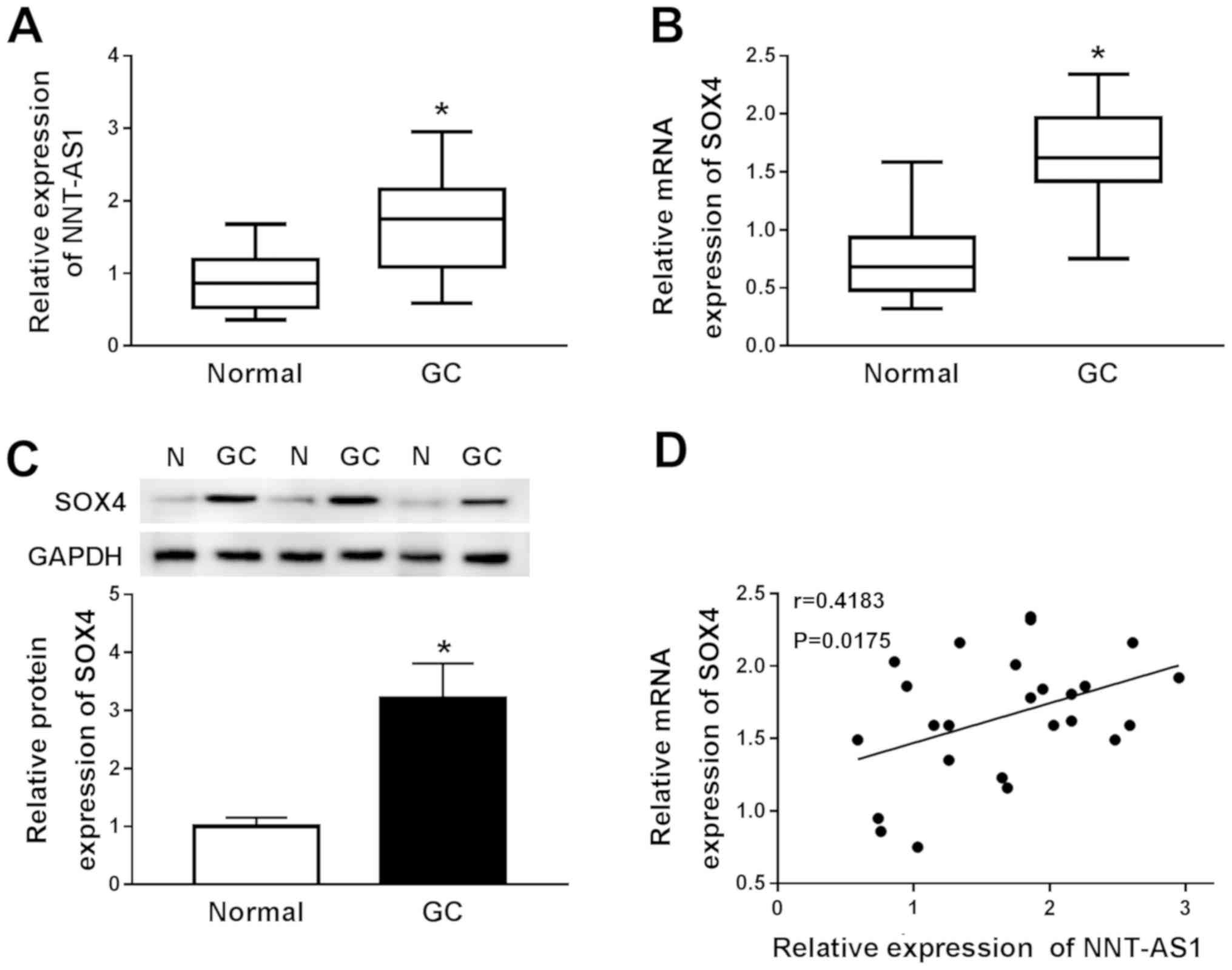
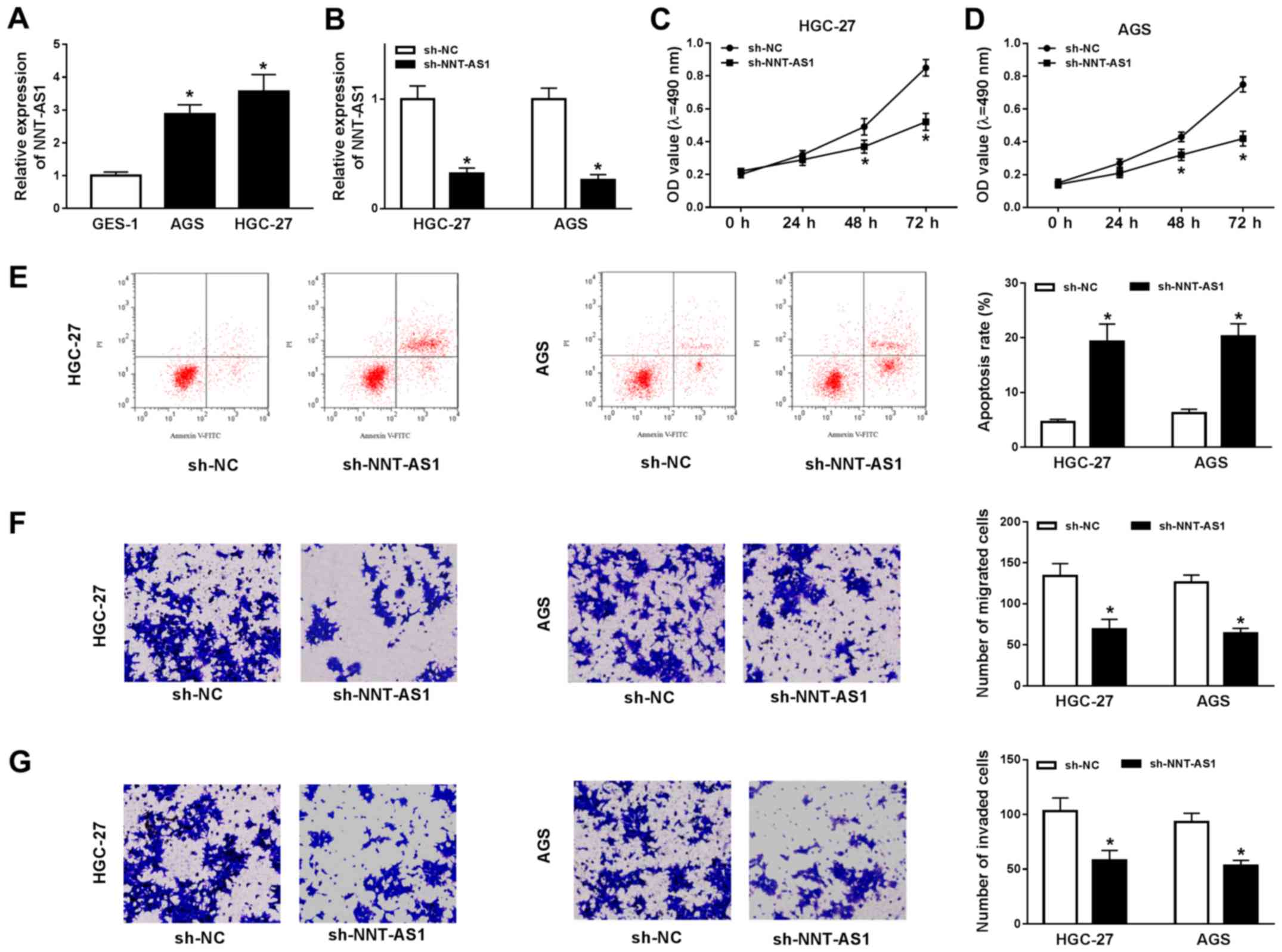
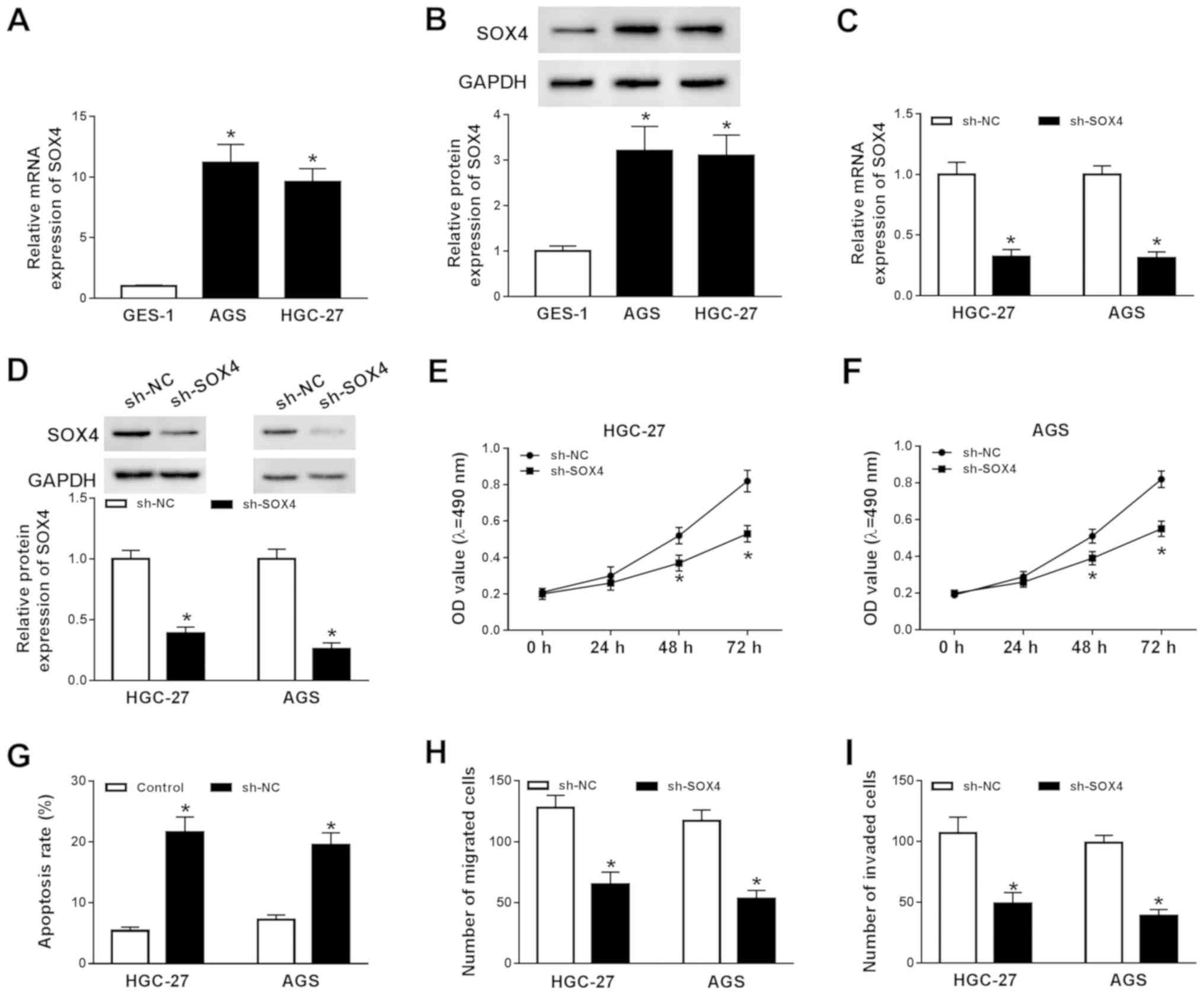
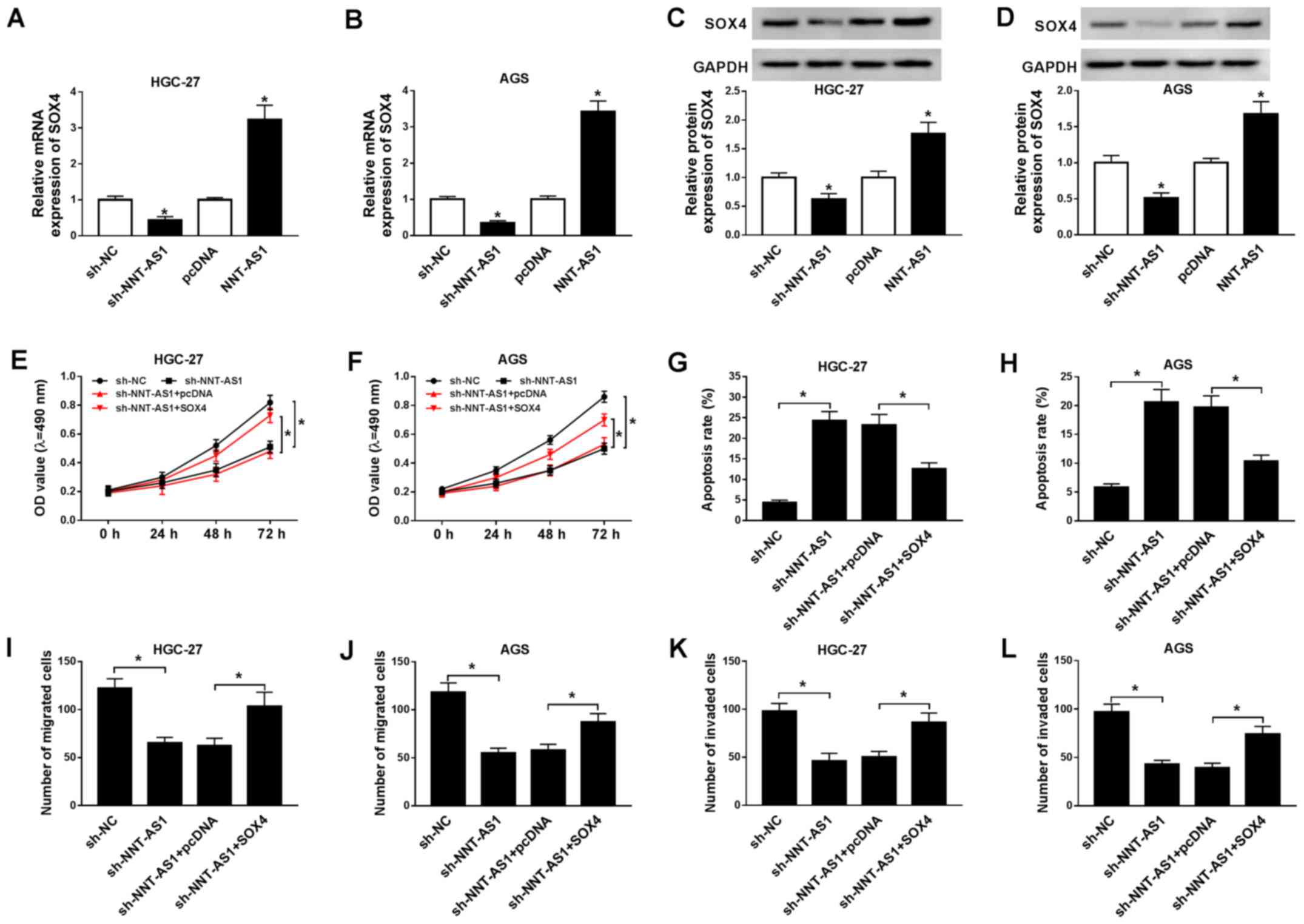
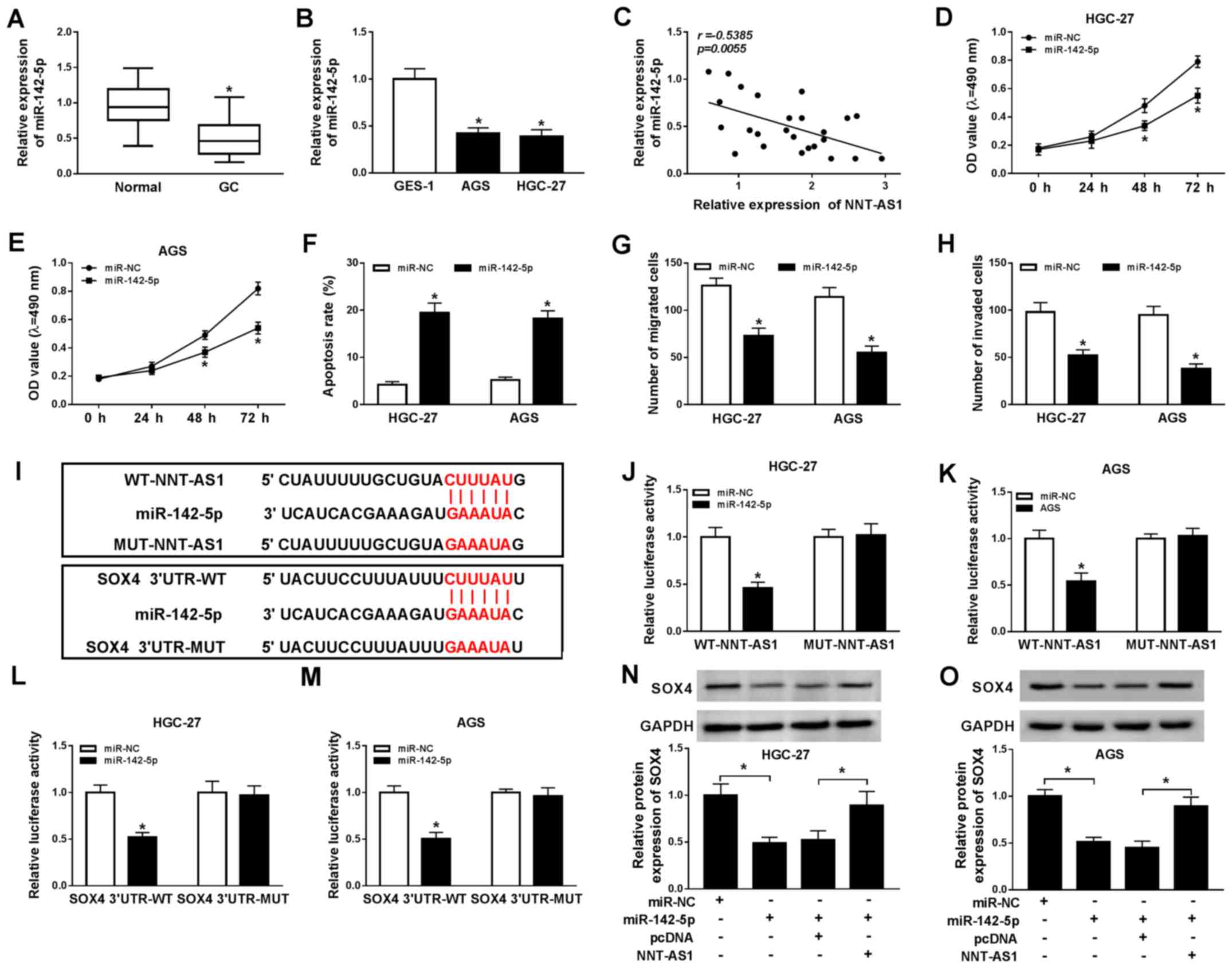
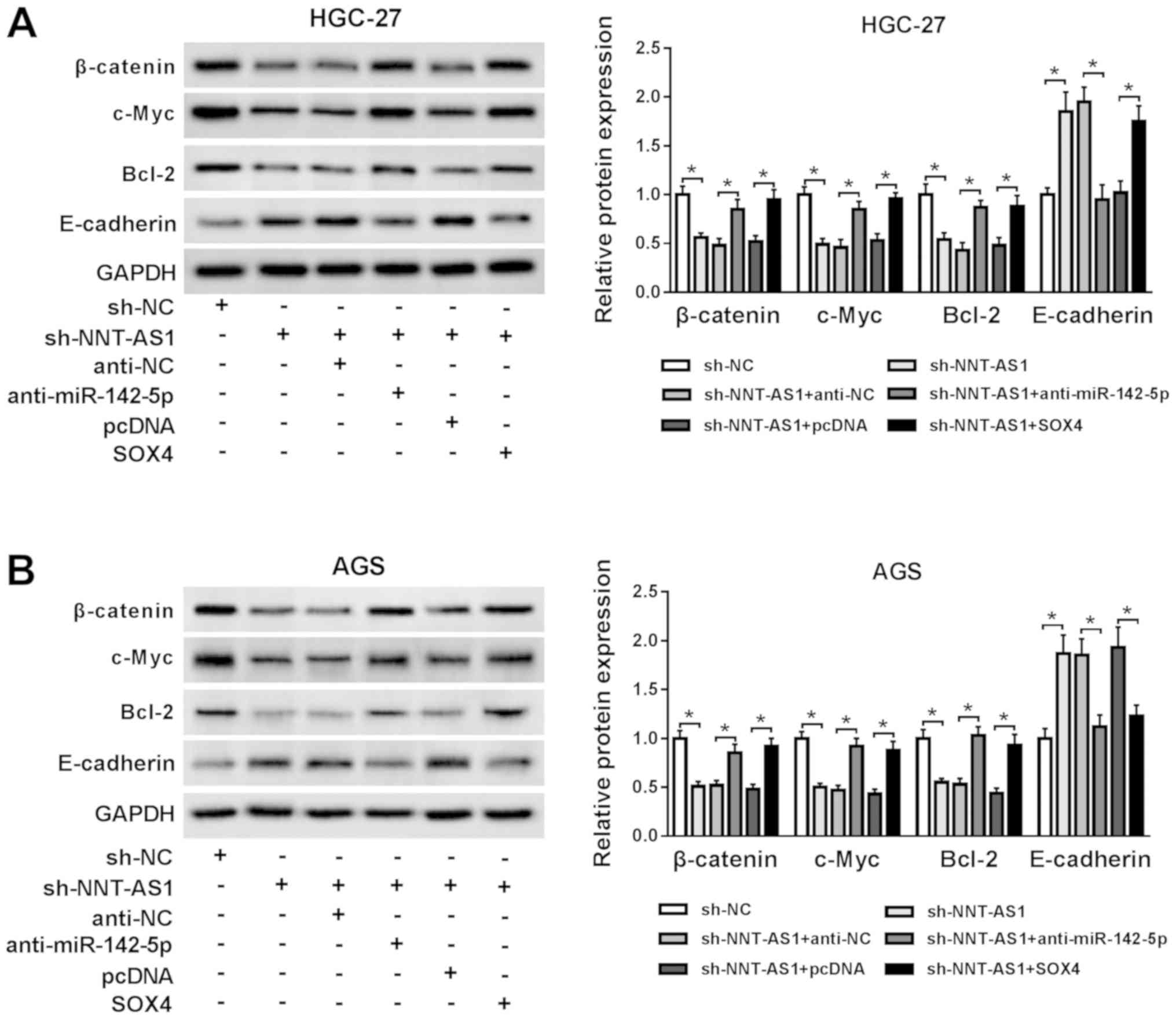
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Isobe Y, Nashimoto A, Akazawa K, Oda I,
Hayashi K, Miyashiro I, Katai H, Tsujitani S, Kodera Y, Seto Y and
Kaminishi M: Gastric cancer treatment in Japan: 2008 annual report
of the JGCA nationwide registry. Gastric Cancer. 14:301–316. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pasechnikov V, Chukov S, Fedorov E,
Kikuste I and Leja M: Gastric cancer: Prevention, screening and
early diagnosis. World J Gastroenterol. 20:13842–13862. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Digklia A and Wagner AD: Advanced gastric
cancer: Current treatment landscape and future perspectives. World
J Gastroenterol. 22:2403–2414. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Iyer MK, Niknafs YS, Malik R, Singhal U,
Sahu A, Hosono Y, Barrette TR, Prensner JR, Evans JR, Zhao S, et
al: The landscape of long noncoding RNAs in the human
transcriptome. Nat Genet. 47:199–208. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chandra Gupta S and Nandan Tripathi Y:
Potential of long non-coding RNAs in cancer patients: From
biomarkers to therapeutic targets. Int J Cancer. 140:1955–1967.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang Q, Yang L, Hu X, Jiang Y, Hu Y, Liu
Z, Liu J, Wen T, Ma Y, An G and Feng G: Upregulated NNT-AS1, a long
noncoding RNA, contributes to proliferation and migration of
colorectal cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget.
8:3441–3453. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li C, Zhang S, Qiu T, Wang Y, Ricketts DM
and Qi C: Upregulation of long non-coding RNA NNT-AS1 promotes
osteosarcoma progression by inhibiting the tumor suppressive
miR-320a. Cancer Biol Ther. 20:413–422. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li Y, Lv M, Song Z, Lou Z, Wang R and
Zhuang M: Long non-coding RNA NNT-AS1 affects progression of breast
cancer through miR-142-3p/ZEB1 axis. Biomed Pharmacother.
103:939–946. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shen Q and Jiang Y: LncRNA NNT-AS1
promotes the proliferation, and invasion of lung cancer cells via
regulating miR-129-5p expression. Biomed Pharmacother. 105:176–181.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang X, Ren M, Li Y, Hu J, Lu G, Ma W, Guo
D, Lu X and He S: Long noncoding RNA NNT-AS1 promotes gastric
cancer proliferation and invasion by regulating microRNA-363
expression. J Cell Biochem. 120:5704–5712. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ye H, Lin J, Yao X, Li Y, Lin X and Lu H:
Overexpression of long non-coding RNA NNT-AS1 correlates with tumor
progression and poor prognosis in osteosarcoma. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 45:1904–1914. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang Y, Shi J and Xu Y: Long non-coding
RNA NNT-AS1 contributes to cell proliferation, metastasis and
apoptosis in human ovarian cancer. Oncol Lett. 15:9264–9270.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen B, Zhao Q, Guan L, Lv H, Bie L, Huang
J and Chen XB: Long non-coding RNA NNT-AS1 sponges miR-424/E2F1 to
promote the tumorigenesis and cell cycle progression of gastric
cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 22:4751–4759. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bhaskaran M and Mohan M: MicroRNAs:
History, biogenesis, and their evolving role in animal development
and disease. Vet Pathol. 51:759–774. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Di Leva G, Garofalo M and Croce CM:
MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 9:287–314. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hayes J, Peruzzi PP and Lawler S:
MicroRNAs in cancer: Biomarkers, functions and therapy. Trends Mol
Med. 20:460–469. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu A, Hou C, Chen H, Zong X and Zong P:
Genetics and epigenetics of glioblastoma: Applications and overall
incidence of IDH1 mutation. Front Oncol. 6:162016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li X, Chen W, Jin Y, Xue R, Su J, Mu Z, Li
J and Jiang S: miR-142-5p enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in
ovarian cancer cells by targeting multiple anti-apoptotic genes.
Biochem Pharmacol. 161:98–112. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu S, Xiao Z, Ai F, Liu F, Chen X, Cao K,
Ren W, Zhang X, Shu P and Zhang D: miR-142-5p promotes development
of colorectal cancer through targeting SDHB and facilitating
generation of aerobic glycolysis. Biomed Pharmacother.
92:1119–1127. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang Z, Liu Z, Fang X and Yang H:
miR-142-5p suppresses tumorigenesis by targeting PIK3CA in
non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 43:2505–2515.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yan J, Yang B, Lin S, Xing R and Lu Y:
Downregulation of miR-142-5p promotes tumor metastasis through
directly regulating CYR61 expression in gastric cancer. Gastric
Cancer. 22:302–313. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hu B, Zhang H, Wang Z, Zhang F, Wei H and
Li L: lncRNA CCAT1/miR-130a-3p axis increases cisplatin resistance
in non-small-cell lung cancer cell line by targeting SOX4. Cancer
Biol Ther. 18:974–983. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee H, Goodarzi H, Tavazoie SF and Alarcón
CR: TMEM2 is a SOX4-regulated gene that mediates metastatic
migration and invasion in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 76:4994–5005.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sandbothe M, Buurman R, Reich N, Greiwe L,
Vajen B, Gürlevik E, Schäffer V, Eilers M, Kühnel F, Vaquero A, et
al: The microRNA-449 family inhibits GF-β-mediated liver cancer
cell migration by targeting SOX4. J Hepatol. 66:1012–1021. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sun R, Jiang B, Qi H, Zhang X, Yang J,
Duan J, Li Y and Li G: SOX4 contributes to the progression of
cervical cancer and the resistance to the chemotherapeutic drug
through ABCG2. Cell Death Dis. 6:e19902015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang KC and Chang HY: Molecular mechanisms
of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 43:904–914. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang L, Wang Y and Wang H: Use of
immunotherapy in the treatment of gastric cancer. Oncol Lett.
18:5681–5690. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fu X, Zhu X, Qin F, Zhang Y, Lin J, Ding
Y, Yang Z, Shang Y, Wang L, Zhang Q and Gao Q: Linc00210 drives
Wnt/β-catenin signaling activation and liver tumor progression
through CTNNBIP1-dependent manner. Mol Cancer. 17:732018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Guo C and Wang X, Chen LP, Li M, Li M, Hu
YH, Ding WH and Wang X: Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 regulates
ovarian cancer cell proliferation, migration and apoptosis through
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
22:3703–3712. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hua F, Liu S, Zhu L, Ma N, Jiang S and
Yang J: Highly expressed long non-coding RNA NNT-AS1 promotes cell
proliferation and invasion through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
in cervical cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 92:1128–1134. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rupaimoole R and Slack FJ: MicroRNA
therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and
other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 16:203–222. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Deris Zayeri Z, Tahmasebi Birgani M,
Mohammadi Asl J, Kashipazha D and Hajjari M: A novel infram
deletion in MSH6 gene in glioma: Conversation on MSH6 mutations in
brain tumors. J Cell Physiol. 234:11092–11102. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lou K, Chen N, Li Z, Zhang B, Wang X, Chen
Y, Xu H, Wang D and Wang H: MicroRNA-142-5p overexpression inhibits
cell growth and induces apoptosis by regulating FOXO in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol Res. 25:65–73. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cheng D, Li J, Zhang L and Hu L:
miR-142-5p suppresses proliferation and promotes apoptosis of human
osteosarcoma cell line, HOS, by targeting PLA2G16 through the
ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 17:1363–1371. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu L, Liu S, Duan Q, Chen L, Wu T, Qian
H, Yang S, Xin D, He Z and Guo Y: MicroRNA-142-5p promotes cell
growth and migration in renal cell carcinoma by targeting BTG3. Am
J Transl Res. 9:2394–2402. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pang L, Li B, Zheng B, Niu L and Ge L:
miR-138 inhibits gastric cancer growth by suppressing SOX4. Oncol
Rep. 38:1295–1302. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang M, Huang S and Long D: miR-381
inhibits migration and invasion in human gastric carcinoma through
downregulatedting SOX4. Oncol Lett. 14:3760–3766. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Nusse R and Clevers H: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling, disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities. Cell.
169:985–999. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shiina H, Igawa M, Shigeno K, Terashima M,
Deguchi M, Yamanaka M, Ribeiro-Filho L, Kane CJ and Dahiya R:
Beta-catenin mutations correlate with over expression of C-myc and
cyclin D1 Genes in bladder cancer. J Urol. 168:2220–2226. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
van Roy F and Berx G: The cell-cell
adhesion molecule E-cadherin. Cell Mol Life Sci. 65:3756–3788.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li L, Backer J, Wong AS, Schwanke EL,
Stewart BG and Pasdar M: Bcl-2 expression decreases
cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion. J Cell Sci. 116:3687–3700.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wu F, Li J, Guo N, Wang XH and Liao YQ:
miRNA-27a promotes the proliferation and invasion of human gastric
cancer MGC803 cells by targeting SFRP1 via Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway. Am J Cancer Res. 7:405–416. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Shan Y, Ying R, Jia Z, Kong W, Wu Y, Zheng
S and Jin H: LINC00052 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation
and metastasis via activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Oncol Res. 25:1589–1599. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|