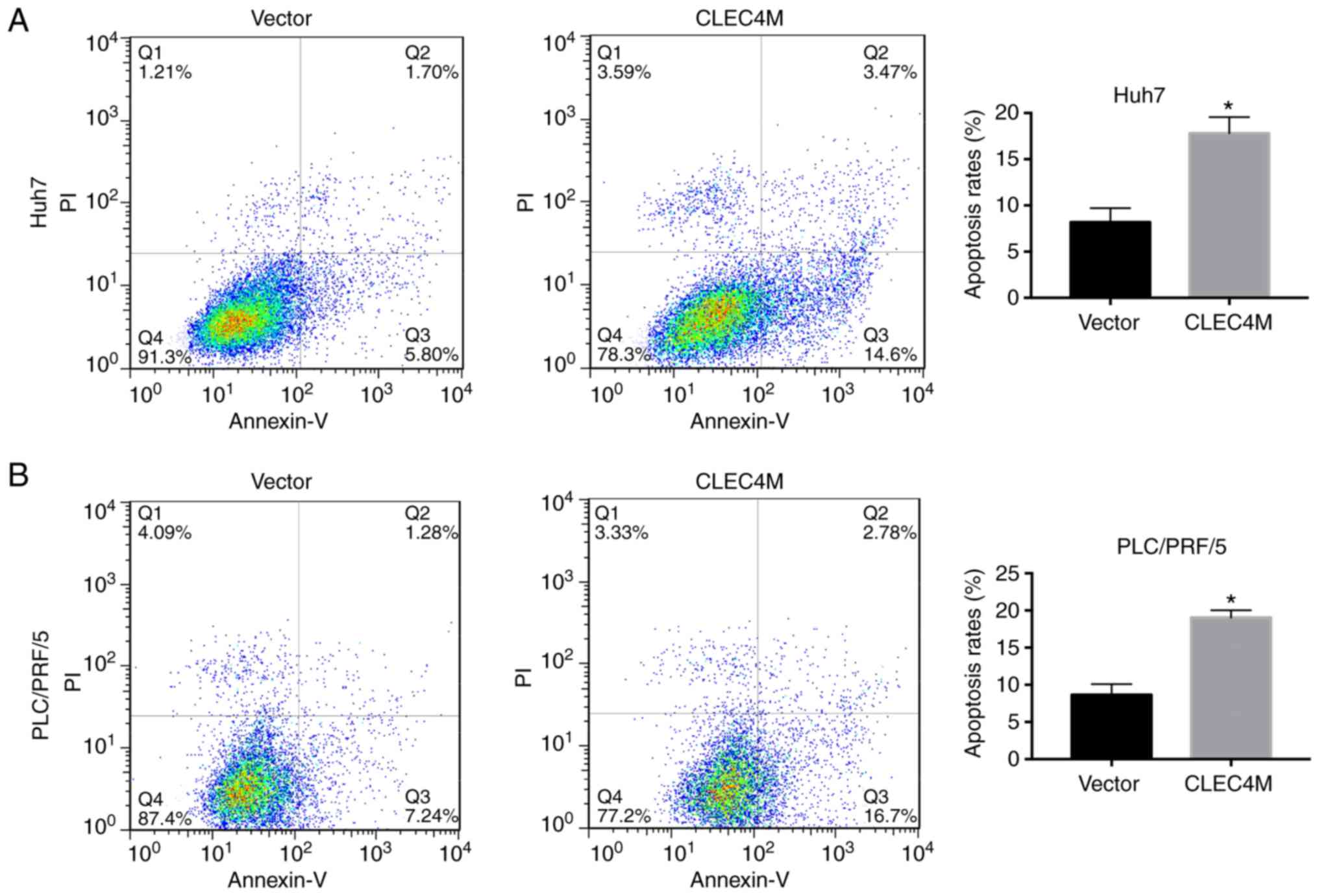
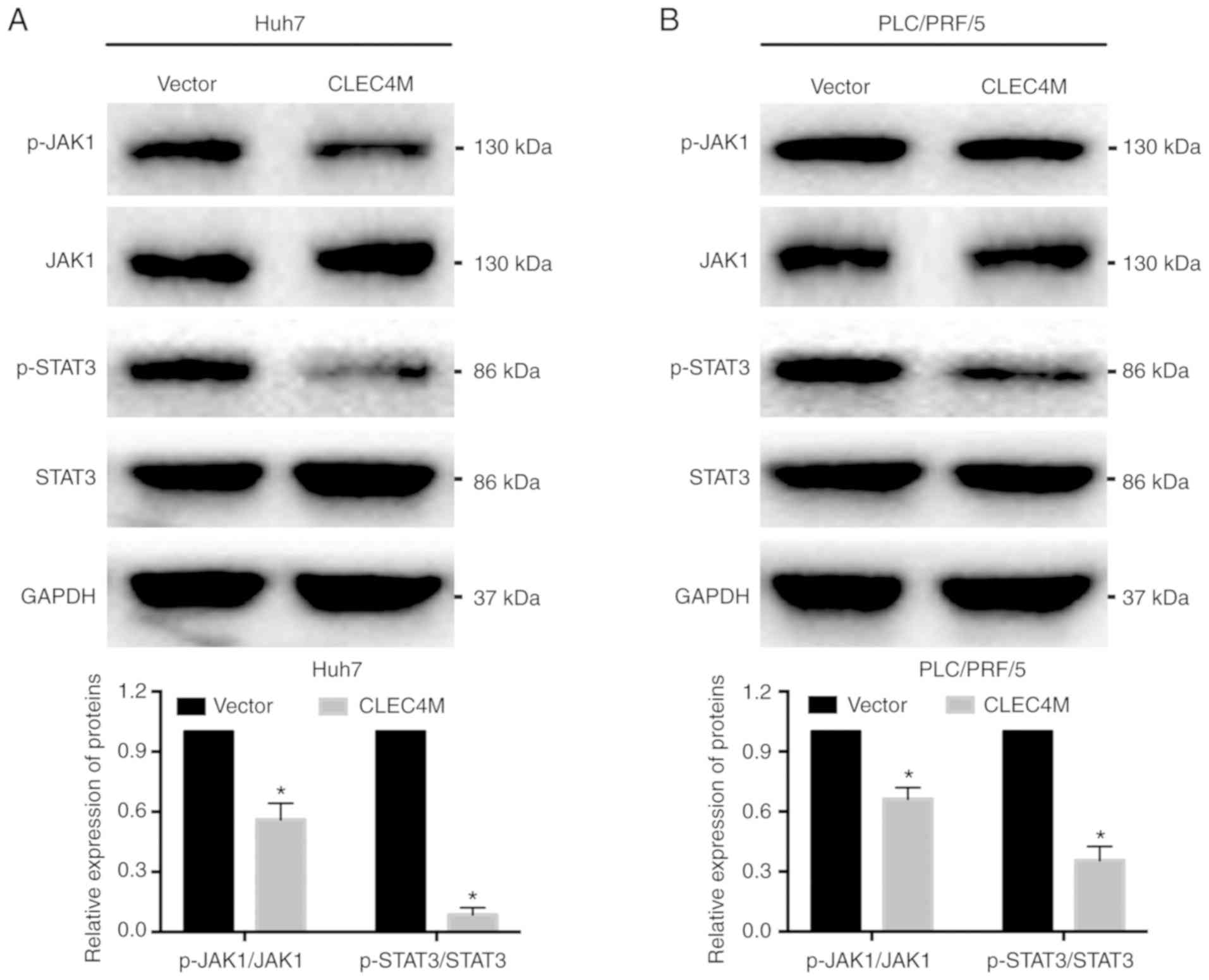
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Llovet JM, Burroughs A and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 362:1907–1917. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
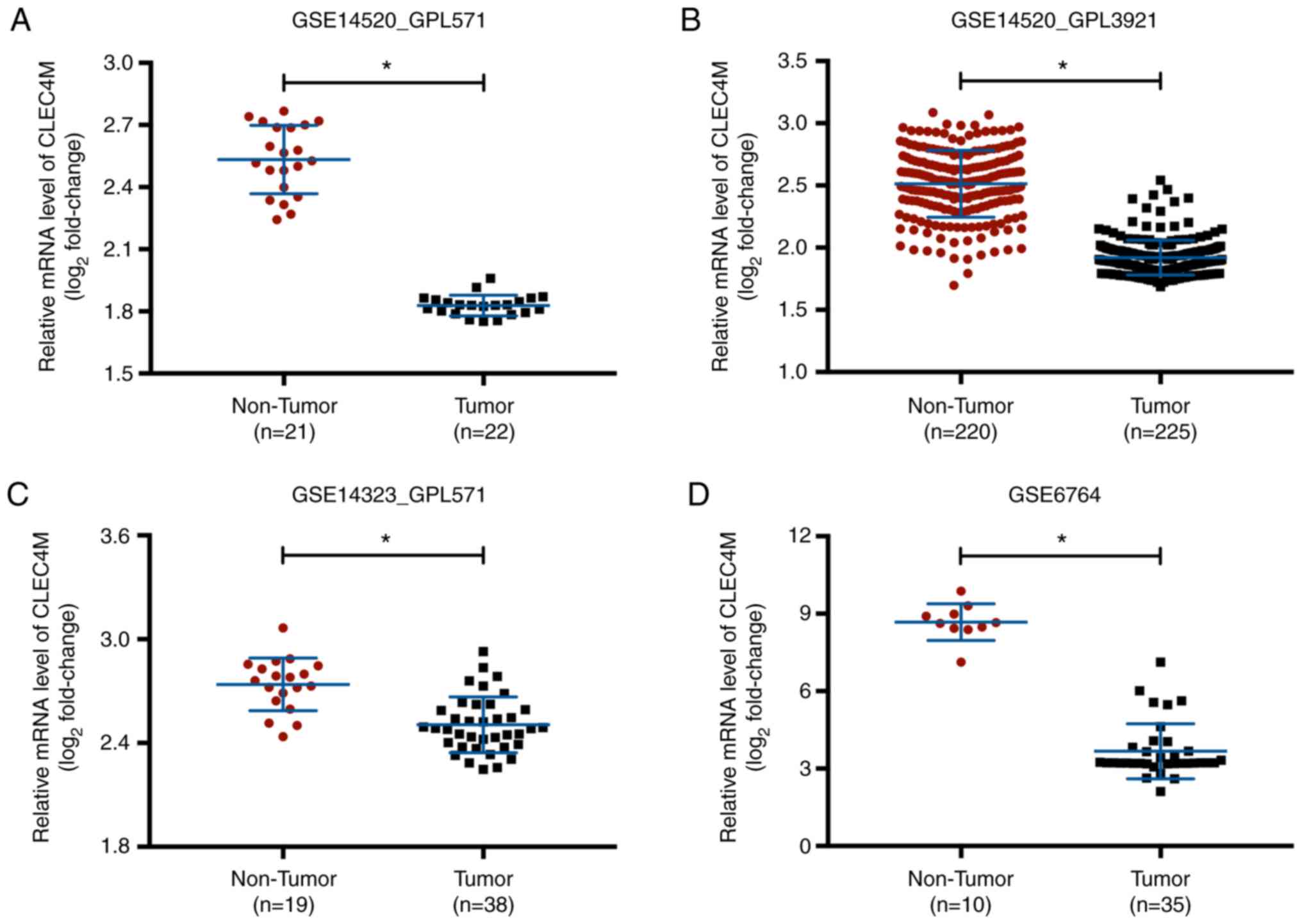
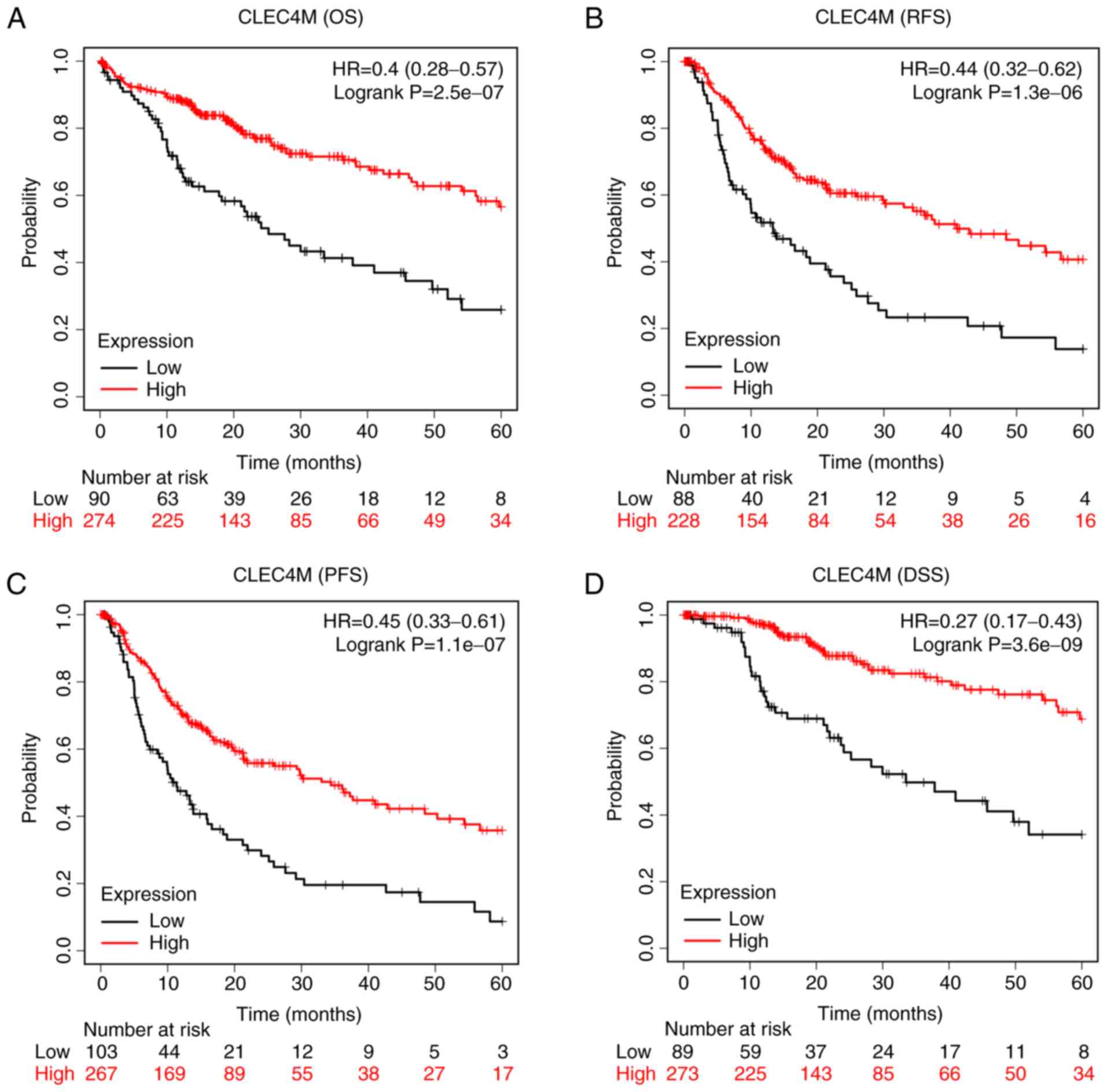
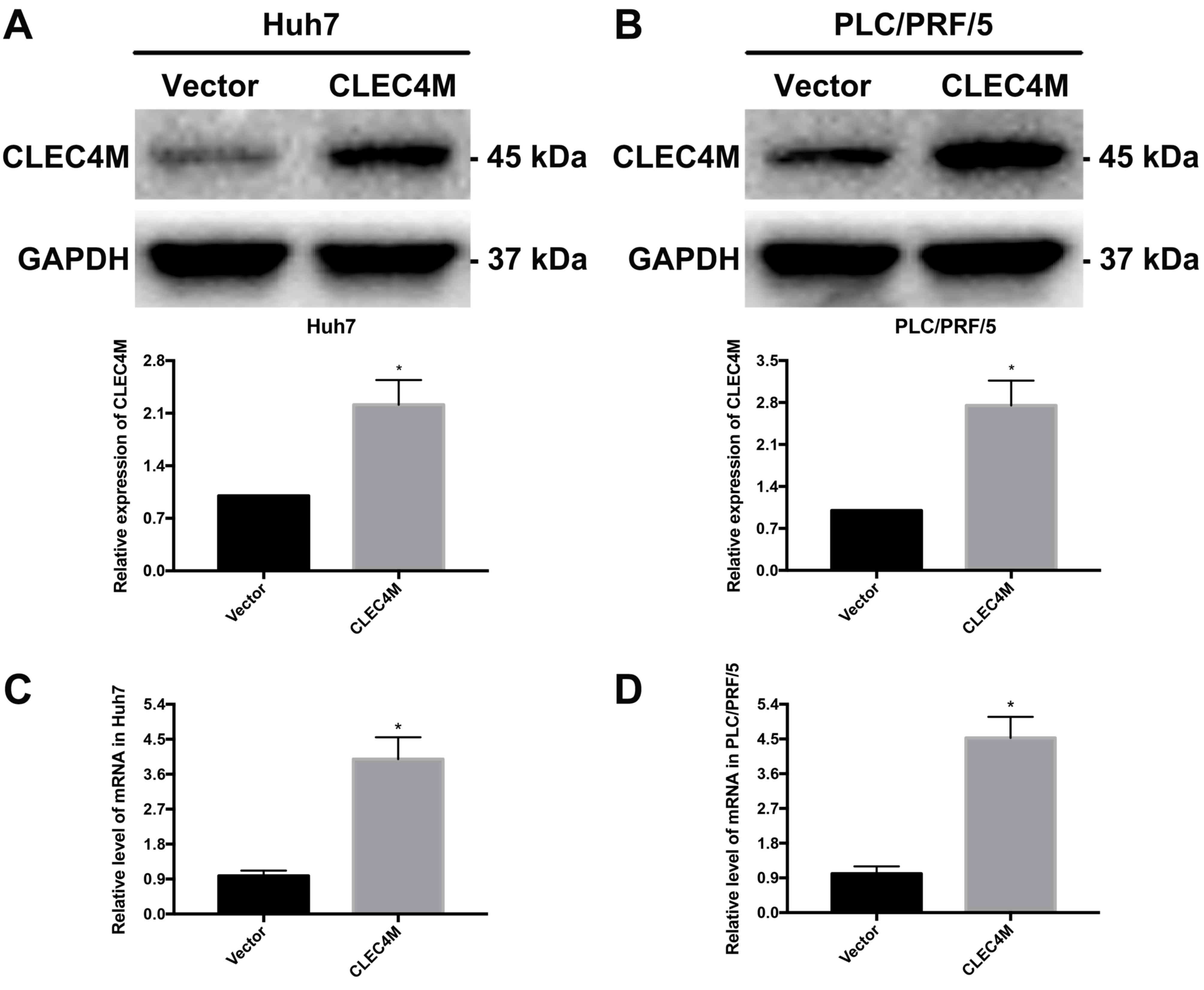
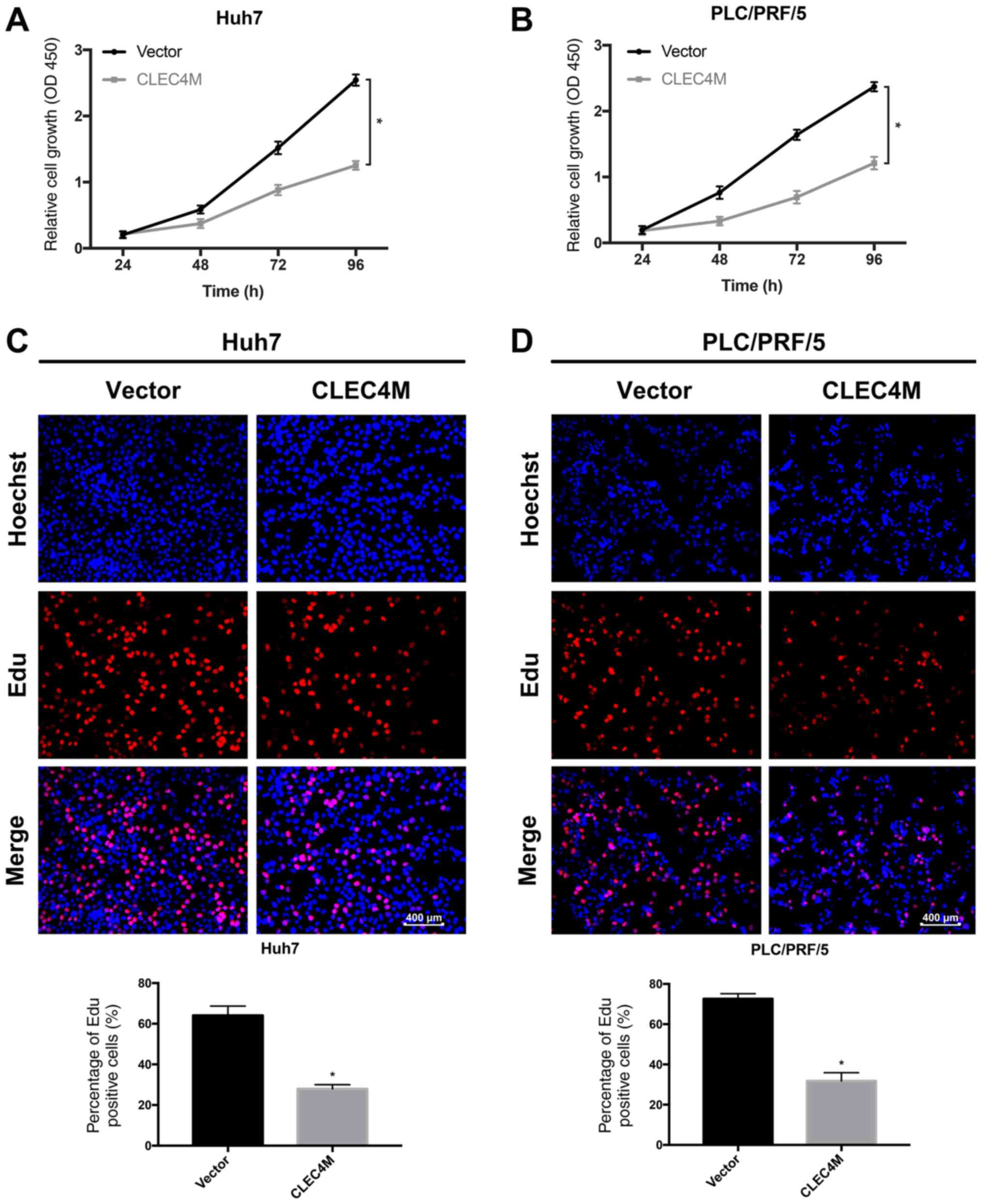
Bruix J and Llovet JM: Major achievements
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 373:614–616. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen C and Wang G: Mechanisms of
hepatocellular carcinoma and challenges and opportunities for
molecular targeted therapy. World J Hepatol. 7:1964–1970. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang F, Ren S and Zuo Y: DC-SIGN,
DC-SIGNR and LSECtin: C-type lectins for infection. Int Rev
Immunol. 33:54–66. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jiang Y, Zhang C, Chen K, Chen Z, Sun Z,
Zhang Z, Ding D, Ren S and Zuo Y: The clinical significance of
DC-SIGN and DC-SIGNR, which are novel markers expressed in human
colon cancer. PLoS One. 9:e1147482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Na H, Liu X, Li X, Zhang X, Wang Y, Wang
Z, Yuan M, Zhang Y, Ren S and Zuo Y: Novel roles of DC-SIGNR in
colon cancer cell adhesion, migration, invasion, and liver
metastasis. J Hematol Oncol. 10:282017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Zhang M, Yuan M, Wang Z,
Zhang J, Zhou X, Zhang Y, Lin F, Na H, et al: DC-SIGNR by
influencing the lncRNA HNRNPKP2 upregulates the expression of CXCR4
in gastric cancer liver metastasis. Mol Cancer. 16:782017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu X, Zhang H, Su L, Yang P, Xin Z, Zou
J, Ren S and Zuo Y: Low expression of dendritic cell-specific
intercellular adhesion molecule-grabbing nonintegrin-related
protein in lung cancer and significant correlations with brain
metastasis and natural killer cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 407:151–160.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liao J, Xu T, Zheng JX, Lin JM, Cai QY, Yu
DB and Peng J: Nitidine chloride inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma
cell growth in vivo through the suppression of the
JAK1/STAT3 signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 32:79–84. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mao J, Hu X, Pang P, Zhou B, Li D and Shan
H: miR-30e acts as a tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma
partly via JAK1/STAT3 pathway. Oncol Rep. 38:393–401. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cao L, Cheng H, Jiang Q, Li H and Wu Z:
APEX1 is a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Aging. 12:4573–4591. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Roessler S, Jia HL, Budhu A, Forgues M, Ye
QH, Lee JS, Thorgeirsson SS, Sun Z, Tang ZY, Qin LX and Wang XW: A
unique metastasis gene signature enables prediction of tumor
relapse in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Cancer
Res. 70:10202–10212. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mas VR, Maluf DG, Archer KJ, Yanek K, Kong
X, Kulik L, Freise CE, Olthoff KM, Ghobrial RM, McIver P and Fisher
R: Genes involved in viral carcinogenesis and tumor initiation in
hepatitis C virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Med.
15:85–94. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wurmbach E, Chen YB, Khitrov G, Zhang W,
Roayaie S, Schwartz M, Fiel I, Thung S, Mazzaferro V, Bruix J, et
al: Genome-wide molecular profiles of HCV-induced dysplasia and
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 45:938–947. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Zhang M, Yuan M, Wang Z,
Zhang J, Zhou X, Zhang Y, Lin F, Na H, et al: DC-SIGNR by
influencing the lncRNA HNRNPKP2 upregulates the expression of CXCR4
in gastric cancer liver metastasis. Mol Cancer. 16:782017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tan LM, Li X, Qiu CF, Zhu T, Hu CP, Yin
JY, Zhang W, Zhou HH and Liu ZQ: CLEC4M is associated with poor
prognosis and promotes cisplatin resistance in NSCLC patients. J
Cancer. 10:6374–6383. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wen W, Liang W, Wu J, Kowolik CM, Buettner
R, Scuto A, Hsieh MY, Hong H, Brown CE, Forman SJ, et al: Targeting
JAK1/STAT3 signaling suppresses tumor progression and metastasis in
a peritoneal model of human ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer Ther.
13:3037–3048. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yan CM, Zhao YL, Cai HY, Miao GY and Ma W:
Blockage of PTPRJ promotes cell growth and resistance to 5-FU
through activation of JAK1/STAT3 in the cervical carcinoma cell
line C33A. Oncol Rep. 33:1737–1744. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xia HB, Wang HJ, Song SS, Zhang JG, He XL,
Hu ZM, Zhang CW, Huang DS and Mou XZ: Decreased DC-SIGNR expression
in hepatocellular carcinoma predicts poor patient prognosis. Oncol
Lett. 19:69–76. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Z, Chen K, Yan L, Yang Z, Zhu Z,
Chen C, Zeng J, Wei W, Qi X, Ren S and Zuo Y: Low expression of
dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule-grabbing
nonintegrin-related protein in non-Hodgkin lymphoma and significant
correlations with lactic acid dehydrogenase and β2-microglobulin.
Biochem Cell Biol. 91:214–220. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dulak AM, Schumacher SE, van Lieshout J,
Imamura Y, Fox C, Shim B, Ramos AH, Saksena G, Baca SC, Baselga J,
et al: Gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas of the esophagus, stomach,
and colon exhibit distinct patterns of genome instability and
oncogenesis. Cancer Res. 72:4383–4393. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cao W, Liu Y, Zhang R, Zhang B, Wang T,
Zhu X, Mei L, Chen H, Zhang H, Ming P and Huang L:
Homoharringtonine induces apoptosis and inhibits STAT3 via
IL-6/JAK1/STAT3 signal pathway in Gefitinib-resistant lung cancer
cells. Sci Rep. 5:84772015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tactacan CM, Phua YW, Liu L, Zhang L,
Humphrey ES, Cowley M, Pinese M, Biankin AV and Daly RJ: The
pseudokinase SgK223 promotes invasion of pancreatic ductal
epithelial cells through JAK1/Stat3 signaling. Mol Cancer.
14:1392015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
van der Zee M, Sacchetti A, Cansoy M,
Joosten R, Teeuwssen M, Heijmans-Antonissen C, Ewing-Graham PC,
Burger CW, Blok LJ and Fodde R: IL6/JAK1/STAT3 signaling blockade
in endometrial cancer affects the ALDHhi/CD126+ Stem-like component
and reduces tumor burden. Cancer Res. 75:3608–3622. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|