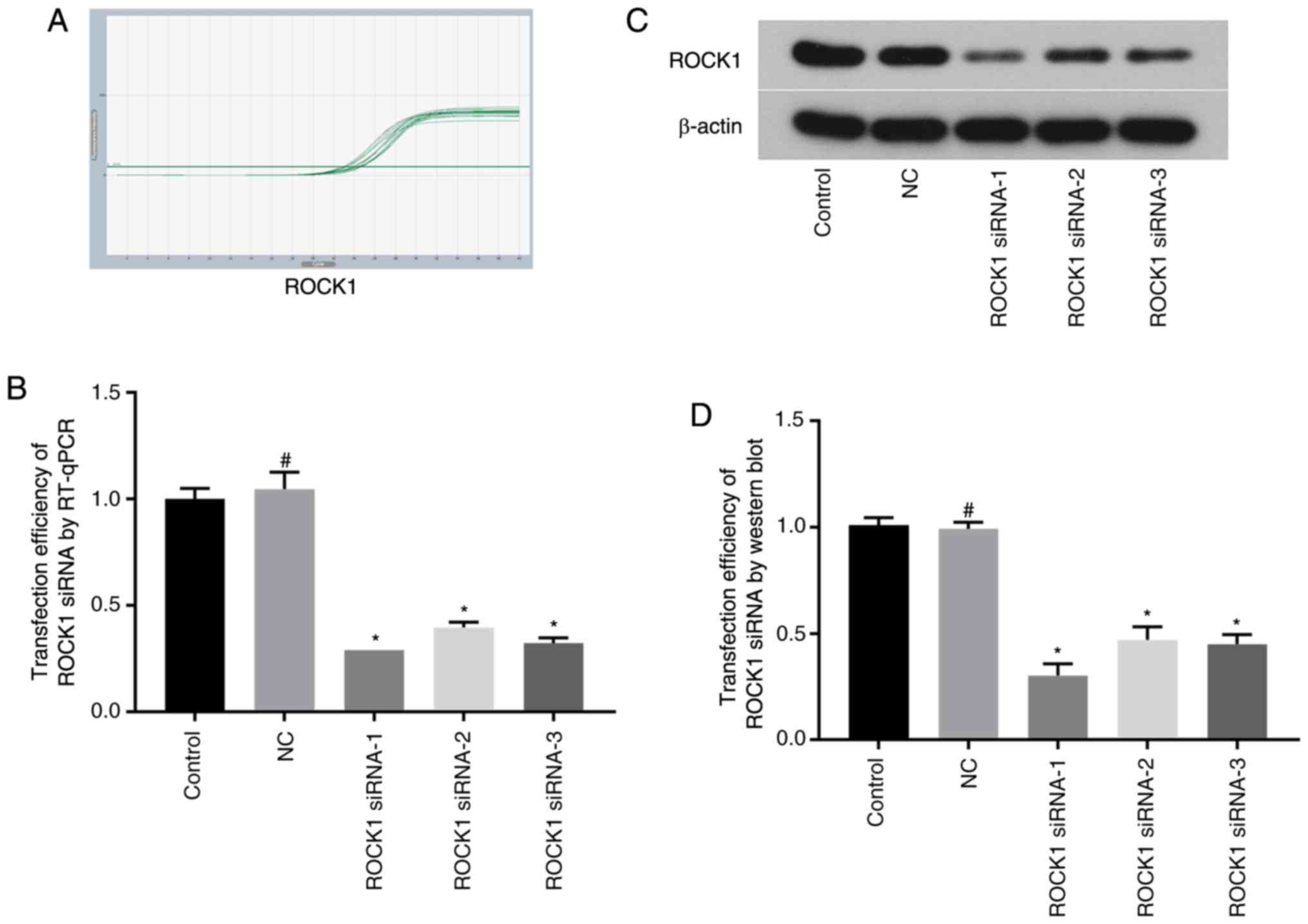
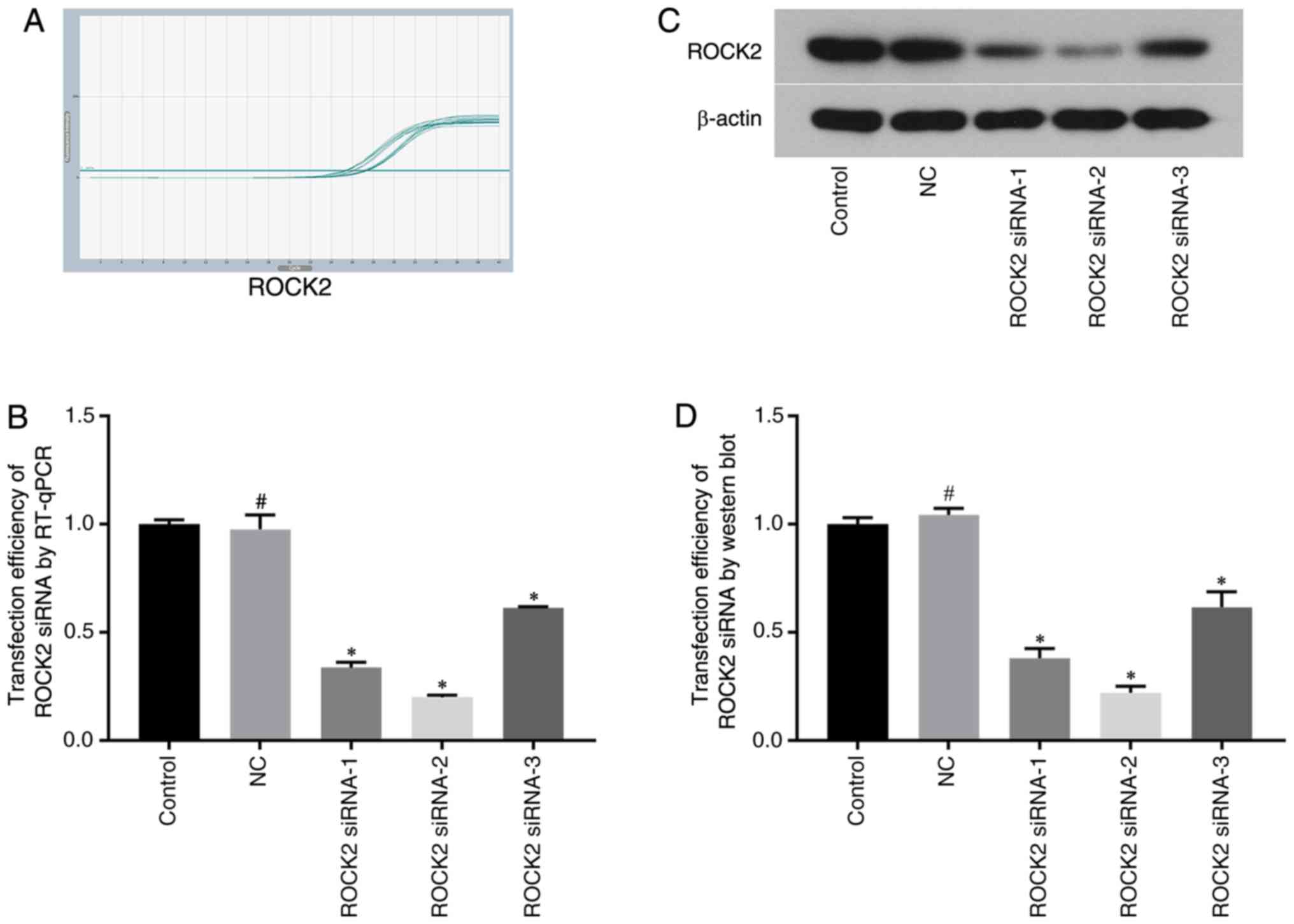
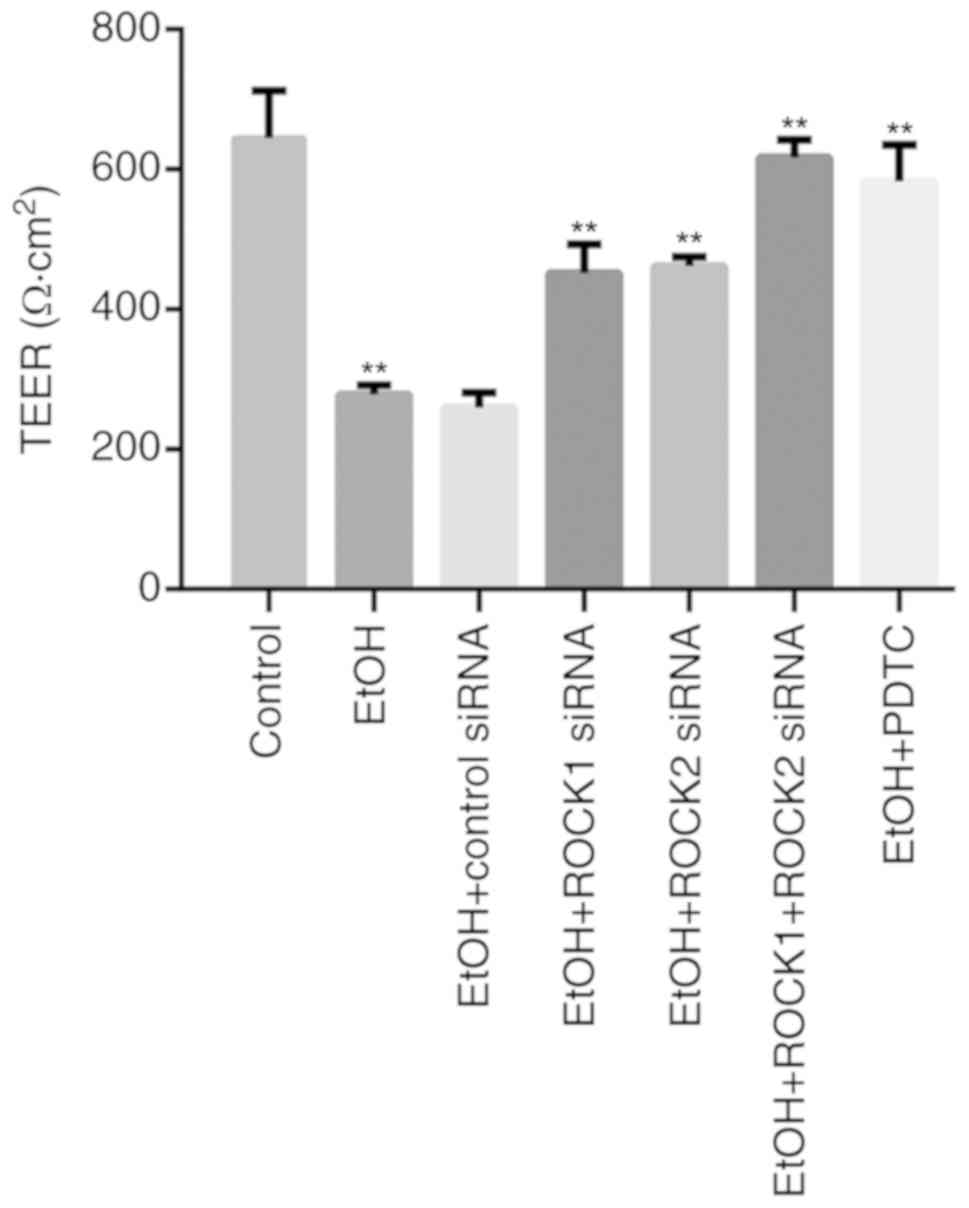
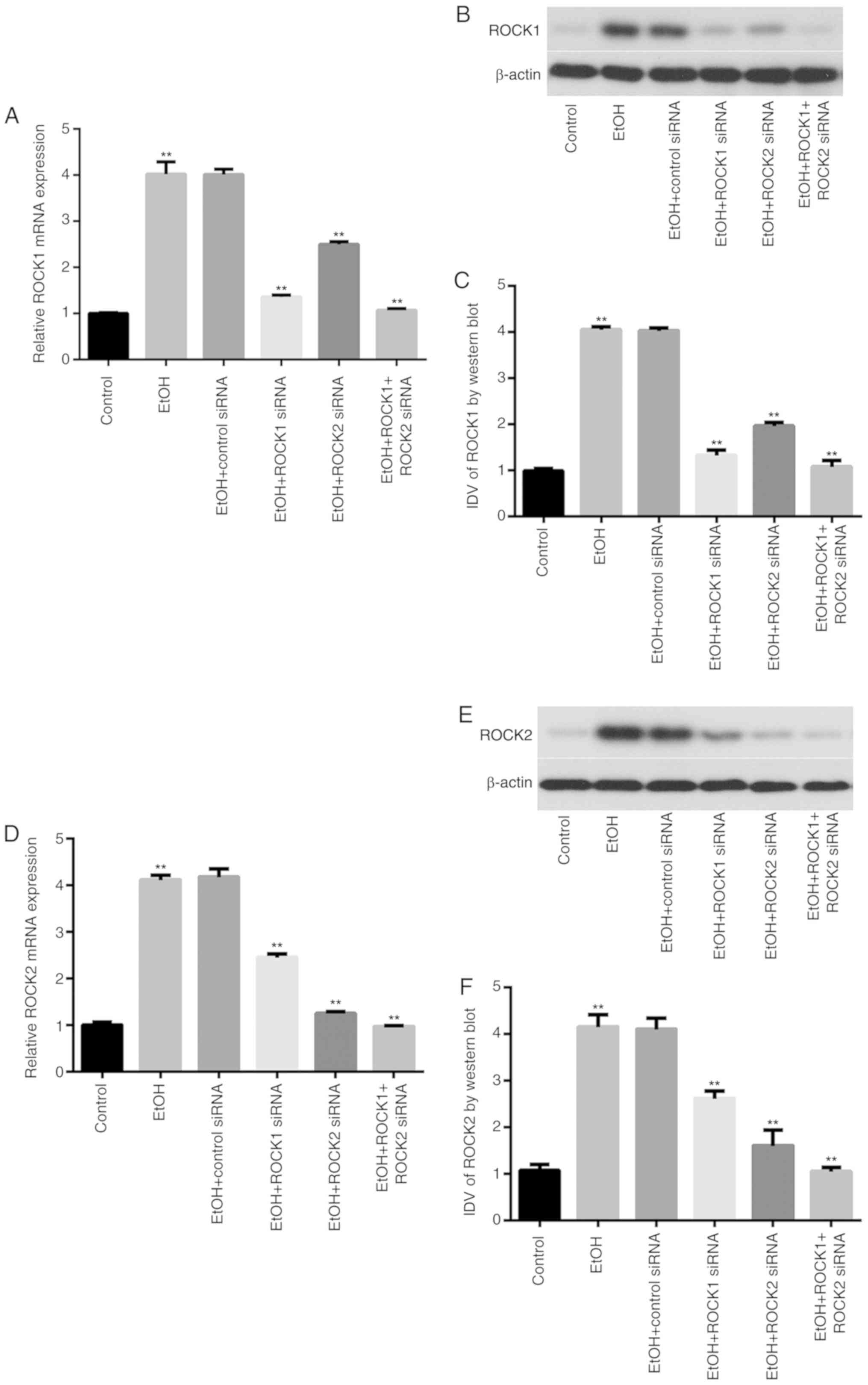
|
1
|
Cheru L, Saylor CF and Lo J:
Gastrointestinal barrier breakdown and adipose tissue inflammation.
Curr Obes Rep. 8:165–174. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hao H, Gokulan K, Piñeiro SA, Williams KM,
Yuan Z, Cerniglia CE and Khare S: Effects of Acute and Chronic
Exposure to Residual Level Erythromycin on Human Intestinal
Epithelium Cell Permeability and Cytotoxicity. Microorganisms.
7:72019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Sunico CR, González-Forero D, Domínguez G,
García-Verdugo JM and Moreno-López B: Nitric oxide induces
pathological synapse loss by a protein kinase G-, Rho
kinase-dependent mechanism preceded by myosin light chain
phosphorylation. J Neurosci. 30:973–984. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liao JK, Seto M and Noma K: Rho kinase
(ROCK) inhibitors. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 50:17–24. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tong J, Wang Y, Chang B, Zhang D and Wang
B: Evidence for the involvement of RhoA signaling in the
ethanol-induced increase in intestinal epithelial barrier
permeability. Int J Mol Sci. 14:3946–3960. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zou Y, Ma L, Zhao Y, Zhang S, Zhou C and
Cai Y: Inhibition of Rho kinase protects against colitis in mice by
attenuating intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction via MLC and
the NF-κB pathway. Int J Mol Med. 41:430–438. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pan P, Shen M, Yu H, Li Y, Li D and Hou T:
Advances in the development of Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK)
inhibitors. Drug Discov Today. 18:1323–1333. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bauer PO, Hudec R, Goswami A, Kurosawa M,
Matsumoto G, Mikoshiba K and Nukina N: ROCK-phosphorylated vimentin
modifies mutant huntingtin aggregation via sequestration of IRBIT.
Mol Neurodegener. 7:432012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Farber MJ, Rizaldy R and Hildebrand JD:
Shroom2 regulates contractility to control endothelial
morphogenesis. Mol Biol Cell. 22:795–805. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rodriguez PL, Sahay S, Olabisi OO and
Whitehead IP: ROCK I-mediated activation of NF-kappaB by RhoB. Cell
Signal. 19:2361–2369. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Verkman AS: Physiological importance of
aquaporin water channels. Ann Med. 34:192–200. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu Q, Yang ZF, Wang KJ, Feng XY, Lv ZJ, Li
Y and Jian ZX: AQP8 inhibits colorectal cancer growth and
metastasis by down-regulating PI3K/AKT signaling and PCDH7
expression. Am J Cancer Res. 8:266–279. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chao G and Zhang S: Aquaporins 1, 3 and 8
expression in irritable bowel syndrome rats colon via NF-κB
pathway. Oncotarget. 8:47175–47183. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang JP, Hou XH and Ma RJ: The clinical
features and colonic epithelium AQP8 expression in
diarrhea-irritable bowel syndrome. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi.
45:1000–1003. 2006.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Escudero-Hernández C, Münch A and Koch S:
The water channel aquaporin 8 is a critical regulator of intestinal
fluid homeostasis in collagenous colitis. J Crohns Colitis. Feb
4–2020.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hidalgo IJ, Raub TJ and Borchardt RT:
Characterization of the human colon carcinoma cell line (Caco-2) as
a model system for intestinal epithelial permeability.
Gastroenterology. 96:736–749. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nighot PK, Hu CA and Ma TY: Autophagy
enhances intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier function by
targeting claudin-2 protein degradation. J Biol Chem.
290:7234–7246. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lin S, Han Y, Jenkin K, Lee SJ, Sasaki M,
Klapproth JM, He P and Yun CC: Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1 Is
Important for Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function and
Susceptibility to Colitis. Am J Pathol. 188:353–366. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Elamin E, Jonkers D, Juuti-Uusitalo K, van
Ijzendoorn S, Troost F, Duimel H, Broers J, Verheyen F, Dekker J
and Masclee A: Effects of ethanol and acetaldehyde on tight
junction integrity: In vitro study in a three dimensional
intestinal epithelial cell culture model. PLoS One. 7:e350082012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tong J, Wang Y, Chang B, Zhang D and Wang
B: Y-27632 inhibits ethanol-induced increase in intestinal
epithelial barrier permeability. Mol Med Rep. 9:2357–2361. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Turner JR, Angle JM, Black ED, Joyal JL,
Sacks DB and Madara JL: PKC-dependent regulation of transepithelial
resistance: Roles of MLC and MLC kinase. Am J Physiol.
277:C554–C562. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mihaescu A, Santén S, Jeppsson B and
Thorlacius H: Rho kinase signalling mediates radiation-induced
inflammation and intestinal barrier dysfunction. Br J Surg.
98:124–131. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tong J, Wang Y, Chang B, Zhang D, Liu P
and Wang B: Activation of RhoA in alcohol-induced intestinal
barrier dysfunction. Inflammation. 36:750–758. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Narumiya S, Ishizaki T and Uehata M: Use
and properties of ROCK-specific inhibitor Y-27632. Methods Enzymol.
325:273–284. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li Z, Gao M, Yang B, Zhang H, Wang K, Liu
Z, Xiao X and Yang M: Naringin attenuates MLC phosphorylation and
NF-kappaB activation to protect sepsis-induced intestinal injury
via RhoA/ROCK pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 103:50–58. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Segain JP, Raingeard de la Blétière D,
Sauzeau V, Bourreille A, Hilaret G, Cario-Toumaniantz C, Pacaud P,
Galmiche JP and Loirand G: Rho kinase blockade prevents
inflammation via nuclear factor kappa B inhibition: Evidence in
Crohns disease and experimental colitis. Gastroenterology.
124:1180–1187. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Anwar KN, Fazal F, Malik AB and Rahman A:
RhoA/Rho-associated kinase pathway selectively regulates
thrombin-induced intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression in
endothelial cells via activation of I kappa B kinase beta and
phosphorylation of RelA/p65. J Immunol. 173:6965–6972. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shimada H and Rajagopalan LE: Rho kinase-2
activation in human endothelial cells drives lysophosphatidic
acid-mediated expression of cell adhesion molecules via NF-kappaB
p65. J Biol Chem. 285:12536–12542. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Amano M, Nakayama M and Kaibuchi K:
Rho-kinase/ROCK: A key regulator of the cytoskeleton and cell
polarity. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 67:545–554. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Duan PY, Ma Y, Li XN, Qu FZ, Ji L, Guo XY,
Zhang WJ, Xiao F, Li L, Hu JS, et al: Inhibition of RIPK1-dependent
regulated acinar cell necrosis provides protection against acute
pancreatitis via the RIPK1/NF-κB/AQP8 pathway. Exp Mol Med.
51:1–17. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|