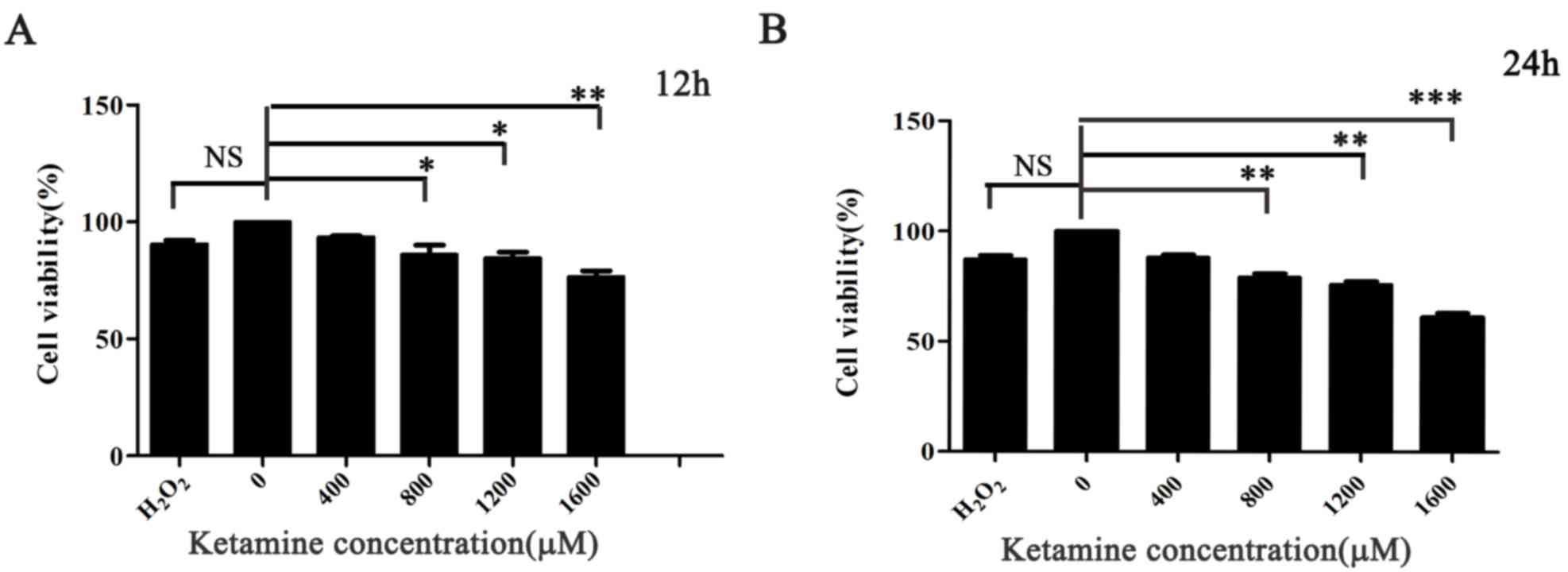
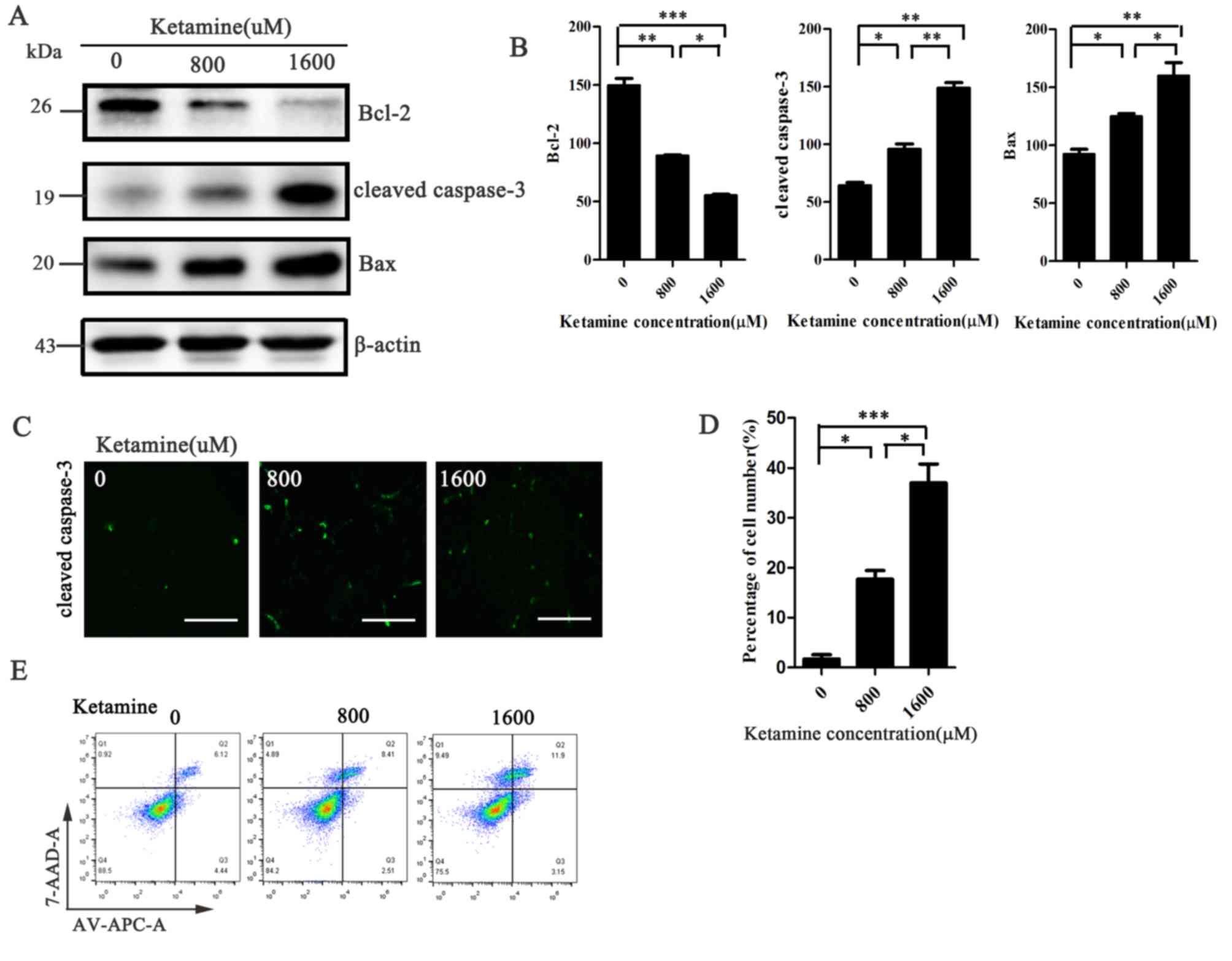
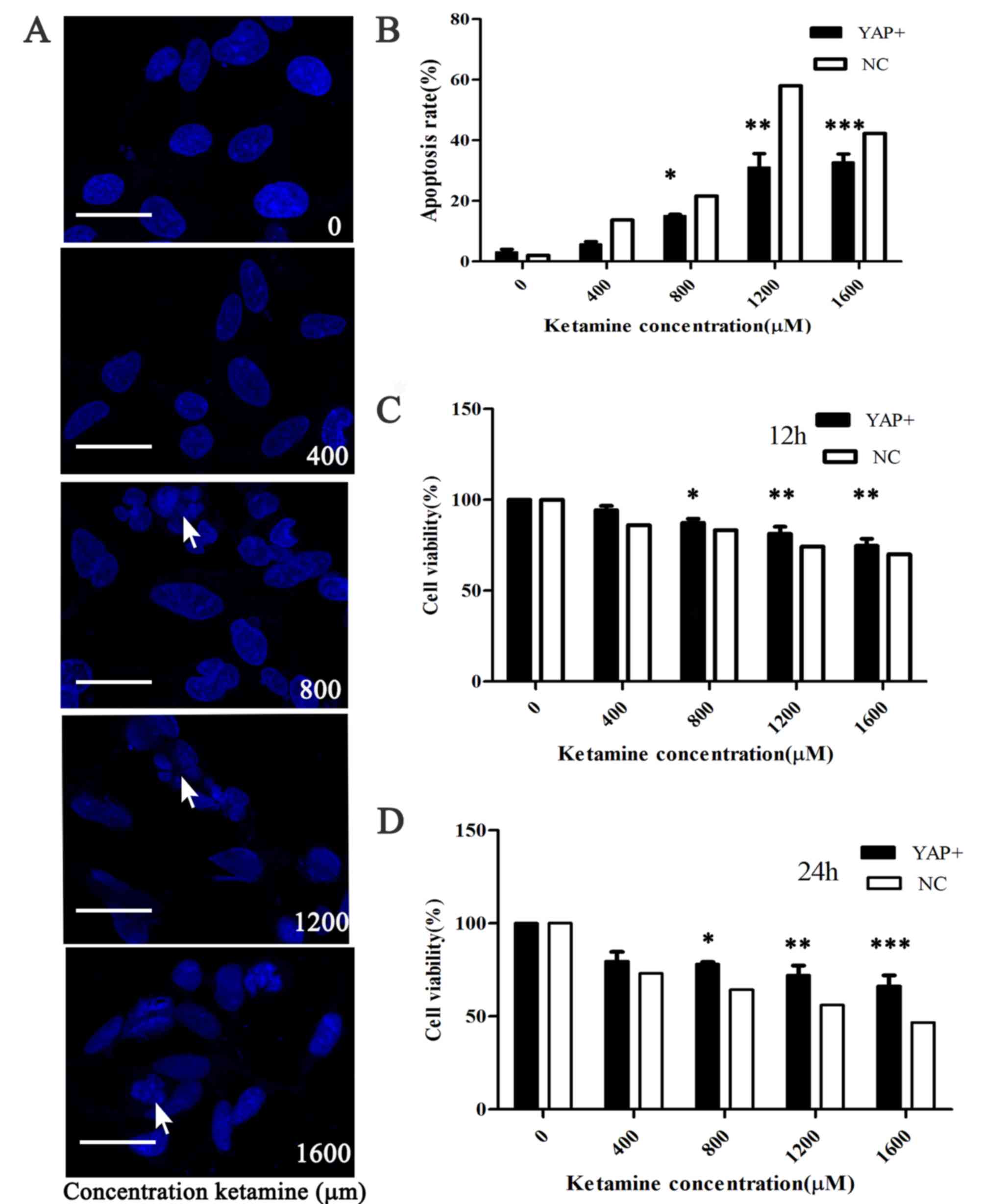
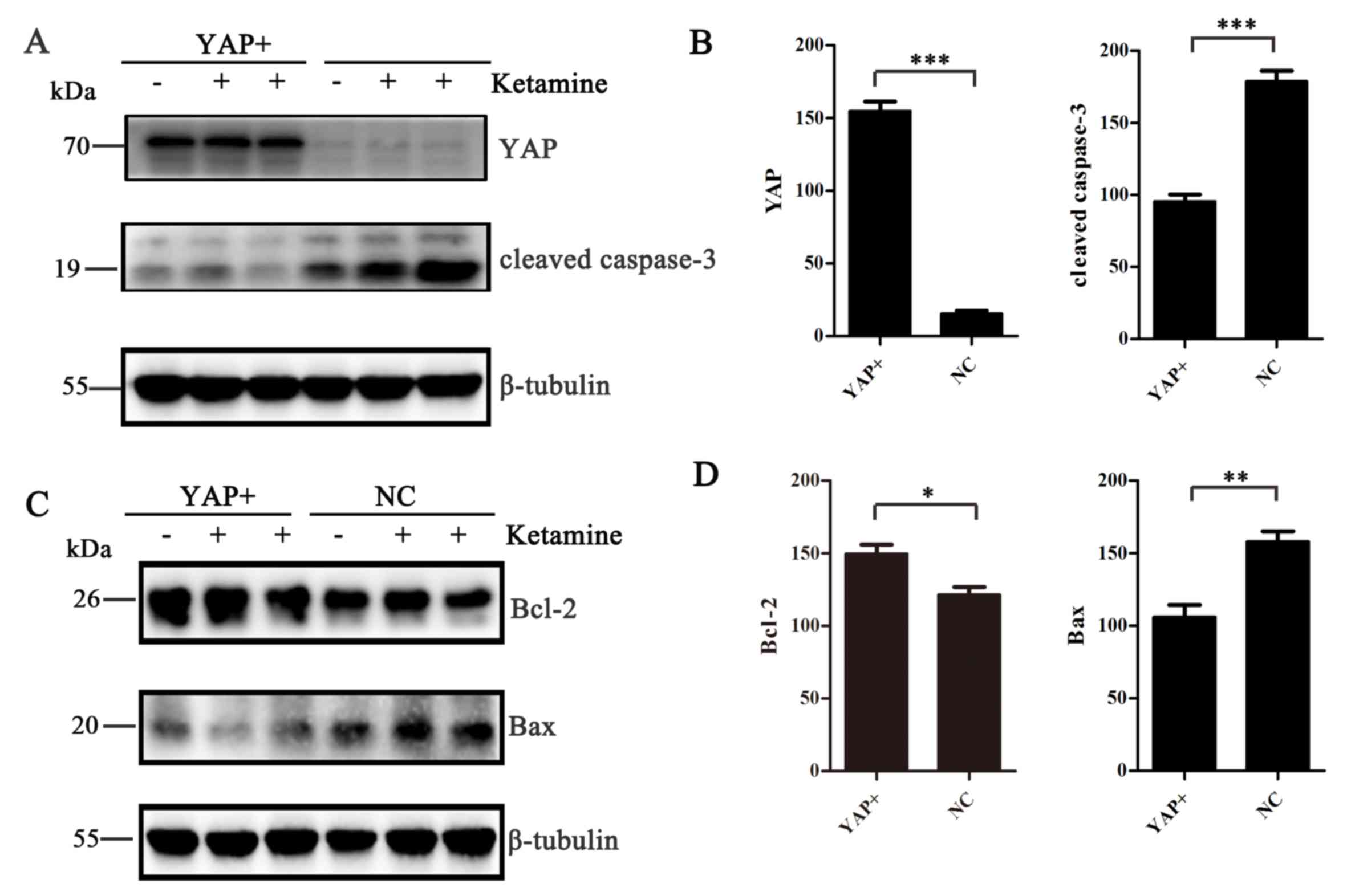
|
1
|
Jiang JD, Zheng XC, Huang FY, Gao F, You
MZ and Zheng T: MicroRNA-107 regulates anesthesia-induced neural
injury in embryonic stem cell derived neurons. IUBMB Life.
71:20–27. 2019. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhou Z and Ma D: Anaesthetics-induced
neurotoxicity in developing brain: An update on preclinical
evidence. Brain Sci. 4:136–149. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yan J, Li YR, Zhang Y, Lu Y and Jiang H:
Repeated exposure to anesthetic ketamine can negatively impact
neurodevelopment in infants: A prospective preliminary clinical
study. J Child Neurol. 29:1333–1338. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zuo D, Lin L, Liu Y, Wang C, Xu J, Sun F,
Li L, Li Z and Wu Y: Baicalin attenuates ketamine-induced
neurotoxicity in the developing rats: Involvement of PI3K/Akt and
CREB/BDNF/Bcl-2 Pathways. Neurotox Res. 30:159–72. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nowak K, Meyza K, Nikolaev E, Hunt MJ and
Kasicki S: Local blockade of NMDA receptors in the rat prefrontal
cortex increases c-Fos expression in multiple subcortical regions.
Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 72:207–218. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Eustaquio T, Wang C, Dugard CK, George NI,
Liu F, Slikker W Jr, Paule MG, Howard PC and Paredes AM: Electron
microscopy techniques employed to explore mitochondrial defects in
the developing rat brain following ketamine treatment. Exp Cell
Res. 373:164–170. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Huang L, Liu Y, Jin W, Ji X and Dong Z:
Ketamine potentiates hippocampal neurodegeneration and persistent
learning and memory impairment through the PKCgamma-ERK signaling
pathway in the developing brain. Brain Res. 1476:164–171. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Green SM and Cote CJ: Ketamine and
neurotoxicity: Clinical perspectives and implications for emergency
medicine. Ann Emerg Med. 54:181–190. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yu FX, Zhao B and Guan KL: Hippo pathway
in organ size control, tissue homeostasis, and cancer. Cell.
163:811–828. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Porazinski S, Wang H, Asaoka Y, Behrndt M,
Miyamoto T, Morita H, Hata S, Sasaki T, Krens SFG, Osada Y, et al:
YAP is essential for tissue tension to ensure vertebrate 3D body
shape. Nature. 521:217–221. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao B, Tumaneng K and Guan KL: The Hippo
pathway in organ size control, tissue regeneration and stem cell
self-renewal. Nat Cell Biol. 13:877–883. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Juan WC and Hong W: Targeting the hippo
signaling pathway for tissue regeneration and cancer therapy. Genes
(Basel). 7:552016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Harvey KF, Zhang X and Thomas DM: The
Hippo pathway and human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:246–257. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu H, Wei L, Fan F, Ji S, Zhang S, Geng J,
Hong L, Fan X, Chen Q, Tian J, et al: Integration of Hippo
signalling and the unfolded protein response to restrain liver
overgrowth and tumorigenesis. Nat Commun. 6:62392015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu M, Zhang Z, Sampson L, Zhou X,
Nalapareddy K, Feng Y, Akunuru S, Melendez J, Davis AK, Bi F, et
al: RHOA GTPase Controls YAP-Mediated EREG signaling in small
intestinal stem cell maintenance. Stem Cell Reports. 9:1961–1975.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen Q, Zhang N, Gray RS, Li H, Ewald AJ,
Zahnow CA and Pan D: A temporal requirement for Hippo signaling in
mammary gland differentiation, growth, and tumorigenesis. Genes
Dev. 28:432–437. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Song H, Mak KK, Topol L, Yun K, Hu J,
Garrett L, Chen Y, Park O, Chang J, Simpson RM, et al: Mammalian
Mst1 and Mst2 kinases play essential roles in organ size control
and tumor suppression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:1431–1436. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cai J, Zhang N, Zheng Y, de Wilde RF,
Maitra A and Pan D: The Hippo signaling pathway restricts the
oncogenic potential of an intestinal regeneration program. Genes
Dev. 24:2383–2388. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bohere J, Mancheno-Ferris A, Al Hayek S,
Zanet J, Valenti P, Akino K, Yamabe Y, Inagaki S, Chanut-Delalande
H, Plaza S, et al: Shavenbaby and Yorkie mediate Hippo signaling to
protect adult stem cells from apoptosis. Nat Commun. 9:51232018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Biedler JL, Roffler-Tarlov S, Schachner M
and Freedman LS: Multiple neurotransmitter synthesis by human
neuroblastoma cell lines and clones. Cancer Res. 38:3751–3757.
1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gilany K, Van Elzen R, Mous K, Coen E, Van
Dongen W, Vandamme S, Gevaert K, Timmerman E, Vandekerckhove J,
Dewilde S, et al: The proteome of the human neuroblastoma cell line
SH-SY5Y: An enlarged proteome. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1784:983–985.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mansouri S, Agartz I, Ogren SO, Patrone C
and Lundberg M: PACAP protects adult neural stem cells from the
neurotoxic effect of ketamine associated with decreased apoptosis,
ER stress and mTOR pathway activation. PLoS One. 12:e01704962017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mak YT, Lam WP, Lu L, Wong YW and Yew DT:
The toxic effect of ketamine on SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell line and
human neuron. Microsc Res Tech. 73:195–201. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mahmood T and Yang PC: Western blot:
Technique, theory, and trouble shooting. N Am J Med Sci. 4:429–434.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sampaio TB, de Oliveira LF, Constantino
LC, Costa AP, Poluceno GG, Martins WC, Dal-Cim T, de Oliveira KA,
Ludka FK, Prediger RD, et al: Long-term neurobehavioral
consequences of a single ketamine neonatal exposure in rats:
Effects on cellular viability and glutamate transport in frontal
cortex and hippocampus. Neurotox Res. 34:649–659. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Davidson AJ: Anesthesia and neurotoxicity
to the developing brain: The clinical relevance. Paediatr Anaesth.
21:716–721. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hayashi H, Dikkes P and Soriano SG:
Repeated administration of ketamine may lead to neuronal
degeneration in the developing rat brain. Paediatr Anaesth.
12:770–774. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pohl D, Bittigau P, Ishimaru MJ, Stadthaus
D, Hübner C, Olney JW, Turski L and Ikonomidou C:
N-Methyl-D-aspartate antagonists and apoptotic cell death triggered
by head trauma in developing rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
96:2508–2513. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yan J and Jiang H: Dual effects of
ketamine: Neurotoxicity versus neuroprotection in anesthesia for
the developing brain. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 26:155–160. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Takadera T, Ishida A and Ohyashiki T:
Ketamine-induced apoptosis in cultured rat cortical neurons.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 210:100–107. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li JM, Liu LL, Su WJ, Wang B, Zhang T,
Zhang Y and Jiang CL: Ketamine may exert antidepressant effects via
suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome to upregulate AMPA receptors.
Neuropharmacology. 146:149–153. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shang Y, Wu Y, Yao S, Wang X, Feng D and
Yang W: Protective effect of erythropoietin against
ketamine-induced apoptosis in cultured rat cortical neurons:
Involvement of PI3K/Akt and GSK-3 beta pathway. Apoptosis.
12:2187–2195. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ye Z, Li Q, Guo Q, Xiong Y, Guo D, Yang H
and Shu Y: Ketamine induces hippocampal apoptosis through a
mechanism associated with the caspase-1 dependent pyroptosis.
Neuropharmacology. 128:63–75. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jiang S, Li X, Jin W, Duan X, Bo L, Wu J,
Zhang R, Wang Y, Kang R and Huang L: Ketamine-induced neurotoxicity
blocked by N-Methyl-d-aspartate is mediated through activation of
PKC/ERK pathway in developing hippocampal neurons. Neurosci Lett.
673:122–131. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li H, He F, Zhao X, Zhang Y, Chu X, Hua C,
Qu Y, Duan Y and Ming L: YAP inhibits the apoptosis and migration
of human rectal cancer cells via suppression of
JNK-Drp1-mitochondrial fission-HtrA2/Omi pathways. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 44:2073–2089. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Deng Y, Wu LMN, Bai S, Zhao C, Wang H,
Wang J, Xu L, Sakabe M, Zhou W, Xin M and Lu QR: A reciprocal
regulatory loop between TAZ/YAP and G-protein Galphas regulates
Schwann cell proliferation and myelination. Nat Commun.
8:151612017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bai X, Yan Y, Canfield S, Muravyeva MY,
Kikuchi C, Zaja I, Corbett JA and Bosnjak ZJ: Ketamine enhances
human neural stem cell proliferation and induces neuronal apoptosis
via reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial pathway. Anesth
Analg. 116:869–880. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Braun S, Gaza N, Werdehausen R, Hermanns
H, Bauer I, Durieux ME, Hollmann MW and Stevens MF: Ketamine
induces apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway in human
lymphocytes and neuronal cells. Br J Anaesth. 105:347–354. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|