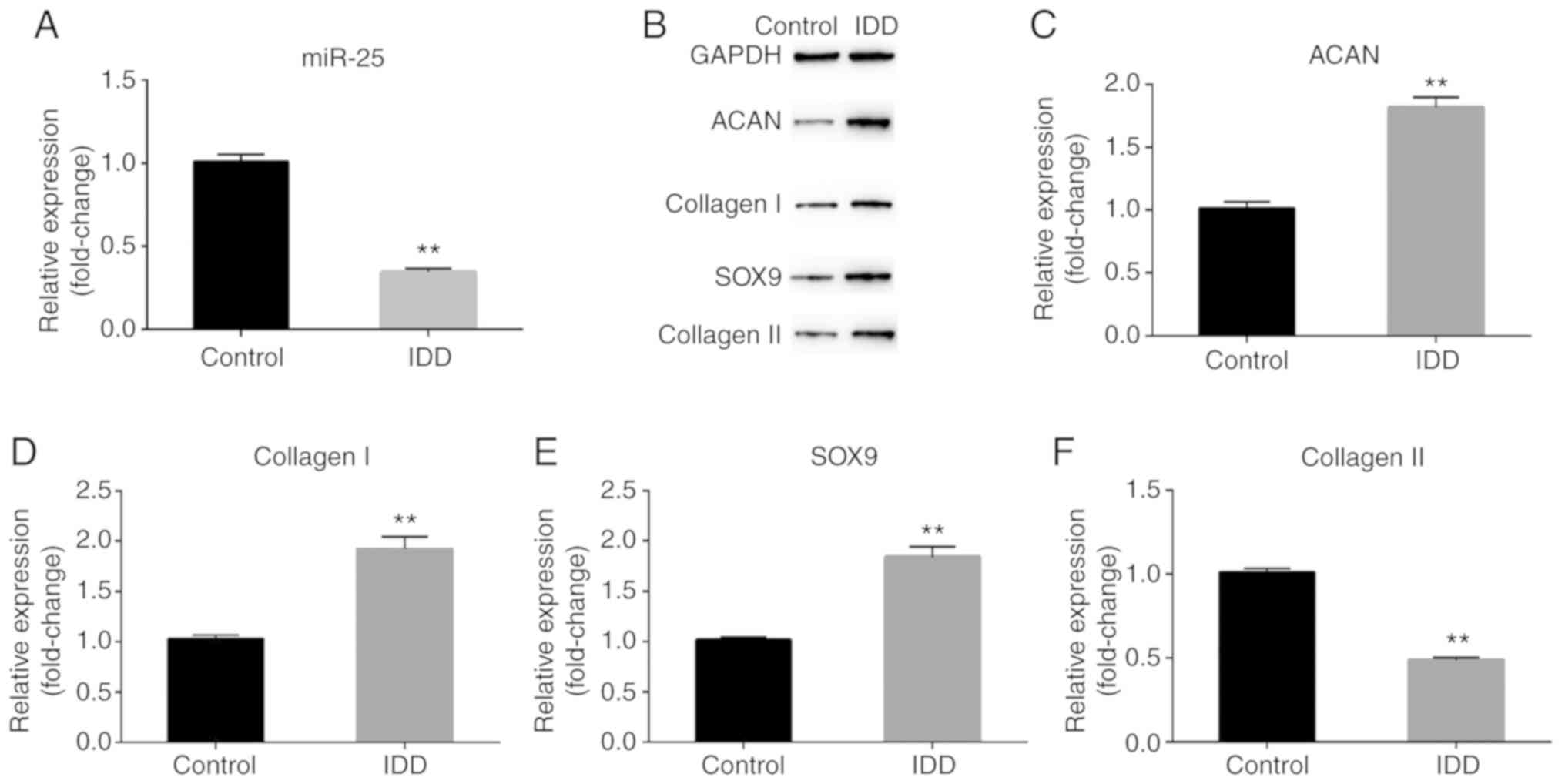
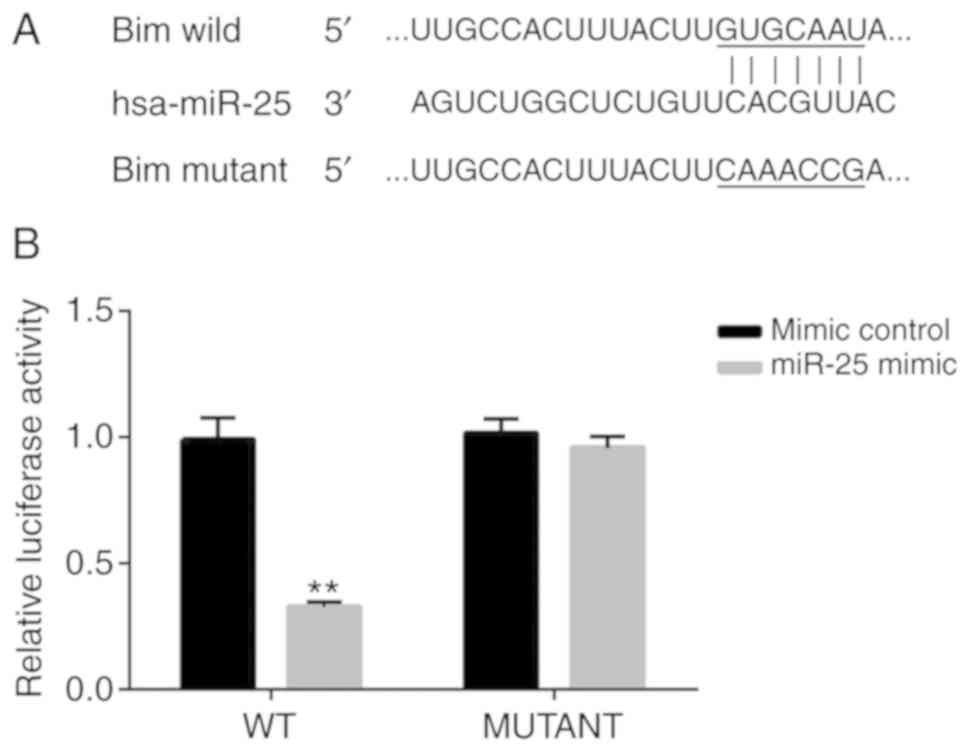
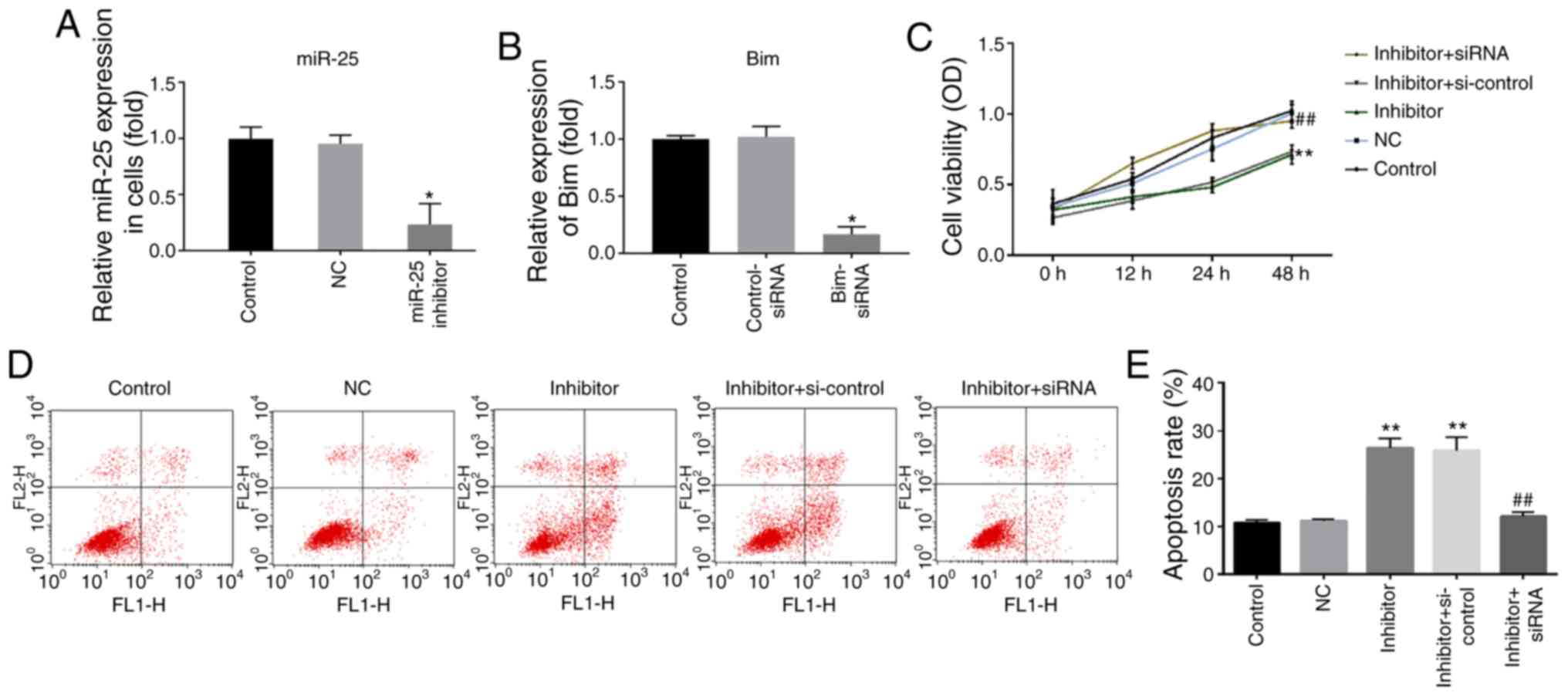
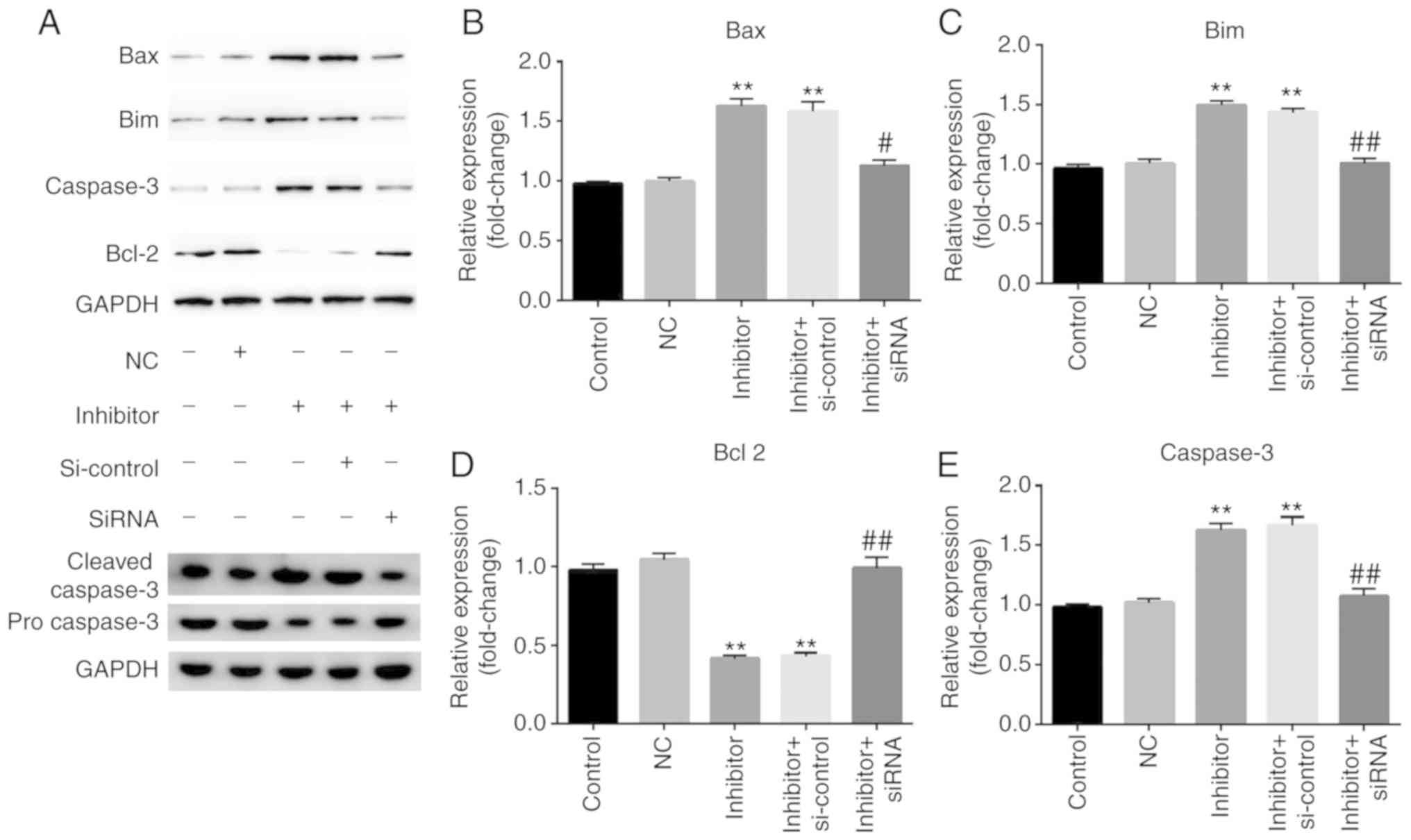
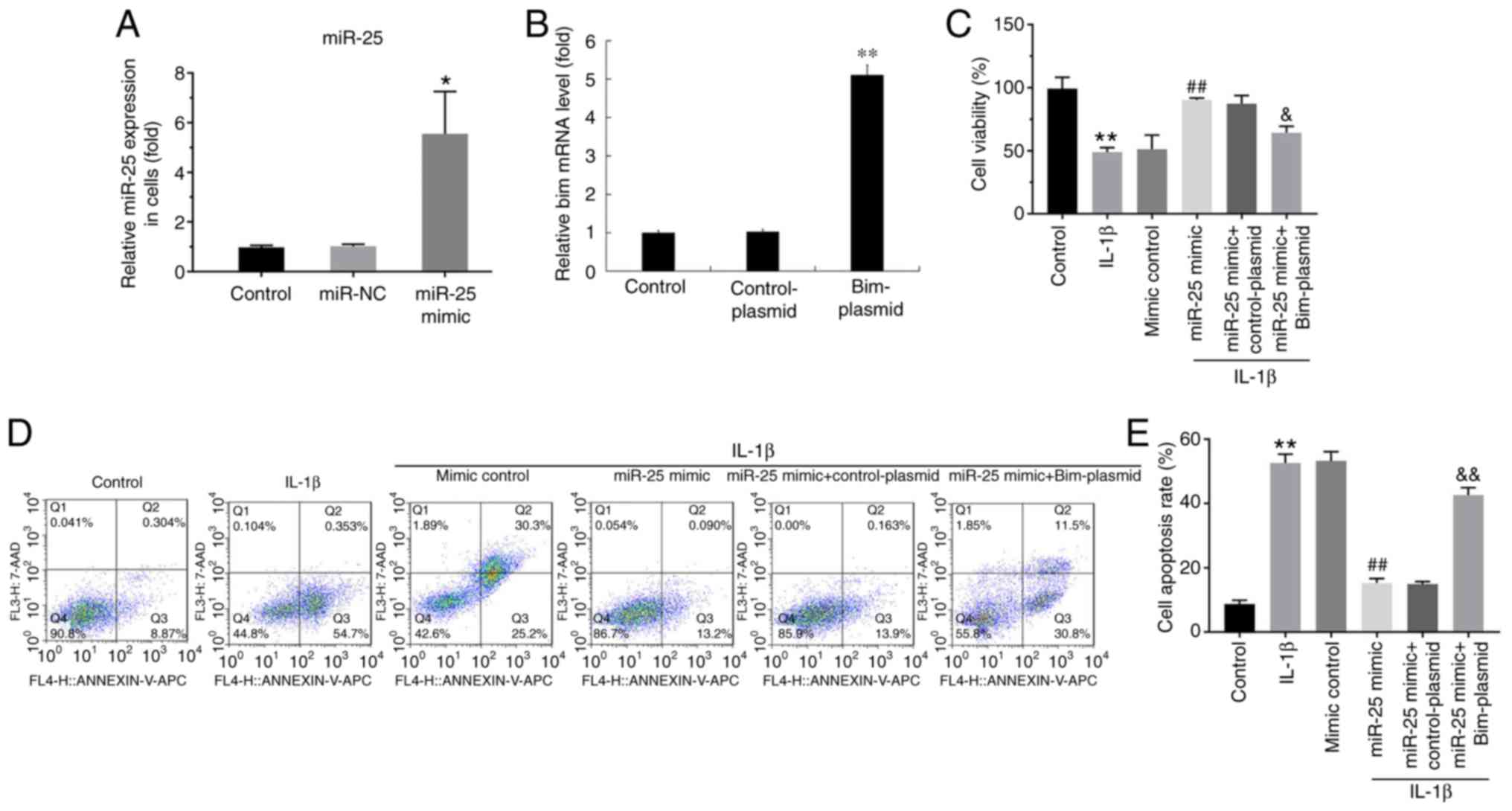
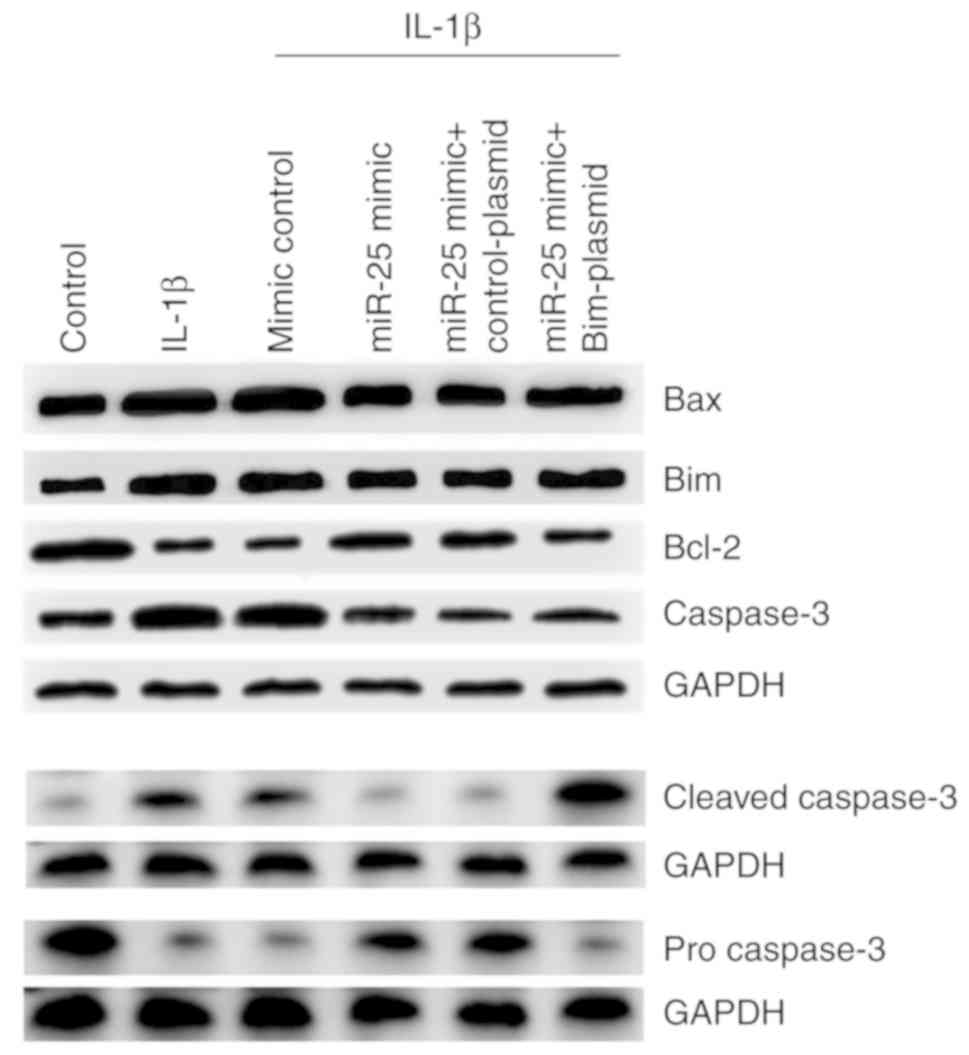
|
1
|
Tang P, Gu JM, Xie ZA, Gu Y, Jie ZW, Huang
KM, Wang JY, Fan SW, Jiang XS and Hu ZJ: Honokiol alleviates the
degeneration of intervertebral disc via suppressing the activation
of TXNIP-NLRP3 inflammasome signal pathway. Free Radic Biol Med.
120:368–379. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wu D, Zheng C, Wu J, Huang R, Chen X,
Zhang T and Zhang L: Molecular biological effects of weightlessness
and hypergravity on intervertebral disc degeneration. Aerosp Med
Hum Perform. 88:1123–1128. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Huang Y, Jiang T, Chen J, Yin GY and Fan
J: Effects of kartogenin on the attenuated nucleus pulposus cell
degeneration of intervertebral discs induced by interleukin-1β and
tumor necrosis factor-α. Int J Mol Med. 41:749–756. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Viguet-Carrin S, Roux JP, Arlot ME,
Merabet Z, Leeming DJ, Byrjalsen I, Delmas PD and Bouxsein ML:
Contribution of the advanced glycation end product pentosidine and
of maturation of type I collagen to compressive biomechanical
properties of human lumbar vertebrae. Bone. 39:1073–1079. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vergroesen PP, Kingma I, Emanuel KS,
Hoogendoorn RJ, Welting TJ, van Royen BJ, van Dieën JH and Smit TH:
Mechanics and biology in intervertebral disc degeneration: A
vicious circle. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 23:1057–1070. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mellis D and Caporali A: MicroRNA-based
therapeutics in cardiovascular disease: screening and delivery to
the target. Biochem Soc Trans. 46:11–21. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ganju A, Khan S, Hafeez BB, Behrman SW,
Yallapu MM, Chauhan SC and Jaggi M: miRNA nanotherapeutics for
cancer. Drug Discov Today. 22:424–432. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Long H, Wang X, Chen Y, Wang L, Zhao M and
Lu Q: Dysregulation of microRNAs in autoimmune diseases:
Pathogenesis, biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets. Cancer
Lett. 428:90–103. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ro S, Park C, Young D, Sanders KM and Yan
W: Tissue-dependent paired expression of miRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res.
35:5944–5953. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mallory AC and Vaucheret H: MicroRNAs:
Something important between the genes. Curr Opin Plant Biol.
7:120–125. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Garzon R, Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNAs
in cancer. Annu Rev Med. 60:167–179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu JY, Yang LL, Ma C, Huang YL, Zhu GX and
Chen QL: miR-25-3p attenuates the proliferation of tongue squamous
cell carcinoma cell line Tca8113. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 6:743–747.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fei Q and Ethell DW: Maneb potentiates
paraquat neurotoxicity by inducing key Bcl-2 family members. J
Neurochem. 105:2091–2097. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bouillet P, Purton JF, Godfrey DI, Zhang
LC, Coultas L, Puthalakath H, Pellegrini M, Cory S, Adams JM and
Strasser A: BH3-only Bcl-2 family member Bim is required for
apoptosis of autoreactive thymocytes. Nature. 415:922–926. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li Y, Deutzmann A and Felsher DW:
BIM-mediated apoptosis and oncogene addiction. Aging (Albany NY).
8:1834–1835. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Guo Y, Schoell MC and Freeman RS: The von
Hippel-Lindau protein sensitizes renal carcinoma cells to apoptotic
stimuli through stabilization of BIM(EL). Oncogene. 28:1864–1874.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Baysan A, Yel L, Gollapudi S, Su H and
Gupta S: Arsenic trioxide induces apoptosis via the mitochondrial
pathway by upregulating the expression of Bax and Bim in human B
cells. Int J Oncol. 30:313–318. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bouillet P, Cory S, Adams J and Strasser
A: Role of BH3-only protein Bim in autoimmune and degenerative
diseases. Arthritis Res Ther. 5 (Suppl 3):S192003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Issy AC, Castania V, Castania M, Salmon
CE, Nogueira-Barbosa MH, Bel ED and Defino HL: Experimental model
of intervertebral disc degeneration by needle puncture in Wistar
rats. Braz J Med Biol Res. 46:235–244. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bayne K: Revised guide for the care and
use of laboratory animals available. American physiological
society. Physiologist. 39:199, 208–211. 1996.
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Juniper M, Le TK and Mladsi D: The
epidemiology, economic burden, and pharmacological treatment of
chronic low back pain in France, Germany, Italy, Spain and the UK:
A literature-based review. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 10:2581–2592.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Phillips C, Main C, Buck R, Aylward M,
Wynne-Jones G and Farr A: Prioritising pain in policy making: The
need for a whole systems perspective. Health Policy. 88:166–175.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Waddell G: Low back pain: A twentieth
century health care enigma. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 21:2820–2825.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang YG, Sun Z, Zhang Z, Liu J and Guo X:
Risk factors for lumbar intervertebral disc herniation in Chinese
population: A case-control study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
34:E918–E922. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kalichman L and Hunter DJ: The genetics of
intervertebral disc degeneration. Associated genes. Joint Bone
Spine. 75:388–396. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Walter BA, Korecki CL, Purmessur D,
Roughley PJ, Michalek AJ and Iatridis JC: Complex loading affects
intervertebral disc mechanics and biology. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 19:1011–1018. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Battié MC and Videman T: Lumbar disc
degeneration: Epidemiology and genetics. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 88
(Suppl 2):S3–S9. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Miyaki S, Nakasa T, Otsuki S, Grogan SP,
Higashiyama R, Inoue A, Kato Y, Sato T, Lotz MK and Asahara H:
MicroRNA-140 is expressed in differentiated human articular
chondrocytes and modulates interleukin-1 responses. Arthritis
Rheum. 60:2723–2730. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang HQ, Yu XD, Liu ZH, Cheng X, Samartzis
D, Jia LT, Wu SX, Huang J, Chen J and Luo ZJ: Deregulated mir-155
promotes Fas-mediated apoptosis in human intervertebral disc
degeneration by targeting FAdd and caspase-3. J Pathol.
225:232–242. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ji ML, Lu J, Shi PL, Zhang XJ, Wang SZ,
Chang Q, Chen H and Wang C: Dysregulated miR-98 contributes to
extracellular matrix degradation by targeting IL-6/StAt3 signaling
pathway in human intervertebral disc degeneration. J Bone Miner
Res. 31:900–909. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wibawa T, Pangemanan L, Rachmawaty FJ,
Rintiswati N, Mustofa and Soesatyo MH: Isoniazid (INH) treatment of
INH-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis inhibits infected
macrophage to produce TNF-alpha. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public
Health. 45:1107–1113. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang XH, Hong X, Zhu L, Wang YT, Bao JP,
Liu L, Wang F and Wu XT: Tumor necrosis factor alpha promotes the
proliferation of human nucleus pulposus cells via nuclear
factor-κB, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38 mitogen-activated
protein kinase. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 240:411–417. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yu X, Li Z, Shen J, Wu WK, Liang J, Weng X
and Qiu G: MicroRNA-10b promotes nucleus pulposus cell
proliferation through RhoC-Akt pathway by targeting HOXD10 in
intervetebral disc degeneration. PLoS One. 8:e830802013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu H, Huang X, Liu X, Xiao S, Zhang Y,
Xiang T, Shen X, Wang G and Sheng B: miR-21 promotes human nucleus
pulposus cell proliferation through PTEN/AKT signaling. Int J Mol
Sci. 15:4007–4018. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dong W, Liu J, Lv Y, Wang F, Liu T, Sun S,
Liao B, Shu Z and Qian J: miR-640 aggravates intervertebral disc
degeneration via NF-κB and WNT signalling pathway. Cell Prolif.
52:e126642019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu G, Cao P, Chen H, Yuan W, Wang J and
Tang X: MiR-27a regulates apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells by
targeting PI3K. PLoS One. 8:e752512013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cheng X, Zhang L, Zhang K, Zhang G, Hu Y,
Sun X, Zhao C, Li H, Li YM and Zhao J: Circular RNA VMA21 protects
against intervertebral disc degeneration through targeting miR-200c
and X linked inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein. Ann Rheum Dis.
77:770–779. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Concannon CG, Tuffy LP, Weisová P, Bonner
HP, Dávila D, Bonner C, Devocelle MC, Strasser A, Ward MW and Prehn
JH: AMP kinase-mediated activation of the BH3-only protein Bim
couples energy depletion to stress-induced apoptosis. J Cell Biol.
189:83–94. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kaufmann T, Jost PJ, Pellegrini M,
Puthalakath H, Gugasyan R, Gerondakis S, Cretney E, Smyth MJ, Silke
J, Hakem R, et al: Fatal hepatitis mediated by tumor necrosis
factor TNFalpha requires caspase-8 and involves the BH3-only
proteins Bid and Bim. Immunity. 30:56–66. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sur S, Steele R, Shi X and Ray RB:
miRNA-29b inhibits prostate tumor growth and induces apoptosis by
increasing Bim expression. Cells. 8:14552019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Labi V, Peng S, Klironomos F, Munschauer
M, Kastelic N, Chakraborty T, Schoeler K, Derudder E, Martella M,
Mastrobuoni G, et al: Context-specific regulation of cell survival
by a miRNA-controlled BIM rheostat. Genes Dev. 33:1673–1687. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Feng Z, Li Z, Zhu D, Ling W, Zheng L, Pu L
and Kong L: Mir-24 regulates hepatocyte apoptosis via BIM during
acute liver failure. Am J Transl Res. 9:4925–4935. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Pan LJ, Wang X, Ling Y and Gong H: MiR-24
alleviates cardiomyocyte apoptosis after myocardial infarction via
targeting BIM. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:3088–3097.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|