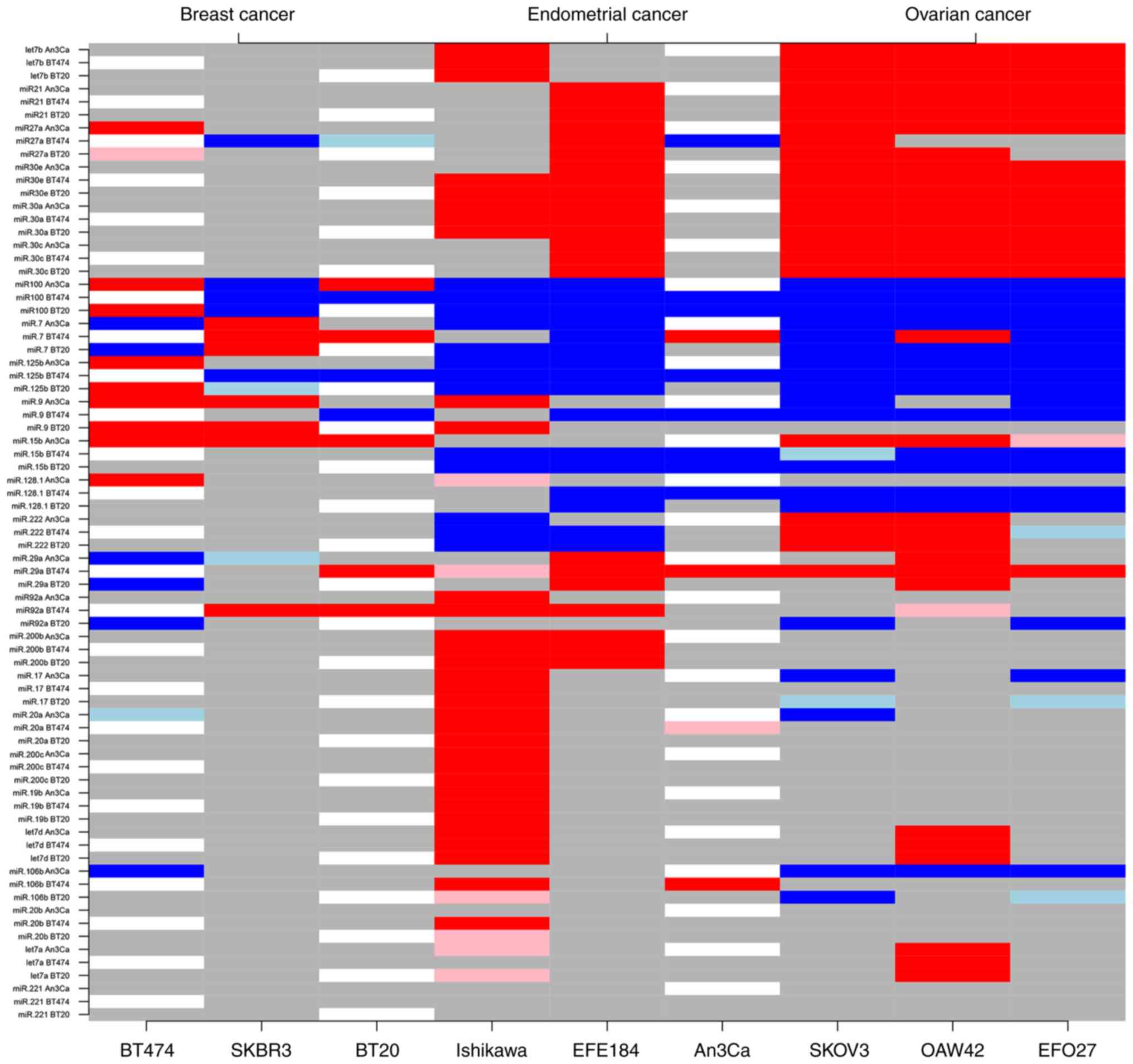
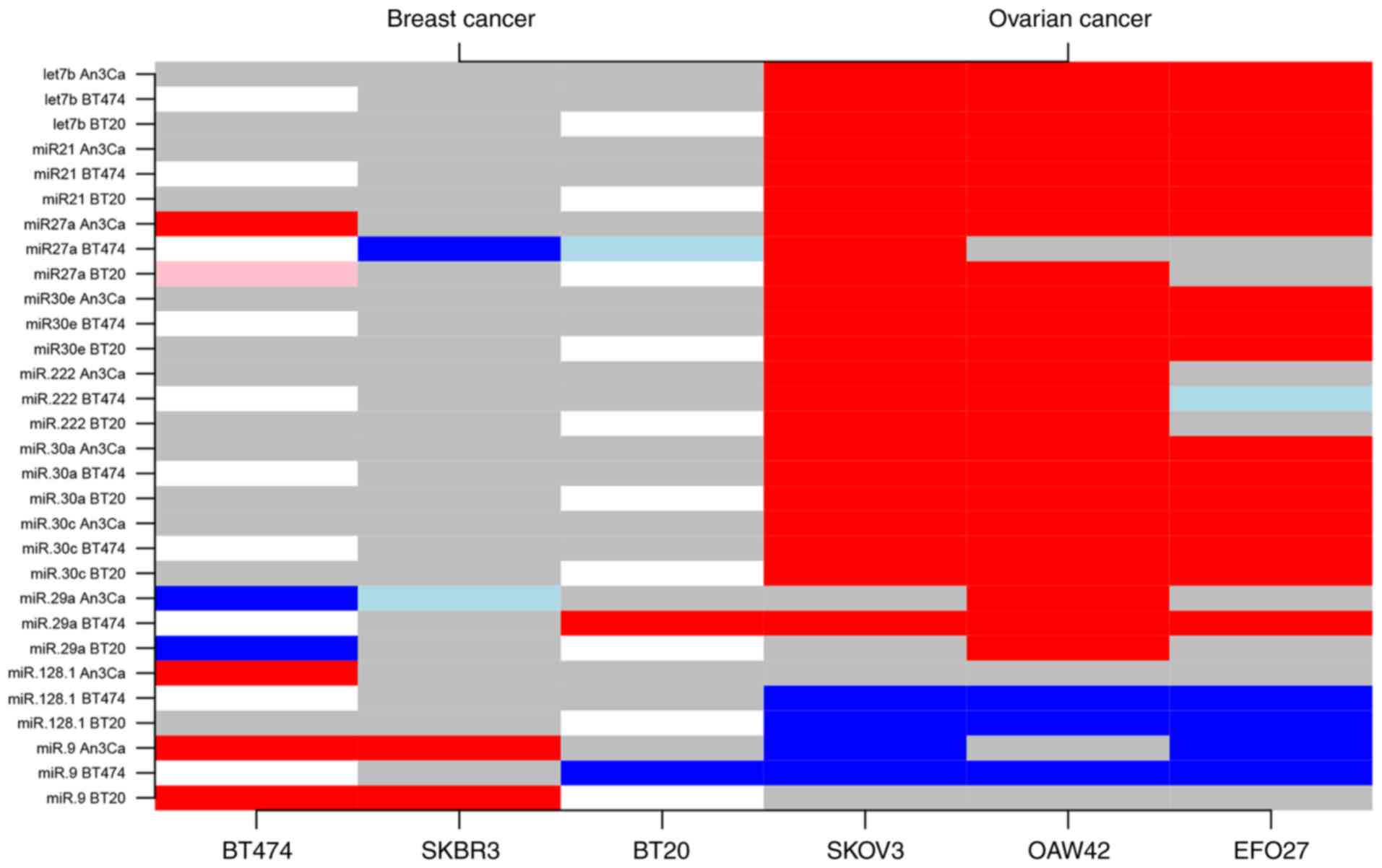
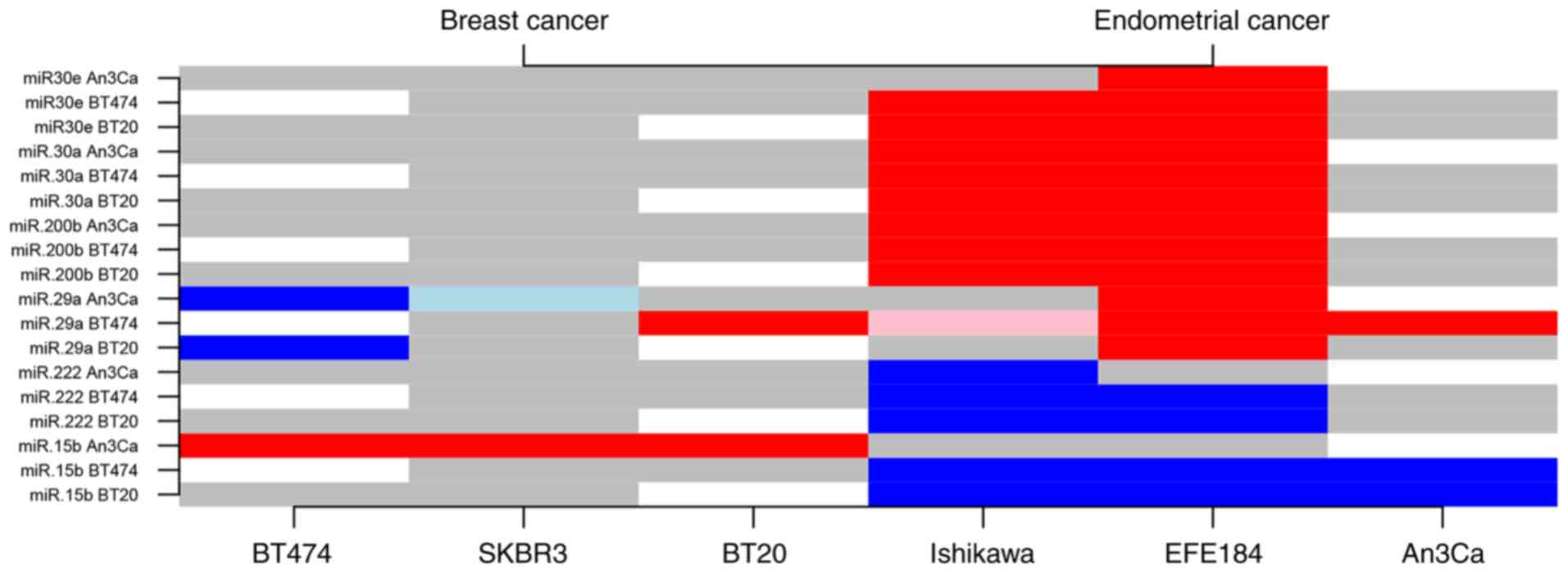
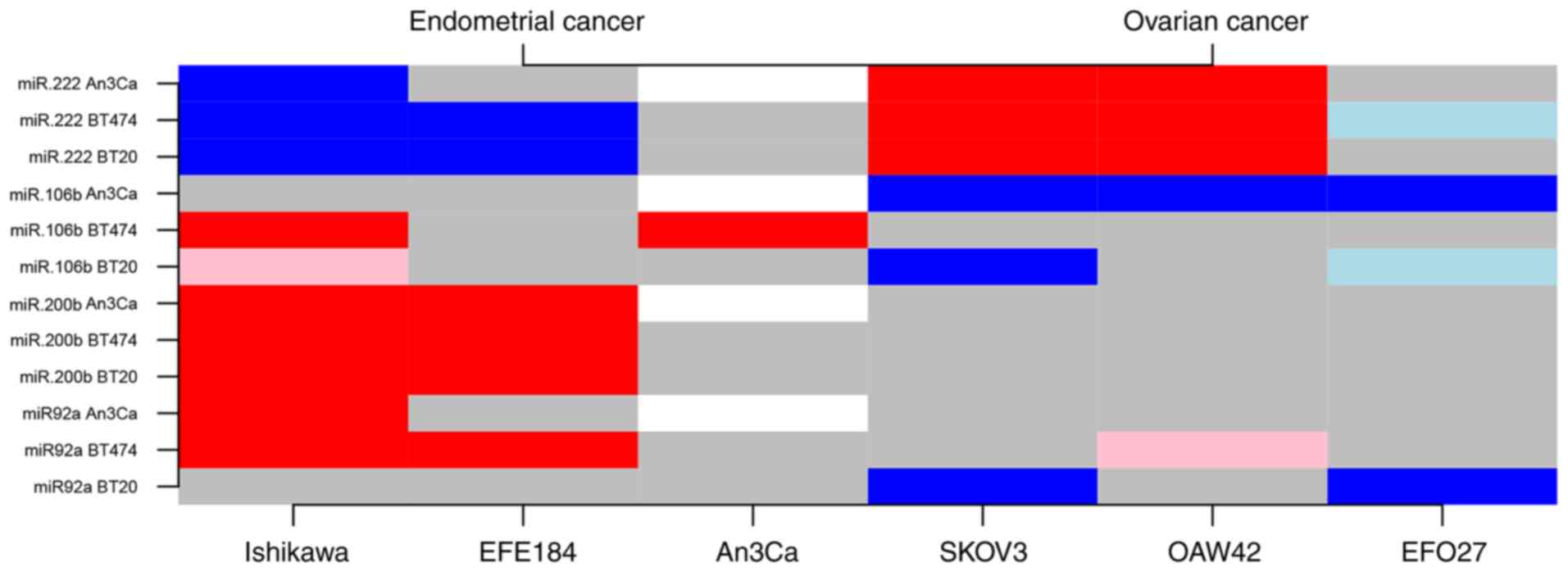
|
1
|
Heywang-Koebrunner S, Bock K, Heindel W,
Hecht G, Regitz-Jedermann L, Hacker A and Kaeaeb-Sanyal V:
Mammography Screening-as of 2013. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd.
73:1007–1016. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Clarke MA, Long BJ, Del Mar Morillo A,
Arbyn M, Bakkum-Gamez JN and Wentzensen N: Association of
endometrial cancer risk with postmenopausal bleeding in Women: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Intern Med.
178:1210–1222. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Steiner E, Eicher O, Sagemüller J, Schmidt
M, Pilch H, Tanner B, Hengstler JG, Hofmann M and Knapstein PG:
Multivariate independent prognostic factors in endometrial
carcinoma: A clinicopathologic study in 181 patients: 10 years
experience at the department of obstetrics and gynecology of the
Mainz University. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 13:197–203. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tejerizo-Garcia A, Jiménez-López JS,
Muñoz-González JL, Bartolomé-Sotillos S, Marqueta-Marqués L,
López-González G and Gómez JF: Overall survival and disease-free
survival in endometrial cancer: Prognostic factors in 276 patients.
Onco Targets Ther. 9:1305–1313. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Das PM and Bast RC Jr: Early detection of
ovarian cancer. Biomark Med. 2:291–303. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Miller D,
Brest A, Yu M, Ruhl J, Tatalovich Z, Mariotto A, Lewis DR, Chen HS,
Feuer EJ and Cronin KA: SEER Cancer Statistics Review. 1975-2017,
National Cancer Institute; Bethesda, MD, USA: https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2017/
|
|
7
|
Frangogiannis NG: Biomarkers: Hopes and
challenges in the path from discovery to clinical practice. Transl
Res. 159:197–204. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Makarova JA, Shkurnikov MU, Wicklein D,
Lange T, Samatov TR, Turchinovich AA and Tonevitsky AG:
Intracellular and extracellular microRNA: An update on localization
and biological role. Prog Histochem Cytochem. 51:33–49. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hayes J, Peruzzi PP and Lawler S:
MicroRNAs in cancer: Biomarkers, functions and therapy. Trends in
Molecular Medicine. 20:460–469. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Croce CM: Causes and consequences of
microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 10:704–714. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kanekura K, Nishi H, Isaka K and Kuroda M:
MicroRNA and gynecologic cancers. J Obstet Gynaecol Res.
42:612–617. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kurozumi S, Yamaguchi Y, Kurosumi M, Ohira
M, Matsumoto H and Horiguchi J: Recent trends in microRNA research
into breast cancer with particular focus on the associations
between microRNAs and intrinsic subtypes. J Hum Genet. 62:15–24.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nakamura K, Sawada K, Yoshimura A, Kinose
Y, Nakatsuka E and Kimura T: Clinical relevance of circulating
cell-free microRNAs in ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer. 15:482016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rapisuwon S, Vietsch EE and Wellstein A:
Circulating biomarkers to monitor cancer progression and treatment.
Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 14:211–222. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Torres A, Torres K, Pesci A, Ceccaroni M,
Paszkowski T, Cassandrini P, Zamboni G and Maciejewski R:
Diagnostic and prognostic significance of miRNA signatures in
tissues and plasma of endometrioid endometrial carcinoma patients.
Int J Cancer. 132:1633–1645. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Widodo, Djati MS and Rifa'i M: Role of
microRNAs in carcinogenesis that potential for biomarker of
endometrial cancer. Ann Med Surg (Lond. 7:9–13. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yanokura M, Banno K, Iida M, Irie H, Umene
K, Masuda K, Kobayashi Y, Tominaga E and Aoki D: MicroRNAS in
endometrial cancer: Recent advances and potential clinical
applications. Excli J. 14:190–198. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hirschfeld M, Rücker G, Weiß D, Berner K,
Ritter A, Jäger M and Erbes T: Urinary exosomal MicroRNAs as
potential non-invasive biomarkers in breast cancer detection. Mol
Diagn Ther. 24:215–232. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ritter A, Hirschfeld M, Berner K, Jaeger
M, Grundner-Culemann F, Schlosser P, Asberger J, Weiss D, Noethling
C, Mayer S and Erbes T: Discovery of potential serum and
urine-based microRNA as minimally-invasive biomarkers for breast
and gynecological cancer. Cancer Biomark. 27:225–242. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ritter A, Hirschfeld M, Berner K, Rücker
G, Jäger M, Weiss D, Medl M, Nöthling C, Gassner S, Asberger J and
Erbes T: Circulating noncoding RNA-biomarker potential in
neoadjuvant chemotherapy of triple negative breast cancer? Int J
Oncol. 56:47–68. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lou Y, Yang X, Wang F, Cui Z and Huang Y:
MicroRNA-21 promotes the cell proliferation, invasion and migration
abilities in ovarian epithelial carcinomas through inhibiting the
expression of PTEN protein. Int J Mol Med. 26:819–827. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qin X, Yan L, Zhao X, Li C and Fu Y:
MicroRNA-21 overexpression contributes to cell proliferation by
targeting PTEN in endometrioid endometrial cancer. Oncol Lett.
4:1290–1296. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Frankel LB, Christoffersen NR, Jacobsen A,
Lindow M, Krogh A and Lund AH: Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is
an important functional target of the microRNA miR-21 in breast
cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 283:1026–1033. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yan LX, Huang XF, Shao Q, Huang MY, Deng
L, Wu QL, Zeng YX and Shao JY: MicroRNA miR-21 overexpression in
human breast cancer is associated with advanced clinical stage,
lymph node metastasis and patient poor prognosis. RNA.
14:2348–2360. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Au Yeung CL, Co NN, Tsuruga T, Yeung TL,
Kwan SY, Leung CS, Li Y, Lu ES, Kwan K, Wong KK, et al: Exosomal
transfer of stroma-derived miR21 confers paclitaxel resistance in
ovarian cancer cells through targeting APAF1. Nat Commun.
7:11502016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Greene SB, Herschkowitz JI and Rosen JM:
Small players with big roles: microRNAs as targets to inhibit
breast cancer progression. Curr Drug Targets. 11:1059–1073. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Encarnacion J, Ortiz C, Vergne R, Vargas
W, Coppola D and Matta JL: High DRC Levels are associated with
Let-7b overexpression in women with breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
17:8652016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Chung YW, Bae HS, Song JY, Lee JK, Lee NW,
Kim T and Lee KW: Detection of microRNA as novel biomarkers of
epithelial ovarian cancer from the serum of ovarian cancer
patients. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 23:673–679. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tang Z, Ow GS, Thiery JP, Ivshina AV and
Kuznetsov VA: Meta-analysis of transcriptome reveals let-7b as an
unfavorable prognostic biomarker and predicts molecular and
clinical subclasses in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma. Int J
Cancer. 134:306–318. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yu F, Yao H, Zhu P, Zhang X, Pan Q, Gong
C, Huang Y, Hu X, Su F, Lieberman J and Song E: let-7 regulates
self renewal and tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells. Cell.
131:1109–1123. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cheng CW, Wang HW, Chang CW, Chu HW, Chen
CY, Yu JC, Chao JI, Liu HF, Ding SL and Shen CY: MicroRNA-30a
inhibits cell migration and invasion by downregulating vimentin
expression and is a potential prognostic marker in breast cancer.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 134:1081–1093. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rodriguez-Gonzalez FG, Sieuwerts AM, Smid
M, Look MP, Meijer-van Gelder ME, de Weerd V, Sleijfer S, Martens
JW and Foekens JA: MicroRNA-30c expression level is an independent
predictor of clinical benefit of endocrine therapy in advanced
estrogen receptor positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
127:43–51. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bockhorn J, Dalton R, Nwachukwu C, Huang
S, Prat A, Yee K, Chang YF, Huo D, Wen Y, Swanson KE, et al:
MicroRNA-30c inhibits human breast tumour chemotherapy resistance
by regulating TWF1 and IL-11. Nat Commun. 4:13932013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lee H, Park CS, Deftereos G, Morihara J,
Stern JE, Hawes SE, Swisher E, Kiviat NB and Feng Q: MicroRNA
expression in ovarian carcinoma and its correlation with
clinicopathological features. World J Surg Oncol. 10:1742012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cabarcas SM, Thomas S, Zhang X, Cherry JM,
Sebastian T, Yerramilli S, Lader E, Farrar WL and Hurt EM: The role
of upregulated miRNAs and the identification of novel mRNA targets
in prostatospheres. Genomics. 99:108–117. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang Y, Li L, Qu Z, Li R, Bi T, Jiang J
and Zhao H: The expression of miR-30a* and miR-30e* is associated
with a dualistic model for grading ovarian papillary serious
carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 44:1904–1914. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shang C, Lu YM and Meng LR: MicroRNA-125b
down-regulation mediates endometrial cancer invasion by targeting
ERBB2. Med Sci Moni. 18:BR149–BR155. 2012.
|
|
38
|
Li C, Gao Y, Zhang K, Chen J, Han S, Feng
B, Wang R and Chen L: Multiple Roles of MicroRNA-100 in human
cancer and its therapeutic potential. Cellular Physiology and
Biochemistry. 37:2143–2159. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A,
Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, Magri E, Pedriali M, Fabbri M, Campiglio M,
et al: MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast
cancer. Cancer research. 65:7065–7070. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mattie MD, Benz CC, Bowers J, Sensinger K,
Wong L, Scott GK, Fedele V, Ginzinger D, Getts R and Haqq C:
Optimized high-throughput microRNA expression profiling provides
novel biomarker assessment of clinical prostate and breast cancer
biopsies. Mol Cancer. 5:242006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Guan Y, Yao H, Zheng Z, Qiu G and Sun K:
miR-125b targets BCL3 and suppresses ovarian cancer proliferation.
Int J Cancer. 128:2274–2283. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pfaffl MW, Tichopad A, Prgomet C and
Neuvians TP: Determination of stable housekeeping genes,
differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity:
BestKeeper-Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations.
Biotechnol Lett. 26:509–515. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang H, Peng R, Wang J, Qin Z and Xue L:
Circulating microRNAs as potential cancer biomarkers: The advantage
and disadvantage. Clin Epigenetics. 10:592018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sun H, Shao Y, Huang J, Sun S, Liu Y, Zhou
P and Yang H: Prognostic value of microRNA-9 in cancers: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 7:67020–67032.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhong S, Li W, Chen Z, Xu J and Zhao J:
miR-222 and miR-29a contribute to the drug-resistance of breast
cancer cells. Gene. 531:8–14. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Dahiya N and Morin PJ: MicroRNAs in
ovarian carcinomas. Endocr Relat Cancer. 17:F77–F89. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Dahiya N, Sherman-Baust CA, Wang TL,
Davidson B, Shih IeM, Zhang Y, Wood W III, Becker KG and Morin PJ:
MicroRNA expression and identification of putative miRNA targets in
ovarian cancer. PLoS One. 3:e24362008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhao C, Wang G, Zhu Y, Li X, Yan F, Zhang
C, Huang X and Zhang Y: Aberrant regulation of miR-15b in human
malignant tumors and its effects on the hallmarks of cancer. Tumour
Biol. 37:177–183. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Madhavan D, Peng C, Wallwiener M, Zucknick
M, Nees J, Schott S, Rudolph A, Riethdorf S, Trumpp A, Pantel K, et
al: Circulating miRNAs with prognostic value in metastatic breast
cancer and for early detection of metastasis. Carcinogenesis.
37:461–470. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Záveský L, Jandáková E, Turyna R,
Langmeierová L, Weinberger V, Záveská Drábková L, Hůlková M,
Hořínek A, Dušková D, Feyereisl J, et al: Evaluation of Cell-Free
Urine microRNAs expression for the use in diagnosis of ovarian and
endometrial cancers. A Pilot Study. Pathol Oncol Res. 21:1027–1035.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Sun C, Li N, Zhou B, Yang Z, Ding D, Weng
D, Meng L, Wang S, Zhou J, Ma D and Chen G: miR-222 is upregulated
in epithelial ovarian cancer and promotes cell proliferation by
downregulating P27kip1. Oncol Lett. 6:507–512. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lin Z, Li JW, Wang Y, Chen T, Ren N, Yang
L, Xu W, He H, Jiang Y, Chen X, et al: Abnormal miRNA-30e
expression is associated with breast cancer progression. Clin Lab.
62:121–128. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kim SJ, Shin JY, Lee KD, Bae YK, Sung KW,
Nam SJ and Chun KH: MicroRNA let-7a suppresses breast cancer cell
migration and invasion through downregulation of C-C chemokine
receptor type 7. Breast Cancer Res. 14:1–12. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Liu K, Zhang C, Li T, Ding Y, Tu T, Zhou
F, Qi W, Chen H and Sun X: Let-7a inhibits growth and migration of
breast cancer cells by targeting HM. Int J Oncol. 46:2526–2534.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wang L, Zheng W, Zhang S, Chen X and
Hornung D: Expression of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 in human
endometrial cancer cells and the effect of treatment with tamoxifen
or buserelin. J Int Med Res. 34:284–290. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chun SM, Park HJ, Kim CH and Kim I: The
Significance of MicroRNA Let-7b, miR-30c, and miR-200c Expression
in Breast Cancers. J Pathol Transl Med. 45:354–360. 2011.
|
|
58
|
Liu P, Qi M, Ma C, Lao G and Liu Y and Liu
Y and Liu Y: Let7a inhibits the growth of endometrial carcinoma
cells by targeting Aurora-B. FEBS Lett. 587:2523–2529. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Bayani J, Kuzmanov U, Saraon P, Fung WA,
Soosaipillai A, Squire JA and Diamandis EP: Copy number and
expression alterations of miRNAs in the ovarian cancer cell line
OVCAR-3: Impact on kallikrein 6 protein expression. Clin Chem.
59:296–305. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Dong P, Ihira K, Xiong Y, Watari H, Hanley
SJ, Yamada T, Hosaka M, Kudo M, Yue J and Sakuragi N: Reactivation
of epigenetically silenced miR-124 reverses the
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and inhibits invasion in
endometrial cancer cells via the direct repression of IQGAP1
expression. Oncotarget. 7:20260–20270. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Nam EJ, Yoon H, Kim SW, Kim H, Kim YT, Kim
JH, Kim JW and Kim S: MicroRNA expression profiles in serous
ovarian carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 14:2690–2695. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Boren T, Xiong Y, Hakam A, Wenham R, Apte
S, Wei Z, Kamath S, Chen DT, Dressman H and Lancaster JM: MicroRNAs
and their target messenger RNAs associated with endometrial
carcinogenesis. Gynecol Oncol. 110:206–215. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kowalewska M, Bakula-Zalewska E,
Chechlinska M, Goryca K, Nasierowska-Guttmejer A, Danska-Bidzinska
A and Bidzinski M: microRNAs in uterine sarcomas and mixed
epithelial-mesenchymal uterine tumors: A preliminary report. Tumour
Biol. 34:2153–2160. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Markou A, Zavridou M, Sourvinou I, Yousef
G, Kounelis S, Malamos N, Georgoulias V and Lianidou E: Direct
comparison of metastasis-related miRNAs expression levels in
circulating tumor cells, corresponding plasma, and primary tumors
of breast cancer patients. Clin Chem. 62:1002–1011. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Bertoli G, Cava C and Castiglioni I:
MicroRNAs: New biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis, therapy
prediction and therapeutic tools for breast cancer. Theranostics.
5:1122–1143. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Echevarria-Vargas IM, Valiyeva F and
Vivas-Mejia PE: Upregulation of miR-21 in cisplatin resistant
ovarian cancer via JNK-1/c-Jun pathway. PLoS One. 9:e970942014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Myatt SS, Wang J, Monteiro LJ, Christian
M, Ho KK, Fusi L, Dina RE, Brosens JJ, Ghaem-Maghami S and Lam EW:
Definition of microRNAs that repress expression of the tumor
suppressor gene FOXO1 in endometrial cancer. 70:367–377.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Ouzounova M, Vuong T, Ancey PB, Ferrand M,
Durand G, Le-Calvez Kelm F, Croce C, Matar C, Herceg Z and
Hernandez-Vargas H: MicroRNA miR-30 family regulates non-attachment
growth of breast cancer cells. BMC Genomics. 14:1392013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Chang CW, Yu JC, Hsieh YH, Yao CC, Chao
JI, Chen PM, Hsieh HY, Hsiung CN, Chu HW, Shen CY and Cheng CW:
MicroRNA-30a increases tight junction protein expression to
suppress the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis by
targeting Slug in breast cancer. Oncotarget. 7:16462–16478. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Berber U, Yilmaz I, Narli G, Haholu A,
Kucukodaci Z and Demirel D: miR-205 and miR-200c: Predictive Micro
RNAs for lymph node metastasis in triple negative breast cancer. J
Breast Cancer. 17:143–148. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Tsukamoto O, Miura K, Mishima H, Abe S,
Kaneuchi M, Higashijima A, Miura S, Kinoshita A, Yoshiura K and
Masuzaki H: Identification of endometrioid endometrial
carcinoma-associated microRNAs in tissue and plasma. Gynecol Oncol.
132:715–721. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Nagaraja AK, Creighton CJ, Yu Z, Zhu H,
Gunaratne PH, Reid JG, Olokpa E, Itamochi H, Ueno NT, Hawkins SM,
et al: A link between mir-100 and FRAP1/mTOR in clear cell ovarian
cancer. Mol Endocrinol. 24:447–463. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Calura E, Fruscio R, Paracchini L,
Bignotti E, Ravaggi A, Martini P, Sales G, Beltrame L, Clivio L,
Ceppi L, et al: MiRNA landscape in stage I epithelial ovarian
cancer defines the histotype specificities. Clin Cancer Res.
19:4114–4123. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zhou J, Gong G, Tan H, Dai F, Zhu X, Chen
Y, Wang J, Liu Y, Chen P, Wu X and Wen J: Urinary microRNA-30a-5p
is a potential biomarker for ovarian serous adenocarcinoma. Oncol
Rep. 33:2915–2923. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Ayaz L, Çayan F, Balci Ş, Görür A, Akbayir
S, Yıldırım Yaroğlu H, Doğruer Unal N and Tamer L: Circulating
microRNA expression profiles in ovarian cancer. J Obstet Gynaecol.
34:620–624. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Hausler SF, Keller A, Chandran PA, Ziegler
K, Zipp K, Heuer S, Krockenberger M, Engel JB, Hönig A, Scheffler
M, et al: Whole blood-derived miRNA profiles as potential new tools
for ovarian cancer screening. Br J Cancer. 103:693–700. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Shukla K, Sharma AK, Ward A, Will R,
Hielscher T, Balwierz A, Breunig C, Münstermann E, König R,
Keklikoglou I and Wiemann S: MicroRNA-30c-2-3p negatively regulates
NF-κB signaling and cell cycle progression through downregulation
of TRADD and CCNE1 in breast cancer. Mol Oncol. 9:1106–1119. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Tanic M, Yanowsky K, Rodriguez-Antona C,
Andrés R, Márquez-Rodas I, Osorio A, Benitez J and Martinez-Delgado
B: Deregulated miRNAs in hereditary breast cancer revealed a role
for miR-30c in regulating KRAS oncogene. PLoS One. 7:e388472012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Sorrentino A, Liu CG, Addario A, Peschle
C, Scambia G and Ferlini C: Role of microRNAs in drug-resistant
ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol. 111:478–486. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Gong Y, He T, Yang L, Yang G, Chen Y and
Zhang X: The role of miR-100 in regulating apoptosis of breast
cancer cells. Sci Rep. 5:116502015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zaman MS, Maher DM, Khan S, Jaggi M and
Chauhan SC: Current status and implications of microRNAs in ovarian
cancer diagnosis and therapy. J Ovarian Res. 5:442012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Okuda H, Xing F, Pandey PR, Sharma S,
Watabe M, Pai SK, Mo YY, Iiizumi-Gairani M, Hirota S, Liu Y, et al:
miR-7 suppresses brain metastasis of breast cancer stem-like cells
by modulating KLF4. Cancer Res. 73:1434–1444. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Banno K, Yanokura M, Iida M, Adachi M,
Nakamura K, Nogami Y, Umene K, Masuda K, Kisu I, Nomura H, et al:
Application of microRNA in diagnosis and treatment of ovarian
cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2014:2328172014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Ramon LA, Braza-Boïls A, Gilabert J,
Chirivella M, España F, Estellés A and Gilabert-Estellés J:
microRNAs related to angiogenesis are dysregulated in endometrioid
endometrial cancer. Hum Reprod. 27:3036–3045. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Kinose Y, Sawada K, Nakamura K and Kimura
T: The Role of MicroRNAs in Ovarian Cancer. Biomed Res Int.
2014:112014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Lu J, Zhang X, Zhang R and Ge Q: MicroRNA
heterogeneity in endometrial cancer cell lines revealed by deep
sequencing. Oncol Lett. 10:3457–3465. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Wu Q, Guo L, Jiang F, Li L, Li Z and Chen
F: Analysis of the miRNA-mRNA-lncRNA networks in ER+ and ER- breast
cancer cell lines. J Cell Mol Med. 19:2874–2887. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Chong GO, Jeon HS, Han HS, Son JW, Lee YH,
Hong DG, Lee YS and Cho YL: Differential MicroRNA Expression
Profiles in Primary and Recurrent Epithelial Ovarian Cancer.
Anticancer Res. 35:2611–2617. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Singh SR and Rameshwar P: MicroRNA in
development and in the progression of cancer. Springer-Verlag; New
York: 2014, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Brockhoff G, Heckel B, Schmidt-Bruecken E,
Plander M, Hofstaedter F, Vollmann A and Diermeier S: Differential
impact of Cetuximab, Pertuzumab and Trastuzumab on BT474 and
SK-BR-3 breast cancer cell proliferation. Cell Prolif. 40:488–507.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Lasfargues EY, Coutinho WG and Redfield
ES: Isolation of two human tumor epithelial cell lines from solid
breast carcinomas. J Natl Cancer Inst. 61:967–978. 1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Subik K, Lee JF, Baxter L, Strzepek T,
Costello D, Crowley P, Xing L, Hung MC, Bonfiglio T, Hicks DG and
Tang P: The Expression Patterns of ER, PR, HER2, CK5/6, EGFR, Ki-67
and AR by immunohistochemical analysis in breast cancer cell lines.
Breast Cancer. 4:35–41. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Lee S, Yang W, Lan KH, Sellappan S, Klos
K, Hortobagyi G, Hung MC and Yu D: Enhanced sensitization to
taxol-induced apoptosis by herceptin pretreatment in
ErbB2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 62:5703–5710.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Kim DJ, Lee WY, Park NW, Kim GS, Lee KM,
Kim J, Choi MK, Lee GH, Han W and Lee SK: Drug response of captured
BT20 cells and evaluation of circulating tumor cells on a silicon
nanowire platform. Biosens Bioelectron. 67:370–378. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Kloten V, Schlensog M, Eschenbruch J,
Gasthaus J, Tiedemann J, Mijnes J, Heide T, Braunschweig T, Knüchel
R and Dahl E: Abundant NDRG2 expression is associated with
aggressiveness and unfavorable patients' outcome in basal-like
breast cancer. PLoS One. 11:e01590732016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Croxtall JD, Elder MG and White JO:
Hormonal control of proliferation in the Ishikawa endometrial
adenocarcinoma cell line. J Steroid Biochem. 35:665–669. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Nishida M, Kasahara K, Kaneko M, Iwasaki H
and Hayashi K: Establishment of a new human endometrial
adenocarcinoma cell line, Ishikawa cells, containing estrogen and
progesterone receptors. Nihon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai zasshi.
37:1103–1111. 1985.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Dawe CJ, Banfield WG, Morgan WD, Slatick
MS and Curth HO: Growth in continuous culture, and in hamsters, of
cells from a neoplasm associated with acanthosis nigricans. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 33:441–456. 1964.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Korch C, Spillman MA, Jackson TA, Jacobsen
BM, Murphy SK, Lessey BA, Jordan VC and Bradford AP: DNA profiling
analysis of endometrial and ovarian cell lines reveals
misidentification, redundancy and contamination. Gynecol Oncol.
127:241–248. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Basu M, Mukhopadhyay S, Chatterjee U and
Roy SS: FGF16 promotes invasive behavior of SKOV-3 ovarian cancer
cells through activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)
signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 289:1415–1428. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Irmer G, Bürger C, Müller R, Ortmann O,
Peter U, Kakar SS, Neill JD, Schulz KD and Emons G: Expression of
the messenger RNAs for luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH)
and its receptor in human ovarian epithelial carcinoma. Cancer Res.
55:817–822. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Yoon J, Kim ES, Lee SJ, Park CW, Cha HJ,
Hong BH and Choi KY: Apoptosis-related mRNA expression profiles of
ovarian cancer cell lines following cisplatin treatment. J Gynecol
Oncol. 21:255–261. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Langdon SP and Lawrie SS: Establishment of
ovarian cancer cell lines. Methods Mol Med. 39:155–159.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Shukla J, Sharma U, Kar R, Varma IK, Juyal
S, Jagannathan NR and Bandopadhyaya GP:
Tamoxifen-2-hydroxylpropyl-beta-cyclodextrin-aggregated
nanoassembly for nonbreast estrogen-receptor-positive cancer
therapy. Nanomedicine (Lond). 4:895–902. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|