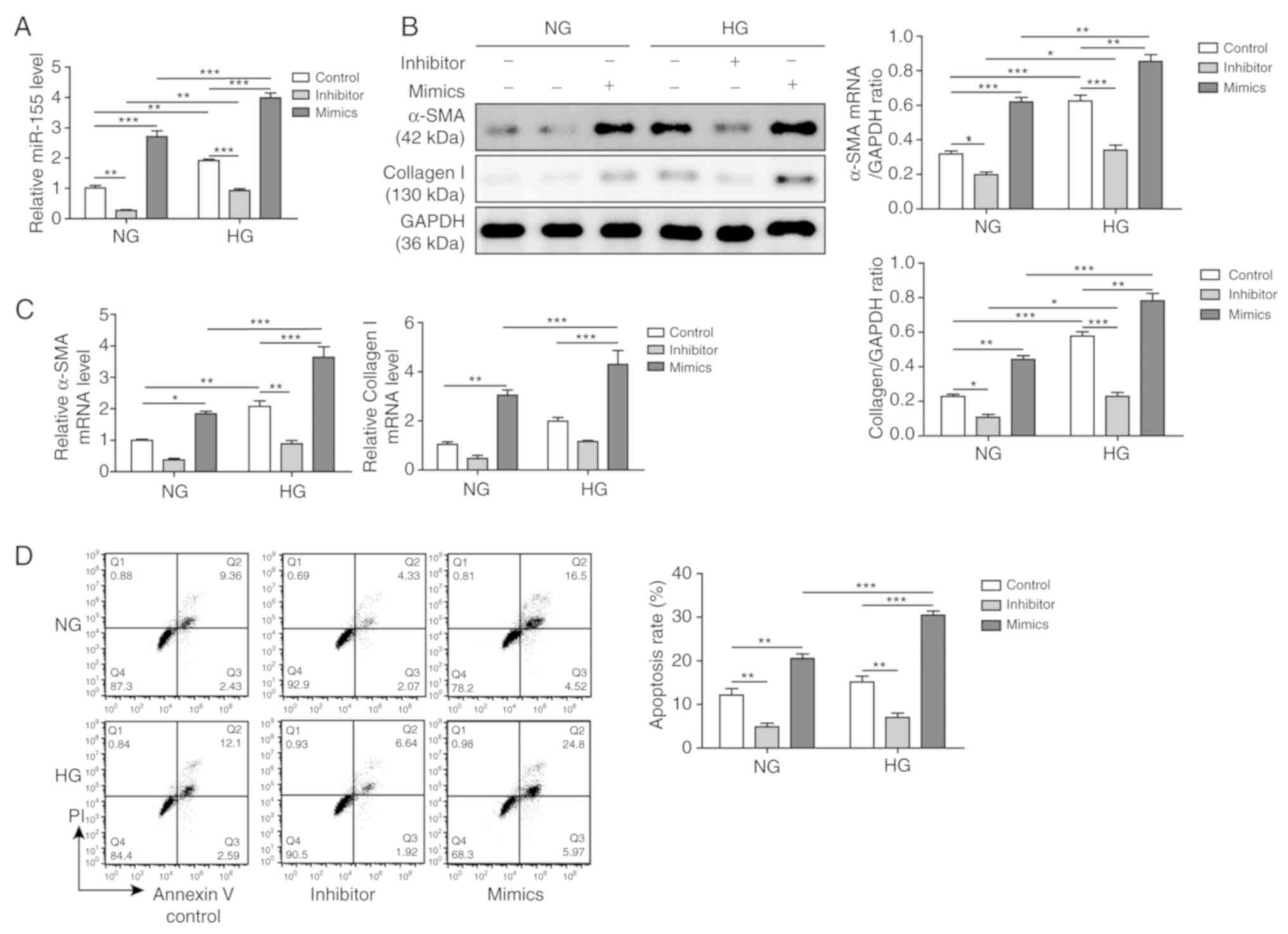
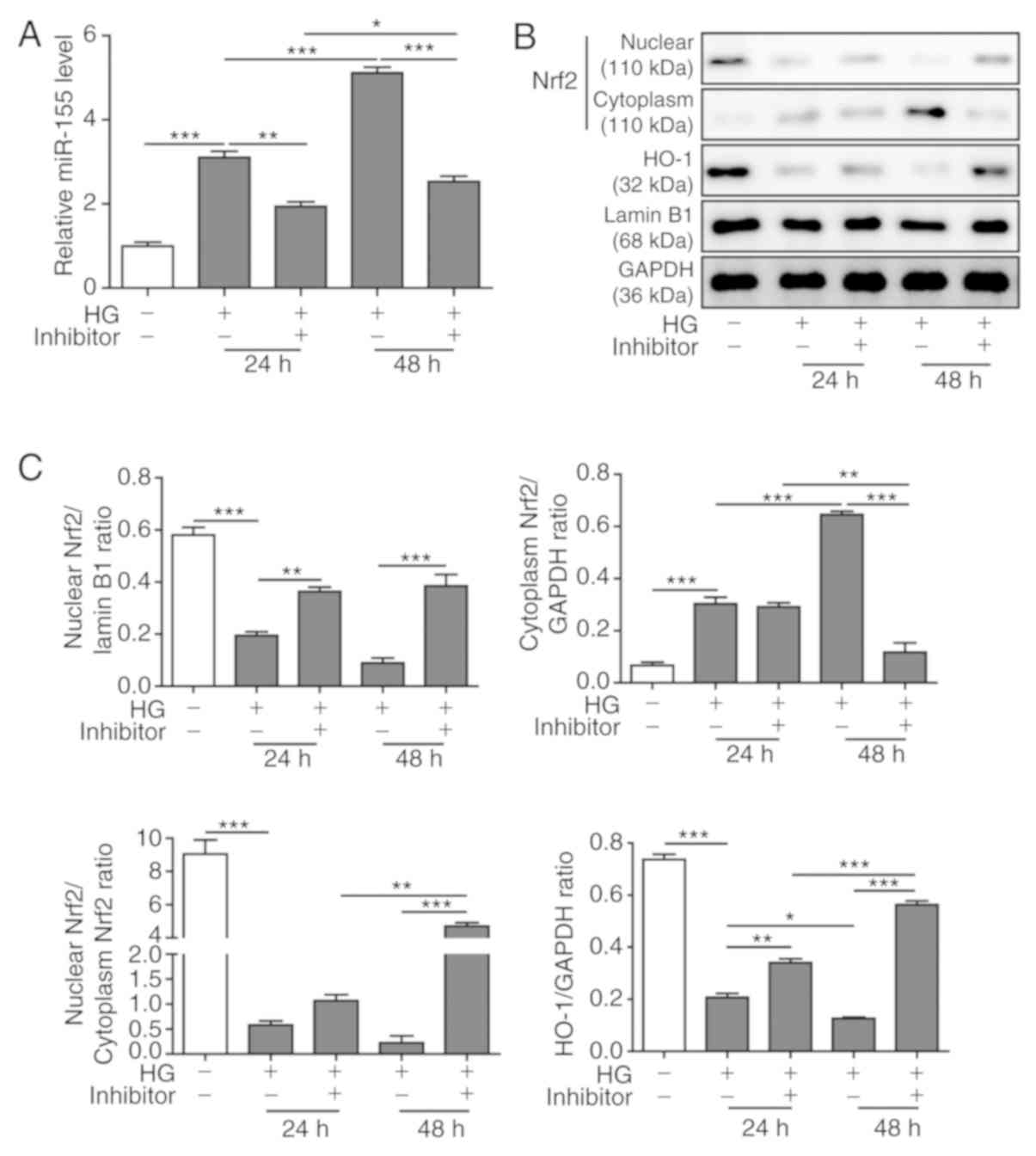
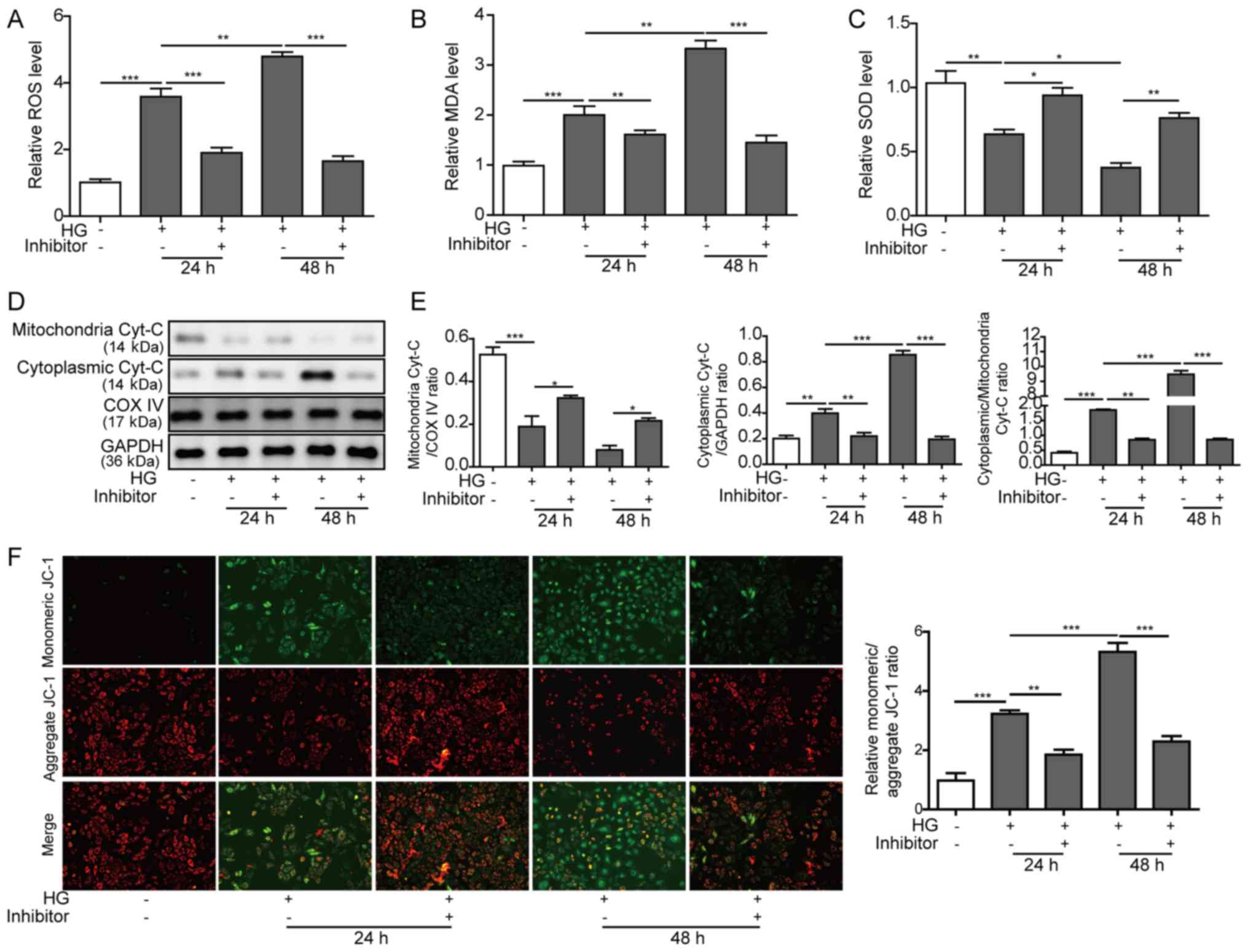
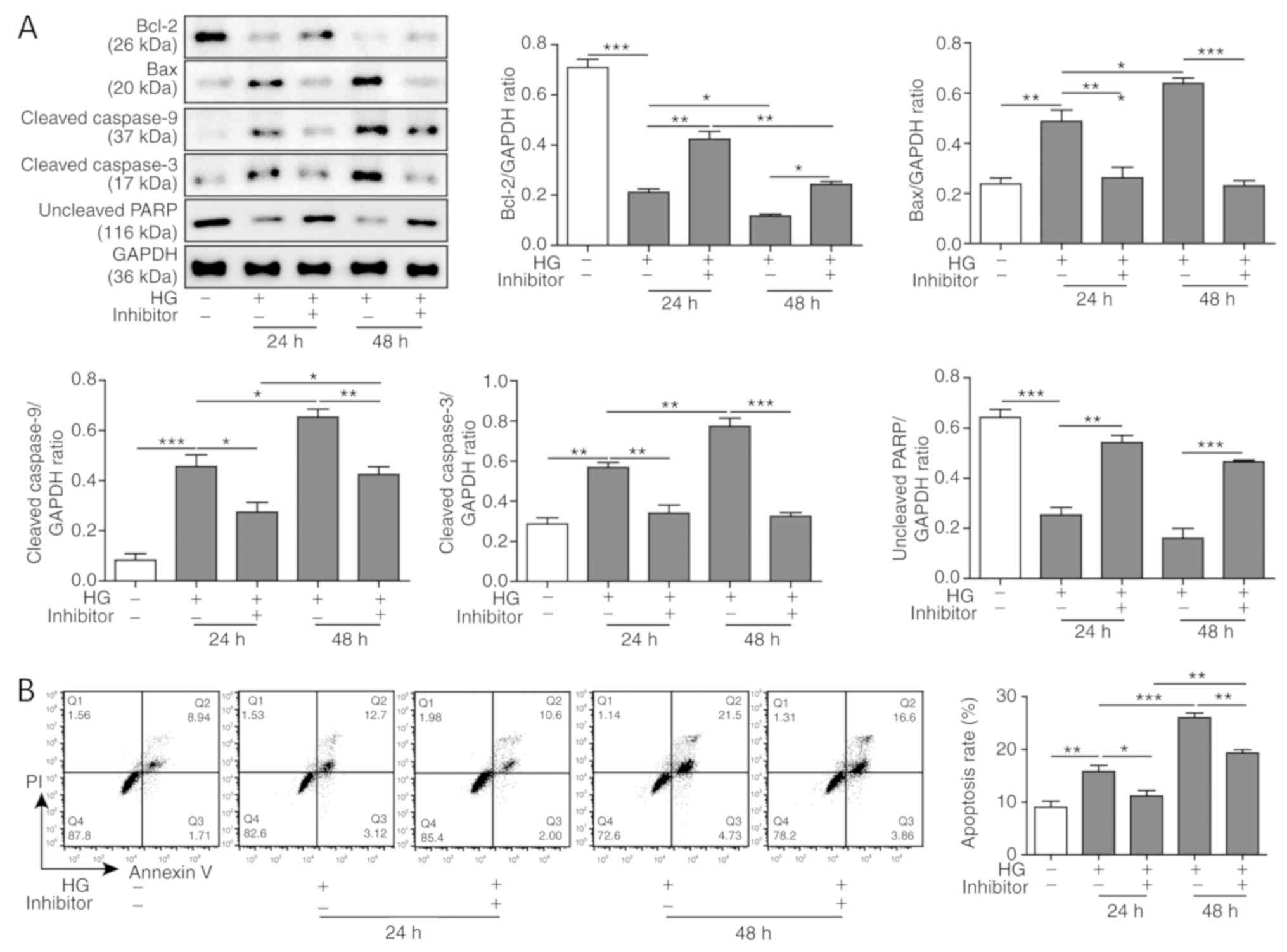
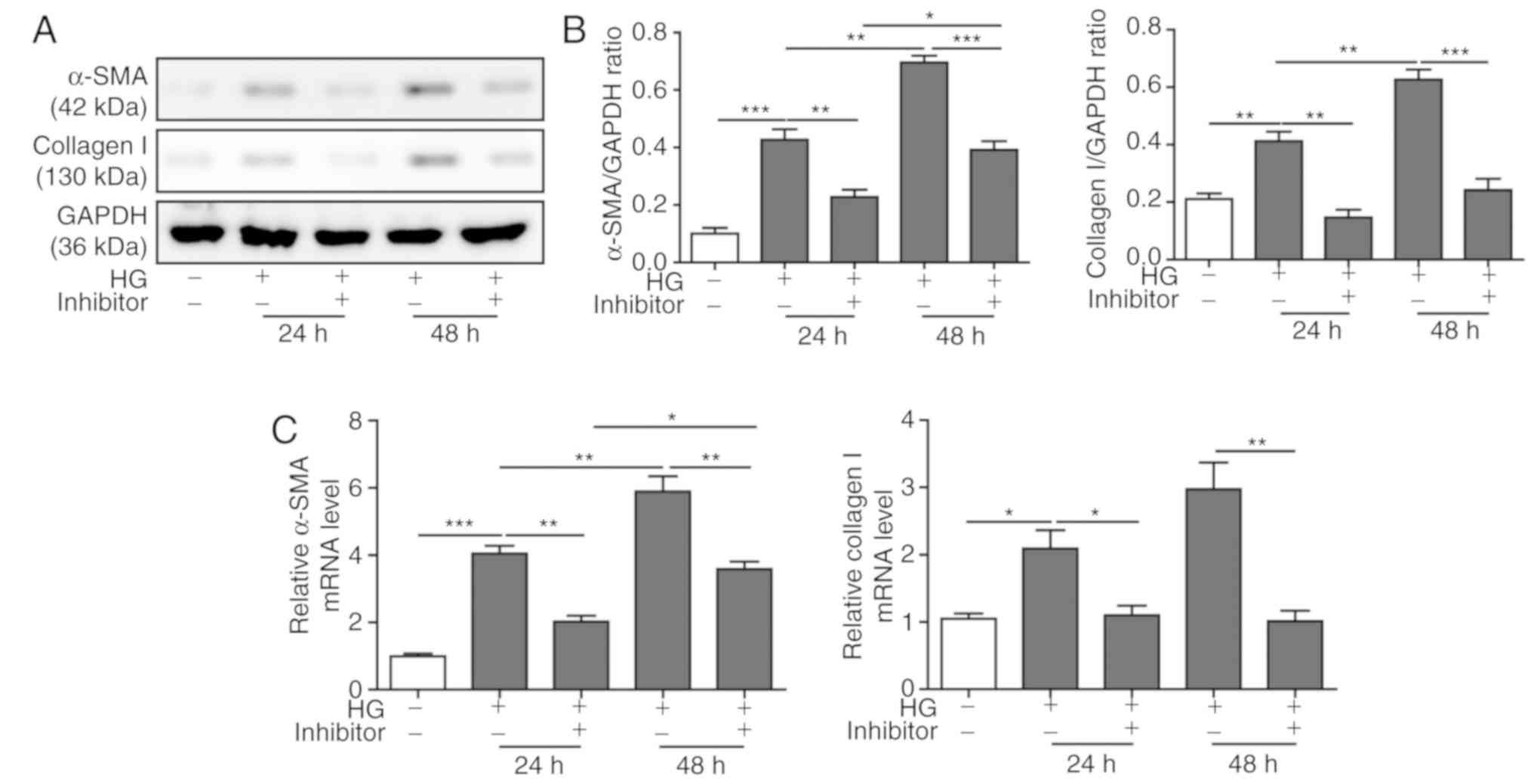
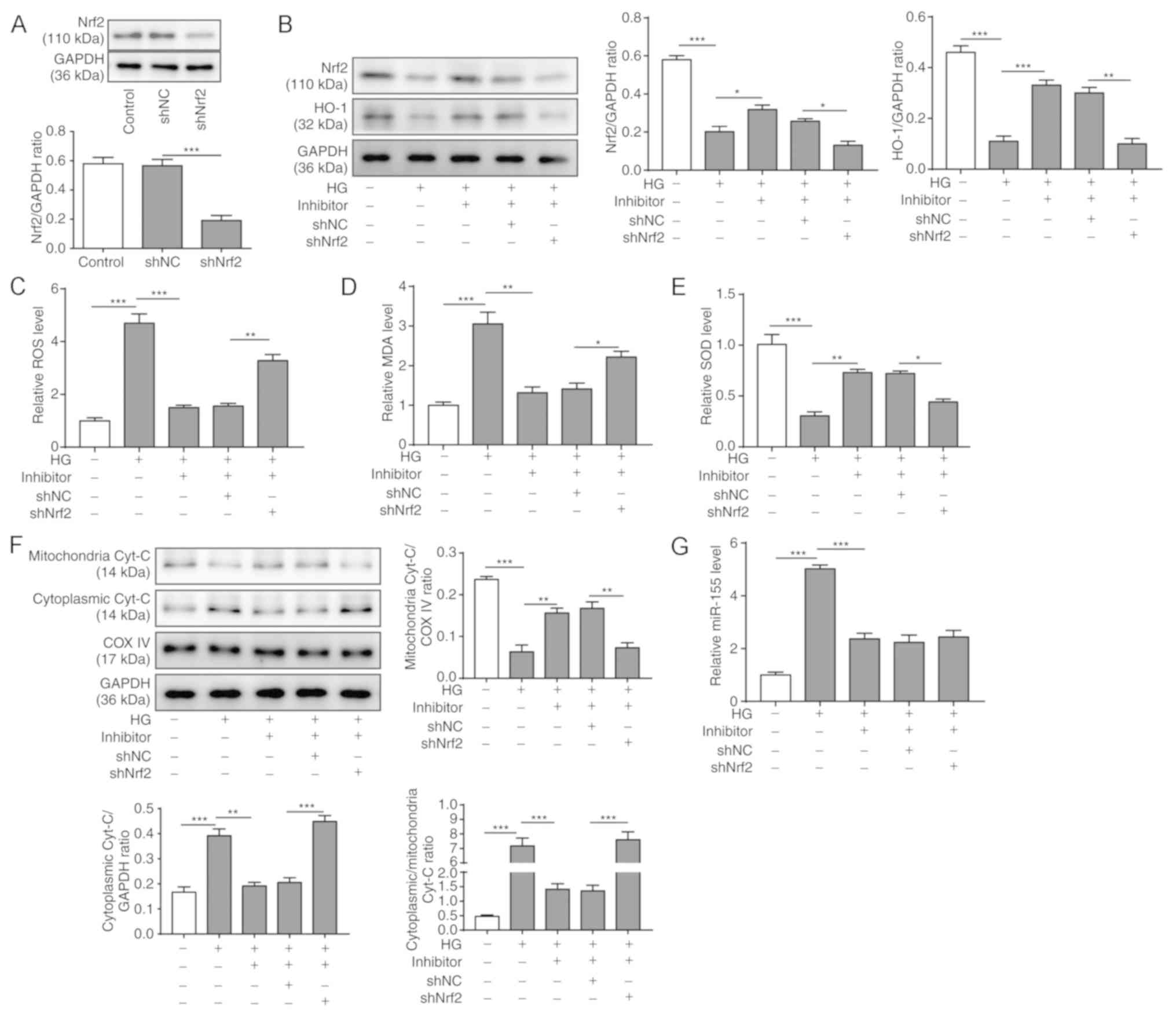
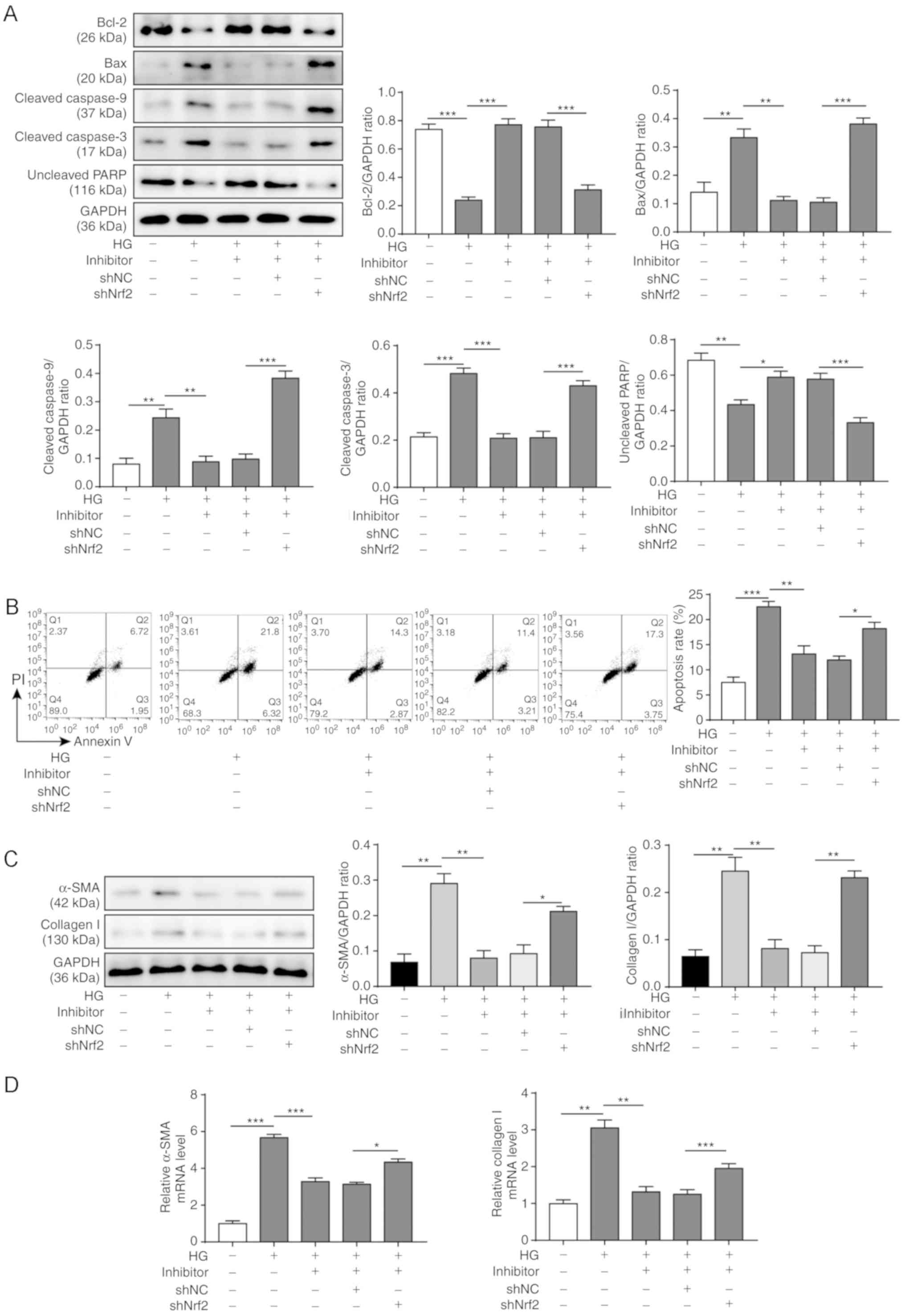
|
1
|
Worke LJ, Barthold JE, Seelbinder B, Novak
T, Main RP, Harbin SL and Neu CP: Densification of type I collagen
matrices as a model for cardiac fibrosis. Adv Healthc Mater.
6:17001142017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Murtha LA, Schuliga MJ, Mabotuwana NS,
Hardy SA, Waters DW, Burgess JK, Knight DA and Boyle AJ: The
processes and mechanisms of cardiac and pulmonary fibrosis. Front
Physiol. 8:7772017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Louridas GE and Lourida KG: Systems
biology and biomechanical model of heart failure. Curr Cardiol Rev.
8:220–230. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang WW, Bai F, Wang J, Zheng RH, Yang
LW, James EA and Zhao ZQ: Edaravone inhibits pressure
overload-induced cardiac fibrosis and dysfunction by reducing
expression of angiotensin II AT1 receptor. Drug Des Devel Ther.
11:3019–3033. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Michael LH, Taffet GE, Entman ML, Reddy
AK, Hartley CJ and Frangogiannis NG: Chapter 2.6-The Cardiovascular
System. The Laboratory Mouse. Second Edition. Hedrich HJ: Academic
Press; Boston: pp. 241–270. 2012, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Asbun J and Villarreal FJ: The
pathogenesis of myocardial fibrosis in the setting of diabetic
cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 47:693–700. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bharati S and Lev M: Cardiac conduction
system involvement in sudden death of obese young people. Am Heart
J. 129:273–281. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dei Cas A, Khan SS, Butler J, Mentz RJ,
Bonow RO, Avogaro A, Tschoepe D, Doehner W, Greene SJ, Senni M, et
al: Impact of diabetes on epidemiology, treatment, and outcomes of
patients with heart failure. JACC Heart Fail. 3:136–145. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wei Y, Yan X, Yan L, Hu F, Ma W, Wang Y,
Lu S, Zeng Q and Wang Z: Inhibition of microRNA-155 ameliorates
cardiac fibrosis in the process of angiotensin II-induced cardiac
remodeling. Mol Med Rep. 16:7287–7296. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Quiat D and Olson EN: MicroRNAs in
cardiovascular disease: From pathogenesis to prevention and
treatment. J Clin Invest. 123:11–18. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang D, Cui Y, Li B, Luo X, Li B and Tang
Y: miR-155 regulates high glucose-induced cardiac fibrosis via the
TGF-β signaling pathway. Mol Biosyst. 13:215–224. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Seok HY, Chen J, Kataoka M, Huang ZP, Ding
J, Yan J, Hu X and Wang DZ: Loss of MicroRNA-155 protects the heart
from pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Circ Res. 114:1585–1595.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tran PL, Tran PT, Tran HNK, Lee S, Kim O,
Min BS and Lee JH: A prenylated flavonoid, 10-oxomornigrol F,
exhibits anti-inflammatory effects by activating the Nrf2/heme
oxygenase-1 pathway in macrophage cells. Int Immunopharmacol.
55:165–173. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen RR, Fan XH, Chen G, Zeng GW, Xue YG,
Liu XT and Wang C: Irisin attenuates angiotensin II-induced cardiac
fibrosis via Nrf2 mediated inhibition of ROS/ TGFβ1/Smad2/3
signaling axis. Chem Biol Interact. 302:11–21. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Meng Z, Li HY, Si CY, Liu YZ and Teng S:
Asiatic acid inhibits cardiac fibrosis throughNrf2/HO-1 and
TGF-β1/Smads signaling pathways in spontaneous hypertension rats.
Int Immunopharmacol. 74:1057122019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jeong JY, Cha HJ, Choi EO, Kim CH, Kim GY,
Yoo YH, Hwang HJ, Park HT, Yoon HM and Choi YH: Activation of the
Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway contributes to the protective effects
of baicalein against oxidative stress-induced DNA damage and
apoptosis in HEI193 Schwann cells. Int J Med Sci. 16:145–155. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Abraham NG and Kappas A: Heme oxygenase
and the cardiovascular-renal system. Free Radic Biol Med. 39:1–25.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen M, Samuel VP, Wu Y, Dang M, Lin Y,
Sriramaneni R, Sah SK, Chinnaboina GK and Zhang G: Nrf2/HO-1
mediated protective activity of genistein against
doxorubicin-induced cardiac toxicity. J Environ Pathol Toxicol
Oncol. 38:143–152. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen C, Jiang X, Gu S and Zhang Z:
MicroRNA-155 regulates arsenite-induced malignant transformation by
targeting Nrf2-mediated oxidative damage in human bronchial
epithelial cells. Toxicol Lett. 278:38–47. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wan C, Han R, Liu L, Zhang F, Li F, Xiang
M and Ding W: Role of miR-155 in fluorooctane sulfonate-induced
oxidative hepatic damage via the Nrf2-dependent pathway. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 295:85–93. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gu S, Lai Y, Chen H, Liu Y and Zhang Z:
miR-155 mediates arsenic trioxide resistance by activating Nrf2 and
suppressing apoptosis in lung cancer cells. Sci Rep. 7:121552017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hu M, Ye P, Liao H, Chen M and Yang F:
Metformin protects H9C2 cardiomyocytes from high-glucose and
hypoxia/reoxygenation injury via inhibition of reactive oxygen
species generation and inflammatory responses: Role of AMPK and
JNK. J Diabetes Res. 2016:29619542016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bugyei-Twum A, Advani A, Advani SL, Zhang
Y, Thai K, Kelly DJ and Connelly KA: High glucose induces Smad
activation via the transcriptional coregulator p300 and contributes
to cardiac fibrosis and hypertrophy. Cardiovasc Diabetol.
13:892014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ahmad A and Abdel Moneim AE: Indigofera
oblongifolia prevents lead acetate-induced hepatotoxicity,
oxidative stress, fibrosis and apoptosis in rats. PLoS One.
11:e01589652016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hüttemann M, Pecina P, Rainbolt M,
Sanderson TH, Kagan VE, Samavati L, Doan JW and Lee I: The multiple
functions of cytochrome c and their regulation in life and death
decisions of the mammalian cell: From respiration to apoptosis.
Mitochondrion. 11:369–381. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Garrido C, Galluzzi L, Brunet M, Puig PE,
Didelot C and Kroemer G: Mechanisms of cytochrome c release from
mitochondria. Cell Death Differ. 13:1423–1433. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tsutsui H, Kinugawa S and Matsushima S:
Mitochondrial oxidative stress and dysfunction in myocardial
remodelling. Cardiovasc Res. 81:449–456. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Opferman JT and Kothari A: Anti-apoptotic
BCL-2 family members in development. Cell Death Differ. 25:37–45.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Czabotar PE, Lessene G, Strasser A and
Adams JM: Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family:
Implications for physiology and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
15:49–63. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ma ZG, Yuan YP, Wu HM, Zhang X and Tang
QZ: Cardiac fibrosis: New insights into the pathogenesis. Int J
Biol Sci. 14:1645–1657. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fang L, Murphy AJ and Dart AM: A Clinical
perspective of anti-fibrotic therapies for cardiovascular disease.
Front Pharmacol. 8:186. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Brahma MK, Pepin ME and Wende AR: My
sweetheart is broken: Role of glucose in diabetic cardiomyopathy.
Diabetes Metab J. 41:1–9. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Costantino S, Paneni F, Lüscher TF and
Cosentino F: MicroRNA profiling unveils hyperglycaemic memory in
the diabetic heart. Eur Heart J. 37:572–576. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huang Y, Liu Y, Li L, Su B, Yang L, Fan W,
Yin Q, Chen L, Cui T, Zhang J, et al: Involvement of
inflammation-related miR-155 and miR-146a in diabetic nephropathy:
implications for glomerular endothelial injury. BMC Nephrol.
15:1422014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gao J, Zhao G, Li W, Zhang J, Che Y, Song
M, Gao S, Zeng B and Wang Y: miR-155 targets PTCH1 to mediate
endothelial progenitor cell dysfunction caused by high glucose. Exp
Cell Res. 366:55–62. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Palma CA, Al Sheikha D, Lim TK, Bryant A,
Vu TT, Jayaswal V and Ma DD: MicroRNA-155 as an inducer of
apoptosis and cell differentiation in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia. Mol
Cancer. 13:792014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Song Y, Wen L, Sun J, Bai W, Jiao R, Hu Y,
Peng X, He Y and Ou S: Cytoprotective mechanism of ferulic acid
against high glucose-induced oxidative stress in cardiomyocytes and
hepatocytes. Food Nutr Res. 60:303232016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
You S, Qian J, Sun C, Zhang H, Ye S, Chen
T, Xu Z, Wang J, Huang W and Liang G: An Aza resveratrol-chalcone
derivative 6b protects mice against diabetic cardiomyopathy by
alleviating inflammation and oxidative stress. J Cell Mol Med.
22:1931–1943. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ying Y, Jin J, Ye L, Sun P, Wang H and
Wang X: Phloretin prevents diabetic cardiomyopathy by dissociating
Keap1/Nrf2 complex and inhibiting oxidative stress. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9:7742018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li L, Luo W, Qian Y, Zhu W, Qian J, Li J,
Jin Y, Xu X and Liang G: Luteolin protects against diabetic
cardiomyopathy by inhibiting NF-κB-mediated inflammation and
activating the Nrf2-mediated antioxidant responses. Phytomedicine.
59:1527742019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tsai CY, Wen SY, Cheng SY, Wang CH, Yang
YC, Viswanadha VP, Huang CY and Kuo WW: Nrf2 activation as a
protective feedback to limit cell death in high glucose-exposed
cardiomyocytes. J Cell Biochem. 118:1659–1669. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhou L, Xu DY, Sha WG, Shen L, Lu GY, Yin
X and Wang MJ: High glucose induces renal tubular epithelial injury
via Sirt1/NF-kappaB/microR-29/Keap1 signal pathway. J Transl Med.
13:3522015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yang ZB, Chen WW, Chen HP, Cai SX, Lin JD
and Qiu LZ: MiR-155 aggravated septic liver injury by oxidative
stress-mediated ER stress and mitochondrial dysfunction via
targeting Nrf-2. Exp Mol Pathol. 105:387–394. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chen J, Li C, Liu W, Yan B, Hu X and Yang
F: miRNA-155 silencing reduces sciatic nerve injury in diabetic
peripheral neuropathy. J Mol Endocrinol. 63:227–238. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kosuru R, Kandula V, Rai U, Prakash S, Xia
Z and Singh S: Pterostilbene decreases cardiac oxidative stress and
inflammation via activation of AMPK/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in
fructose-fed diabetic rats. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 32:147–163.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Holmström KM, Kostov RV and
Dinkova-Kostova AT: The multifaceted role of Nrf2 in mitochondrial
function. Curr Opin Toxicol. 1:80–91. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Liang J, Li L, Sun Y, He W, Wang X and Su
Q: The protective effect of activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
on cardiomyocyte apoptosis after coronary microembolization in
rats. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 17:2722017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhang YF, Meng NN, Li HZ, Wen YJ, Liu JT,
Zhang CL, Yuan XH and Jin XD: Effect of naringin on oxidative
stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress in diabetic cardiomyopathy.
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 43:596–602. 2018.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Peng C, Ma J, Gao X, Tian P, Li W and
Zhang L: High glucose induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in
cardiac microvascular endothelial cells are regulated by FoxO3a.
PLoS One. 8:e797392013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wang R, Lu L, Guo Y, Lin F, Chen H, Chen W
and Chen M: Effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 on
high-glucose-induced oxidative stress and cell apoptosis in human
endothelial cells and its underlying mechanism. J Cardiovasc
Pharmacol. 66:135–140. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhang M, Niu X, Hu J, Yuan Y, Sun S, Wang
J, Yu W, Wang C, Sun D and Wang H: Lin28a Protects against
hypoxia/reoxygenation induced cardiomyocytes apoptosis by
alleviating mitochondrial dysfunction under high glucose/high fat
conditions. PLoS One. 9:e1105802014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gao CL, Zhu C, Zhao YP, Chen XH, Ji CB,
Zhang CM, Zhu JG, Xia ZK, Tong ML and Guo XR: Mitochondrial
dysfunction is induced by high levels of glucose and free fatty
acids in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 320:25–33. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Hung KY, Liu SY, Yang TC, Liao TL and Kao
SH: High-dialysate-glucose-induced oxidative stress and
mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis in human peritoneal mesothelial
cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014:642793. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ho FM, Liu SH, Liau CS, Huang PJ and
Lin-Shiau SY: High glucose-induced apoptosis in human endothelial
cells is mediated by sequential activations of c-Jun NH(2)-terminal
kinase and caspase-3. Circulation. 101:2618–2624. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Liu J, Wu Y, Wang B, Yuan X and Fang B:
High levels of glucose induced the caspase-3/PARP signaling
pathway, leading to apoptosis in human periodontal ligament
Fibroblasts. Cell Biochem Biophys. 66:229–237. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yang LL, Liu JQ, Bai XZ, Fan L, Han F, Jia
WB, Su LL, Shi JH, Tang CW and Hu DH: Acute downregulation of
miR-155 at wound sites leads to a reduced fibrosis through
attenuating inflammatory response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
453:153–159. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|