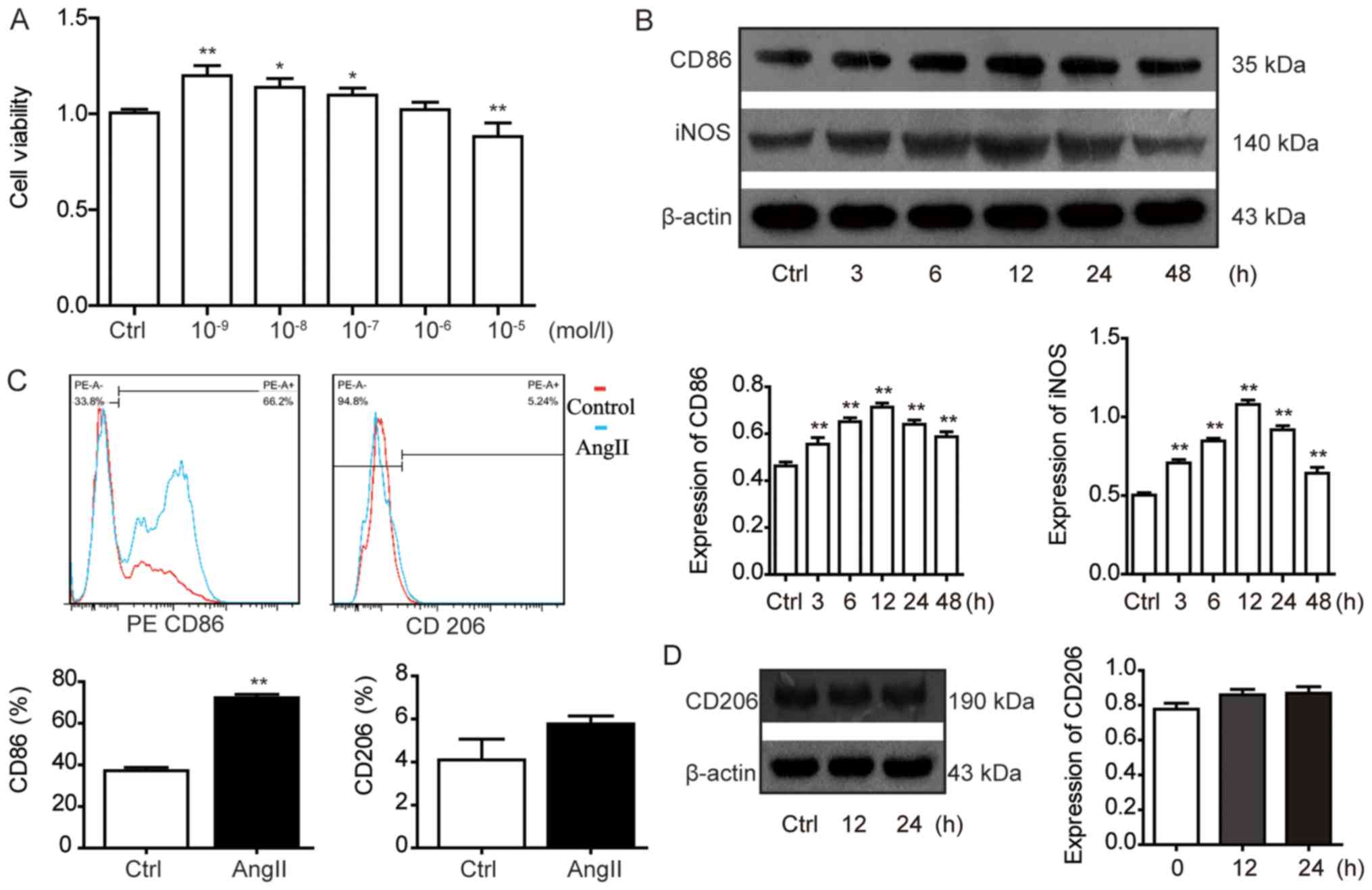
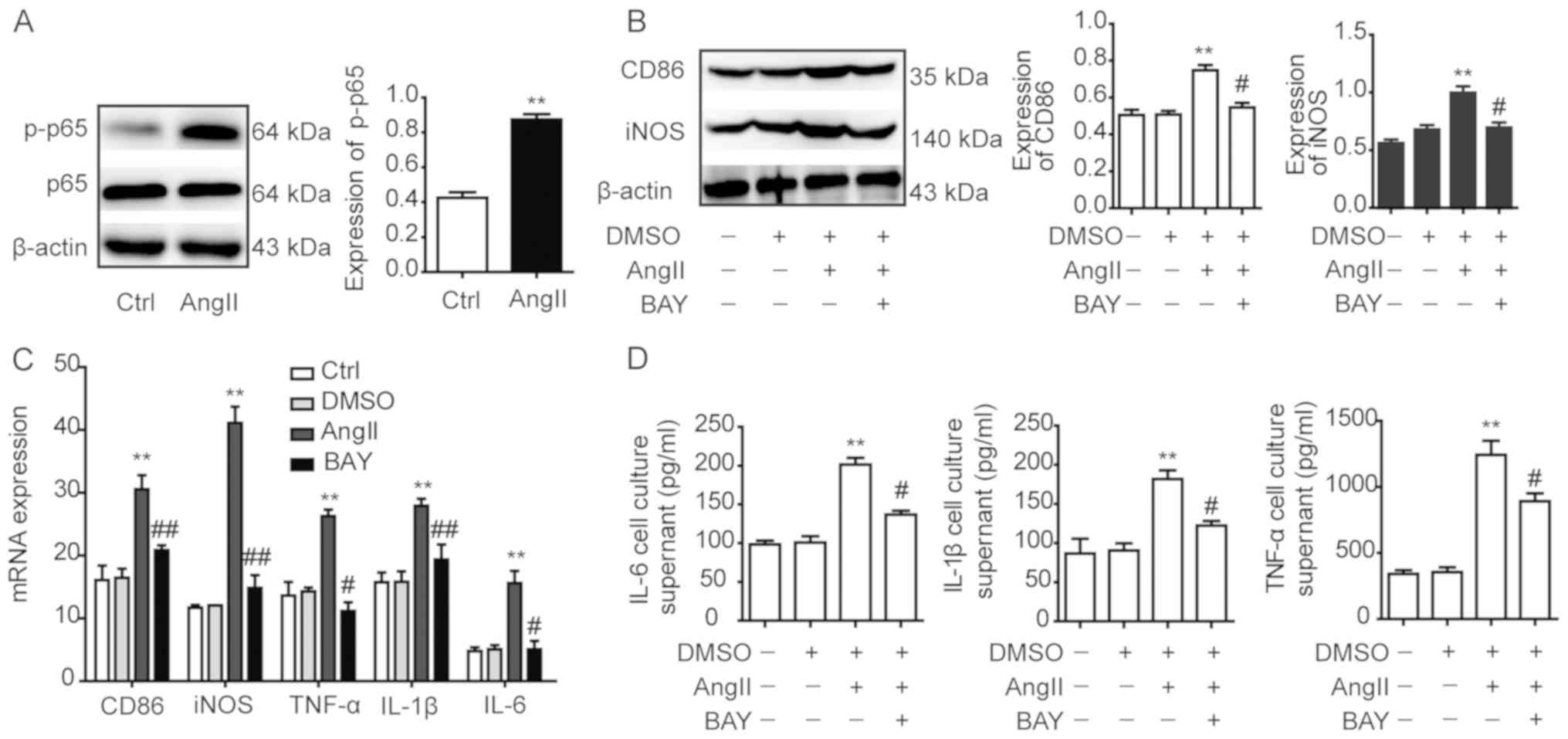
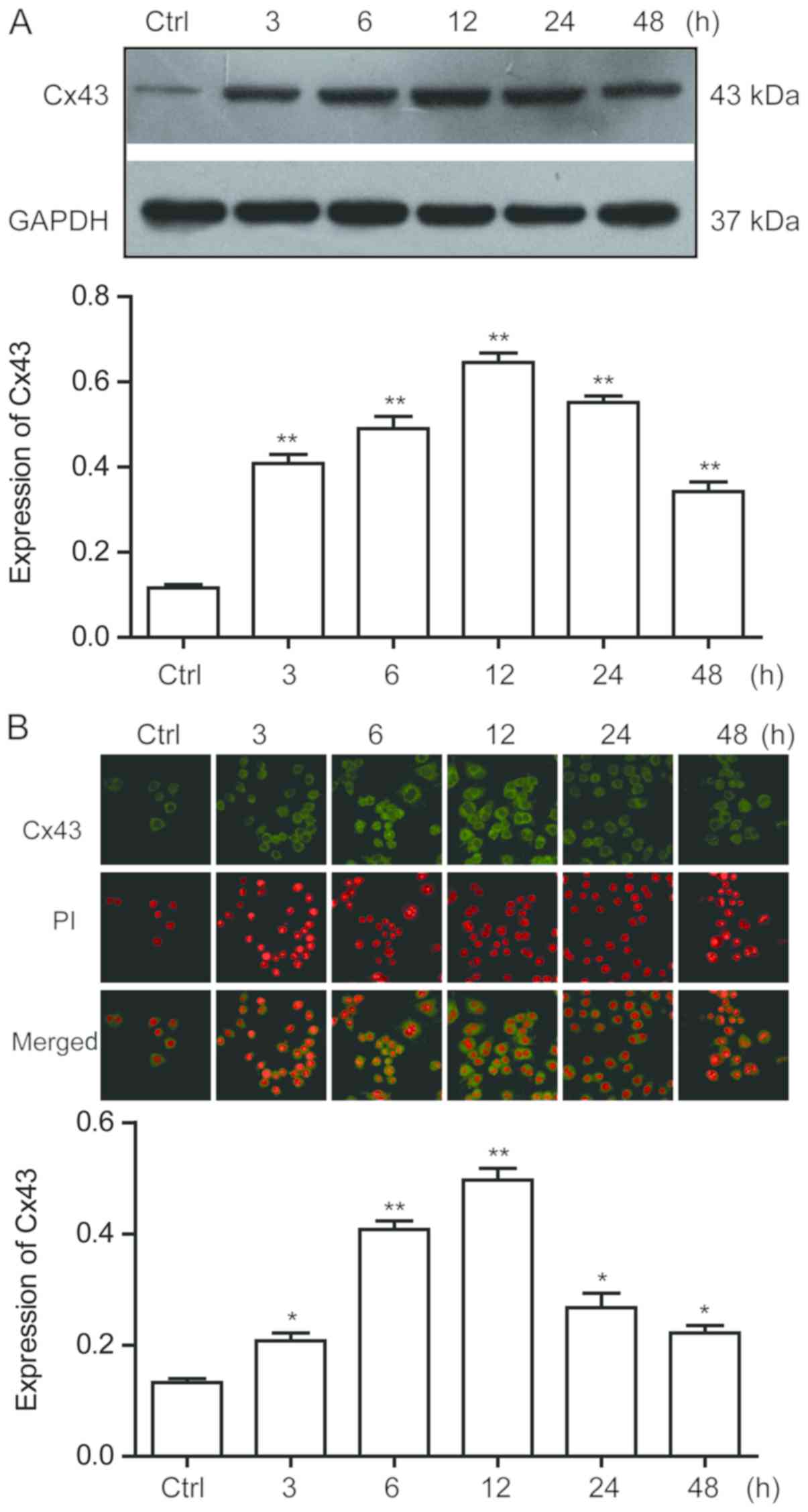
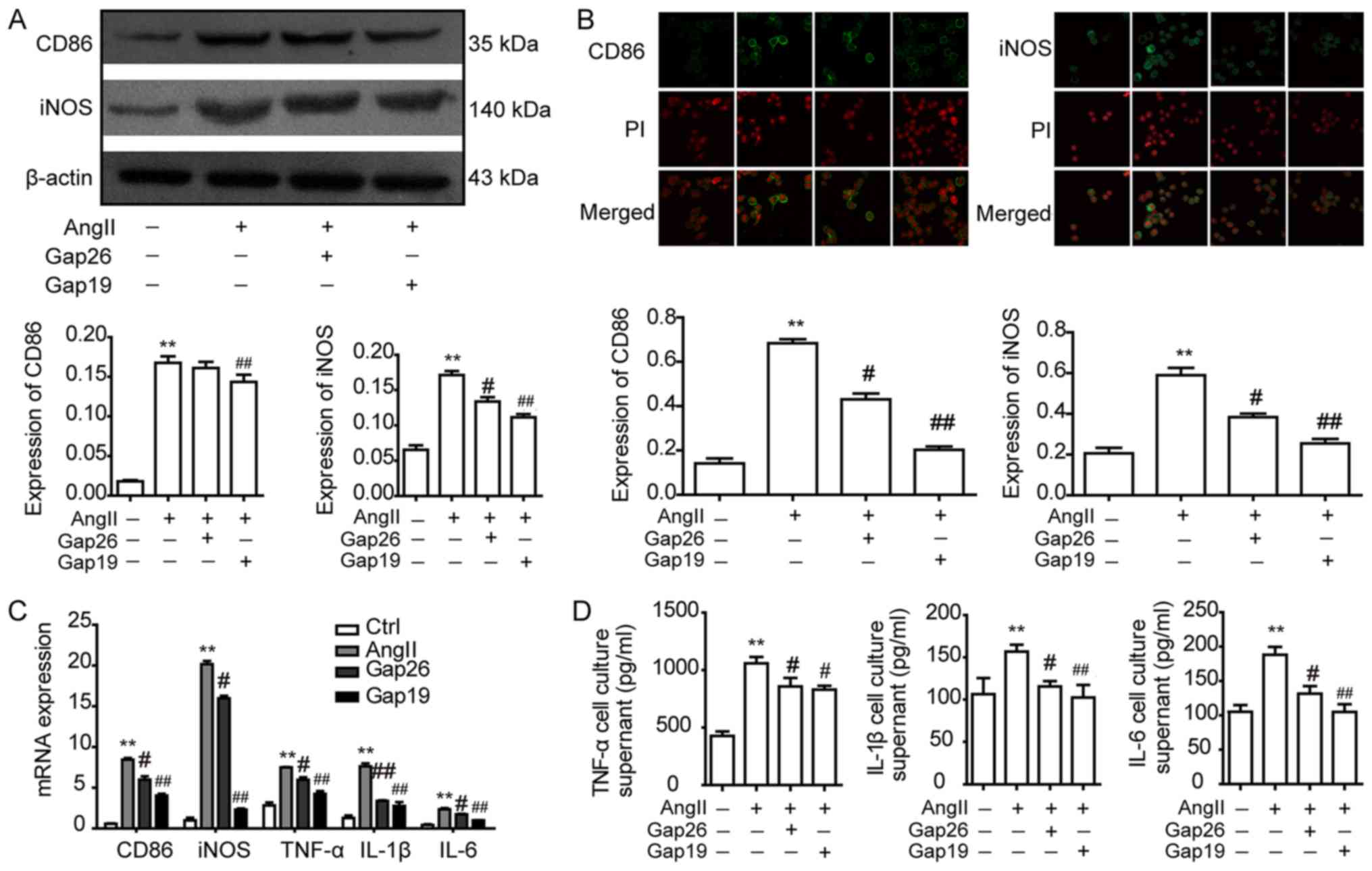
|
1
|
Wang Y, Xie Y, Zhang A, Wang M, Fang Z and
Zhang J: Exosomes: An emerging factor in atherosclerosis. Biomed
Pharmacother. 115:1089512019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhou M, Ren P, Zhang Y, Li S, Li M, Li P,
Shang J, Liu W and Liu H: Shen-Yuan-Dan capsule attenuates
atherosclerosis and foam cell formation by enhancing autophagy and
inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTORC1 signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol.
10:6032019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Moore KJ, Sheedy FJ and Fisher EA:
Macrophages in atherosclerosis: A dynamic balance. Nat Rev Immunol.
13:709–721. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Groh L, Keating ST, Joosten LAB, Netea MG
and Riksen NP: Monocyte and macrophage immunometabolism in
atherosclerosis. Semin Immunopathol. 40:203–214. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mohammadi S, Saghaeian-Jazi M, Sedighi S
and Memarian A: Sodium valproate modulates immune response by
alternative activation of monocyte-derived macrophages in systemic
lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol. 37:719–727. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Stöger JL, Gijbels MJ, van der Velden S,
Manca M, van der Loos CM, Biessen EA, Daemen MJ, Lutgens E and de
Winther MP: Distribution of macrophage polarization markers in
human atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 225:461–468. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Binesh A, Devaraj SN and Devaraj H:
Expression of chemokines in macrophage polarization and
downregulation of NF-κB in aorta allow macrophage polarization by
diosgenin in atherosclerosis. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 34:e224222020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhou S, Lu H, Chen R, Tian Y, Jiang Y,
Zhang S, Ni D, Su Z and Shao X: Angiotensin II enhances the
acetylation and release of HMGB1 in RAW264.7 macrophage. Cell Biol
Int. 42:1160–1169. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Manucha W: Mitochondria and oxidative
stress participation in renal inflammatory process. Medicina (B
Aires). 74:254–258. 2014.(In Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mitchell S, Vargas J and Hoffmann A:
Signaling via the NF-κB system. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol
Med. 8:227–241. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ding H, Zhou Y and Huang H: MiR-101a
ameliorates AngII-mediated hypertensive nephropathy by blockade of
TGFβ/Smad3 and NF-κB signalling in a mouse model of hypertension.
Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 46:246–254. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Willebrords J, Crespo Yanguas S, Maes M,
Decrock E, Wang N, Leybaert L, Kwak BR, Green CR, Cogliati B and
Vinken M: Connexins and their channels in inflammation. Crit Rev
Biochem Mol Biol. 51:413–439. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Donahue HJ, Qu RW and Genetos DC: Joint
diseases: From connexins to gap junctions. Nat Rev Rheumatol.
14:42–51. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Glass AM, Snyder EG and Taffet SM:
Connexins and pannexins in the immune system and lymphatic organs.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 72:2899–2910. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jia G, Mitra AK, Cheng G, Gangahar DM and
Agrawal DK: Angiotensin II and IGF-1 regulate connexin43 expression
via ERK and p38 signaling pathways in vascular smooth muscle cells
of coronary artery bypass conduits. J Surg Res. 142:137–142. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sarieddine MZ, Scheckenbach KE, Foglia B,
Maass K, Garcia I, Kwak BR and Chanson M: Connexin43 modulates
neutrophil recruitment to the lung. J Cell Mol Med. 13:4560–4570.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li M, Liu JT, Pang XM, Han CJ and Mao JJ:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits angiotensin II and
interleukin-6-induced C-reactive protein production in macrophages.
Pharmacol Rep. 64:912–918. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang LX, Liu H, Guo RW, Ye J, Wang XM, Qi
F, Guo CM and Liang X: Angiotensin II induces EMMPRIN expression in
THP-1 macrophages via the NF-kappaB pathway. Regul Pept. 163:88–95.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Desplantez T, Verma V, Leybaert L, Evans
WH and Weingart R: Gap26, a connexin mimetic peptide, inhibits
currents carried by connexin43 hemichannels and gap junction
channels. Pharmacol Res. 65:546–552. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li W, Bao G, Chen W, Qiang X, Zhu S, Wang
S, He M, Ma G, Ochani M, Al-Abed Y, et al: Connexin 43 hemichannel
as a novel mediator of sterile and infectious inflammatory
diseases. Sci Rep. 8:1662018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liang S, Chen Z, Jiang G, Zhou Y, Liu Q,
Su Q, Wei W, Du J and Wang H: Activation of GPER suppresses
migration and angiogenesis of triple negative breast cancer via
inhibition of NF-κB/IL-6 signals. Cancer Lett. 386:12–23. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Strickson S, Campbell DG, Emmerich CH,
Knebel A, Plater L, Ritorto MS, Shpiro N and Cohen P: The
anti-inflammatory drug BAY 11-7082 suppresses the MyD88-dependent
signalling network by targeting the ubiquitin system. Biochem J.
451:427–437. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hansson GK, Robertson AK and
Söderberg-Nauclér C: Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Annu Rev
Pathol. 1:297–329. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shao BZ, Han BZ, Zeng YX, Su DF and Liu C:
The roles of macrophage autophagy in atherosclerosis. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 37:150–156. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Han X, Ni J, Wu Z, Wu J, Li B, Ye X, Dai
J, Chen C, Xue J, Wan R, et al: Myeloid-specific dopamine D2
receptor signaling controls inflammation in acute pancreatitis via
inhibiting M1 macrophage. Br J Pharmacol. Feb 14–2020.(Epub ahead
of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Tabas I and Bornfeldt KE: Macrophage
phenotype and function in different stages of atherosclerosis. Circ
Res. 118:653–667. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Guo F, Chen XL, Wang F, Liang X, Sun YX
and Wang YJ: Role of angiotensin II type 1 receptor in angiotensin
II-induced cytokine production in macrophages. J Interferon
Cytokine Res. 31:351–361. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jiang Q, Pan D, Yang Y, Hu Y, Fang L,
Shang P, Xia Y and Li D: Luteolin regulates macrophage polarization
via the PI3K/Akt pathway to inhibit the apoptosis stimulated by
angiotensin II. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 19:428–437. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim KN, Ko SC, Ye BR, Kim MS, Kim J, Ko
EY, Cho SH, Kim D, Heo SJ and Jung WK:
5-Bromo-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-benzaldehyde inhibited LPS-induced
production of pro-inflammatory mediators through the inactivation
of ERK, p38, and NF-κB pathways in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Chem Biol
Interact. 258:108–114. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gupta A, Niger C, Buo AM, Eidelman ER,
Chen RJ and Stains JP: Connexin43 enhances the expression of
osteoarthritis-associated genes in synovial fibroblasts in culture.
BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 15:4252014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen D, Chen Y, Li T, Shi L, Pan M and
Chen D: Role of cx43-mediated NFкB signaling pathway in
ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament: An in vivo and in
vitro study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 42:E1334–E1341. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Legein B, Temmerman L, Biessen EA and
Lutgens E: Inflammation and immune system interactions in
atherosclerosis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 70:3847–3869. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yin X, Feng L, Ma D, Yin P, Wang X, Hou S,
Hao Y, Zhang J, Xin M and Feng J: Roles of astrocytic connexin-43,
hemichannels, and gap junctions in oxygen-glucose
deprivation/reperfusion injury induced neuroinflammation and the
possible regulatory mechanisms of salvianolic acid B and
carbenoxolone. J Neuroinflammation. 15:972018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pfenniger A, Chanson M and Kwak BR:
Connexins in atherosclerosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1828:157–166.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shen C, Chen JH, Lee Y, Hassan MM, Kim SJ,
Choi EY, Hong ST, Park BH and Park JH: mTOR- and SGK-mediated
connexin 43 expression participates in
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophage migration through the
iNOS/Src/FAK axis. J Immunol. 201:2986–2997. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nie W, Yan H, Li S, Zhu W, Fan F and Zhu
J: Angiotensin II promotes atherogenesis through upregulating the
expression of connexin 43 in dendritic cells. Cell Mol Biol
(Noisy-le-grand). 61:96–101. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kim Y, Davidson JO, Green CR, Nicholson
LFB, O'Carroll SJ and Zhang J: Connexins and pannexins in cerebral
ischemia. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 1860:224–236. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Huang JQ, Chen XY, Huang F, Fan JM, Shi XW
and Ju YK: Effects of connexin 43 inhibition in an
ovalbumin-induced mouse model of asthma. Iran J Allergy Asthma
Immunol. 17:29–38. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hawat G, Benderdour M, Rousseau G and
Baroudi G: Connexin 43 mimetic peptide Gap26 confers protection to
intact heart against myocardial ischemia injury. Pflugers Arch.
460:583–592. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Deng Y, Ren J, Chen G, Li G, Wu X, Wang G,
Gu G and Li J: Injectable in situ cross-linking chitosan-hyaluronic
acid based hydrogels for abdominal tissue regeneration. Sci Rep.
7:26992017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Messeha SS, Zarmouh NO, Mendonca P, Kolta
MG and Soliman KFA: The attenuating effects of plumbagin on
pro-inflammatory cytokine expression in LPS-activated BV-2
microglial cells. J Neuroimmunol. 313:129–137. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Alonso F, Krattinger N, Mazzolai L, Simon
A, Waeber G, Meda P and Haefliger JA: An angiotensin II- and
NF-kappaB-dependent mechanism increases connexin 43 in murine
arteries targeted by renin-dependent hypertension. Cardiovasc Res.
87:166–176. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang M, Wu Y, Yu Y, Fu Y, Yan H, Wang X,
Li T, Peng W and Luo D: Rutaecarpine prevented ox-LDL-induced VSMCs
dysfunction through inhibiting overexpression of connexin 43. Eur J
Pharmacol. 853:84–92. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|