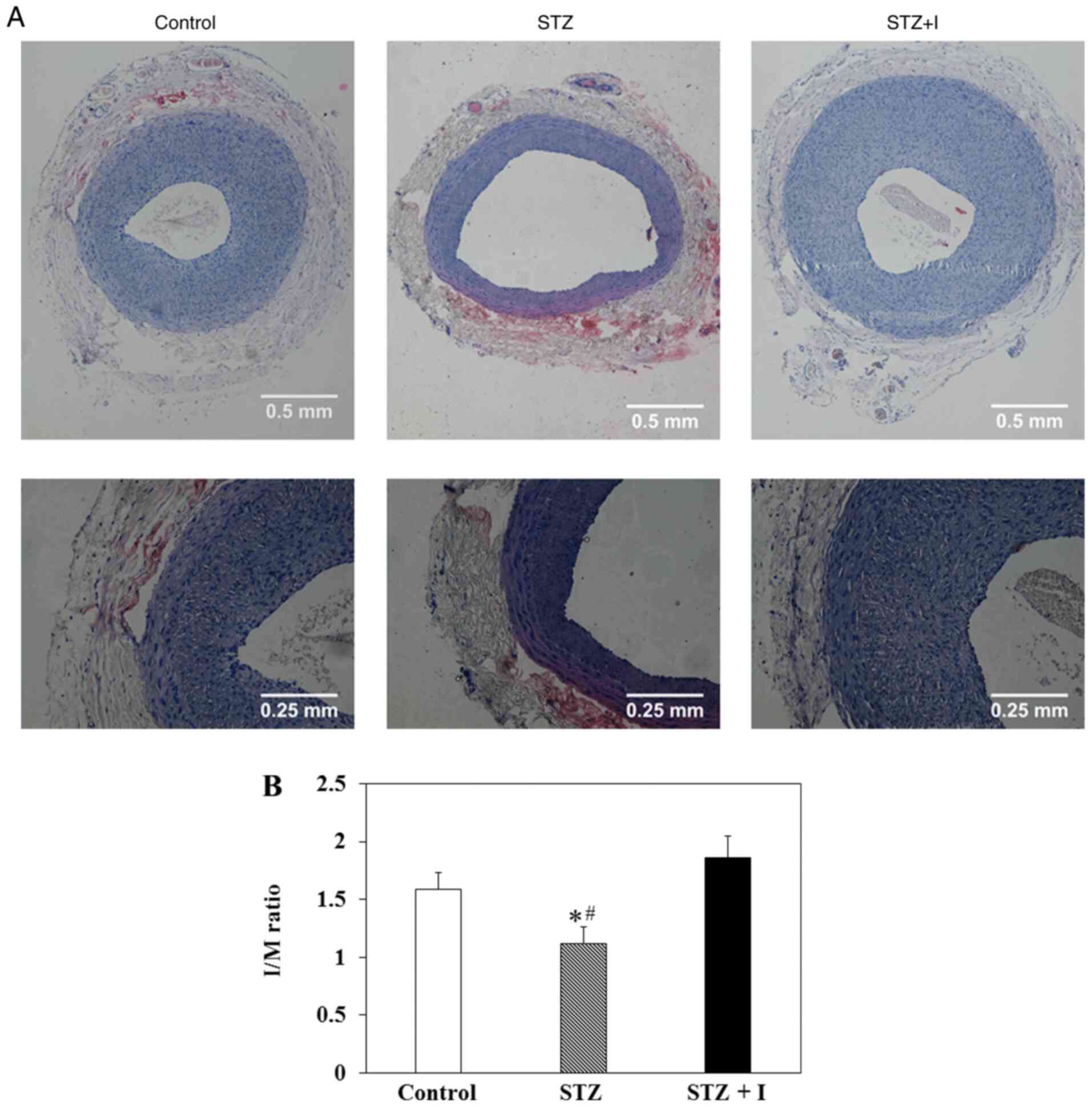
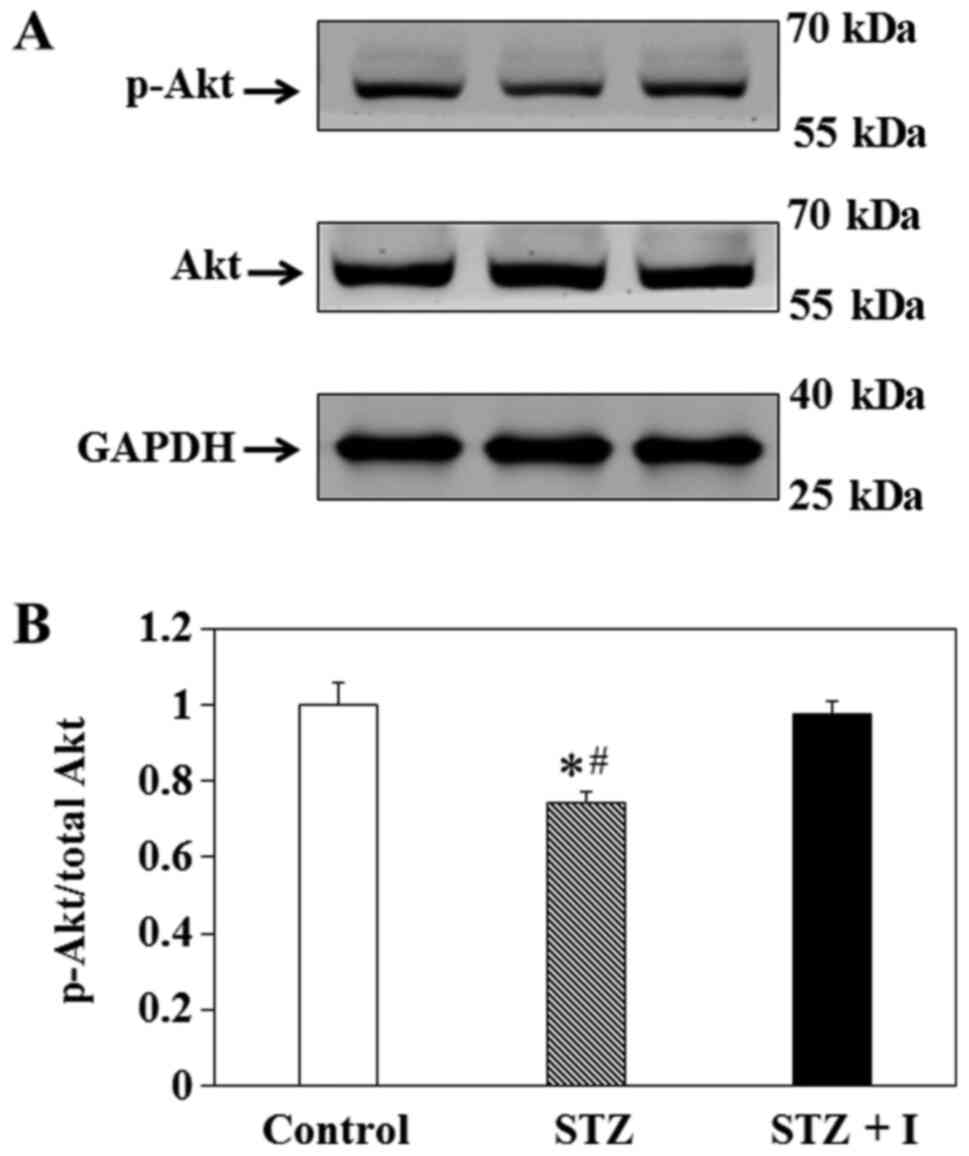
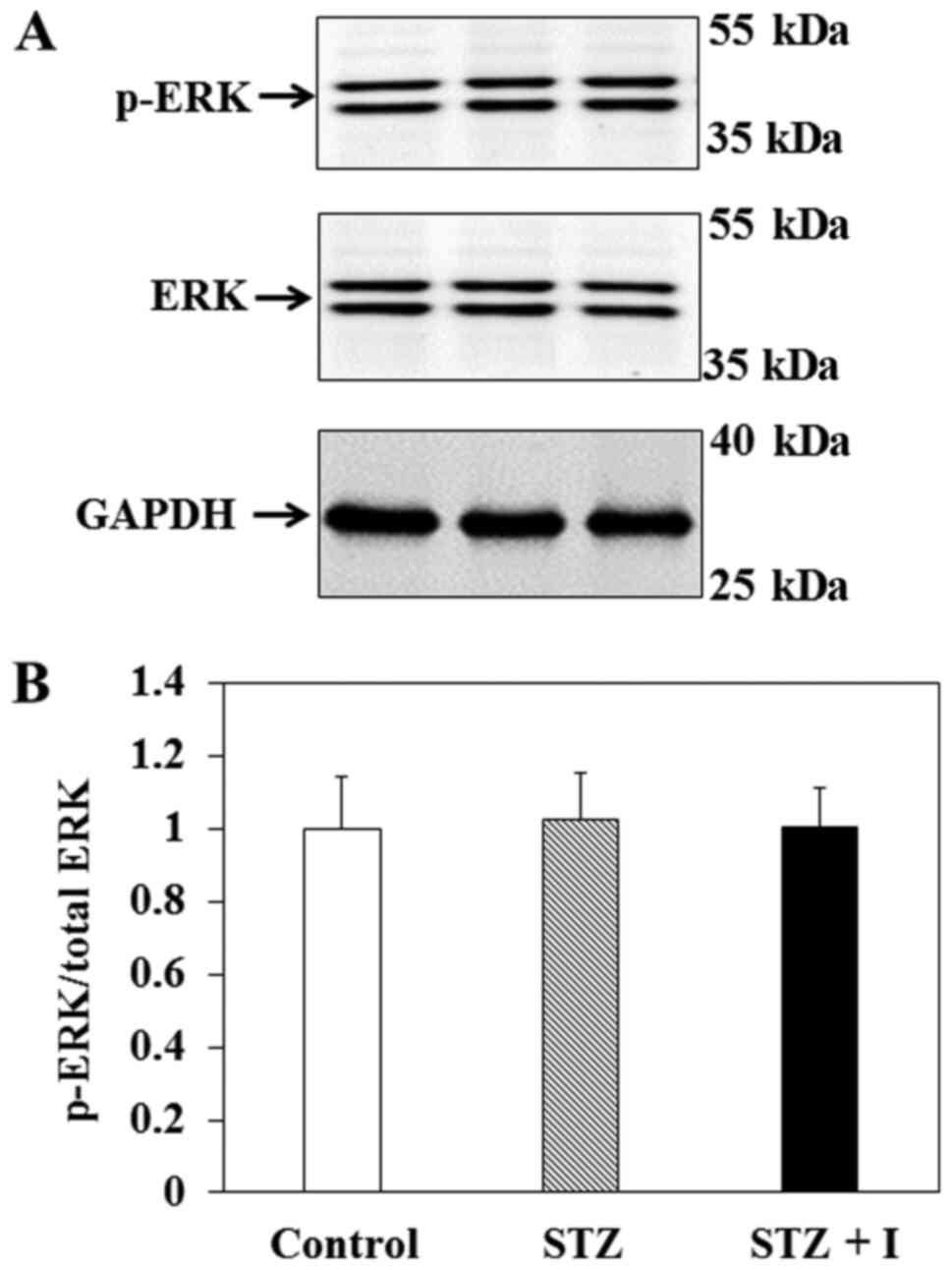
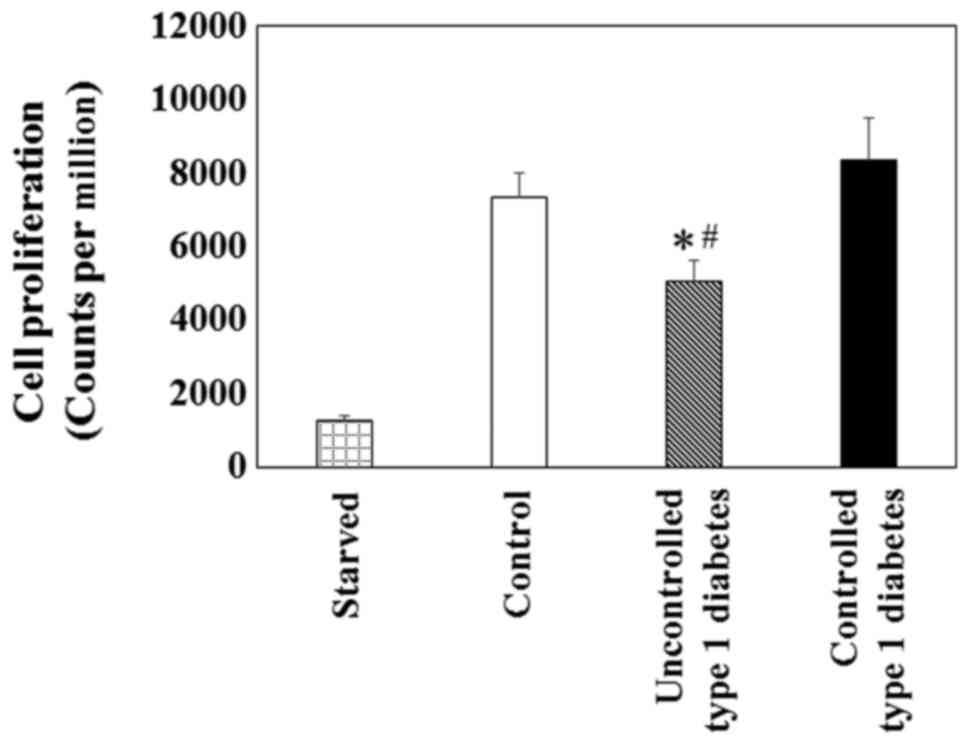
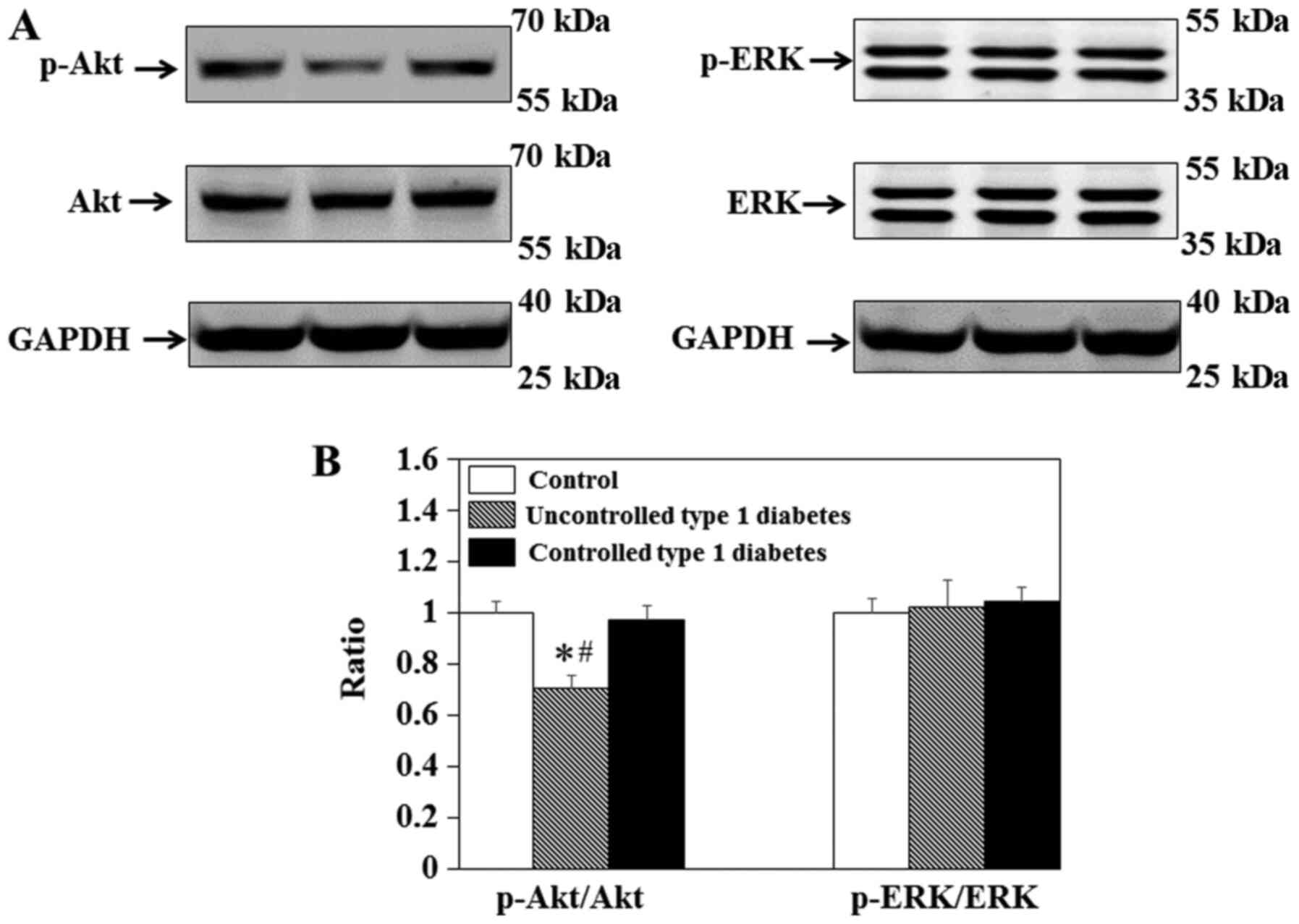
|
1
|
Narayan KM, Boyle JP, Thompson TJ,
Sorensen SW and Williamson DF: Lifetime risk for diabetes mellitus
in the United States. JAMA. 290:1884–1890. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Beckman JA, Creager MA and Libby P:
Diabetes and atherosclerosis: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and
management. JAMA. 287:2570–2581. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu X, Yu C, Wang Y, Bi Y, Liu Y and Zhang
ZJ: Trends in the incidence and mortality of diabetes in China from
1990 to 2017: A joinpoint and age-period-cohort analysis. Int J
Environ Res Public Health. 16:1582019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC),
. Worldwide trends in diabetes since 1980: A pooled analysis of 751
population-based studies with 4.4 million participants. Lancet.
387:1513–1530. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang G, Wang Y, Zeng Y, Gao GF, Liang X,
Zhou M, Wan X, Yu S, Jiang Y, Naghavi M, et al: Rapid health
transition in China, 1990–2010: Findings from the global burden of
disease study 2010. Lancet. 381:1987–2015. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu L, Wang D, Wong KS and Wang Y: Stroke
and stroke care in China: Huge burden, significant workload, and a
national priority. Stroke. 42:3651–3654. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sakai N and Sakai C: Current indication of
carotid diseases, CEA vs CAS. Nihon Geka Gakkai Zasshi. 111:75–78.
2010.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Varu VN, Ahanchi SS, Hogg ME,
Bhikhapurwala HA, Chen A, Popowich DA, Vavra AK, Martinez J, Jiang
Q, Saavedra JE, et al: Insulin enhances the effect of nitric oxide
at inhibiting neointimal hyperplasia in a rat model of type 1
diabetes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 299:H772–H779. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cao Y, Wang S, Sun W, Dai Q, Li W, Cai J,
Fan X, Zhu W, Xiong Y, Han Y, et al: Prediction of favorable
outcome by percent improvement in patients with acute ischemic
stroke treated with endovascular stent thrombectomy. J Clin
Neurosci. 38:100–105. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Park SH, Marso SP, Zhou Z, Foroudi F,
Topol EJ and Lincoff AM: Neointimal hyperplasia after arterial
injury is increased in a rat model of non-insulin-dependent
diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 104:815–819. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jonas M, Edelman ER, Groothuis A, Baker
AB, Seifert P and Rogers C: Vascular neointimal formation and
signaling pathway activation in response to stent injury in
insulin-resistant and diabetic animals. Circ Res. 97:725–733. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ahanchi SS, Varu VN, Tsihlis ND, Martinez
J, Pearce CG, Kapadia MR, Jiang Q, Saavedra JE, Keefer LK, Hrabie
JA and Kibbe MR: Heightened efficacy of nitric oxide-based
therapies in type II diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 295:H2388–H2398. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
White MF: Insulin signaling in health and
disease. Science. 302:1710–1711. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang CC, Gurevich I and Draznin B: Insulin
affects vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype and migration via
distinct signaling pathways. Diabetes. 52:2562–2569. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sang H, Qiu Z, Cai J, Lan W, Yu L, Zhang
H, Li M, Xie Y, Guo R, Ye R, et al: Early increased bradykinin 1
receptor contributes to hemorrhagic transformation after ischemic
stroke in type 1 diabetic rats. Transl Stroke Res. 8:597–611. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sang H, Liu L, Wang L, Qiu Z, Li M, Yu L,
Zhang H, Shi R, Yu S, Guo R, et al: Opposite roles of bradykinin B1
and B2 receptors during cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion injury in
experimental diabetic rats. Eur J Neurosci. 43:53–65. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kenny JD, Chemali JJ, Cotten JF, Van Dort
CJ, Kim SE, Ba D, Taylor NE, Brown EN and Solt K: Physostigmine and
methylphenidate induce distinct arousal states during isoflurane
general anesthesia in rats. Anesth Analg. 123:1210–1219. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shears LL II, Kibbe MR, Murdock AD,
Billiar TR, Lizonova A, Watkins SC and Tzeng E: Efficient
inhibition of intimal hyperplasia by adenovirus-mediated inducible
nitric oxide synthase gene transfer to rats and pigs in vivo. J Am
Coll Surg. 187:295–306. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li Z, Yu C, Han Y, Ren H, Shi W, Fu C, He
D, Huang L, Yang C, Wang X, et al: Inhibitory effect of D1-like and
D3 dopamine receptors on norepinephrine-induced proliferation in
vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
294:H2761–H2768. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou Y, Shi W, Luo H, Yue R, Wang Z, Wang
W, Liu L, Wang WE, Wang H and Zeng C: Inhibitory effect of D1-like
dopamine receptors on neuropeptide Y-induced proliferation in
vascular smooth muscle cells. Hypertens Res. 38:807–812. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Torella D, Iaconetti C, Tarallo R, Marino
F, Giurato G, Veneziano C, Aquila I, Scalise M, Mancuso T,
Cianflone E, et al: miRNA regulation of the hyperproliferative
phenotype of vascular smooth muscle cells in diabetes. Diabetes.
67:2554–2568. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cai J, Han Y, Ren H, Chen C, He D, Zhou L,
Eisner GM, Asico LD, Jose PA and Zeng C: Extracellular
vesicle-mediated transfer of donor genomic DNA to recipient cells
is a novel mechanism for genetic influence between cells. J Mol
Cell Biol. 5:227–238. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu G, Cai J, Han Y, Chen J, Huang ZP, Chen
C, Cai Y, Huang H, Yang Y, Liu Y, et al: LincRNA-p21 regulates
neointima formation, vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation,
apoptosis, and atherosclerosis by enhancing p53 activity.
Circulation. 130:1452–1465. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gong Z, Han Y, Wu L, Xia T, Ren H, Yang D,
Gu D, Wang H, Hu C, He D, et al: Translocator protein 18 kDa ligand
alleviates neointimal hyperplasia in the diabetic rat artery injury
model via activating PKG. Life Sci. 221:72–82. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zeng G, Nystrom FH, Ravichandran LV, Cong
LN, Kirby M, Mostowski H and Quon MJ: Roles for insulin receptor,
PI3-kinase, and Akt in insulin-signaling pathways related to
production of nitric oxide in human vascular endothelial cells.
Circulation. 101:1539–1545. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kuboki K, Jiang ZY, Takahara N, Ha SW,
Igarashi M, Yamauchi T, Feener EP, Herbert TP, Rhodes CJ and King
GL: Regulation of endothelial constitutive nitric oxide synthase
gene expression in endothelial cells and in vivo: A specific
vascular action of insulin. Circulation. 101:676–681. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Montagnani M, Chen H, Barr VA and Quon MJ:
Insulin-stimulated activation of eNOS is independent of
Ca2+ but requires phosphorylation by Akt at Ser(1179). J
Biol Chem. 276:30392–30398. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Indolfi C, Torella D, Cavuto L, Davalli
AM, Coppola C, Esposito G, Carriero MV, Rapacciuolo A, Di Lorenzo
E, Stabile E, et al: Effects of balloon injury on neointimal
hyperplasia in streptozotocin-induced diabetes and in
hyperinsulinemic nondiabetic pancreatic islet-transplanted rats.
Circulation. 103:2980–2986. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhuang D, Pu Q, Ceacareanu B, Chang Y,
Dixit M and Hassid A: Chronic insulin treatment amplifies
PDGF-induced motility in differentiated aortic smooth muscle cells
by suppressing the expression and function of PTP1B. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 295:H163–H173. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|