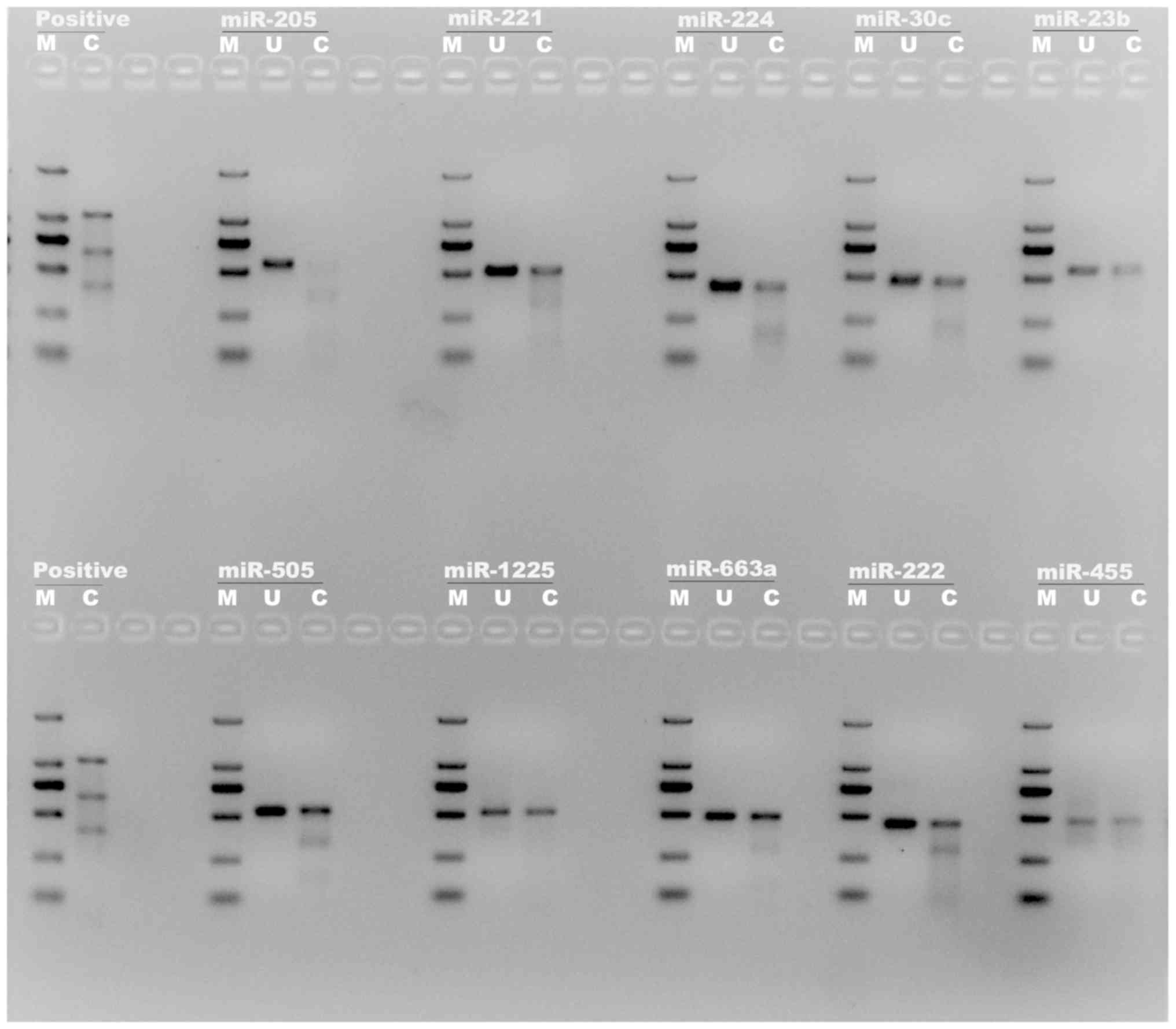
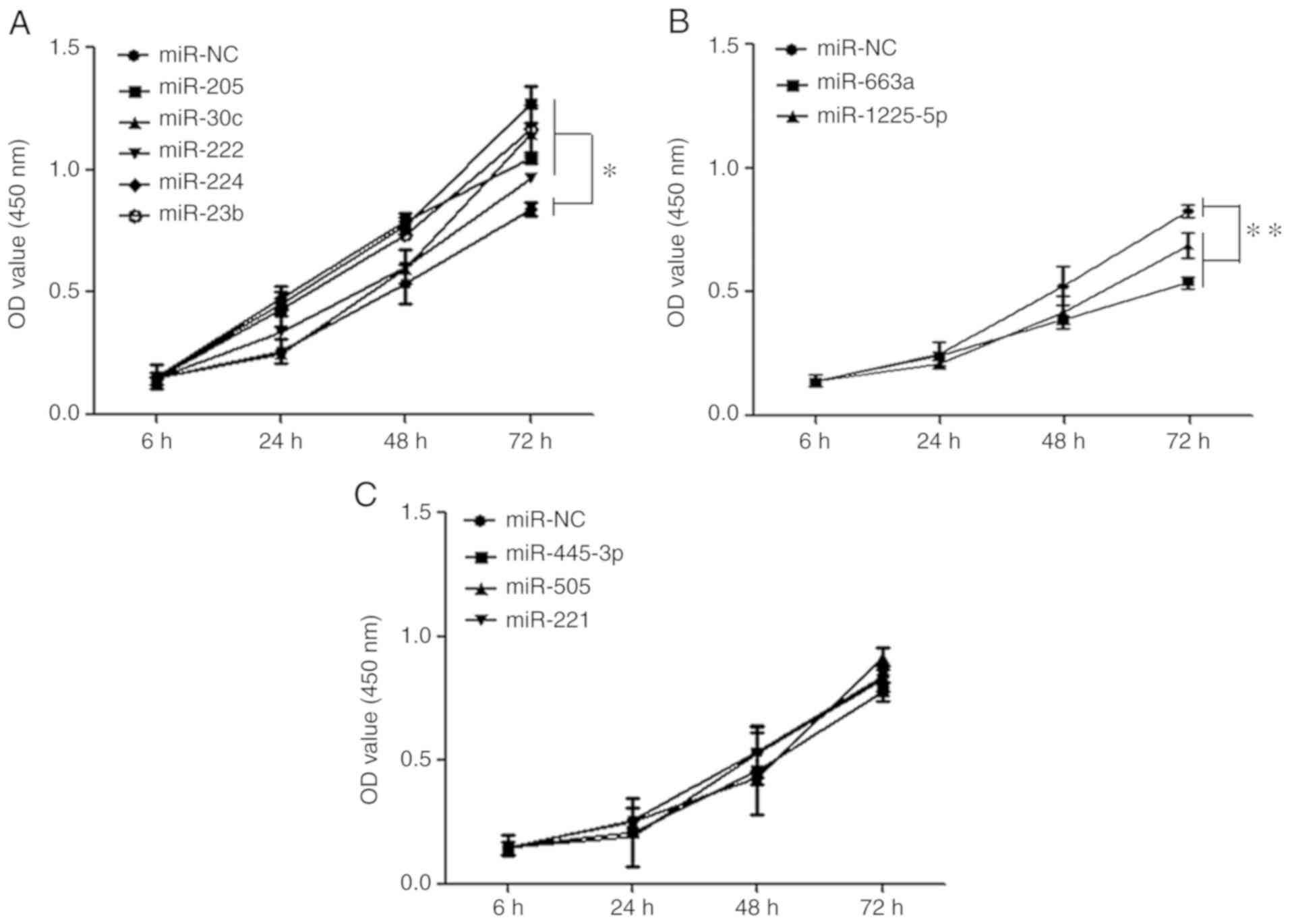
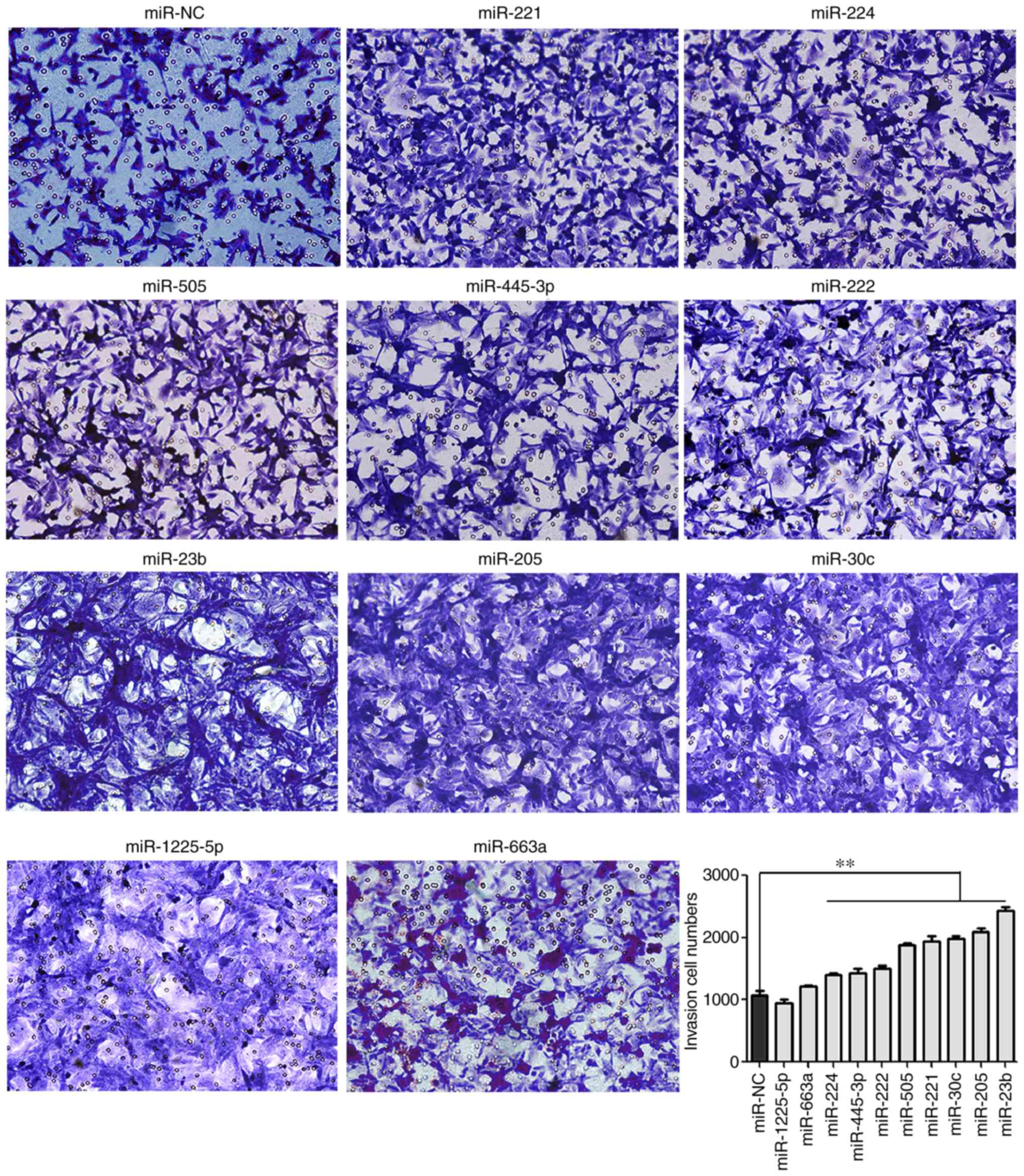
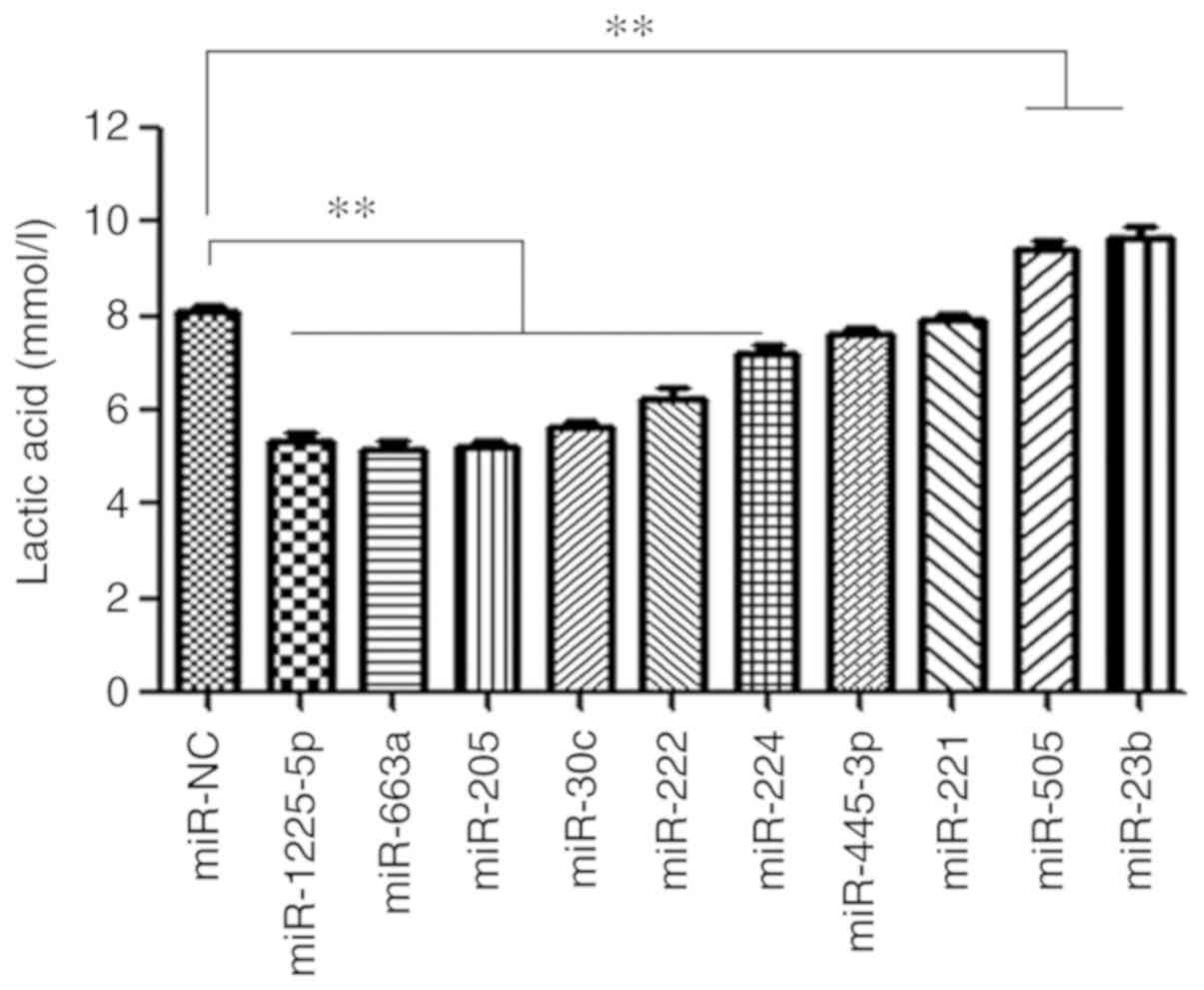
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
Statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 69:7–34. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bartel DP: MiRNAs: Target recognition and
regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ayub SG, Kaul D and Ayub T:
Microdissecting the role of miRNAs in the pathogenesis of prostate
cancer. Cancer Genet. 208:289–302. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhao Y, Cong L and Lukiw WJ: Plant and
Animal microRNAs (miRNAs) and their potential for inter-kingdom
communication. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 38:133–140. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S,
Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, et
al: A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines
cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2257–2261. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Porkka KP, Pfeiffer MJ, Waltering KK,
Vessella RL, Tammela TL and Visakorpi T: MicroRNA expression
profiling in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 167:6130–6135. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Plaisier CL, Pan M and Baliga NS: A
miRNA-regulatory network explains how dysregulated miRNAs perturb
oncogenic processes across diverse cancers. Genome Res.
22:2302–2314. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Song CJ, Chen H, Chen LZ, Ru GM, Guo JJ
and Ding QN: The potential of microRNAs as human prostate cancer
biomarkers: A meta-analysis of related studies. J Cell Biochem.
119:2763–2786. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
He HC, Han ZD, Dai QS, Ling XH, Fu X, Lin
ZY, Deng YH, Qin GQ, Cai C, Chen JH, et al: Global analysis of the
differentially expressed miRNAs of prostate cancer in Chinese
patients. BMC Genomics. 14:7572013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cho SW, Kim S, Kim JM and Kim JS: Targeted
genome engineering in human cells with the Cas9 RNA-guided
endonuclease. Nat Biotechnol. 31:230–232. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cong L, Ran FA, Cox D, Lin S, Barretto R,
Habib N, Hsu PD, Wu X, Jiang W, Marraffini LA and Zhang F:
Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science.
339:819–823. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mali P, Yang L, Esvelt KM, Aach J, Guell
M, DiCarlo JE, Norville JE and Church GM: RNA-guided human genome
engineering via Cas9. Science. 339:823–826. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sanjana NE, Shalem O and Zhang F: Improved
vectors and genome-wide libraries for CRISPR screening. Nat
Methods. 11:783–784. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mussolino C, Morbitzer R, Lütge F,
Dannemann N, Lahaye T and Cathomen T: A novel TALE nuclease
scaffold enables high genome editing activity in combination with
low toxicity. Nucleic Acids Res. 39:9283–9293. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim D, Bae S, Park J, Kim E, Kim S, Yu HR,
Hwang J, Kim JI and Kim JS: Digenome-seq: Genome-wide profiling of
CRISPR-Cas9 off-target effects in human cells. Nat Methods.
12:237–243. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Baranwal S and Alahari SK: miRNA control
of tumor cell invasion and metastasis. Int J Cancer. 126:1283–1290.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Saini S, Majid S and Dahiya R: Diet,
microRNAs and prostate cancer. Pharm Res. 27:1014–1026. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Szczyrba J, Löprich E, Wach S, Jung V,
Unteregger G, Barth S, Grobholz R, Wieland W, Stöhr R, Hartmann A,
et al: The microRNA profile of prostate carcinoma obtained by deep
sequencing. Mol Cancer Res. 8:529–538. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Schaefer A, Jung M, Mollenkopf HJ, Wagner
I, Stephan C, Jentzmik F, Miller K, Lein M, Kristiansen G and Jung
K: Diagnostic and prognostic implications of microRNA profiling in
prostate carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 126:1166–1176. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gatenby RA and Gillies RJ: Why do cancers
have high aerobic glycolysis? Nat Rev Cancer. 4:891–899. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Airley RE and Mobasheri A: Hypoxic
regulation of glucose transport, anaerobic metabolism and
angiogenesis in cancer: Novel pathways and targets for anticancer
therapeutics. Chemotherapy. 53:233–256. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gandellini P, Folini M, Longoni N, Pennati
M, Binda M, Colecchia M, Salvioni R, Supino R, Moretti R, Limonta
P, et al: miR-205 exerts tumor-suppressive functions in human
prostate through down-regulation of protein kinase Cepsilon. Cancer
Res. 69:2287–2295. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Majid S, Dar AA, Saini S, Yamamura S,
Hirata H, Tanaka Y, Deng G and Dahiya R: MicroRNA-205-directed
transcriptional activation of tumor suppressor genes in prostate
cancer. Cancer. 116:5637–5649. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang N, Li Q, Feng NH, Cheng G, Guan ZL,
Wang Y, Qin C, Yin CJ and Hua LX: miR-205 is frequently
downregulated in prostate cancer and acts as a tumor suppressor by
inhibiting tumor growth. Asian J Androl. 15:735–741. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Verdoodt B, Neid M, Vogt M, Kuhn V,
Liffers ST, Palisaar RJ, Noldus J, Tannapfel A and
Mirmohammadsadegh A: MicroRNA-205, a novel regulator of the
anti-apoptotic protein Bcl2, is downregulated in prostate cancer.
Int J Oncol. 43:307–314. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pang H and Yue X: MiR-205 serves as a
prognostic factor and suppresses proliferation and invasion by
targeting insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 in human cervical
cancer. Tumour Biol. 39:10104283177013082017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen S, Jin L, Nie S, Han L, Lu N and Zhou
Y: MiR-205 inhibits growth and invasion of neuroblastoma by
targeting cAMP responsive element binding protein 1. Oncol Res.
26:445–455. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tong AW, Fulgham P, Jay C, Chen P, Khalil
I, Liu S, Senzer N, Eklund AC, Han J and Nemunaitis J: MicroRNA
profile analysis of human prostate cancers. Cancer Gene Ther.
16:206–216. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ling XH, Han ZD, Xia D, He HC, Jiang FN,
Lin ZY, Fu X, Deng YH, Dai QS, Cai C, et al: MicroRNA-30c serves as
an independent biochemical recurrence predictor and potential tumor
suppressor for prostate cancer. Mol Biol Rep. 41:2779–2788. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang J, Wang X, Wang Y, Peng R, Lin Z,
Wang Y, Hu B, Wang J and Shi G: Low expression of microRNA-30c
promotes prostate cancer cells invasion involved in downregulation
of KRAS protein. Oncol Lett. 14:363–368. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Huang Y, Li Y, Wang FF, Lv W, Xie X and
Cheng X: Over-expressed miR-224 promotes the progression of
cervical cancer via targeting RASSF8. PLoS One. 11:e01623782016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
He C, Wang L, Zhang J and Xu H:
Hypoxia-inducible microRNA-224 promotes the cell growth, migration
and invasion by directly targeting RASSF8 in gastric cancer. Mol
Cancer. 16:352017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu F, Liu Y, Shen J, Zhang G and Han J:
MicroRNA-224 inhibits proliferation and migration of breast cancer
cells by down-regulating Fizzled 5 expression. Oncotarget.
7:49130–49142. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhao Y, Yan M, Yun Y, Zhang J, Zhang R, Li
Y, Wu X, Liu Q, Miao W and Jiang H: MicroRNA-455-3p functions as a
tumor suppressor by targeting eIF4E in prostate cancer. Oncol Rep.
37:2449–2458. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Negrete-Garcia MC, Ramírez-Rodriguez SL,
Rangel-Escareño C, Muñoz-Montero S, Kelly-García J,
Vázquez-Manríquez ME, Santillán P, Ramírez MM, Ramírez-Martínez G,
Ramírez- Venegas A and Ortiz-Quintero B: Deregulated MicroRNAs in
cancer-associated fibroblasts from front tumor tissues of lung
adenocarcinoma as potential predictors of tumor promotion. Tohoku J
Exp Med Oct. 246:107–120. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Rice MA, Ishteiwy RA, Magani F, Udayakumar
T, Reiner T, Yates TJ, Miller P, Perez-Stable C, Rai P, Verdun R,
et al: The microRNA-23b/-27b cluster suppresses prostate cancer
metastasis via Huntingtin-interacting protein 1-related. Oncogene.
35:4752–4761. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang Y, Xu X, Zhang M, Wang X, Bai X, Li
H, Kan L, Zhou Y, Niu H and He P: MicroRNA-663a is downregulated in
non-small cell lung cancer and inhibits proliferation and invasion
by targeting JunD. BMC Cancer. 16:3152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zheng H, Zhang F and Lin X, Huang C, Zhang
Y, Li Y, Lin J, Chen W and Lin X: MicroRNA-1225-5p inhibits
proliferation and metastasis of gastric carcinoma through
repressing insulin receptor substrate-1 and activation of β-catenin
signaling. Oncotarget. 7:4647–4663. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|