|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:3347–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Eisenhauer EA: Real-world evidence in the
treatment of ovarian cancer. Ann Oncol. 28 (Suppl 8):VIII61–VVIII5.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
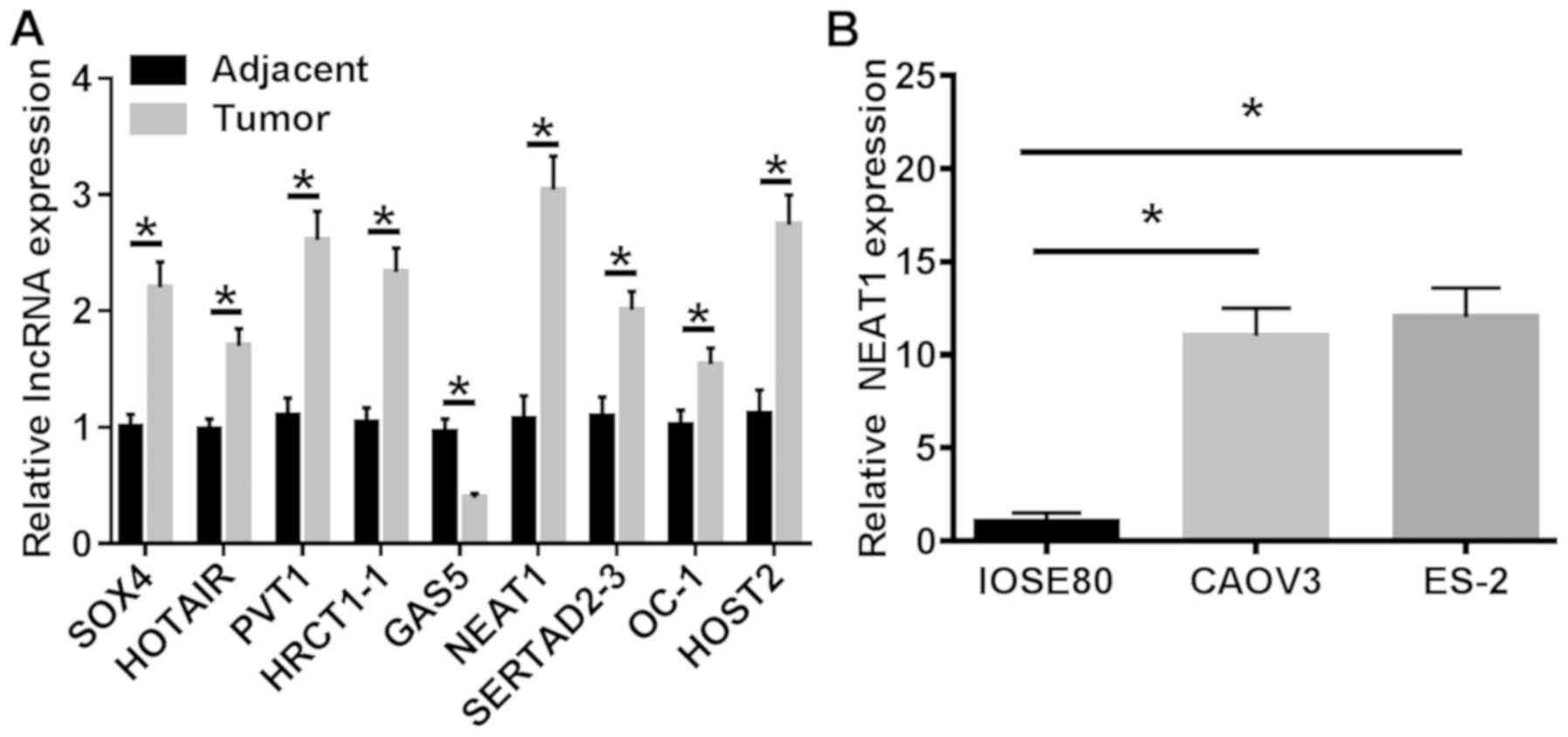
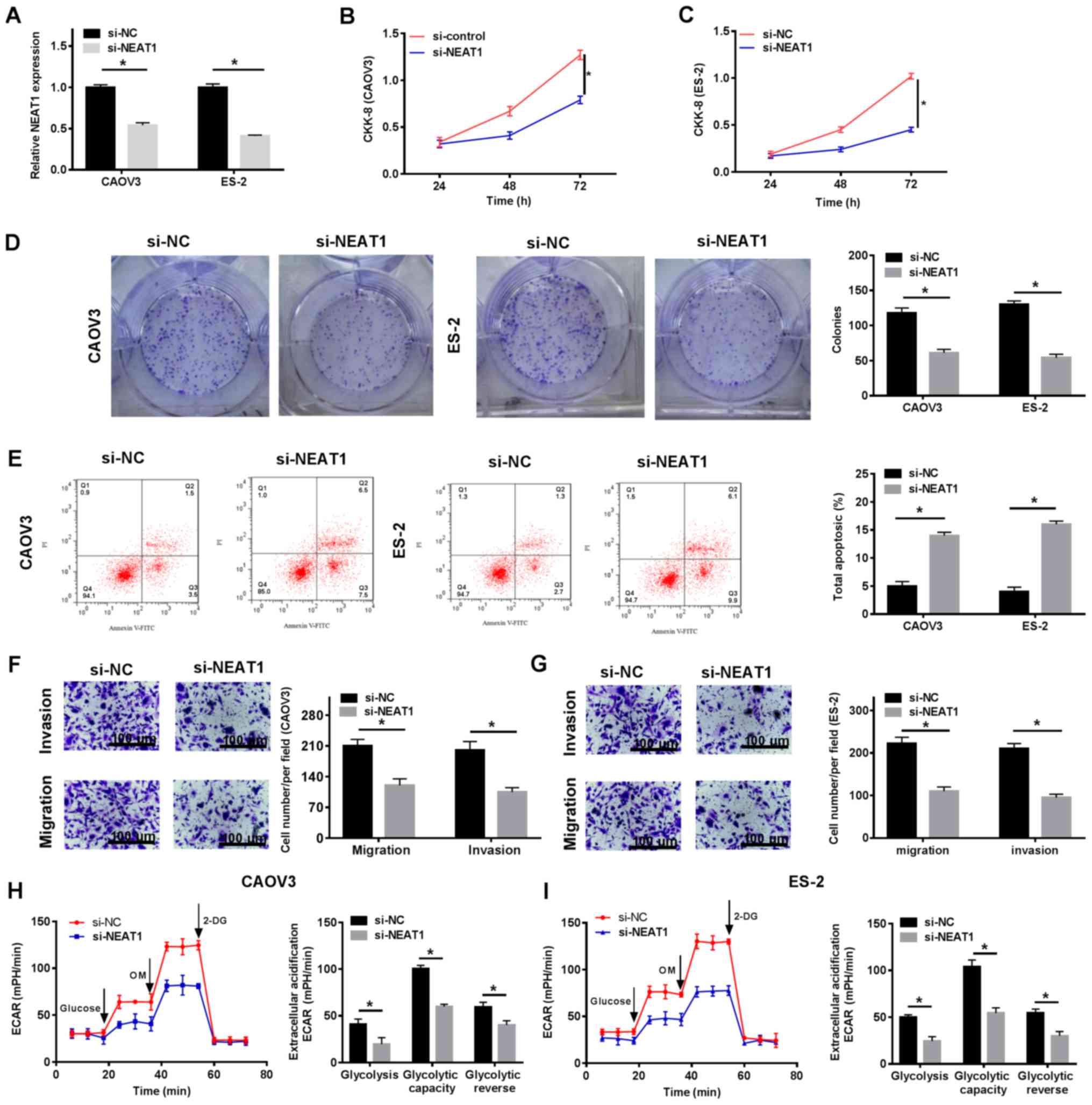
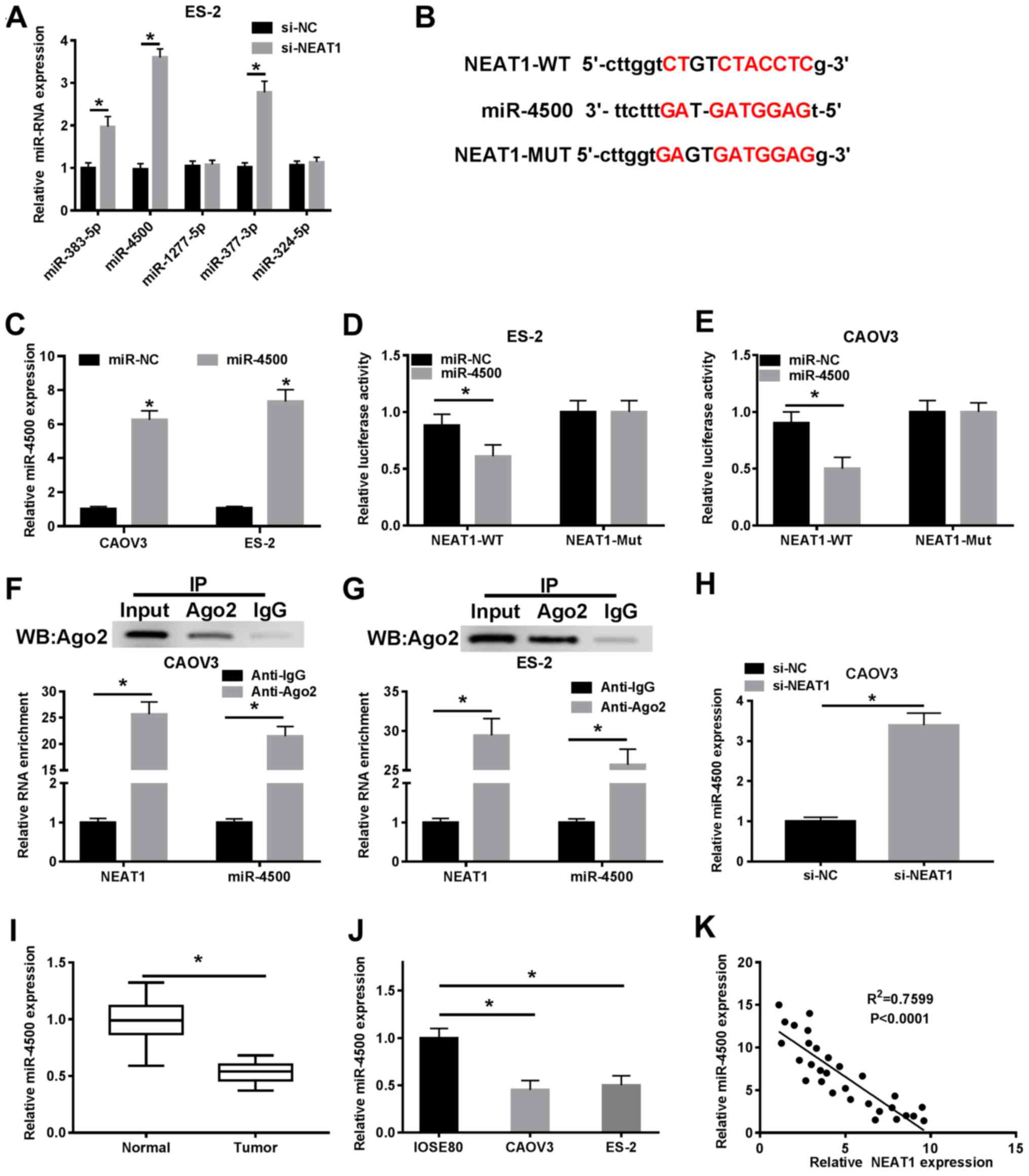
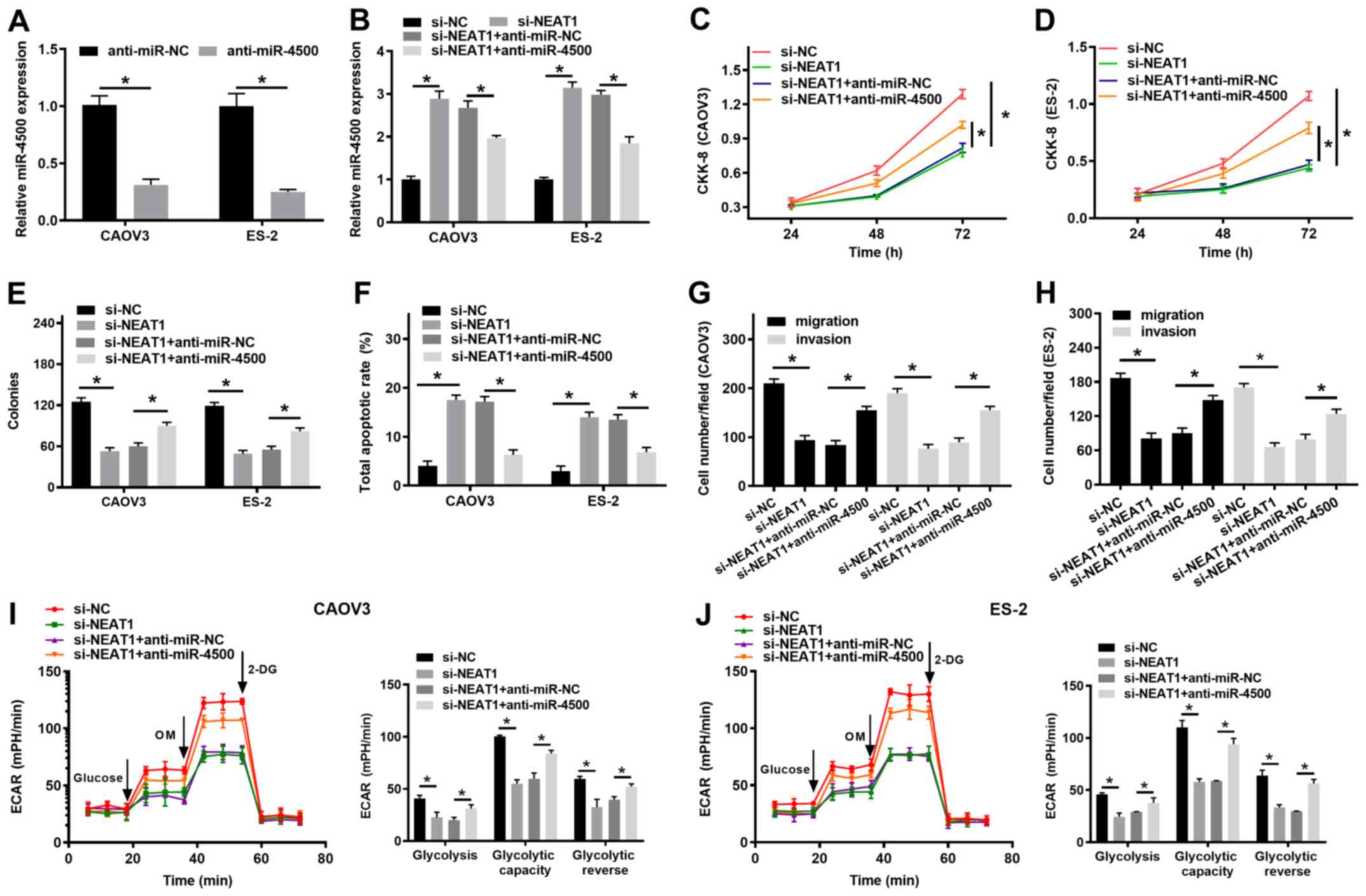
|
Rustin GJ, Van Der Burg MEL, Griffin CL,
Guthrie D, Lamont A, Jayson GC, Kristensen G, Mediola C, Coens C,
Qian W, et al: Early versus delayed treatment of relapsed ovarian
cancer (MRC OV05/EORTC 55955): A randomised trial. Lancet.
376:1155–1163. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jayson GC, Kohn EC, Kitchener HC and
Ledermann JA: Ovarian cancer. Lancet. 384:1376–1388. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kroeger Jr PT and Drapkin R: Pathogenesis
and heterogeneity of ovarian cancer. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol.
29:26–34. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mattick JS and Rinn JL: Discovery and
annotation of long noncoding RNAs. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 22:5–7.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sun M, Nie F, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Hou J, He
D, Xie M, Xu L, De W, Wang Z and Wang J: LncRNA HOXA11-AS promotes
proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer by scaffolding the
chromatin modification factors PRC2, LSD1, and DNMT1. Cancer Res.
76:6299–6310. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Peter S, Borkowska E, Drayton RM, Rakhit
CP, Noon A, Chen W and Catto JW: Identification of differentially
expressed long noncoding RNAs in bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
20:5311–5321. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang K, Liu CY, Zhou LY, Wang JX, Wang M,
Zhao B, Zhao WK, Xu SJ, Fan LH, Zhang XJ, et al: APF lncRNA
regulates autophagy and myocardial infarction by targeting
miR-188-3p. Nat Commun. 6:67792015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang G, Lu X and Yuan L: LncRNA: A link
between RNA and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1839:1097–1109. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schmitt AM and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell. 29:452–463. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liang H, Yu T, Han Y, Jiang H, Wang C, You
T, Zhao X, Shan H, Yang R, Yang L, et al: LncRNA PTAR promotes EMT
and invasion-metastasis in serous ovarian cancer by competitively
binding miR-101-3p to regulate ZEB1 expression. Mol Cancer.
17:1192018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zheng HT, Shi DB, Wang YW, Li XX, Xu Y,
Tripathi P, Gu WL, Cai GX and Cai SJ: High expression of lncRNA
MALAT1 suggests a biomarker of poor prognosis in colorectal cancer.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:3174–3181. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Qiu JJ, Lin YY, Ye LC, Ding JX, Feng WW,
Jin HY, Zhang Y, Li Q and Hua KQ: Overexpression of long non-coding
RNA HOTAIR predicts poor patient prognosis and promotes tumor
metastasis in epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol.
134:121–128. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen ZJ, Zhang Z, Xie BB and Zhang HY:
Clinical significance of up-regulated lncRNA NEAT1 in prognosis of
ovarian cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:3373–3377.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
An J, Lv W and Zhang Y: LncRNA NEAT1
contributes to paclitaxel resistance of ovarian cancer cells by
regulating ZEB1 expression via miR-194. Onco Targets Ther.
10:5377–5390. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chai Y, Liu J, Zhang Z and Liu L:
HuR-regulated lnc RNA NEAT 1 stability in tumorigenesis and
progression of ovarian cancer. Cancer Med. 5:1588–1598. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Garzon R, Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNAs
in cancer. Annu Rev Med. 60:167–179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zuberi M, Khan I, Mir R, Gandhi G, Ray PC
and Saxena A: Utility of serum miR-125b as a diagnostic and
prognostic indicator and its alliance with a panel of tumor
suppressor genes in epithelial ovarian cancer. PLoS One.
11:e01539022016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cai M, Chen Q, Shen J, Lv C and Cai L:
Epigenetic silenced miR-125a-5p could be self-activated through
targeting Suv39H1 in gastric cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 22:4721–4731.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu J, Miao J, Ding Y, Zhang Y, Huang X,
Zhou X and Tang R: MiR-4458 inhibits breast cancer cell growth,
migration, and invasiveness by targeting CPSF4. Biochem Cell Biol.
97:722–730. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jima DD, Zhang J, Jacobs C, Richards KL,
Dunphy CH, Choi WW, Au WY, Srivastava G, Czader MB, Rizzieri DA, et
al: Deep sequencing of the small RNA transcriptome of normal and
malignant human B cells identifies hundreds of novel microRNAs.
Blood. 116:e118–e127. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Griffiths-Jones S, Grocock RJ, Van Dongen
S, Bateman A and Enright AJ: miRBase: microRNA sequences, targets
and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res. 34:D140–D144. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang L, Qian J, Qiang Y, Huang H, Wang C,
Li D and Xu B: Down-regulation of miR-4500 promoted non-small cell
lung cancer growth. Cell Physiol Biochem. 34:1166–1174. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yu FY, Tu Y, Deng Y, Guo C, Ning J, Zhu Y,
Lv X and Ye H: MiR-4500 is epigenetically downregulated in
colorectal cancer and functions as a novel tumor suppressor by
regulating HMGA2. Cancer Biol Ther. 17:1149–1157. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mitra P, Vaughan PS, Stein JL, Stein GS
and van Wijnen AJ: Purification and functional analysis of a novel
leucine-zipper/nucleotide-fold protein, BZAP45, stimulating cell
cycle regulated histone H4 gene transcription. Biochemistry.
40:10693–10699. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li S, Chai Z, Li Y, Liu D, Bai Z, Li Y and
Situ Z: BZW1, a novel proliferation regulator that promotes growth
of salivary muocepodermoid carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 284:86–94. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kurman RJ, Carcangiu ML, Herrington CS and
Young RH: WHO classification of tumours of female reproductive
organs, fourth edition. Lyon: IACR; 2014
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sun M, Liu X, Lu K, Nie F, Xia R, Kong R,
Yang J, Xu T, Liu Y, Zou Y, et al: EZH2-mediated epigenetic
suppression of long noncoding RNA SPRY4-IT1 promotes NSCLC cell
proliferation and metastasis by affecting the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cell Death Dis. 5:e12982014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mercer TR, Dinger ME and Mattick JS: Long
non-coding RNAs: Insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet.
10:155–159. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mourtada-Maarabouni M, Pickard M, Hedge V,
Farzaneh F and Williams G: GAS5, a non-protein-coding RNA, controls
apoptosis and is downregulated in breast cancer. Oncogene.
28:195–208. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sun M, Jin FY, Xia R, Kong R, Li JH, Xu
TP, Liu YW, Zhang EB, Liu XH and De W: Decreased expression of long
noncoding RNA GAS5 indicates a poor prognosis and promotes cell
proliferation in gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 14:3192014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pickard MR and Williams GT: Regulation of
apoptosis by long non-coding RNA GAS5 in breast cancer cells:
Implications for chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
145:359–370. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hirose T, Virnicchi G, Tanigawa A,
Naganuma T, Li R, Kimura H, Yokoi T, Nakagawa S, Bénard M, Fox AH
and Pierron G: NEAT1 long noncoding RNA regulates transcription via
protein sequestration within subnuclear bodies. Mol Biol Cell.
25:169–183. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Choudhry H, Albukhari A, Morotti M, Haider
S, Moralli D, Smythies J, Schödel J, Green CM, Camps C, Buffa F, et
al: Tumor hypoxia induces nuclear paraspeckle formation through
HIF-2α dependent transcriptional activation of NEAT1 leading to
cancer cell survival. Oncogene. 34:4482–4490. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chakravarty D, Sboner A, Nair SS,
Giannopoulou E, Li R, Hennig S, Mosquera JM, Pauwels J, Park K,
Kossai M, et al: The oestrogen receptor alpha-regulated lncRNA
NEAT1 is a critical modulator of prostate cancer. Nat Commun.
5:53832014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ding N, Wu H, Tao T and Peng E: NEAT1
regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis of ovarian cancer by
miR-34a-5p/BCL2. Onco Targets Ther. 10:4905–4915. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Paraskevopoulou MD and Hatzigeorgiou AG:
Analyzing miRNA-lncRNA interactions. Methods Mol Biol.
1402:271–286. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jalali S, Bhartiya D, Lalwani MK,
Sivasubbu S and Scaria V: Systematic transcriptome wide analysis of
lncRNA-miRNA interactions. PLoS One. 8:e538232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li JH, Zhang SQ, Qiu XG, Zhang SJ, Zheng
SH and Zhang DH: Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes malignant
progression of thyroid carcinoma by regulating miRNA-214. Int J
Oncol. 50:708–716. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu F, Zhao H, Gong L, Yao L, Li Y and
Zhang W: MicroRNA-129-3p functions as a tumor suppressor in serous
ovarian cancer by targeting BZW1. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
11:5901–5908. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|