptosis through targeting PDCD4 in
polycystic ovarian syndrome. Cell Physiol Biochem. 48:670–682.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|