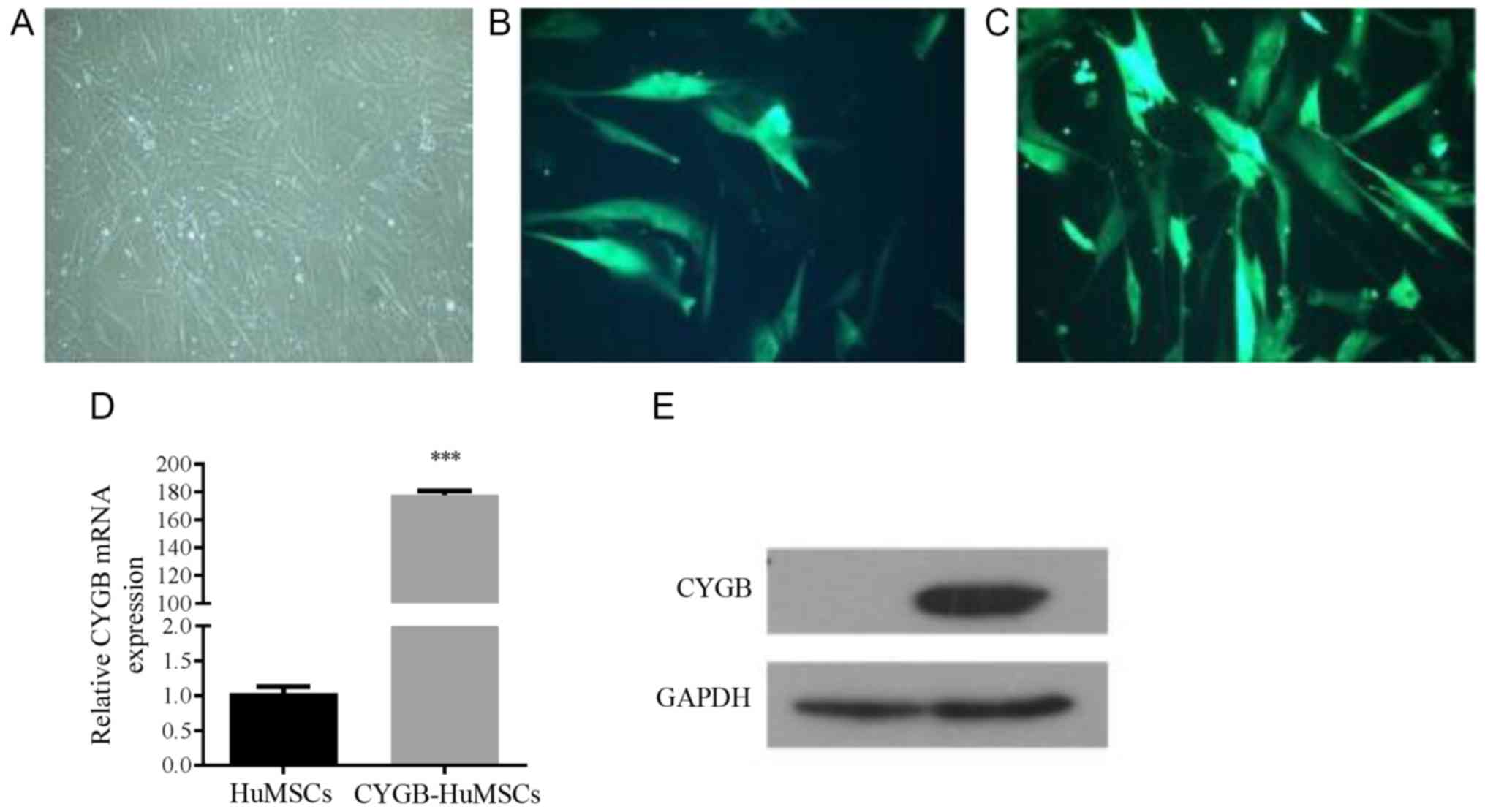
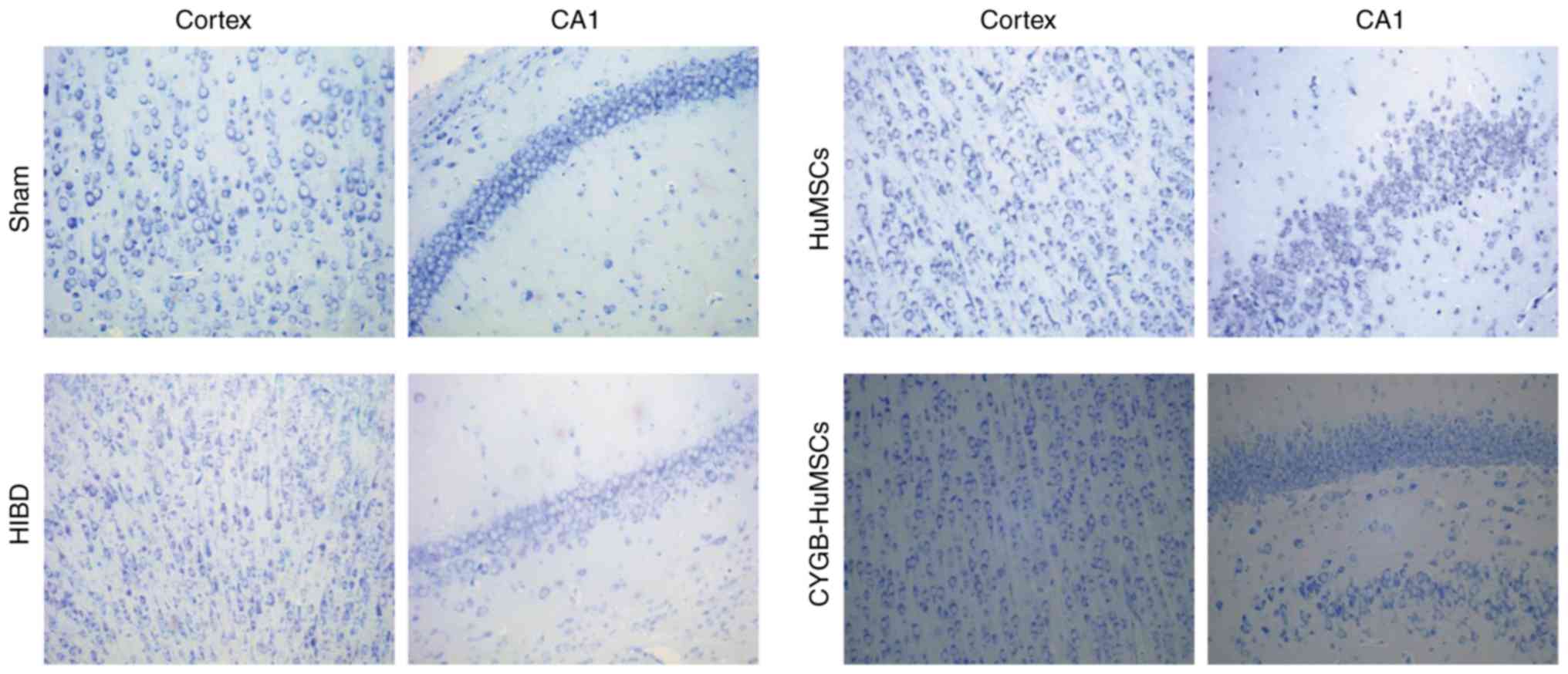
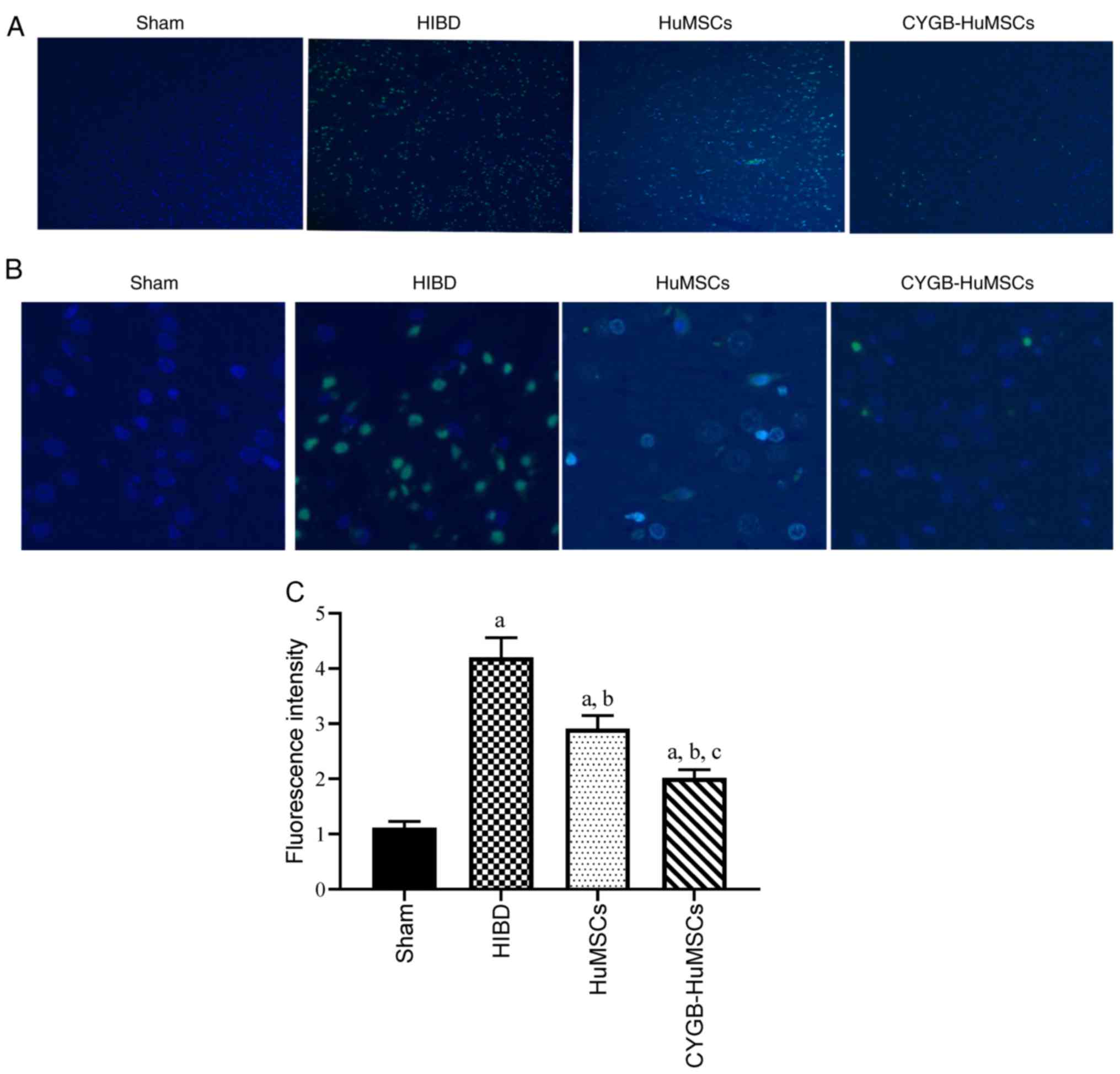
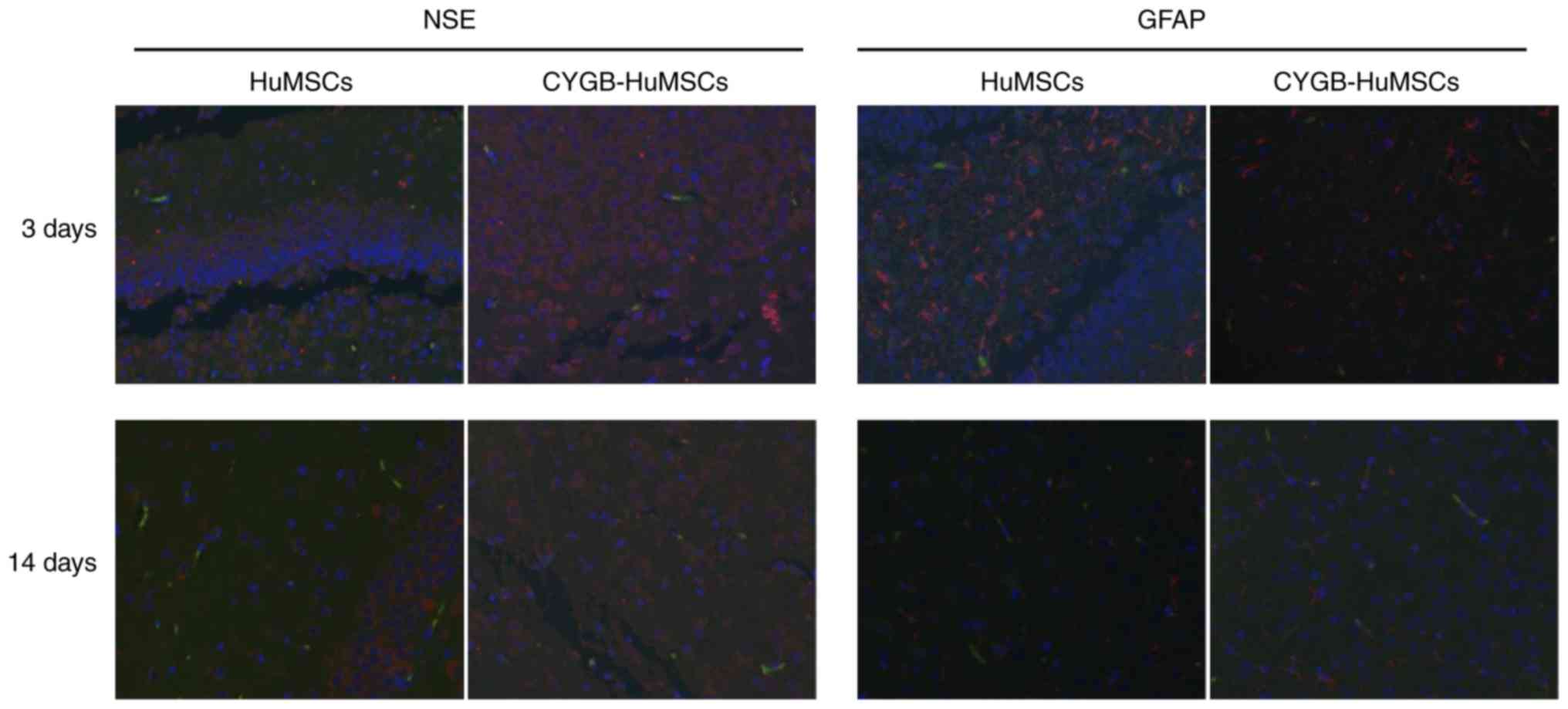
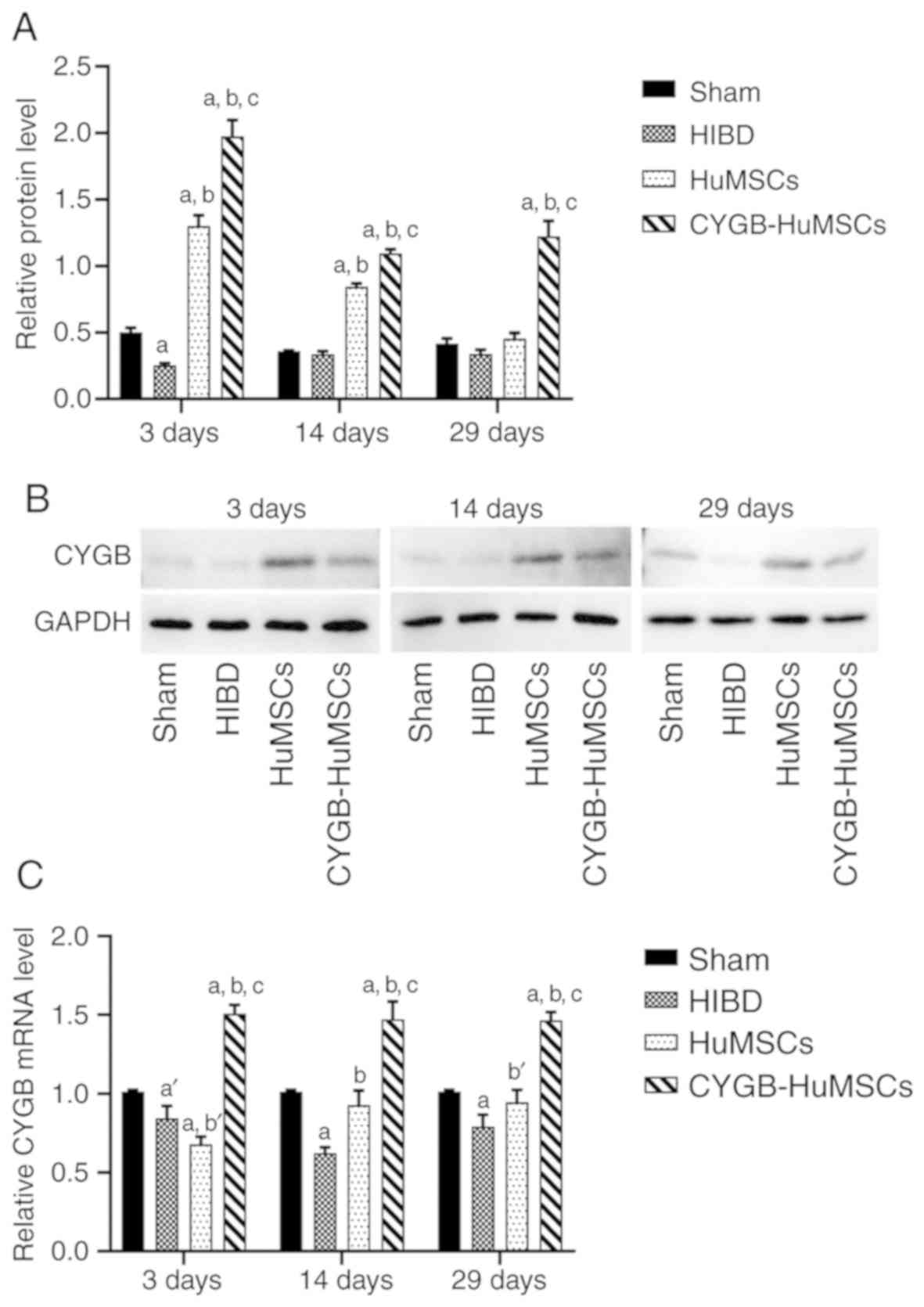
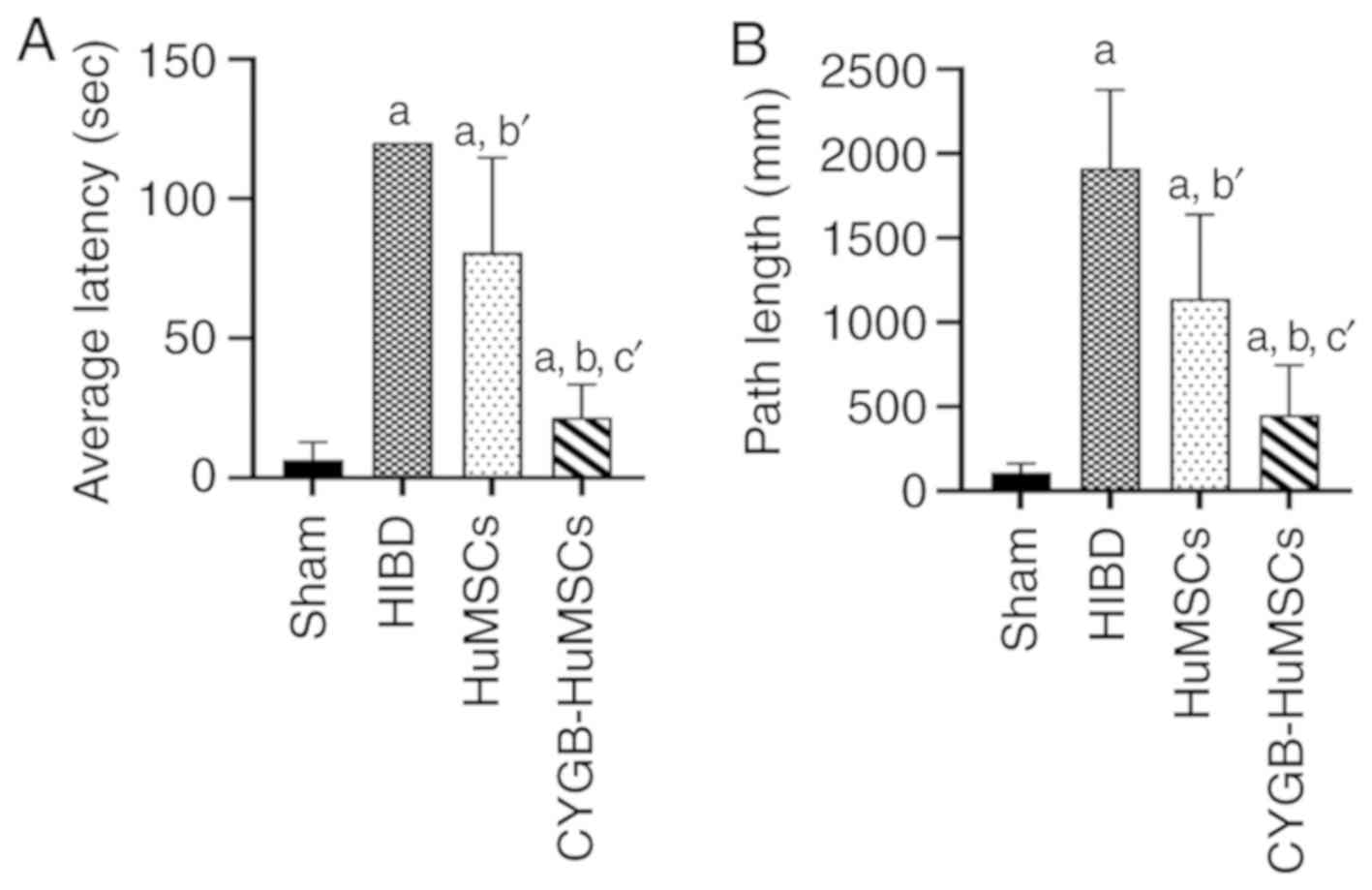
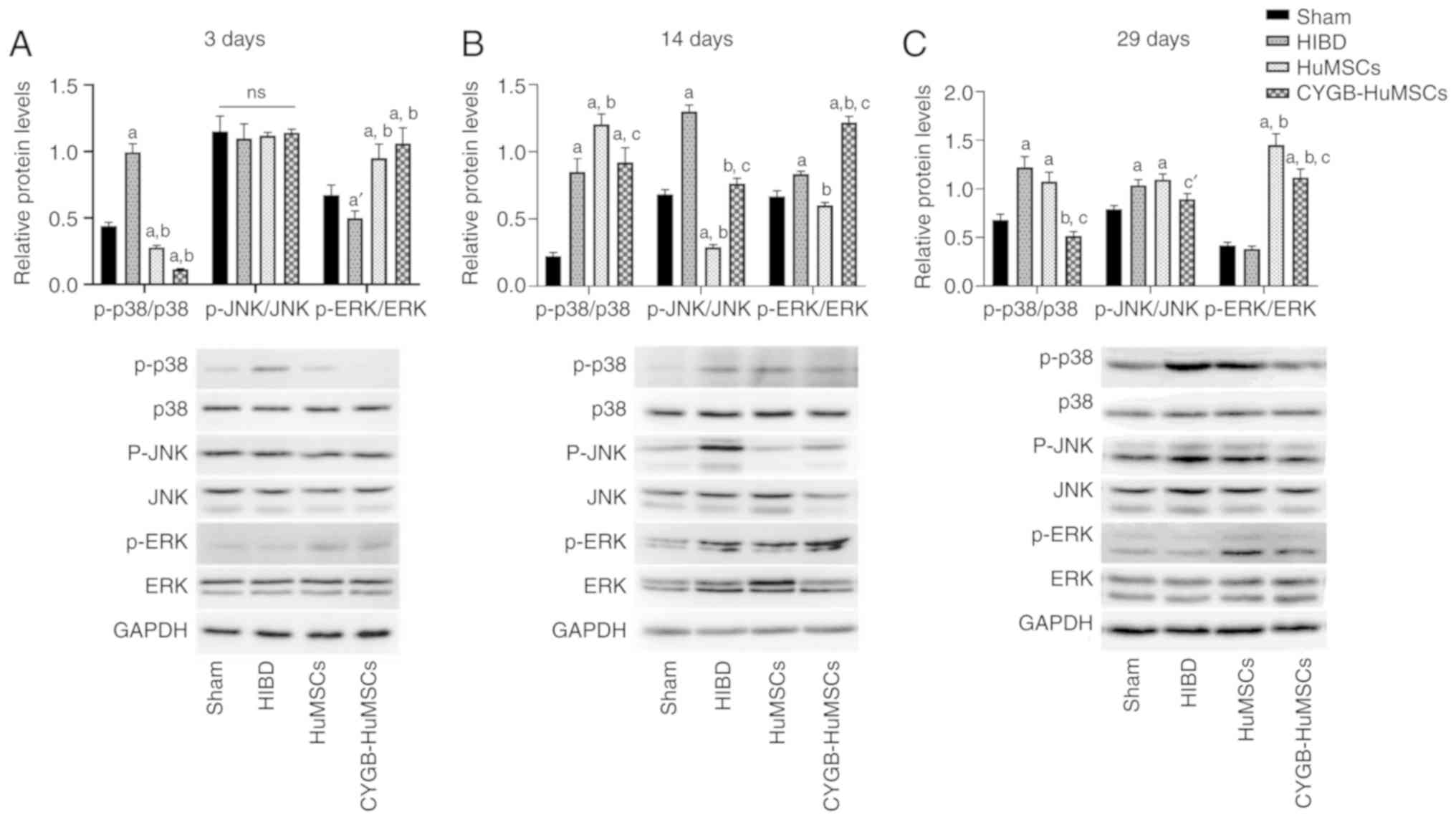
|
1
|
Novak CM, Ozen M and Burd I: Perinatal
brain injury: Mechanisms, prevention, and outcomes. Clin Perinatol.
45:3493–375. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
du Plessis AJ and Volpe JJ: Perinatal
brain injury in the preterm and term newborn. Curr Opin Neurol.
15:151–157. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Triulzi F, Parazzini C and Righini A:
Patterns of damage in the mature neonatal brain. Pediatr Radiol.
36:608–620. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gale C, Statnikov Y, Jawad S, Uthaya SN
and Modi N; Brain Injuries expert working group, : Neonatal brain
injuries in England: Population-based incidence derived from
routinely recorded clinical data held in the National Neonatal
Research Database. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 103:301–306.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bass JL, Corwin M, Gozal D, Moore C,
Nishida H, Parker S, Schonwald A, Wilker RE, Stehle S and Kinane
TB: The effect of chronic or intermittent hypoxia on cognition in
childhood: A review of the evidence. Pediatrics. 114:805–816. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yildiz EP, Ekici B and Tatli B: Neonatal
hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy: An update on disease pathogenesis
and treatment. Expert Rev Neurother. 17:449–459. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chiang MC, Jong YJ and Lin CH: Therapeutic
hypothermia for neonates with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy.
Pediatr Neonatol. 58:475–483. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Srinivasakumar P, Zempel J, Wallendorf M,
Lawrence R, Inder T and Mathur A: Therapeutic hypothermia in
neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy: Electrographic seizures
and magnetic resonance imaging evidence of injury. J Pediatr.
163:465–470. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ma H, Sinha B, Pandya RS, Lin N, Popp AJ,
Li J, Yao J and Wang X: Therapeutic hypothermia as a
neuroprotective strategy in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury
and traumatic brain injury. Curr Mol Med. 12:1282–1296. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pesce A, Bolognesi M, Bocedi A, Ascenzi P,
Dewilde S, Moens L, Hankeln T and Burmester T: Neuroglobin and
cytoglobin. Fresh blood for the vertebrate globin family. EMBO Rep.
3:1146–1151. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gell DA: Structure and function of
haemoglobins. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 70:13–42. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Burmester T and Hankeln T: Function and
evolution of vertebrate globins. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 211:501–514.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Trent JT III and Hargrove MS: A
ubiquitously expressed human hexacoordinate hemoglobin. J Biol
Chem. 277:19538–19545. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Stagner JI, Parthasarathy SN, Wyler K and
Parthasarathy RN: Protection from ischemic cell death by the
induction of cytoglobin. Transplant Proc. 37:3452–3453. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hankeln T, Ebner B, Fuchs C, Gerlach F,
Haberkamp M, Laufs TL, Roesner A, Schmidt M, Weich B, Wystub S, et
al: Neuroglobin and cytoglobin in search of their role in the
vertebrate globin family. J Inorg Biochem. 99:110–119. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Avivi A, Gerlach F, Joel A, Reuss S,
Burmester T, Nevo E and Hankeln T: Neuroglobin, cytoglobin, and
myoglobin contribute to hypoxia adaptation of the subterranean mole
rat Spalax. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:21570–21575. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Singh S, Manda SM, Sikder D, Birrer MJ,
Rothermel BA, Garry DJ and Mammen PP: Calcineurin activates
cytoglobin transcription in hypoxic myocytes. J Biol Chem.
284:10409–10421. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tian SF, Yang HH, Xiao DP, Huang YJ, He
GY, Ma HR, Xia F and Shi XC: Mechanisms of neuroprotection from
hypoxia-ischemia (HI) brain injury by up-regulation of cytoglobin
(CYGB) in a neonatal rat model. J Biol Chem. 288:15988–16003. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li Y and Chopp M: Marrow stromal cell
transplantation in stroke and traumatic brain injury. Neurosci
Lett. 456:120–123. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao L, Johnson T and Liu D: Therapeutic
angiogenesis of adipose-derived stem cells for ischemic diseases.
Stem Cell Res Ther. 8:1252017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Park WS, Sung SI, Ahn SY, Yoo HS, Sung DK,
Im GH, Choi SJ and Chang YS: Hypothermia augments neuroprotective
activity of mesenchymal stem cells for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic
encephalopathy. PLoS One. 10:e01208932015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gonzales-Portillo GS, Reyes S, Aguirre D,
Pabon MM and Borlongan CV: Stem cell therapy for neonatal
hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Front Neurol. 5:1472014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
van Velthoven CT, Kavelaars A and Heijnen
CJ: Mesenchymal stem cells as a treatment for neonatal ischemic
brain damage. Pediatr Res. 71:474–481. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang X, Zhang Q, Li W, Nie D, Chen W, Xu
C, Yi X, Shi J, Tian M, Qin J, et al: Therapeutic effect of human
umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on neonatal rat
hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. J Neurosci Res. 92:35–45. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhou X, Gu J, Gu Y, He M, Bi Y, Chen J and
Li T: Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve
learning and memory function in hypoxic-ischemic brain-damaged rats
via an IL-8-mediated secretion mechanism rather than
differentiation pattern induction. Cell Physiol Biochem.
35:2383–2401. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim YS, Hwang KA, Go RE, Kim CW and Choi
KC: Gene therapy strategies using engineered stem cells for
treating gynecologic and breast cancer patients (Review). Oncol
Rep. 33:2107–2112. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
High KA and Roncarolo MG: Gene therapy. N
Engl J Med. 381:455–464. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Aiuti A, Slavin S, Aker M, Ficara F, Deola
S, Mortellaro A, Morecki S, Andolfi G, Tabucchi A, Carlucci F, et
al: Correction of ADA-SCID by stem cell gene therapy combined with
nonmyeloablative conditioning. Science. 296:2410–2413. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang H, Qiu X, Ni P, Qiu X, Lin X, Wu W,
Xie L, Lin L, Min J, Lai X, et al: Immunological characteristics of
human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells and the therapeutic
effects of their transplantion on hyperglycemia in diabetic rats.
Int J Mol Med. 33:263–270. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kilkenny C, Browne WJ, Cuthill IC, Emerson
M and Altman DG: Improving bioscience research reporting: The
ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol.
8:e10004122010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rice JE III, Vannucci RC and Brierley JB:
The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the
rat. Ann Neurol. 9:131–141. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Donega V, Nijboer CH, van Tilborg G,
Dijkhuizen RM, Kavelaars A and Heijnen CJ: Intranasally
administered mesenchymal stem cells promote a regenerative niche
for repair of neonatal ischemic brain injury. Exp Neurol.
261:53–64. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hoogewijs D, Vogler M, Zwenger E, Krull S
and Zieseniss A: Oxygen-dependent regulation of aquaporin-3
expression. Hypoxia (Auckl). 4:91–97. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Douglas-Escobar M and Weiss MD:
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: A review for the clinician. JAMA
Pediatr. 169:397–403. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Burmester T, Ebner B, Weich B and Hankeln
T: Cytoglobin: A novel globin type ubiquitously expressed in
vertebrate tissues. Mol Biol Evol. 19:416–421. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ascenzi P, Gustincich S and Marino M:
Mammalian nerve globins in search of functions. IUBMB life.
66:268–276. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Amdahl MB, DeMartino AW, Tejero J and
Gladwin MT: Cytoglobin at the crossroads of vascular remodeling.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 37:1803–1805. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Vinogradov SN and Moens L: Diversity of
globin function: Enzymatic, transport, storage, and sensing. J Biol
Chem. 283:8773–8777. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tejero J and Gladwin MT: The globin
superfamily: Functions in nitric oxide formation and decay. Biol
Chem. 395:631–639. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hodges NJ, Innocent N, Dhanda S and Graham
M: Cellular protection from oxidative DNA damage by over-expression
of the novel globin cytoglobin in vitro. Mutagenesis. 23:293–298.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
De Beuf A, Hou XH, D'Haese PC and Verhulst
A: Epoetin delta reduces oxidative stress in primary human renal
tubular cells. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010:3957852010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lv W, Booz GW, Fan F, Wang Y and Roman RJ:
Oxidative stress and renal fibrosis: Recent insights for the
development of novel therapeutic strategies. Front Physiol.
9:1052018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lilly B, Dammeyer K, Marosis S,
McCallinhart PE, Trask AJ, Lowe M and Sawant D: Endothelial
cell-induced cytoglobin expression in vascular smooth muscle cells
contributes to modulation of nitric oxide. Vascul Pharmacol.
110:7–15. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hong SQ, Zhang HT, You J, Zhang MY, Cai
YQ, Jiang XD and Xu RX: Comparison of transdifferentiated and
untransdifferentiated human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells in
rats after traumatic brain injury. Neurochem Res. 36:2391–2400.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lin YC, Ko TL, Shih YH, Lin MY, Fu TW,
Hsiao HS, Hsu JY and Fu YS: Human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells
promote recovery after ischemic stroke. Stroke. 42:2045–2053. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
van Velthoven CT, Kavelaars A, van Bel F
and Heijnen CJ: Nasal administration of stem cells: A promising
novel route to treat neonatal ischemic brain damage. Pediatr Res.
68:419–422. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Cunningham CJ, Redondo-Castro E and Allan
SM: The therapeutic potential of the mesenchymal stem cell
secretome in ischaemic stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
38:1276–1292. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li Y, Cheng Q, Hu G, Deng T, Wang Q, Zhou
J and Su X: Extracellular vesicles in mesenchymal stromal cells: A
novel therapeutic strategy for stroke. Exp Ther Med. 15:4067–4079.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Gu Y, He M, Zhou X, Liu J, Hou N, Bin T,
Zhang Y, Li T and Chen J: Endogenous IL-6 of mesenchymal stem cell
improves behavioral outcome of hypoxic-ischemic brain damage
neonatal rats by supressing apoptosis in astrocyte. Sci Rep.
6:185872016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Cuadrado A and Nebreda AR: Mechanisms and
functions of p38 MAPK signalling. Biochem J. 429:403–417. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Sanchez A, Tripathy D, Yin X, Desobry K,
Martinez J, Riley J, Gay D, Luo J and Grammas P: p38 MAPK: A
mediator of hypoxia-induced cerebrovascular inflammation. J
Alzheimers Dis. 32:587–597. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cakmak H, Seval-Celik Y, Arlier S,
Guzeloglu-Kayisli O, Schatz F, Arici A and Kayisli UA: p38
Mitogen-activated protein kinase is involved in the pathogenesis of
endometriosis by modulating inflammation, but not cell survival.
Reprod Sci. 25:587–597. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Amir M, Somakala K and Ali S: p38 MAP
kinase inhibitors as anti inflammatory agents. Mini Rev Med Chem.
13:2082–2096. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Cheung WD and Hart GW: AMP-activated
protein kinase and p38 MAPK activate O-GlcNAcylation of neuronal
proteins during glucose deprivation. J Biol Chem. 283:13009–13020.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Park EC and Rongo C: The p38 MAP kinase
pathway modulates the hypoxia response and glutamate receptor
trafficking in aging neurons. Elife. 5:e120102016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Tormos AM, Taléns-Visconti R, Nebreda AR
and Sastre J: p38 MAPK: A dual role in hepatocyte proliferation
through reactive oxygen species. Free Radic Res. 47:905–916. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhang H, Tao L, Jiao X, Gao E, Lopez BL,
Christopher TA, Koch W and Ma XL: Nitrative thioredoxin
inactivation as a cause of enhanced myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
injury in the aging heart. Free Radic Biol Med. 43:39–47. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Xu ZJ, Shu S, Li ZJ, Liu YM, Zhang RY and
Zhang Y: Liuwei Dihuang pill treats diabetic nephropathy in rats by
inhibiting of TGF-β/SMADS, MAPK, and NF-kB and upregulating
expression of cytoglobin in renal tissues. Medicine (Baltimore).
96:e58792017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|