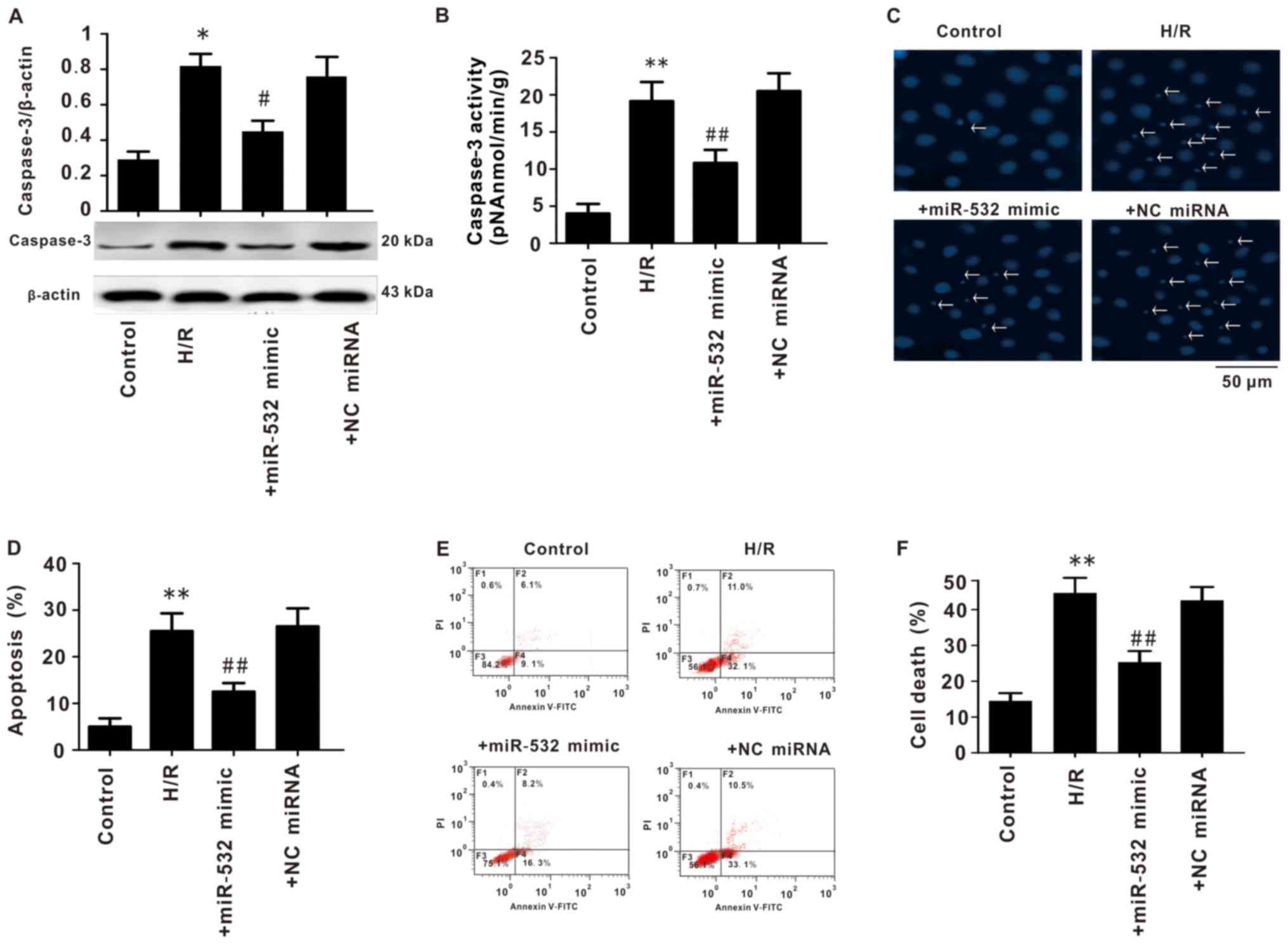
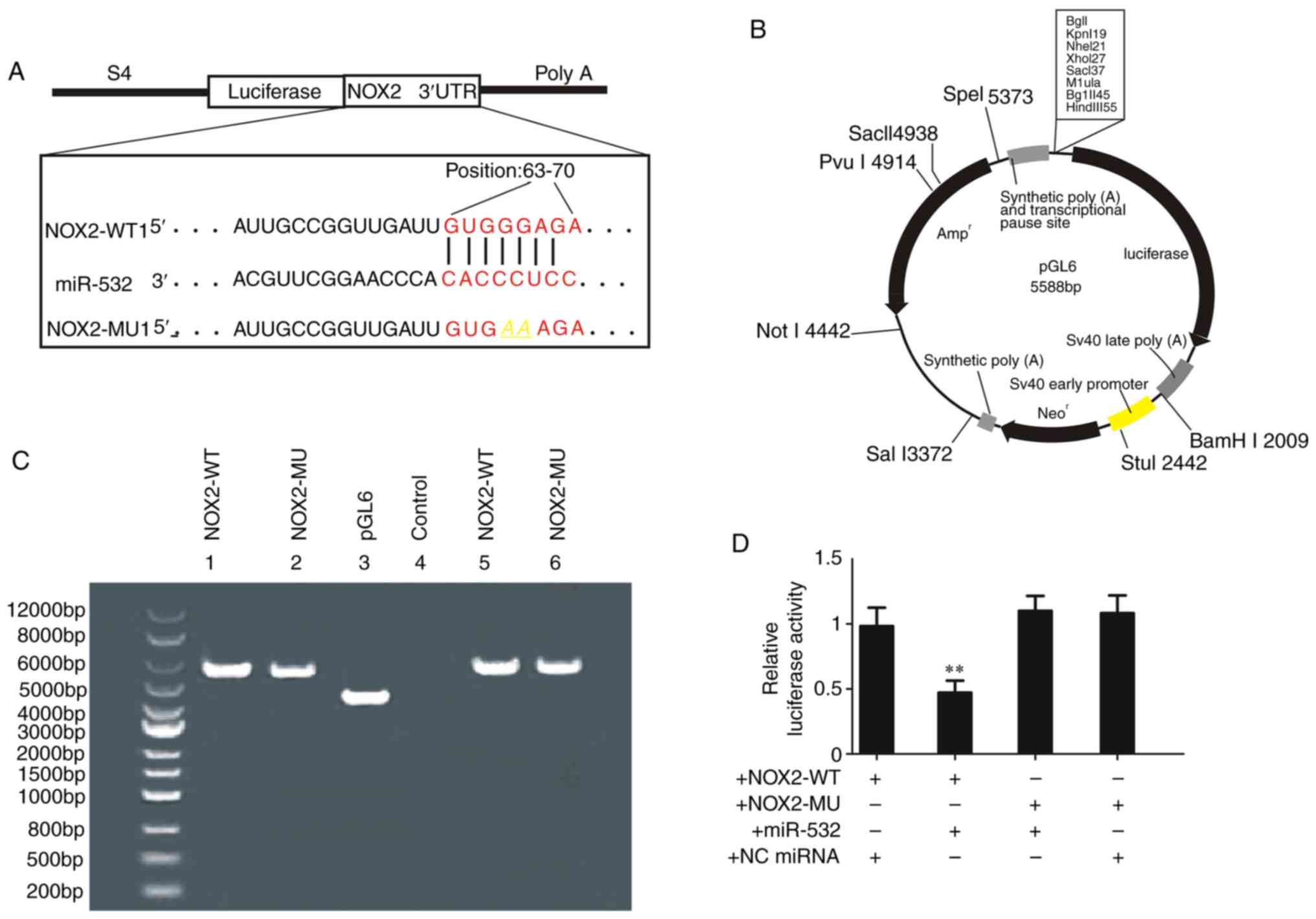
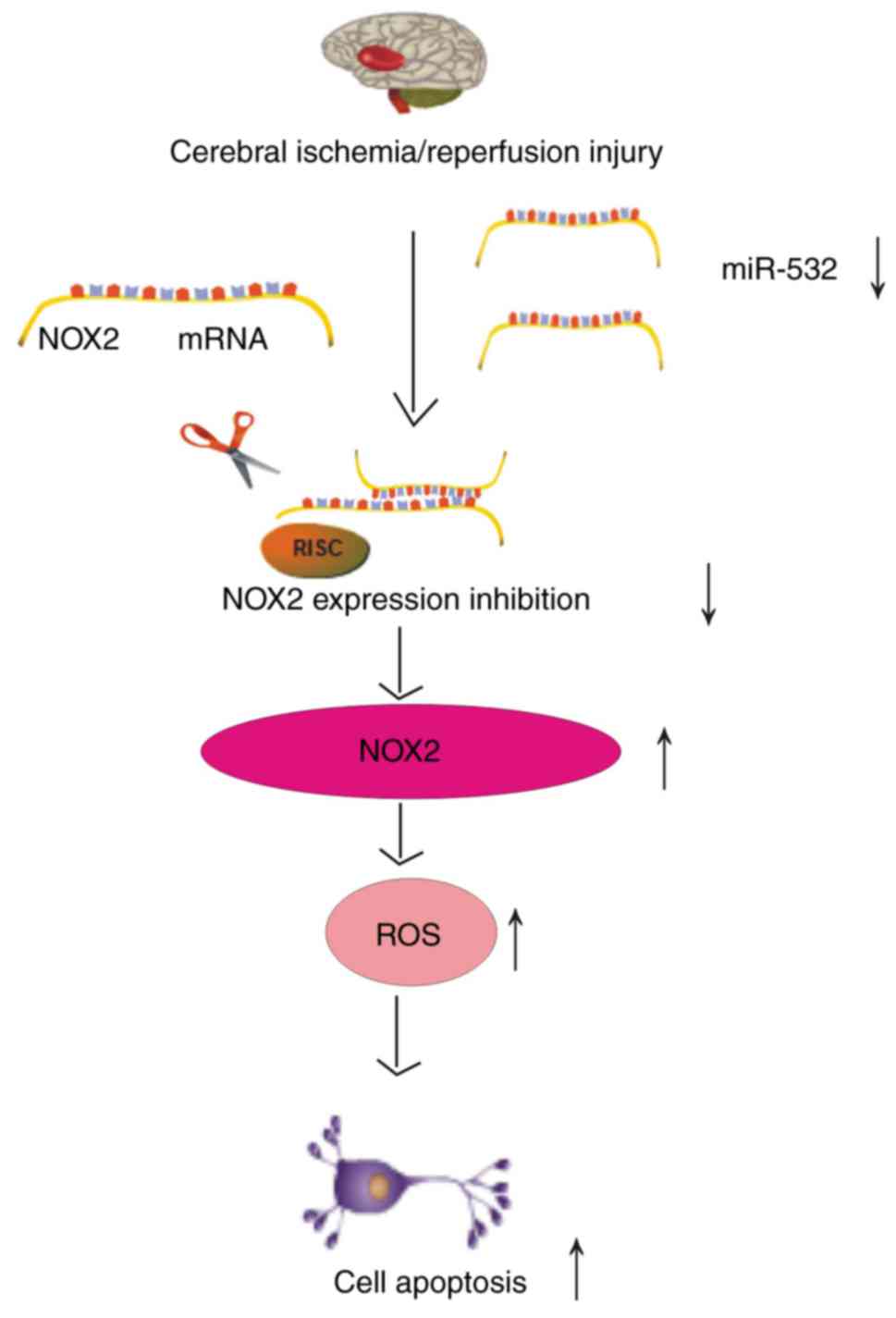
|
1
|
Randolph SA: Ischemic Stroke. Workplace
Health Saf. 64:4442016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Khoshnam SE, Winlow W, Farzaneh M, Farbood
Y and Moghaddam HF: Pathogenic mechanisms following ischemic
stroke. Neurol Sci. 38:1167–1186. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Enzmann G, Kargaran S and Engelhardt B:
Ischemia-reperfusion injury in stroke: Impact of the brain barriers
and brain immune privilege on neutrophil function. Ther Adv Neurol
Disord. 11:17562864187941842018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Siti HN, Kamisah Y and Kamsiah J: The role
of oxidative stress, antioxidants and vascular inflammation in
cardiovascular disease (a review). Vascul Pharmacol. 71:40–56.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ma MW, Wang J, Zhang Q, Wang R, Dhandapani
KM, Vadlamudi RK and Brann DW: NADPH oxidase in brain injury and
neurodegenerative disorders. Mol Neurodegener. 12:72017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lou Z, Wang AP, Duan XM, Hu GH, Song GL,
Zuo ML and Yang ZB: Upregulation of NOX2 and NOX4 mediated by TGF-β
signaling pathway exacerbates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion
oxidative stress injury. Cell Physiol Biochem. 46:2103–2113. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Sun JB, Li Y, Cai YF, Huang Y, Liu S,
Yeung PK, Deng MZ, Sun GS, Zilundu PL, Hu QS, et al: Scutellarin
protects oxygen/glucose-deprived astrocytes and reduces focal
cerebral ischemic injury. Neural Regen Res. 13:1396–1407. 2015.
|
|
8
|
Xu W, Gao L, Zheng J, Li T, Shao A, Reis
C, Chen S and Zhang J: The roles of microRNAs in stroke: Possible
therapeutic targets. Cell Transplant. 27:1778–1788. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Majdi A, Mahmoudi J, Sadigh-Eteghad S,
Farhoudi M and Shotorbani SS: The interplay of microRNAs and
post-ischemic glutamate excitotoxicity: An emergent research field
in stroke medicine. Neurol Sci. 37:1765–1771. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mao L, Zuo ML, Hu GH, Duan XM and Yang ZB:
mir-193 targets ALDH2 and contributes to toxic aldehyde
accumulation and tyrosine hydroxylase dysfunction in cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Oncotarget. 8:99681–99692. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang ZB, Zhang Z, Li TB, Lou Z, Li SY,
Yang H, Yang J, Luo XJ and Peng J: Up-regulation of brain-enriched
miR-107 promotes excitatory neurotoxicity through down-regulation
of glutamate transporter-1 expression following ischaemic stroke.
Clin Sci. 127:679–689. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu Z, Tuo YH, Chen JW, Wang QY, Li S, Li
MC, Dai G, Wang JS, Zhang YL, Feng L and Shi ZS: NADPH oxidase
inhibitor regulates microRNAs with improved outcome after
mechanical reperfusion. J Neurointerv Surg. 9:702–706. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ma J, Zhang J, Wang Y, Long K, Wang X, Jin
L, Tang Q, Zhu L, Tang G, Li X and Li M: MiR-532-5p alleviates
hypoxia-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by targeting PDCD4. Gene.
675:36–43. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sun W, Liu Q, Leng J, Zheng Y and Li J:
The role of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex in cardiovascular
diseases. Life Sci. 121:97–103. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li P, Teng F, Gao F, Zhang M, Wu J and
Zhang C: Identification of circulating microRNAs as potential
biomarkers for detecting acute ischemic stroke. Cell Mol Neurobiol.
35:433–447. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sepramaniam S, Tan JR, Tan KS, DeSilva DA,
Tavintharan S, Woon FP, Wang CW, Yong FL, Karolina DS, Kaur P, et
al: Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers of acute stroke. Int J Mol
Sci. 15:1418–1432. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals, . Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th
edition. National Academicals Press (US). (Washington, DC).
2011.
|
|
18
|
Whiteside G, Cougnon N, Hunt SP and
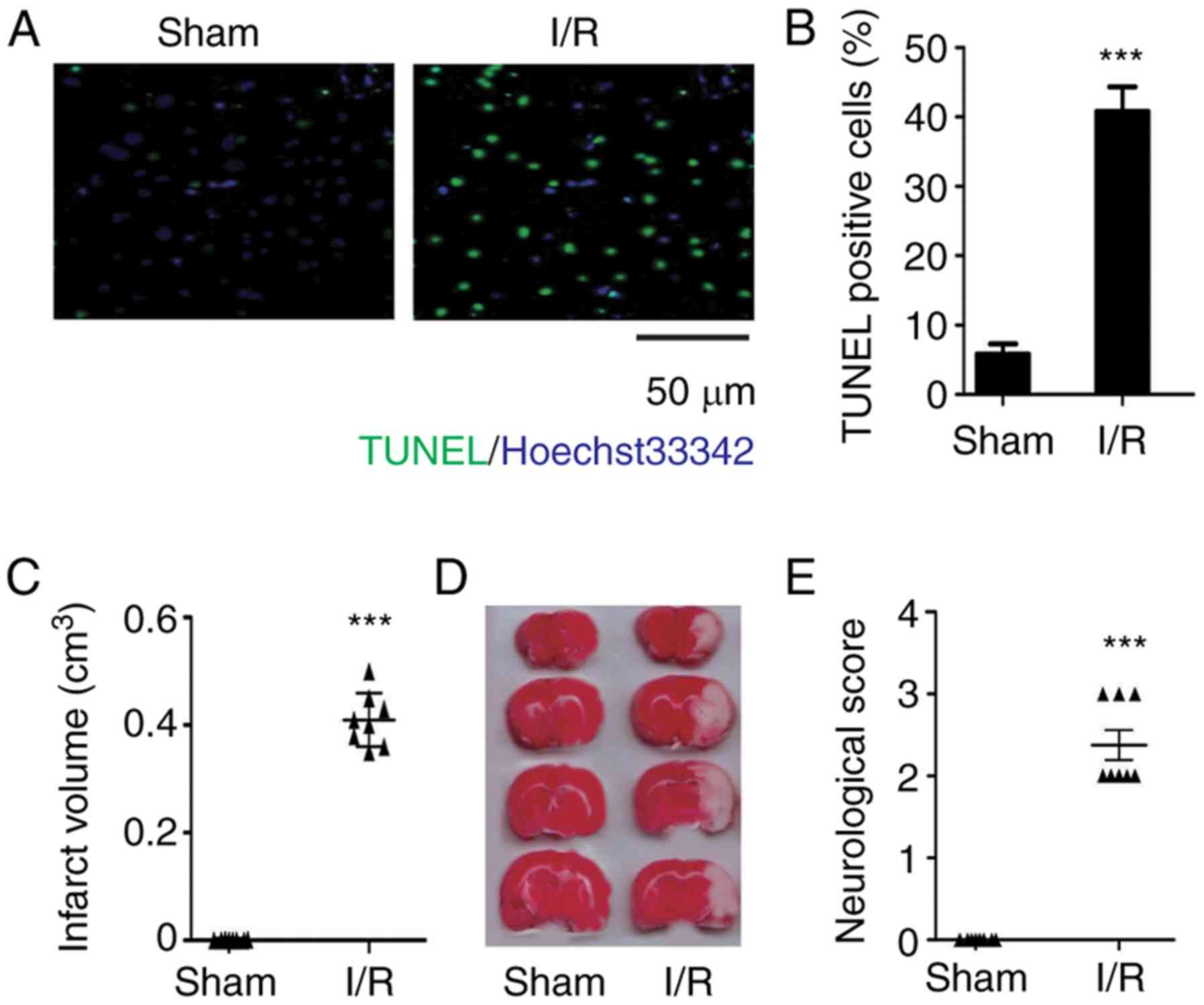
Munglani R: An improved method for detection of apoptosis in tissue
sections and cell culture, using the TUNEL technique combined with
Hoechst stain. Brain Res Protoc. 2:160–164. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Brandes RP, Weissmann N and Schröder K:
Redox-mediated signal transduction by cardiovascular Nox NADPH
oxidases. J Mol Cell Cardio. 73:70–79. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Patel M: Targeting oxidative stress in
central nervous system disorders. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 37:768–778.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Awooda HA, Lutfi MF, Sharara GGM and Saeed
AM: Oxidative/nitrosative stress in rats subjected to focal
cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 9:17–24.
2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Davis SM and Pennypacker KR: Targeting
antioxidant enzyme expression as a therapeutic strategy for
ischemic stroke. Neurochem Int. 107:23–32. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
De Silva TM, Brait VH, Drummond GR, Sobey
CG and Miller AA: Nox2 oxidase activity accounts for the oxidative
stress and vasomotor dysfunction in mouse cerebral arteries
following ischemic stroke. PLoS One. 6:e283932011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang Z, Wei X, Liu K, Zhang X, Yang F,
Zhang H, He Y, Zhu T, Li F, Shi W, et al: NOX2 deficiency
ameliorates cerebral injury through reduction of complexin
II-mediated glutamate excitotoxicity in experimental stroke. Free
Radic Biol Med. 65:942–951. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jackman KA, Miller AA, De Silva TM, Crack
PJ, Drummond GR and Sobey CG: Reduction of cerebral infarct volume
by apocynin requires pretreatment and is absent in Nox2-deficient
mice. Br J Pharmacol. 156:680–688. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wingler K, Altenhoefer SA, Kleikers PWM,
Radermacher KA, Kleinschnitz C and Schmidt HH: VAS2870 is a
pan-NADPH oxidase inhibitor. Cell Mol Life Sci. 69:3159–3160. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Surace MJ and Block ML: Targeting
microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: The potential of NOX2 inhibitors.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 69:2409–2427. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kelly KA, Li X, Tan Z, VanGilder RL, Rosen
CL and Huber JD: NOX2 inhibition with apocynin worsens stroke
outcome in aged rats. Brain Res. 1292:165–172. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu NN, Dong ZL and Han LL: MicroRNA-410
inhibition of the TIMP2-dependent MAPK pathway confers
neuroprotection against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis after
ischemic stroke in mice. Brain Res Bull. 143:45–57. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang SW, Liu Z and Shi ZS: Non-Coding RNA
in acute ischemic stroke: Mechanisms, biomarkers and therapeutic
targets. Cell Transplant. 27:1763–1777. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Huang R, Ma J, Niu B, Li J, Chang J, Zhang
Y, Liu P and Luan X: MiR-34b protects against focal cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury in rat by targeting keap1. J
Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 28:1–9. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zheng Y, Pan C, Chen M, Pei A, Xie L and
Zhu S: miR-29a ameliorates ischemic injury of astrocytes in vitro
by targeting the water channel protein aquaporin 4. Oncol Rep.
41:1707–1717. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Deng Y, Ma G, Dong Q, Sun X, Liu L, Miao Z
and Gao F: Overexpression of miR-224-3p alleviates apoptosis from
cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury by targeting FIP200. J Cell
Biochem. 1200:17151–17158. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Fu C, Chen S, Cai N, Liu Z, Wang P and
Zhao J: Potential neuroprotective effect of miR-451 against
cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in stroke patients and a mouse
model. World Neurosurgery. 130:e54–e61. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rink C and Khanna S: MicroRNA in ischemic
stroke etiology and pathology. Physiol Genomics. 43:521–528. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tan JR, Koo YX, Kaur P, Liu F, Armugam A,
Wong PT and Jeyaseelan K: microRNAs in stroke pathogenesis. Curr
Mol Med. 11:76–92. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhao H, Han Z, Ji X and Luo Y: Epigenetic
regulation of oxidative stress in ischemic stroke. Aging Dis.
7:295–306. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kahles T and Brandes RP: Which NADPH
oxidase isoform is relevant for ischemic stroke? The case for nox
2. Antioxid Redox Signal. 18:1400–1417. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li J, Hui L, Kang Q and Li R:
Down-regulation of microRNA-27b promotes retinal pigment epithelial
cell proliferation and migration by targeting Nox2. Pathol Res
Pract. 214:925–933. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kim SM, Hur DY, Hong SW and Kim JH:
EBV-encoded EBNA1 regulates cell viability by modulating
miR34a-NOX2-ROS signaling in gastric cancer cells. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 494:550–555. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang J, Brown ME, Zhang H, Martinez M,
Zhao Z, Bhutani S, Yin S, Trac D, Xi JJ and Davis ME:
High-throughput screening identifies microRNAs that target Nox2 and
improve function after acute myocardial infarction. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physio. 312:H1002–H1012. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Wang XH and Wang TL: MicroRNAs of
microglia: Wrestling with central nervous system disease. Neural
Regen Res. 13:2067–2072. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|