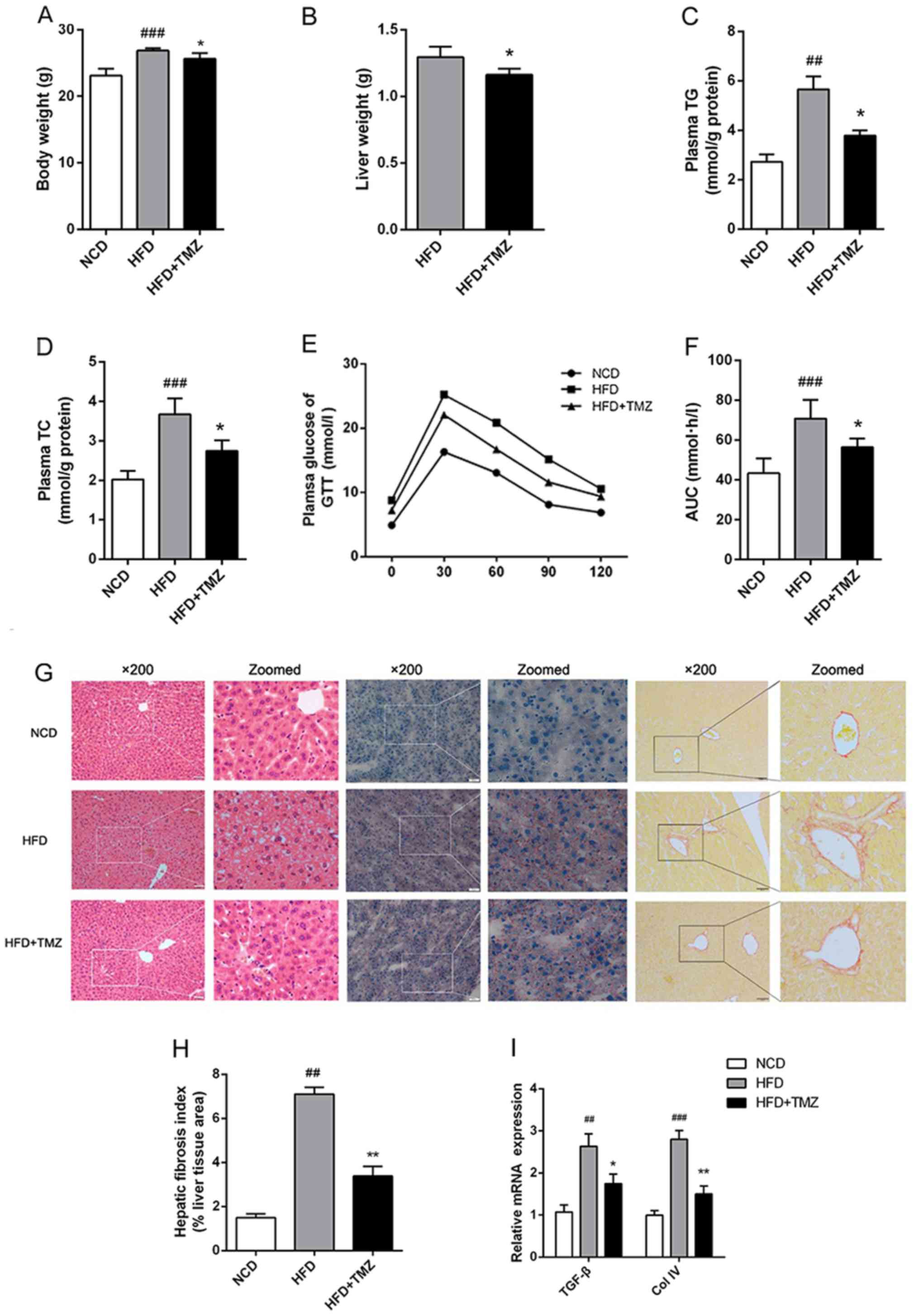
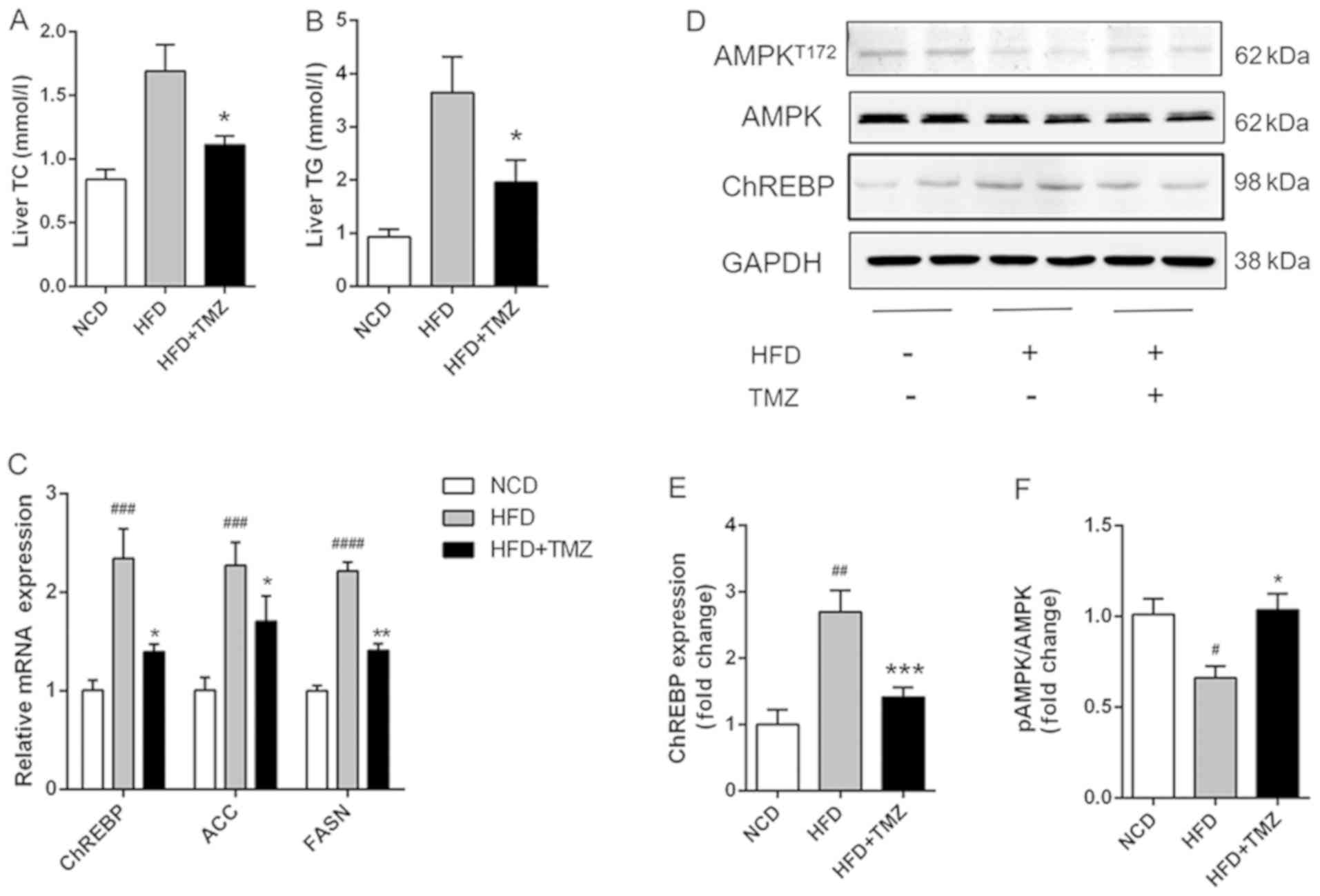
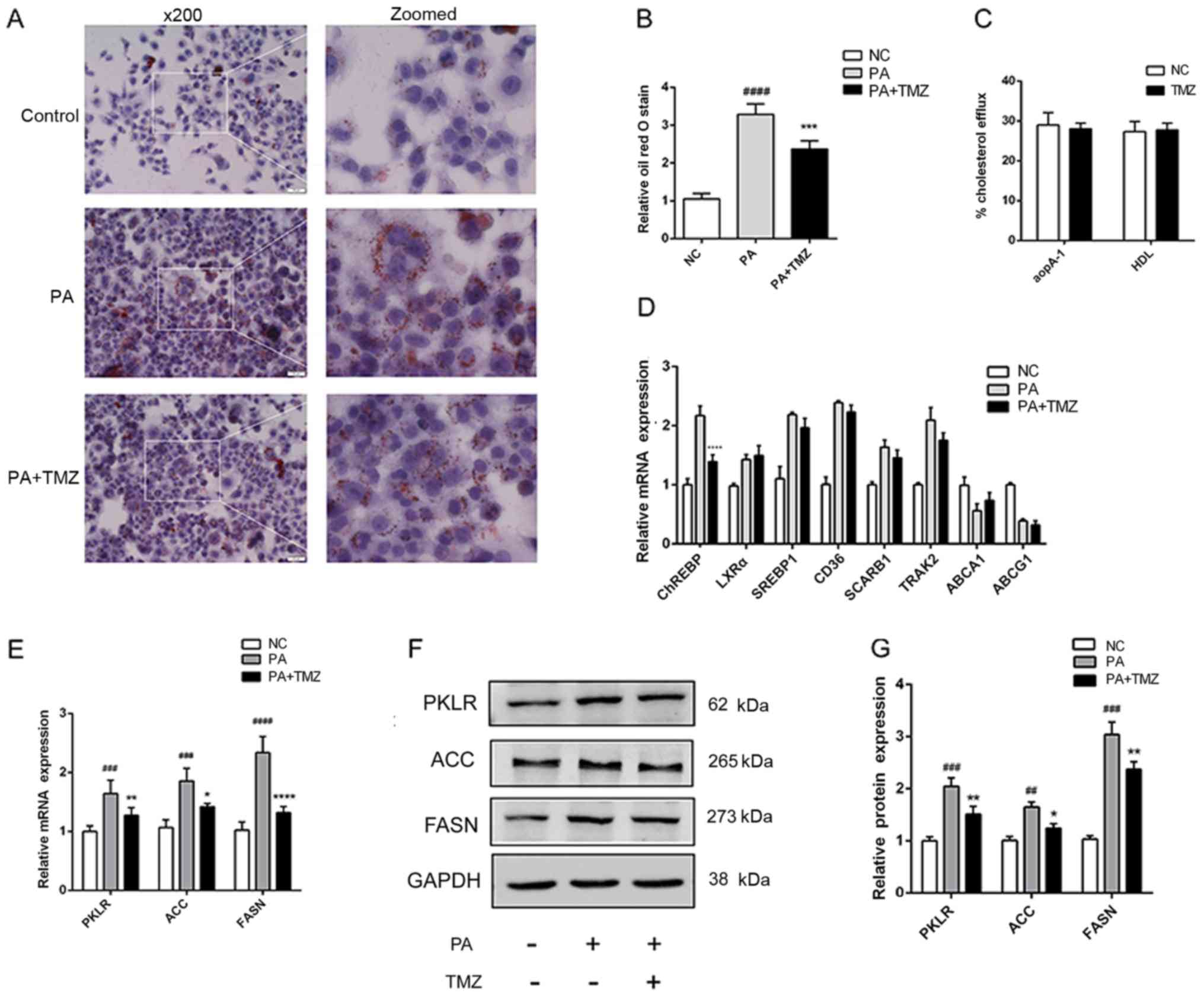
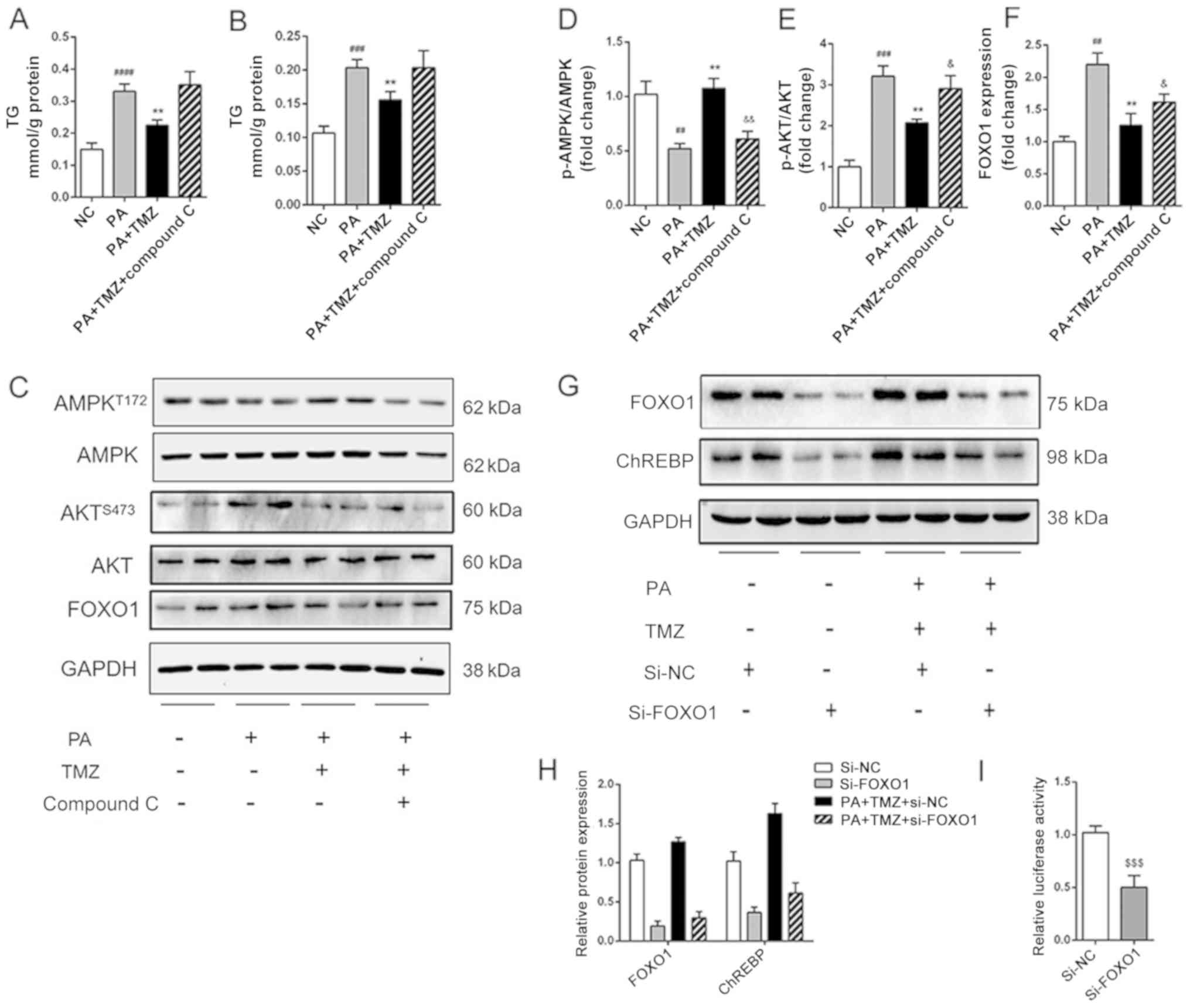
|
1
|
Yki-Järvinen H: Non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease as a cause and a consequence of metabolic syndrome. Lancet
Diabetes Endocrinol. 2:901–910. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Malik VS, Willett WC and Hu FB: Global
obesity: Trends, risk factors and policy implications. Nat Rev
Endocrinol. 9:13–27. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Alberti KGMM, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet
PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA, Fruchart J-C, James WPT, Loria CM and
Smith SC Jr; International Diabetes Federation Task Force on
Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood
Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation;
International Atherosclerosis Society; International Association
for the Study of Obesity, : Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A
joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation
Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung,
and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart
Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and
International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation.
120:1640–1645. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wong VW-S: Nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease in Asia: A story of growth. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
28:18–23. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lazo M, Hernaez R, Eberhardt MS, Bonekamp
S, Kamel I, Guallar E, Koteish A, Brancati FL and Clark JM:
Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the United
States: The Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey,
1988–1994. Am J Epidemiol. 178:38–45. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Marengo A, Jouness RIK and Bugianesi E:
Progression and natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
in adults. Clin Liver Dis. 20:313–324. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, Diehl
AM, Brunt EM, Cusi K, Charlton M and Sanyal AJ; American
Gastroenterological Association; American Association for the Study
of Liver Diseases; American College of Gastroenterologyh, : The
diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease:
Practice guideline by the American Gastroenterological Association,
American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, and American
College of Gastroenterology. Gastroenterology. 142:1592–1609. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jaswal JS, Keung W, Wang W, Ussher JR and
Lopaschuk GD: Targeting fatty acid and carbohydrate oxidation--a
novel therapeutic intervention in the ischemic and failing heart.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:1333–1350. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lopaschuk GD, Barr R, Thomas PD and Dyck
JRB: Beneficial effects of trimetazidine in ex vivo working
ischemic hearts are due to a stimulation of glucose oxidation
secondary to inhibition of long-chain 3-ketoacyl coenzyme a
thiolase. Circ Res. 93:e33–e37. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen H and Xu Y: Clinical trial of
trimetazidine combined with atorvastatin calcium in the treatment
of coronary heart disease and angina pectoris with dyslipidemia.
Zhongguo Lin Chuang Yao Li Xue Za Zhi. 32:966–968.
2016.(Chinese).
|
|
11
|
Zhou X and Huang H: Therapeutic effect of
atorvastatin combined trimetazidine on blood lipids, inflammatory
factors and cardiac function in patients with coronary heart
disease. Chin J Cardiovasc Rehabil Med. 25:276–279.
2016.(Chinese).
|
|
12
|
Hardie DG, Ross FA and Hawley SA: AMPK: A
nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 13:251–262. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hardie DG: AMPK: Positive and negative
regulation, and its role in whole-body energy homeostasis. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 33:1–7. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ideta T, Shirakami Y, Miyazaki T, Kochi T,
Sakai H, Moriwaki H and Shimizu M: The dipeptidyl peptidase-4
inhibitor teneligliptin attenuates hepatic lipogenesis via AMPK
activation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease model mice. Int J
Mol Sci. 16:29207–29218. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cheng S, Liang S, Liu Q, Deng Z, Zhang Y,
Du J, Zhang Y, Li S, Cheng B and Ling C: Diosgenin prevents
high-fat diet-induced rat non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through
the AMPK and LXR signaling pathways. Int J Mol Med. 41:1089–1095.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Smith BK, Marcinko K, Desjardins EM, Lally
JS, Ford RJ and Steinberg GR: Treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease: Role of AMPK. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
311:E730–E740. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang ZQ, Zhang XH, Yu Y, Tipton RC, Raskin
I, Ribnicky D, Johnson W and Cefalu WT: Artemisia scoparia extract
attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in diet-induced
obesity mice by enhancing hepatic insulin and AMPK signaling
independently of FGF21 pathway. Metabolism. 62:1239–1249. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Woods A, Williams JR, Muckett PJ, Mayer
FV, Liljevald M, Bohlooly-Y M and Carling D: Liver-specific
activation of AMPK prevents steatosis on a high-fructose diet. Cell
Rep. 18:3043–3051. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Postic C, Dentin R, Denechaud P-D and
Girard J: ChREBP, a transcriptional regulator of glucose and lipid
metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr. 27:179–192. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang Y, Viscarra J, Kim S-J and Sul HS:
Transcriptional regulation of hepatic lipogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 16:678–689. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Saline M, Badertscher L, Wolter M, Lau R,
Gunnarsson A, Jacso T, Norris T, Ottmann C and Snijder A: AMPK and
AKT protein kinases hierarchically phosphorylate the N-terminus of
the FOXO1 transcription factor, modulating interactions with 14-3-3
proteins. J Biol Chem. 294(35): 13106–13116. 2019.pii:
jbc.RA119.008649. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bandyopadhyay GK, Lu M, Avolio E, Siddiqui
JA, Gayen JR, Wollam J, Vu CU, Chi NW, O'Connor DT and Mahata SK:
Pancreastatin-dependent inflammatory signaling mediates
obesity-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes. 64:104–116. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhao L, Zhang C, Luo X, Wang P, Zhou W,
Zhong S, Xie Y, Jiang Y, Yang P, Tang R, et al: CD36 palmitoylation
disrupts free fatty acid metabolism and promotes tissue
inflammation in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J Hepatol.
69:705–717. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2 (-Delta DeltaC (T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
DeWeerdt S: Disease progression. Divergent
paths. Nature. 551:S92–S93. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Michelotti GA, Machado MV and Diehl AM:
NAFLD, NASH and liver cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
10:656–665. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wong VW-S and Wong GL-H: A LEAN treatment
for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Lancet. 387:628–630. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kantor PF, Lucien A, Kozak R and Lopaschuk
GD: The antianginal drug trimetazidine shifts cardiac energy
metabolism from fatty acid oxidation to glucose oxidation by
inhibiting mitochondrial long-chain 3-ketoacyl coenzyme A thiolase.
Circ Res. 86:580–588. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen J, Lai J, Yang L, Ruan G, Chaugai S,
Ning Q, Chen C and Wang DW: Trimetazidine prevents
macrophage-mediated septic myocardial dysfunction via activation of
the histone deacetylase sirtuin 1. Br J Pharmacol. 173:545–561.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Abdul-Wahed A, Guilmeau S and Postic C:
Sweet sixteenth for ChREBP: Established roles and future goals.
Cell Metab. 26:324–341. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jump DB, Tripathy S and Depner CM: Fatty
acid-regulated transcription factors in the liver. Annu Rev Nutr.
33:249–269. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Benhamed F, Denechaud P-D, Lemoine M,
Robichon C, Moldes M, Bertrand-Michel J, Ratziu V, Serfaty L,
Housset C, Capeau J, et al: The lipogenic transcription factor
ChREBP dissociates hepatic steatosis from insulin resistance in
mice and humans. J Clin Invest. 122:2176–2194. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang Y, Hu SL, Hu D, Jiang JG, Cui GL,
Liu XD and Wang DW: miR-1322 regulates ChREBP expression via
binding a 3′-UTR variant (rs1051943). J Cell Mol Med. 22:5322–5332.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xie X, Yan D, Li H, Zhu Q, Li J, Fang YP,
Cheung CW, Irwin MG, Xia Z and Lian Q: Enhancement of adiponectin
ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via inhibition of
FoxO1 in Type I Diabetic Rats. J Diabetes Res. 2018:62543402018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
O-Sullivan IS, Zhang W, Wasserman DH, Liew
CW, Liu J, Paik J, DePinho RA, Stolz DB, Kahn CR, Schwartz MW, et
al: FoxO1 integrates direct and indirect effects of insulin on
hepatic glucose production and glucose utilization. Nat Commun.
6:70792015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|