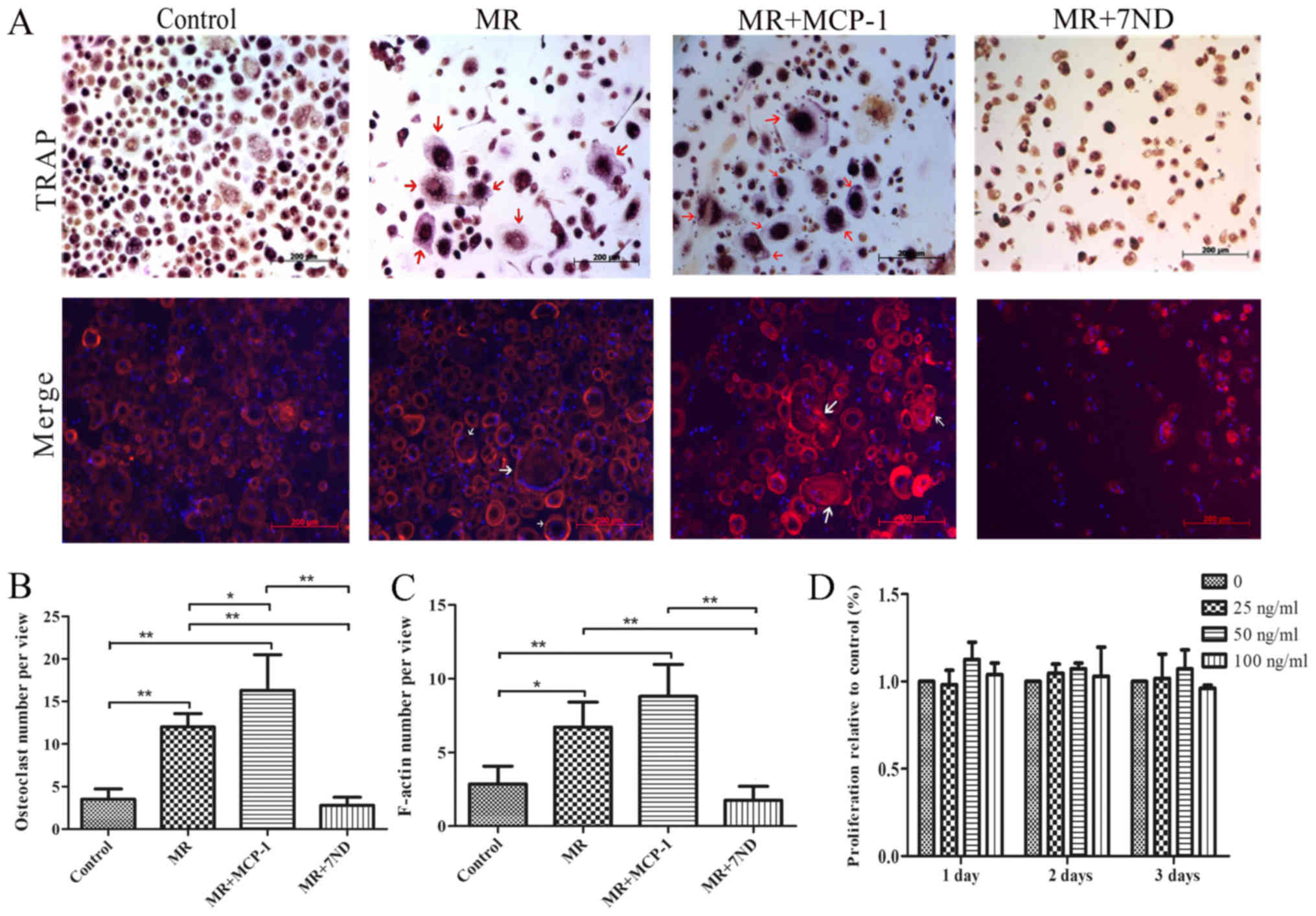
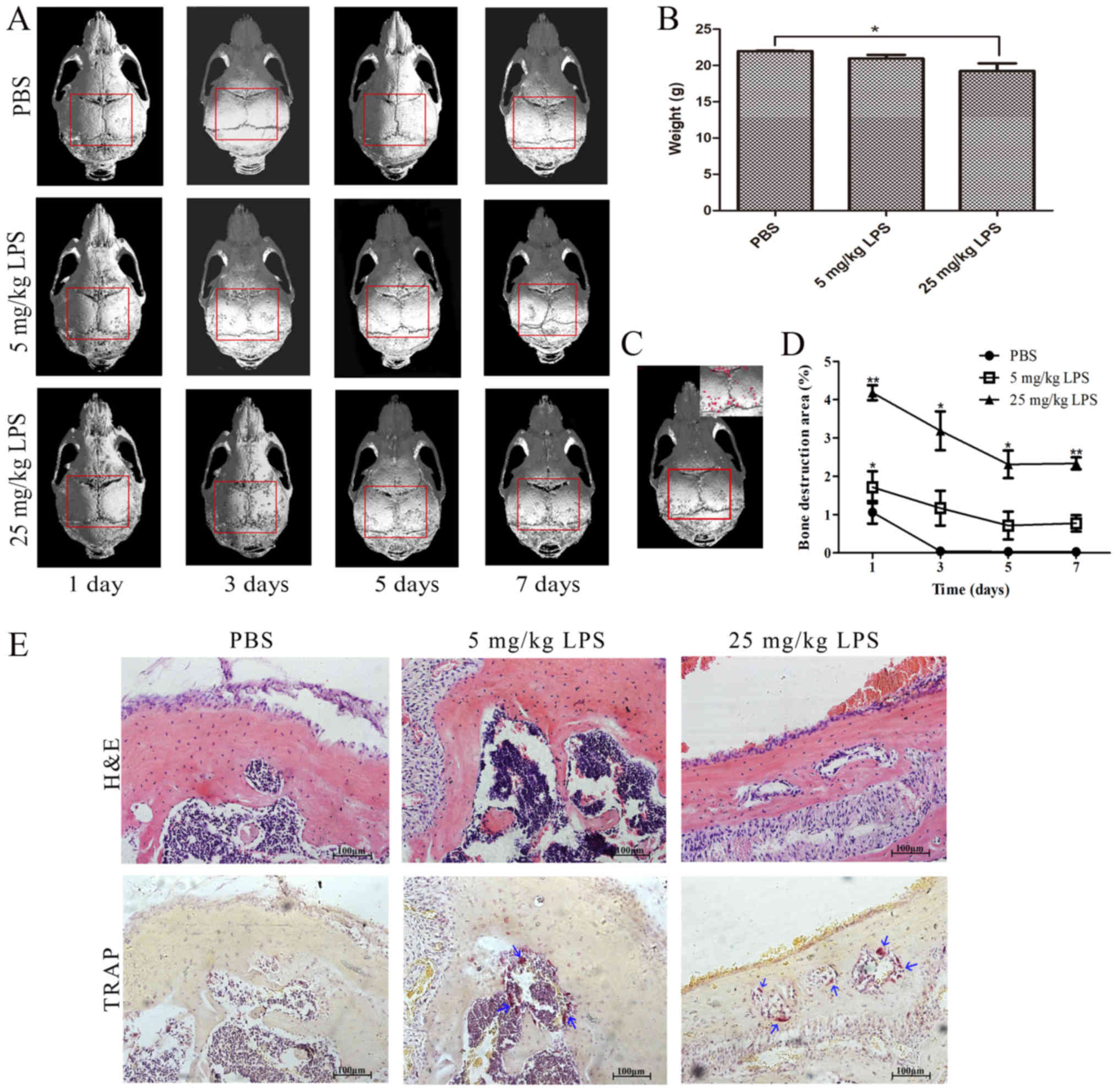
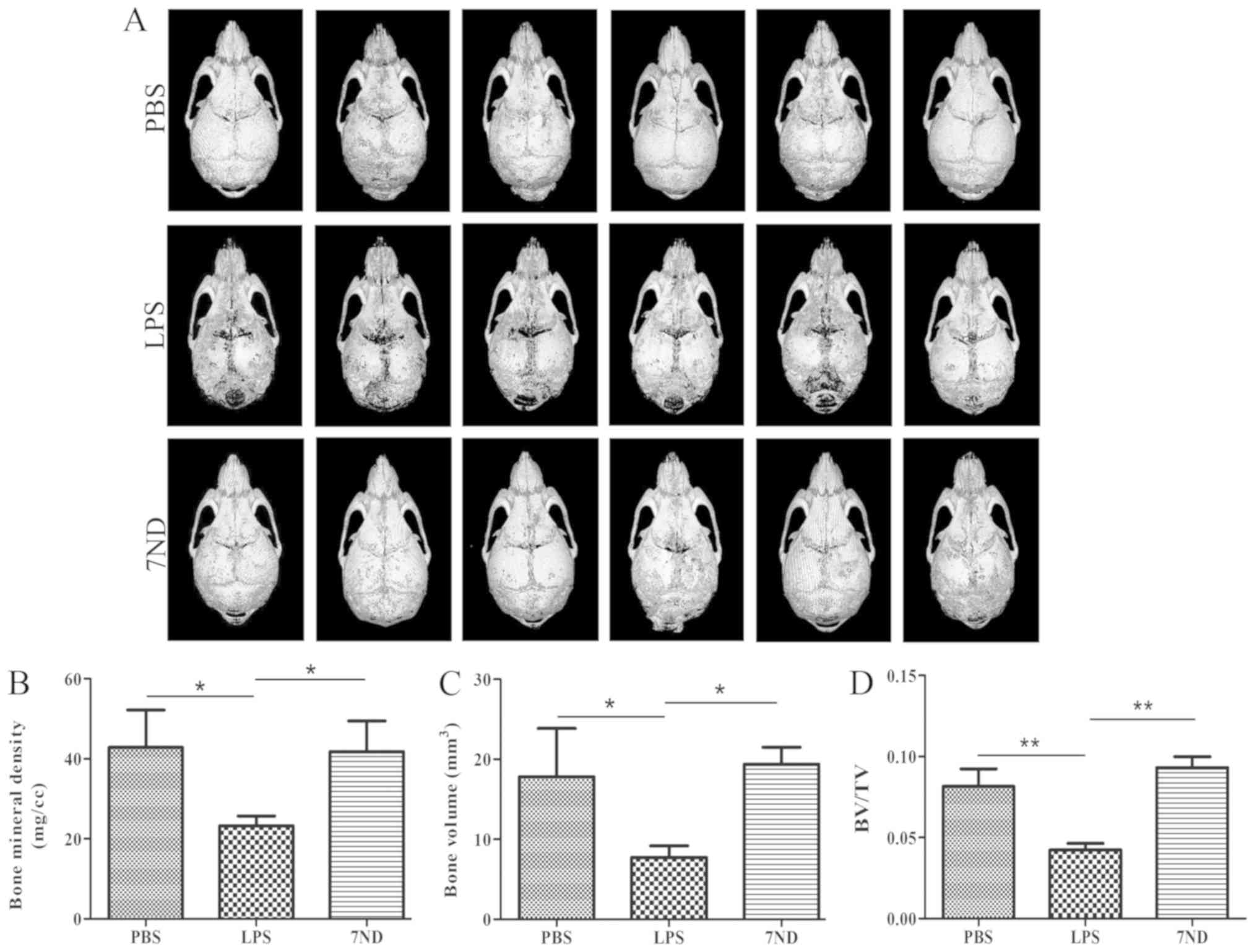
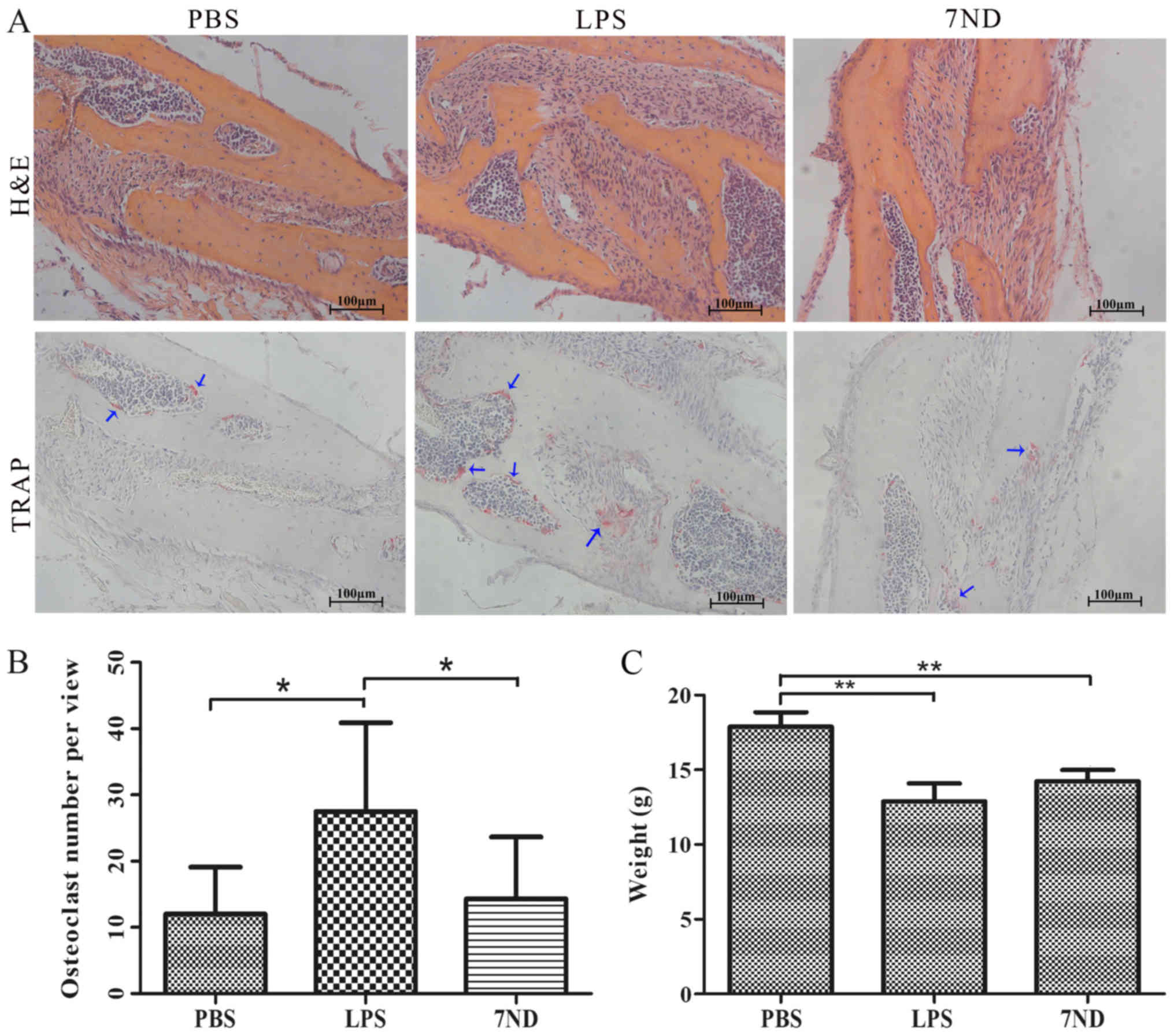
|
1
|
Lenertz LY, Baughman CJ, Waldschmidt NV,
Thaler R and van Wijnen AJ: Control of bone development by P2X and
P2Y receptors expressed in mesenchymal and hematopoietic cells.
Gene. 570:1–7. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nakashima T and Takayanagi H: New
regulation mechanisms of osteoclast differentiation. Ann N Y Acad
Sci. 1240:E13–E18. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Boyce BF: Advances in the regulation of
osteoclasts and osteoclast functions. J Dent Res. 92:860–867. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Muto A, Mizoguchi T, Udagawa N, Ito S,
Kawahara I, Abiko Y, Arai A, Harada S, Kobayashi Y, Nakamichi Y, et
al: Lineage-committed osteoclast precursors circulate in blood and
settle down into bone. J Bone Miner Res. 26:2978–2990. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ko SY: Myricetin suppresses LPS-induced
MMP expression in human gingival fibroblasts and inhibits
osteoclastogenesis by downregulating NFATc1 in RANKL-induced RAW
264.7 cells. Arch Oral Biol. 57:1623–1632. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yao Z, Keeney M, Lin TH, Pajarinen J,
Barcay K, Waters H, Egashira K, Yang F and Goodman S: Mutant
monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 protein attenuates migration of
and inflammatory cytokine release by macrophages exposed to
orthopedic implant wear particles. J Biomed Mater Res A.
102:3291–3297. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jiang X, Sato T, Yao Z, Keeney M,
Pajarinen J, Lin TH, Loi F, Egashira K, Goodman S and Yang F: Local
delivery of mutant CCL2 protein-reduced orthopaedic implant wear
particle-induced osteolysis and inflammation in vivo. J Orthop Res.
34:58–64. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen W, Foo SS, Taylor A, Lulla A, Merits
A, Hueston L, Forwood MR, Walsh NC, Sims NA, Herrero LJ and
Mahalingam S: An inhibitor of monocyte chemotactic protein
synthesis, protects against bone loss induced by chikungunya virus
infection. J Virol. 89:581–593. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sierra-Filardi E, Nieto C, Domínguez-Soto
A, Barroso R, Sánchez-Mateos P, Puig-Kroger A, López-Bravo M, Joven
J, Ardavín C, Rodríguez-Fernández JL, et al: CCL2 shapes macrophage
polarization by GM-CSF and M-CSF: Identification of
CCL2/CCR2-dependent gene expression profile. J Immunol.
192:3858–3867. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhang Y, Ernst CA and Rollins BJ: MCP-1:
Structure/activity analysis. Methods. 10:93–103. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Keeney M, Waters H, Barcay K, Jiang X, Yao
Z, Pajarinen J, Egashira K, Goodman SB and Yang F: Mutant MCP-1
protein delivery from layer-by-layer coatings on orthopedic
implants to modulate inflammatory response. Biomaterials.
34:10287–10295. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Luo S, Zhou C, Zhang J, Chen M, Li H,
Zheng S and Quan J: Mutant monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
protein (7ND) inhibits osteoclast differentiation and reduces oral
squamous carcinoma cell bone invasion. Oncol Lett. 15:7760–7768.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim MS, Day CJ, Selinger CI, Magno CL,
Stephens SR and Morrison NA: MCP-1-induced human osteoclast-like
cells are tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase, NFATc1, and
calcitonin receptor-positive but require receptor activator of
NFkappaB ligand for bone resorption. J Biol Chem. 281:1274–1285.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim MS, Day CJ and Morrison NA: MCP-1 is
induced by receptor activator of nuclear factor-{kappa}B ligand,
promotes human osteoclast fusion, and rescues granulocyte
macrophage colony-stimulating factor suppression of osteoclast
formation. J Biol Chem. 280:16163–16169. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gibon E, Ma T, Ren PG, Fritton K, Biswal
S, Yao Z, Smith L and Goodman SB: Selective inhibition of the
MCP-1-CCR2 ligand-receptor axis decreases systemic trafficking of
macrophages in the presence of UHMWPE particles. J Orthop Res.
30:547–553. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang Y and Rollins BJ: A dominant
negative inhibitor indicates that monocyte chemoattractant protein
1 functions as a dimer. Mol Cell Biol. 15:4851–4855. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Morrison NA, Day CJ and Nicholson GC:
Dominant negative MCP-1 blocks human osteoclast differentiation. J
Cell Biochem. 115:303–312. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nabeshima A, Pajarinen J, Lin TH, Jiang X,
Gibon E, Córdova LA, Loi F, Lu L, Jämsen E, Egashira K, et al:
Mutant CCL2 protein coating mitigates wear particle-induced bone
loss in a murine continuous polyethylene infusion model.
Biomaterials. 117:1–9. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou X, Zhang C, Wang X, An B, Zhang P and
Zhu Z: Berberine inhibits lipopolysaccharide- and polyethylene
particle-induced mouse calvarial osteolysis in vivo. J Surg Res.
73:e47–e52. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Hou GQ, Guo C, Song GH, Fang N, Fan WJ,
Chen XD, Yuan L and Wang ZQ: Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) promotes
osteoclast differentiation and activation by enhancing the MAPK
pathway and COX-2 expression in RAW264.7 cells. Int J Mol Med.
32:503–510. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Robertson Remen KM, Lerner UH, Gustafsson
JÅ and Andersson G: Activation of the liver X receptor-β potently
inhibits osteoclastogenesis from lipopolysaccharide-exposed bone
marrow-derived macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 93:71–82. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Baek JM, Kim JY, Ahn SJ, Cheon YH, Yang M,
Oh J and Choi MK: Dendrobium moniliforme exerts inhibitory effects
on both receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B
ligand-Mediated osteoclast differentiation in vitro and
lipopolysaccharide-induced bone erosion in vivo. Molecules.
21:2952016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Baek JM, Kim JY, Cheon YH, Park SH, Ahn
SJ, Yoon KH, Oh J and Lee MS: Aconitum pseudo-laeve var. erectum
inhibits receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B
ligand-induced osteoclastogenesis via the c-Fos/nuclear factor of
activated T-Cells, cytoplasmic 1 signaling pathway and prevents
lipopolysaccharide-induced bone loss in mice. Molecules.
19:11628–11644. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Baek JM, Kim JY, Jung Y, Moon SH, Choi MK,
Kim SH, Lee MS, Kim I and Oh J: Mollugin from rubea cordifolia
suppresses receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand-induced
osteoclastogenesis and bone resorbing activity in vitro and
prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced bone loss in vivo.
Phytomedicine. 22:27–35. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim JY, Baek JM, Ahn SJ, Cheon YH, Park
SH, Yang M, Choi MK and Oh J: Ethanolic extract of schizonepeta
tenuifolia attenuates osteoclast formation and activation in vitro
and protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced bone loss in vivo.
BMC Complement Altern Med. 16:3012016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li L, Khansari A, Shapira L, Graves DT and
Amar S: Contribution of interleukin-11 and prostaglandin(s) in
lipopolysaccharide-induced bone resorption in vivo. Infect Immun.
70:3915–3922. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Espirito Santo AI, Ersek A, Freidin A,
Feldmann M, Stoop AA and Horwood NJ: Selective inhibition of TNFR1
reduces osteoclast numbers and is differentiated from anti-TNF in a
LPS-driven model of inflammatory bone loss. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 464:1145–1150. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|