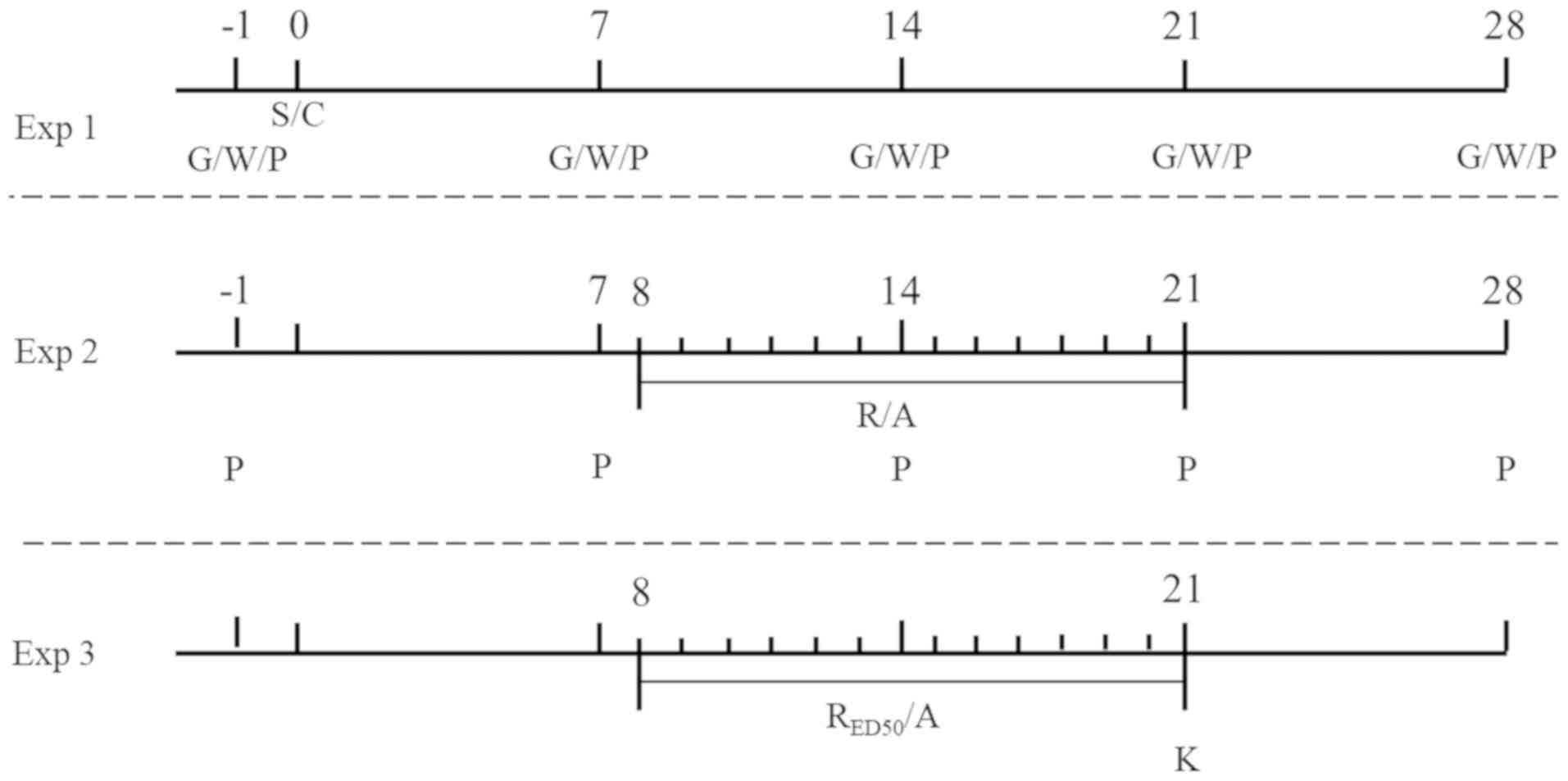
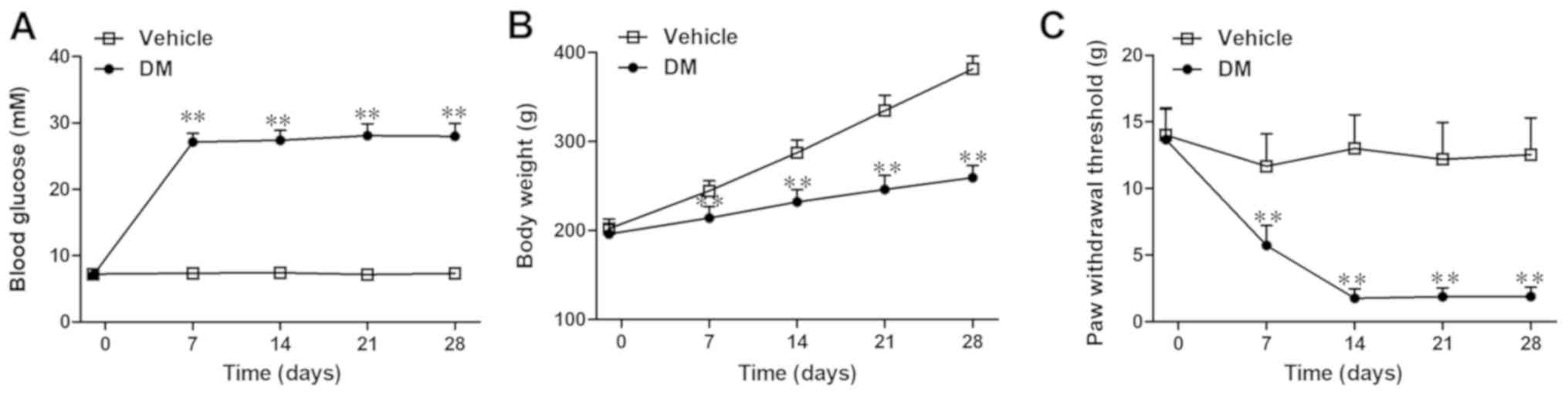
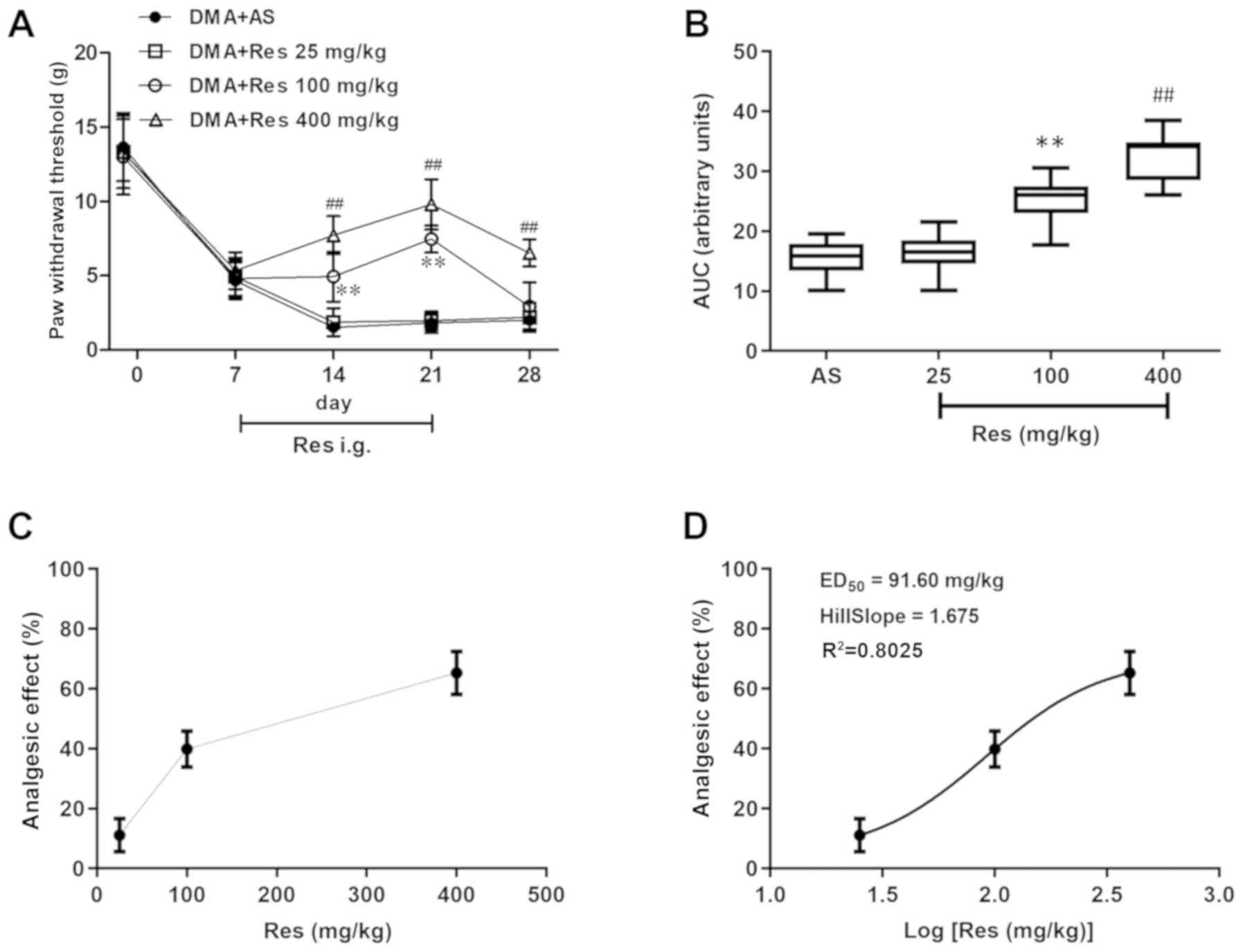
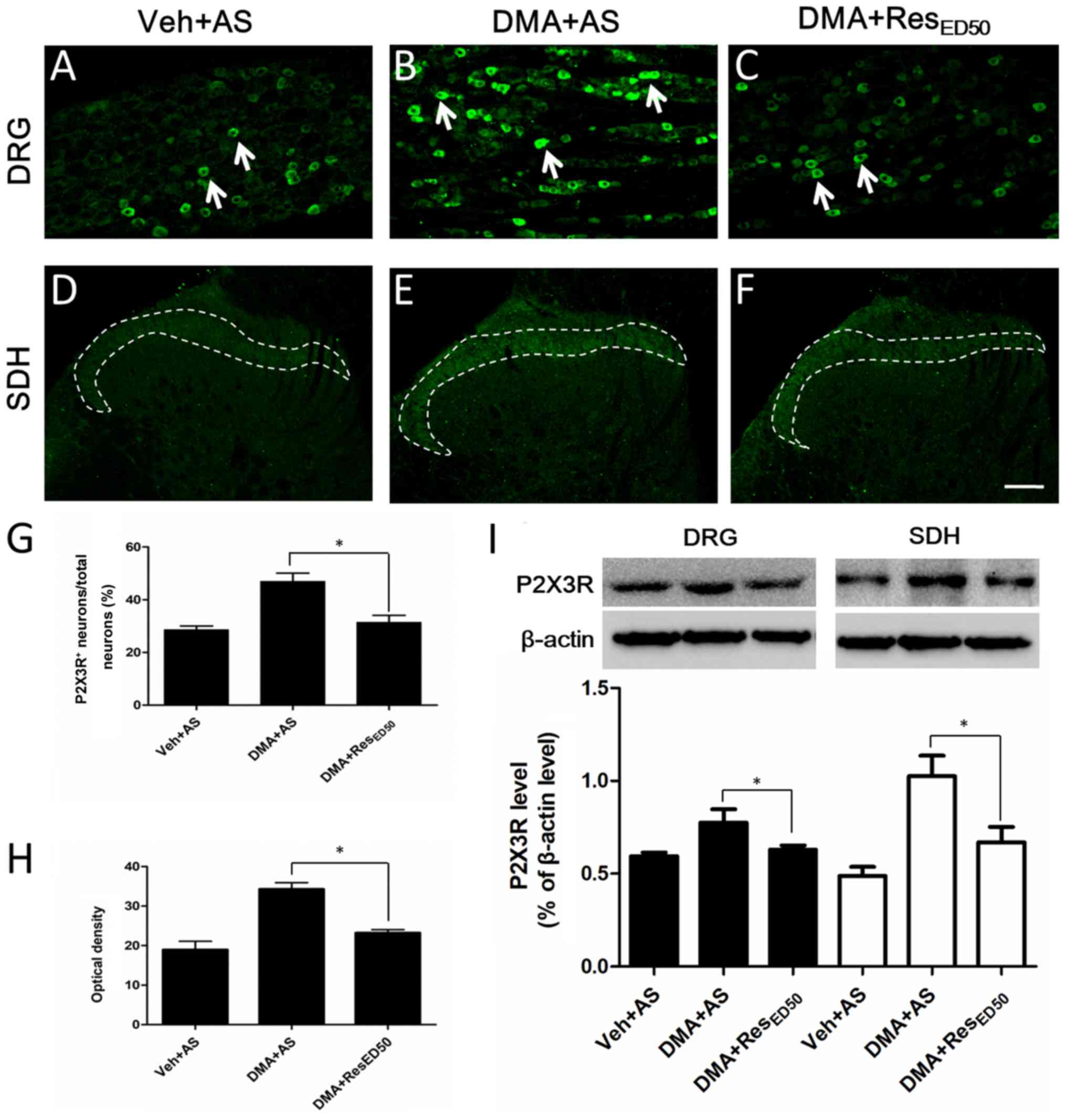
|
1
|
American Diabetes Association, . (2)
Classification and diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 38
(Suppl):S8–S16. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Guastella V and Mick G: Strategies for the
diagnosis and treatment of neuropathic pain secondary to diabetic
peripheral sensory polyneuropathy. Diabetes Metab. 35:12–19.
2009.
|
|
3
|
Rajchgot T, Thomas SC, Wang JC, Ahmadi M,
Balood M, Crosson T, Dias JP, Couture R, Claing A and Talbot S:
Neurons and Microglia; A sickly-sweet duo in diabetic pain
neuropathy. Front Neurosci. 13:252019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Scholz J, Rathmell JP, David WS, Chad DA,
Broderick AC, Perros SG, Shin NS, Wells JL, Davis JB, DiMaggio CJ,
et al: A standardized clinical evaluation of phenotypic diversity
in diabetic polyneuropathy. Pain. 157:2297–2308. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dubin AE and Patapoutian A: Nociceptors:
The sensors of the pain pathway. J Clin Invest. 120:3760–3772.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Castro OW, Upadhya D, Kodali M and Shetty
AK: Resveratrol for easing status epilepticus induced brain injury,
inflammation, epileptogenesis, and cognitive and memory
dysfunction-are we there yet? Front Neurol. 8:6032017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Daverey A and Agrawal SK: Pre and post
treatment with curcumin and resveratrol protects astrocytes after
oxidative stress. Brain Res. 1692:45–55. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lancon A, Frazzi R and Latruffe N:
Anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-angiogenic properties of
resveratrol in ocular diseases. Molecules. 21:3042016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ding Z, Cao J, Shen Y, Zou Y, Yang X, Zhou
W, Guo Q and Huang C: Resveratrol promotes nerve regeneration via
activation of p300 acetyltransferase-mediated VEGF signaling in a
rat model of sciatic nerve crush injury. Front Neurosci.
12:3412018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Oda H, Ohta S, Ikeguchi R, Noguchi T,
Kaizawa Y, Yurie H, Takeuchi H, Mitsuzawa S and Matsuda S:
Pretreatment of nerve grafts with resveratrol improves axonal
regeneration following replantation surgery for nerve root avulsion
injury in rats. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 36:647–658. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xie J, Liu S, Wu B, Li G, Rao S, Zou L, Yi
Z, Zhang C, Jia T, Zhao S, et al: The protective effect of
resveratrol in the transmission of neuropathic pain mediated by the
P2X7 receptor in the dorsal root ganglia. Neurochem Int.
103:24–35. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zou P, Liu X, Li G and Wang Y: Resveratrol
pretreatment attenuates traumatic brain injury in rats by
suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation via SIRT1. Mol Med Rep.
17:3212–3217. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhao H, Chen S, Gao K, Zhou Z, Wang C,
Shen Z, Guo Y, Li Z, Wan Z, Liu C and Mei X: Resveratrol protects
against spinal cord injury by activating autophagy and inhibiting
apoptosis mediated by the SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway.
Neuroscience. 348:241–251. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tao L, Ding Q, Gao C and Sun X:
Resveratrol attenuates neuropathic pain through balancing
pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines release in mice.
Int Immunopharmacol. 34:165–172. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang YJ, Hu L, Xia YP, Jiang CY, Miao C,
Yang CQ, Yuan M and Wang L: Resveratrol suppresses glial activation
and alleviates trigeminal neuralgia via activation of AMPK. J
Neuroinflammation. 13:842016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sharma S, Kulkarni SK and Chopra K: Effect
of resveratrol, a polyphenolic phytoalexin, on thermal hyperalgesia
in a mouse model of diabetic neuropathic pain. Fundam Clin
Pharmacol. 21:89–94. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sharma S, Chopra K and Kulkarni SK: Effect
of insulin and its combination with resveratrol or curcumin in
attenuation of diabetic neuropathic pain: participation of nitric
oxide and TNF-alpha. Phytother Res. 21:278–283. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sharma SS, Kumar A, Arora M and Kaundal
RK: Neuroprotective potential of combination of resveratrol and
4-amino 1,8 naphthalimide in experimental diabetic neuropathy:
Focus on functional, sensorimotor and biochemical changes. Free
Radic Res. 43:400–408. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Edwards FA and Gibb AJ: ATP-a fast
neurotransmitter. FEBS Lett. 325:86–89. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bernier LP, Ase AR and Séguéla P: P2X
receptor channels in chronic pain pathways. Br J Pharmacol.
175:2219–2230. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang HH, Hu J, Zhou YL, Qin X, Song ZY,
Yang PP, Hu S, Jiang X and Xu GY: Promoted interaction of nuclear
factor-κB with demethylated purinergic P2X3 receptor gene
contributes to neuropathic pain in rats with diabetes. Diabetes.
64:4272–4284. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Guo J, Wang C, Niu X, Zhou F, Li H and Gao
W: Effects of resveratrol in the signaling of neuropathic pain
involving P2X3 in the dorsal root ganglion of rats. Acta Neurol
Belg. Apr 19–2019.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Cui YY, Wu HH, Wa L, Shi J and Li YQ:
Spatio-temporal expression of P2X3 receptor in rats with diabetic
mechanical allodynia. Acta Anatomica Sinica. 45:540–544. 2014.
|
|
24
|
Zimmermann M: Ethical guidelines for
investigations of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain.
16:109–110. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM
and Yaksh TL: Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the
rat paw. J Neurosci Methods. 53:55–63. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu HH, Yin JB, Zhang T, Cui YY, Dong YL,
Chen GZ and Wang W: Inhibiting spinal neuron-astrocytic activation
correlates with synergistic analgesia of dexmedetomidine and
ropivacaine. PLoS One. 9:e923742014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yin JB, Zhou KC, Wu HH, Hu W, Ding T,
Zhang T, Wang LY, Kou JP, Kaye AD and Wang W: Analgesic effects of
Danggui-Shaoyao-San on various ‘Phenotypes’ of nociception and
inflammation in a formalin pain model. Mol Neurobiol. 53:6835–6848.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tallarida RJ: Drug synergism: Its
detection and applications. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 298:865–872.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ke HH, Wu HH, Zhu Q, Zhang Y, Xiao JR, Su
XZ, Zheng WJ, Cai YP, Wu XZ, Wang YT and Chen GZ: Neuromuscular
effect of dexmedetomidine on sevoflurane: An open-label,
dose-escalation clinical trial. Minerva Anestesiol. 83:790–797.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bai L, Wang W, Dong YL, Wang W, Huang J,
Wang XY, Wang LY, Li YQ and Wu SX: Attenuation of mouse somatic and
emotional inflammatory pain by hydralazine through scavenging
acrolein and inhibiting neuronal activation. Pain Physician.
15:311–326. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cui YY, Xu H, Wu HH, Qi J, Shi J and Li
YQ: Spatio-temporal expression and functional involvement of
transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 in diabetic mechanical
allodynia in rats. PLoS One. 9:e1020522014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Baur JA and Sinclair DA: Therapeutic
potential of resveratrol: The in vivo evidence. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 5:493–506. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shimazu Y, Shibuya E, Takehana S,
Sekiguchi K, Oshima K, Kamata H, Karibe H and Takeda M: Local
administration of resveratrol inhibits excitability of nociceptive
wide-dynamic range neurons in rat trigeminal spinal nucleus
caudalis. Brain Res Bull. 124:262–268. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Takehana S, Sekiguchi K, Inoue M, Kubota
Y, Ito Y, Yui K, Shimazu Y and Takeda M: Systemic administration of
resveratrol suppress the nociceptive neuronal activity of spinal
trigeminal nucleus caudalis in rats. Brain Res Bull. 120:117–122.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xu M, Cheng Z, Ding Z, Wang Y, Guo Q and
Huang C: Resveratrol enhances IL-4 receptor-mediated
anti-inflammatory effects in spinal cord and attenuates neuropathic
pain following sciatic nerve injury. Mol Pain.
14:17448069187675492018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zou L, Gong Y, Liu S and Liang S: Natural
compounds acting at P2 receptors alleviate peripheral neuropathy.
Brain Res Bull. 151:125–131. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Schreiber AK, Nones CF, Reis RC, Chichorro
JG and Cunha JM: Diabetic neuropathic pain: Physiopathology and
treatment. World J Diabetes. 6:432–444. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
McDonnell A, Collins S, Ali Z, Iavarone L,
Surujbally R, Kirby S and Butt RP: Efficacy of the Nav1.7 blocker
PF-05089771 in a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind
clinical study in subjects with painful diabetic peripheral
neuropathy. Pain. 159:1465–1476. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Schiavuzzo JG, Teixeira JM, Melo B, da
Silva dos Santos DF, Jorge CO, Oliveira-Fusaro MC and Parada CA:
Muscle hyperalgesia induced by peripheral P2X3 receptors is
modulated by inflammatory mediators. Neuroscience. 285:24–33. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Han Y, Jiang C, Tang J, Wang C, Wu P,
Zhang G, Liu W, Jamangulova N, Wu X and Song X: Resveratrol reduces
morphine tolerance by inhibiting microglial activation via AMPK
signalling. Eur J Pain. 18:1458–1470. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|