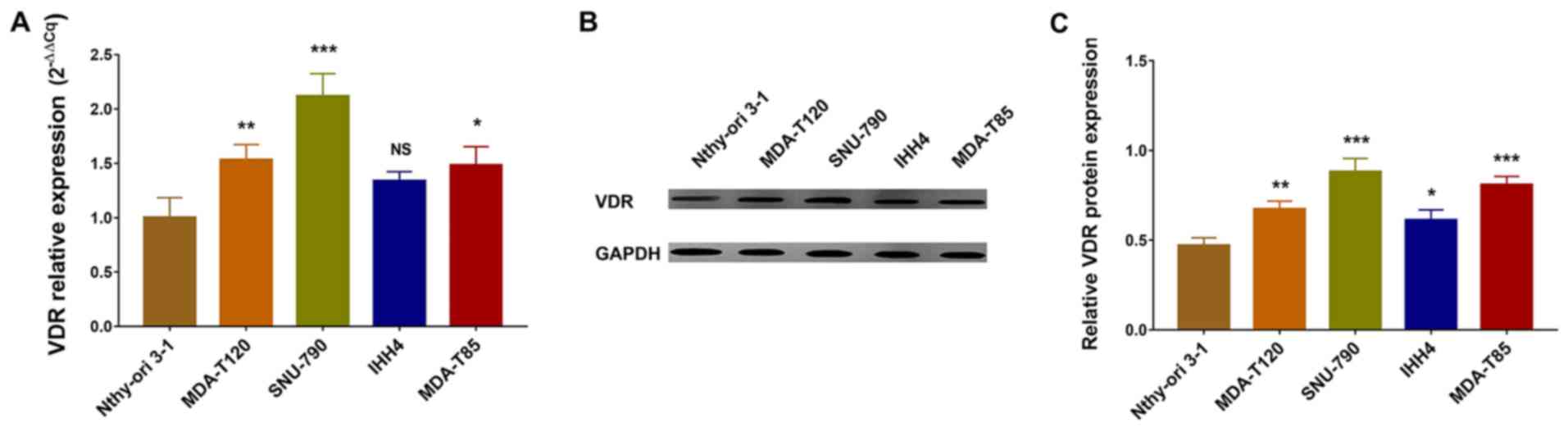
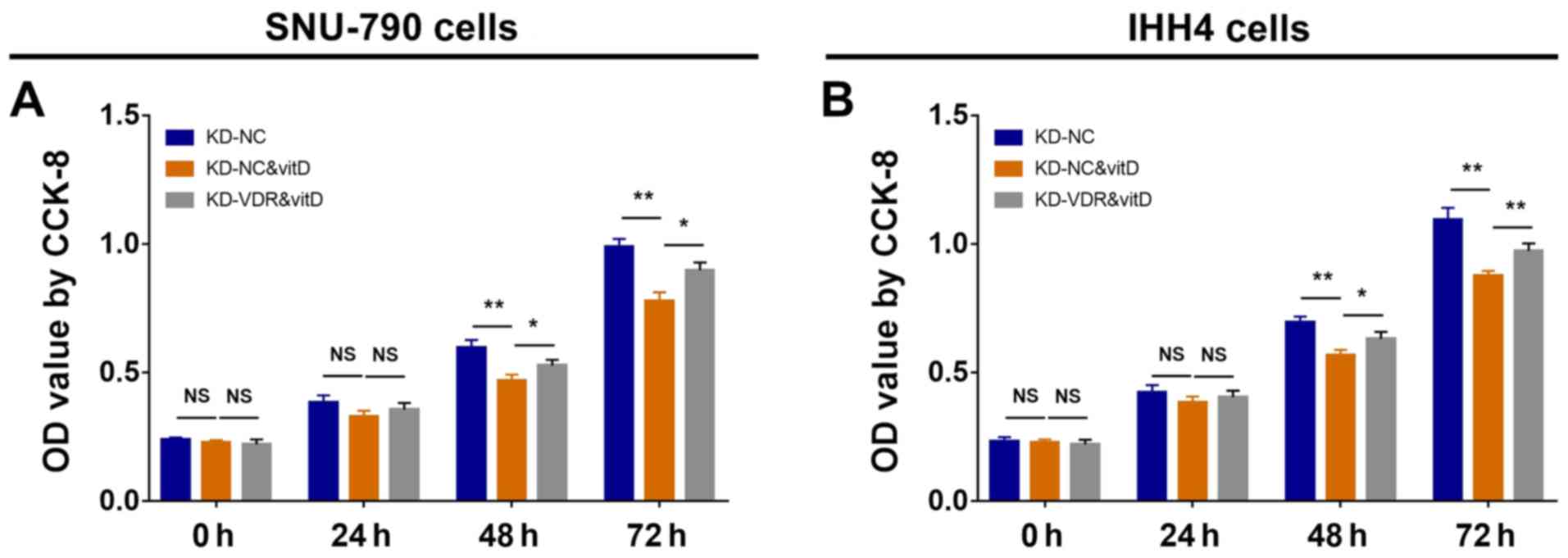
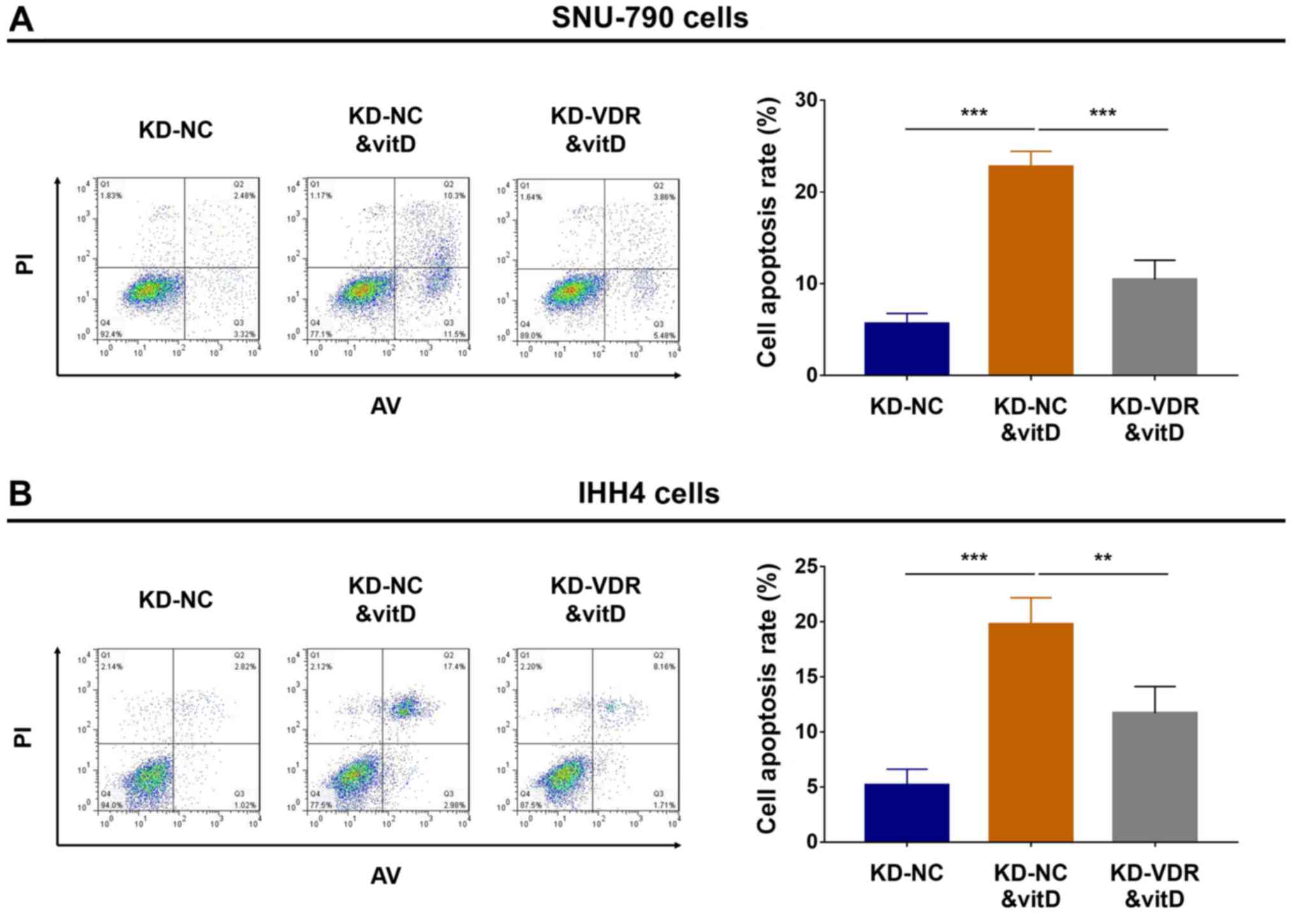
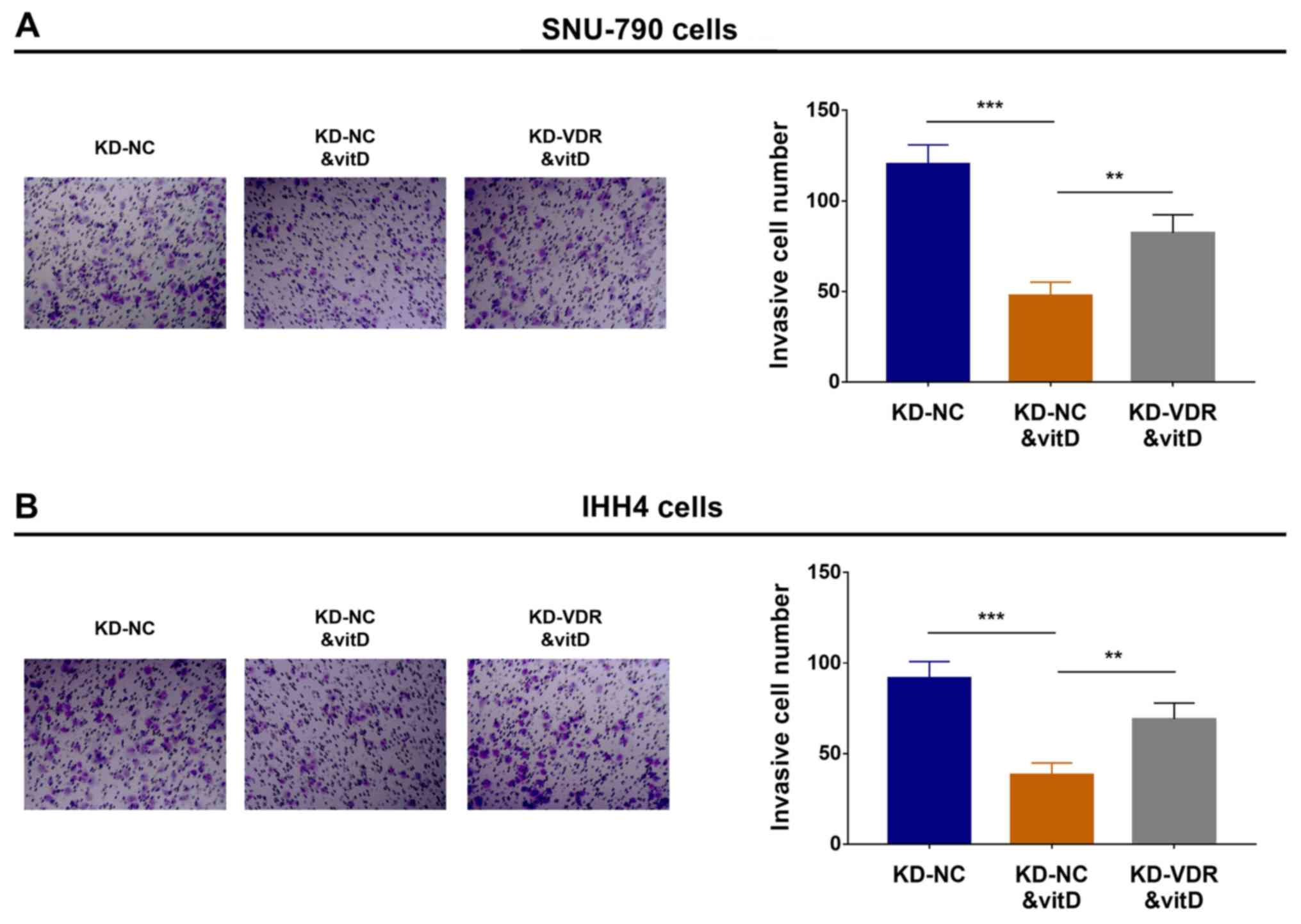
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang J, Yu F, Shang Y, Ping Z and Liu L:
Thyroid cancer: Incidence and mortality trends in China, 2005–2015.
Endocrine. 68:163–173. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Haddad RI, Nasr C, Bischoff L, Busaidy NL,
Byrd D, Callender G, Dickson P, Duh QY, Ehya H, Goldner W, et al:
NCCN Guidelines insights: Thyroid carcinoma, version 2.2018. J Natl
Compr Canc Netw. 16:1429–1440. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kim HI, Jang HW, Ahn HS, Ahn S, Park SY,
Oh YL, Hahn SY, Shin JH, Kim JH, Kim JS, et al: High serum TSH
level is associated with progression of papillary thyroid
microcarcinoma during active surveillance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
103:446–451. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Amouri W, Charfeddine S, Charfi S, Jardak
I, Boudawara T and Guermazi F: Clinicopathological features and
outcomes after radioactive iodine treatment of oncocytic
well-differentiated thyroid carcinomas. Nucl Med Commun.
40:888–893. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Price AK, Randle RW, Schneider DF, Sippel
RS and Pitt SC: Papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: Decision-making,
extent of surgery, and outcomes. J Surg Res. 218:237–245. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee YC, Na SY, Park GC, Han JH, Kim SW and
Eun YG: Occult lymph node metastasis and risk of regional
recurrence in papillary thyroid cancer after bilateral prophylactic
central neck dissection: A multi-institutional study. Surgery.
161:465–471. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Uitterlinden AG, Fang Y, Van Meurs JB,
Pols HA and Van Leeuwen JP: Genetics and biology of vitamin D
receptor polymorphisms. Gene. 338:143–156. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bizzaro G, Antico A, Fortunato A and
Bizzaro N: Vitamin D and autoimmune diseases: Is Vitamin D receptor
(VDR) polymorphism the culprit? Isr Med Assoc J. 19:438–443.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hewison M: Vitamin D and the
intracrinology of innate immunity. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
321:103–111. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huss L, Butt ST, Borgquist S, Elebro K,
Sandsveden M, Rosendahl A and Manjer J: Vitamin D receptor
expression in invasive breast tumors and breast cancer survival.
Breast Cancer Res. 21:842019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li M, Liu X, Liu N, Yang T, Shi P, He R
and Chen M: Association between polymorphisms of Vitamin D receptor
and lung cancer susceptibility: Evidence from an updated
Meta-analysis. J Cancer. 10:3639–3649. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Joanna B, Jolanta B, Agnieszka G, Diana HZ
and Krystyna S: Vitamin D, linoleic acid, arachidonic acid and
COX-2 in colorectal cancer patients in relation to disease stage,
tumour localisation and disease progression. Arab J Gastroenterol.
20:121–126. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Trump DL and Aragon-Ching JB: Vitamin D in
prostate cancer. Asian J Androl. 20:244–252. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Feldman D, Krishnan AV, Swami S,
Giovannucci E and Feldman BJ: The role of vitamin D in reducing
cancer risk and progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:342–357. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Skrajnowska D and Bobrowska-Korczak B:
Potential Molecular Mechanisms of the Anti-cancer Activity of
Vitamin D. Anticancer Res. 39:3353–3363. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Al-Hendy A, Diamond MP, Boyer TG and
Halder SK: Vitamin D3 inhibits Wnt/β-catenin and mTOR signaling
pathways in human uterine fibroid cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
101:1542–1551. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Samuel S and Sitrin MD: Vitamin Ds role in
cell proliferation and differentiation. Nutr Rev. 66 (Suppl
2):S116–S124. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang T, Zhang H, He L, Wang Z, Dong W,
Sun W and Zhang P: Potential use of 1–25-dihydroxyvitamin D in the
diagnosis and treatment of papillary thyroid cancer. Med Sci Monit.
24:1614–1623. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Izkhakov E, Somjen D, Sharon O, Knoll E,
Aizic A, Fliss DM, Limor R and Stern N: Vitamin D receptor
expression is linked to potential markers of human thyroid
papillary carcinoma. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 159:26–30. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang J, Gill AJ, Issacs JD, Atmore B,
Johns A, Delbridge LW, Lai R and McMullen TP: The Wnt/β-catenin
pathway drives increased cyclin D1 levels in lymph node metastasis
in papillary thyroid cancer. Hum Pathol. 43:1044–1050. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang Y, Huang H, Hu F, Li J, Zhang L and
Pang H: CITED1 contributes to the progression of papillary thyroid
carcinoma via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Onco Targets
Ther. 12:6769–6777. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tomas G, Tarabichi M, Gacquer D, Hebrant
A, Dom G, Dumont JE, Keutgen X, Fahey TJ III, Maenhaut C and
Detours V: A general method to derive robust organ-specific gene
expression-based differentiation indices: Application to thyroid
cancer diagnostic. Oncogene. 31:4490–4498. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Giordano TJ, Kuick R, Thomas DG, Misek DE,
Vinco M, Sanders D, Zhu Z, Ciampi R, Roh M, Shedden K, et al:
Molecular classification of papillary thyroid carcinoma: Distinct
BRAF, RAS, and RET/PTC mutation-specific gene expression profiles
discovered by DNA microarray analysis. Oncogene. 24:6646–6656.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
He H, Jazdzewski K, Li W, Liyanarachchi S,
Nagy R, Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Franssila K, Suster S, et al:
The role of microRNA genes in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:19075–19080. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhu X, Yao J and Tian W: Microarray
technology to investigate genes associated with papillary thyroid
carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 11:3729–3733. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tagliabue E, Raimondi S and Gandini S:
Vitamin D, cancer risk, and mortality. Adv Food Nutr Res. 75:1–52.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Robsahm TE, Tretli S, Torjesen PA,
Babigumira R and Schwartz GG: Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels
predict cancer survival: A prospective cohort with measurements
prior to and at the time of cancer diagnosis. Clin Epidemiol.
11:695–705. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rohan JN and Weigel NL:
1Alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 reduces c-Myc expression, inhibiting
proliferation and causing G1 accumulation in C4-2 prostate cancer
cells. Endocrinology. 150:2046–2054. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Choi JY, Yi JW, Lee JH, Song RY, Yu H,
Kwon H, Chai YJ, Kim SJ and Lee KE: VDR mRNA overexpression is
associated with worse prognostic factors in papillary thyroid
carcinoma. Endocr Connect. 6:172–178. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu KH, Fu J, Zhou N, Yin W, Yang YY,
Ouyang SX and Liang YM: 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 prevents
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of HMrSV5 human peritoneal
mesothelial cells by inhibiting histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3) and
increasing Vitamin D receptor (VDR) expression through the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Med Sci Monit. 25:5892–5902. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Horas K, Zheng Y, Fong-Yee C, Macfarlane
E, Manibo J, Chen Y, Qiao J, Gao M, Haydar N, McDonald MM, et al:
Loss of the vitamin d receptor in human breast cancer cells
promotes epithelial to mesenchymal cell transition and skeletal
colonization. J Bone Miner Res. 34:1721–1732. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kim D: The role of Vitamin D in thyroid
diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 18:19492017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zheng Y, Trivedi T, Lin RC, Fong-Yee C,
Nolte R, Manibo J, Chen Y, Hossain M, Horas K, Dunstan C, et al:
Loss of the vitamin D receptor in human breast and prostate cancers
strongly induces cell apoptosis through downregulation of
Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Bone Res. 5:170232017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang X, Li M, Zuo K, Li D, Ye M, Ding L,
Cai H, Fu D, Fan Y and Lv Z: Upregulated miR-155 in papillary
thyroid carcinoma promotes tumor growth by targeting APC and
activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
98:E1305–E1313. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Welsh J: Vitamin D and breast cancer: Past
and present. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 177:15–20. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|