|
1
|
Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel
Y, Henry L and Wymer M: Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence,
and outcomes. Hepatology. 64:73–84. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Younossi Z, Tacke F, Arrese M, Chander
Sharma B, Mostafa I, Bugianesi E, Wai-Sun Wong V, Yilmaz Y, George
J, Fan J and Vos MB: Global perspectives on non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology.
69:2672–2682. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Angulo P and Lindor KD: Treatment of
non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol.
16:797–810. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Malaguarnera M, Di Rosa M, Nicoletti F and
Malaguarnera L: Molecular mechanisms involved in NAFLD progression.
J Mol Med (Berl). 87:679–695. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Leamy AK, Egnatchik RA and Young JD:
Molecular mechanisms and the role of saturated fatty acids in the
progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Prog Lipid Res.
52:165–174. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cao L, Zhou Y, Zhai B, Liao J, Xu W, Zhang
R, Li J, Zhang Y, Chen L, Qian H, et al: Sphere-forming cell
subpopulations with cancer stem cell properties in human hepatoma
cell lines. BMC Gastroenterol. 11:712011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Huang P, Qiu J, Li B, Hong J, Lu C, Wang
L, Wang J, Hu Y, Jia W and Yuan Y: Role of Sox2 and Oct4 in
predicting survival of hepatocellular carcinoma patients after
hepatectomy. Clin Biochem. 44:582–589. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sun C, Sun L, Li Y, Kang X, Zhang S and
Liu Y: Sox2 expression predicts poor survival of hepatocellular
carcinoma patients and it promotes liver cancer cell invasion by
activating Slug. Med Oncol. 30:5032013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yin X, Li YW, Zhang BH, Ren ZG, Qiu SJ, Yi
Y and Fan J: Coexpression of stemness factors Oct4 and Nanog
predict liver resection. Ann Surg Oncol. 19:2877–2887. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ma XL, Sun YF, Wang BL, Shen MN, Zhou Y,
Chen JW, Hu B, Gong ZJ, Zhang X, Cao Y, et al: Sphere-forming
culture enriches liver cancer stem cells and reveals Stearoyl-CoA
desaturase 1 as a potential therapeutic target. BMC Cancer.
19:7602019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Stafman LL, Williams AP, Garner EF, Aye
JM, Stewart JE, Yoon KJ, Whelan K and Beierle EA: Targeting PIM
kinases affects maintenance of CD133 tumor cell population in
hepatoblastoma. Transl Oncol. 12:200–208. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Maehara O, Ohnishi S, Asano A, Suda G,
Natsuizaka M, Nakagawa K, Kobayashi M, Sakamoto N and Takeda H:
Metformin regulates the expression of CD133 through the AMPK-CEBPβ
pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Neoplasia.
21:545–556. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen WC, Chang YS, Hsu HP, Yen MC, Huang
HL, Cho CY, Wang CY, Weng TY, Lai PT, Chen CS, et al: Therapeutics
targeting CD90-integrin-AMPK-CD133 signal axis in liver cancer.
Oncotarget. 6:42923–42937. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
He J, Liu Y, Zhu T, Zhu J, Dimeco F,
Vescovi AL, Heth JA, Muraszko KM, Fan X and Lubman DM: CD90 is
identified as a candidate marker for cancer stem cells in primary
high-grade gliomas using tissue microarrays. Mol Cell Proteomics.
11:M111.010744. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhang K, Che S, Pan C, Su Z, Zheng S, Yang
S, Zhang H, Li W, Wang W and Liu J: The SHH/Gli axis regulates
CD90-mediated liver cancer stem cell function by activating the
IL6/JAK2 pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 22:3679–3690. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wei S, Liu K, He Q, Gao Y and Shen L: PES1
is regulated by CD44 in liver cancer stem cells via miR-105-5p.
FEBS Lett. 593:1777–1786. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yamashita T, Honda M, Nakamoto Y, Baba M,
Nio K, Hara Y, Zeng SS, Hayashi T, Kondo M, Takatori H, et al:
Discrete nature of EpCAM+ and CD90+ cancer stem cells in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 57:1484–1497. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Christ B, Stock P and Dollinger MM: CD13:
Waving the flag for a novel cancer stem cell target. Hepatology.
53:1388–1390. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Reynolds BA and Weiss S: Clonal and
population analyses demonstrate that an EGF-responsive mammalian
embryonic CNS precursor is a stem cell. Dev Biol. 175:1–13. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dontu G, Abdallah WM, Foley JM, Jackson
KW, Clarke MF, Kawamura MJ and Wicha MS: In vitro propagation and
transcriptional profiling of human mammary stem/progenitor cells.
Genes Dev. 17:1253–1270. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Suzuki A, Oyama K, Fukao K, Nakauchi H and
Taniguchi H: Establishment of clonal colony-forming assay system
for pancreatic stem/progenitor cells. Cell Transplant. 11:451–453.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shi X, Gipp J and Bushman W:
Anchorage-independent culture maintains prostate stem cells. Dev
Biol. 312:396–406. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ponti D, Costa A, Zaffaroni N, Pratesi G,
Petrangolini G, Coradini D, Pilotti S, Pierotti MA and Daidone MG:
Isolation and in vitro propagation of tumorigenic breast cancer
cells with stem/progenitor cell properties. Cancer Res.
65:5506–5511. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gou S, Liu T, Wang C, Yin T, Li K, Yang M
and Zhou J: Establishment of clonal colony-forming assay for
propagation of pancreatic cancer cells with stem cell properties.
Pancreas. 34:429–435. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rappa G, Mercapide J, Anzanello F,
Prasmickaite L, Xi Y, Ju J, Fodstad O and Lorico A: Growth of
cancer cell lines under stem cell-like conditions has the potential
to unveil therapeutic targets. Exp Cell Res. 314:2110–2122. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wobser H, Dorn C, Weiss TS, Amann T,
Bollheimer C, Büttner R, Schölmerich J and Hellerbrand C: Lipid
accumulation in hepatocytes induces fibrogenic activation of
hepatic stellate cells. Cell Res. 19:996–1005. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
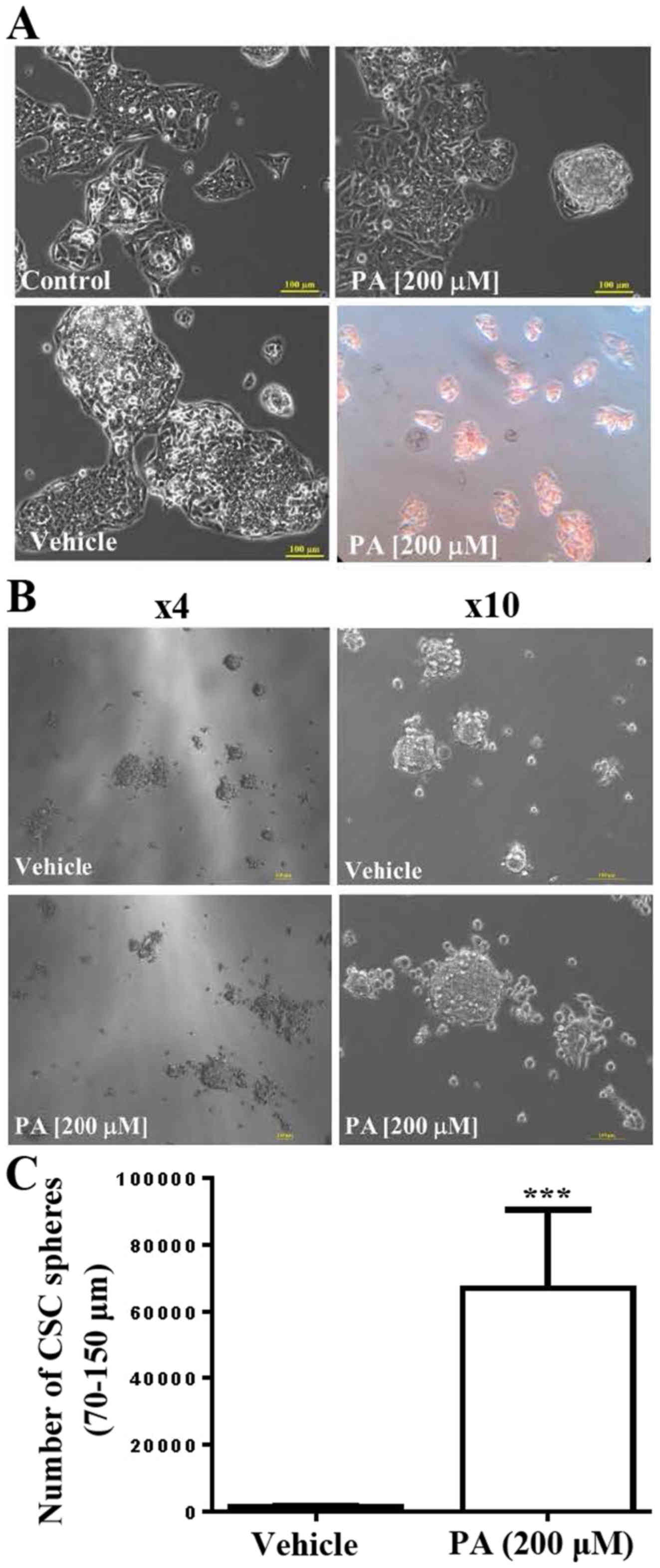
Chong LW, Chou RH, Liao CC, Lee TF, Lin Y,
Yang KC and Hsu YC: Saturated fatty acid induces cancer stem
cell-like properties in human hepatoma cells. Cell Mol Biol
(Noisy-le-Grand). 61:85–91. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Anderson AM and Ragan MA: Palmitoylation:
A protein S-acylation with implications for breast cancer. NPJ
Breast Cancer. 2:160282016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang MH, Liao CC, Hung JH, Lai XT, Yen CH
and Chen YA: Utilizing proteomic approach to identify nuclear
translocation related serine kinase phosphorylation site of GNMT as
downstream effector for benzo[a]pyrene. J Food Drug Anal.
27:603–609. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chong LW, Hsu YC, Lee TF, Lin Y, Chiu YT,
Yang KC, Wu JC and Huang YT: Fluvastatin attenuates hepatic
steatosis-induced fibrogenesis in rats through inhibiting paracrine
effect of hepatocyte on hepatic stellate cells. BMC Gastroenterol.
15:222015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Alessio N, Del Gaudio S, Capasso S, Di
Bernardo G, Cappabianca S, Cipollaro M, Peluso G and Galderisi U:
Low dose radiation induced senescence of human mesenchymal stromal
cells and impaired the autophagy process. Oncotarget. 6:8155–8166.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Buckley BJ and Whorton AR: Tunicamycin
increases intracellular calcium levels in bovine aortic endothelial
cells. Am J Physiol. 273:C1298–C1305. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sobocińska J, Roszczenko-Jasińska P,
Zaręba-Kozioł M, Hromada-Judycka A, Matveichuk OV, Traczyk G,
Łukasiuk K and Kwiatkowska K: Lipopolysaccharide upregulates
palmitoylated enzymes of the phosphatidylinositol cycle: An insight
from proteomic studies. Mol Cell Proteomics. 17:233–254. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Patterson SI and Skene JH: Novel
inhibitory action of tunicamycin homologues suggests a role for
dynamic protein fatty acylation in growth cone-mediated neurite
extension. J Cell Biol. 124:521–536. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|