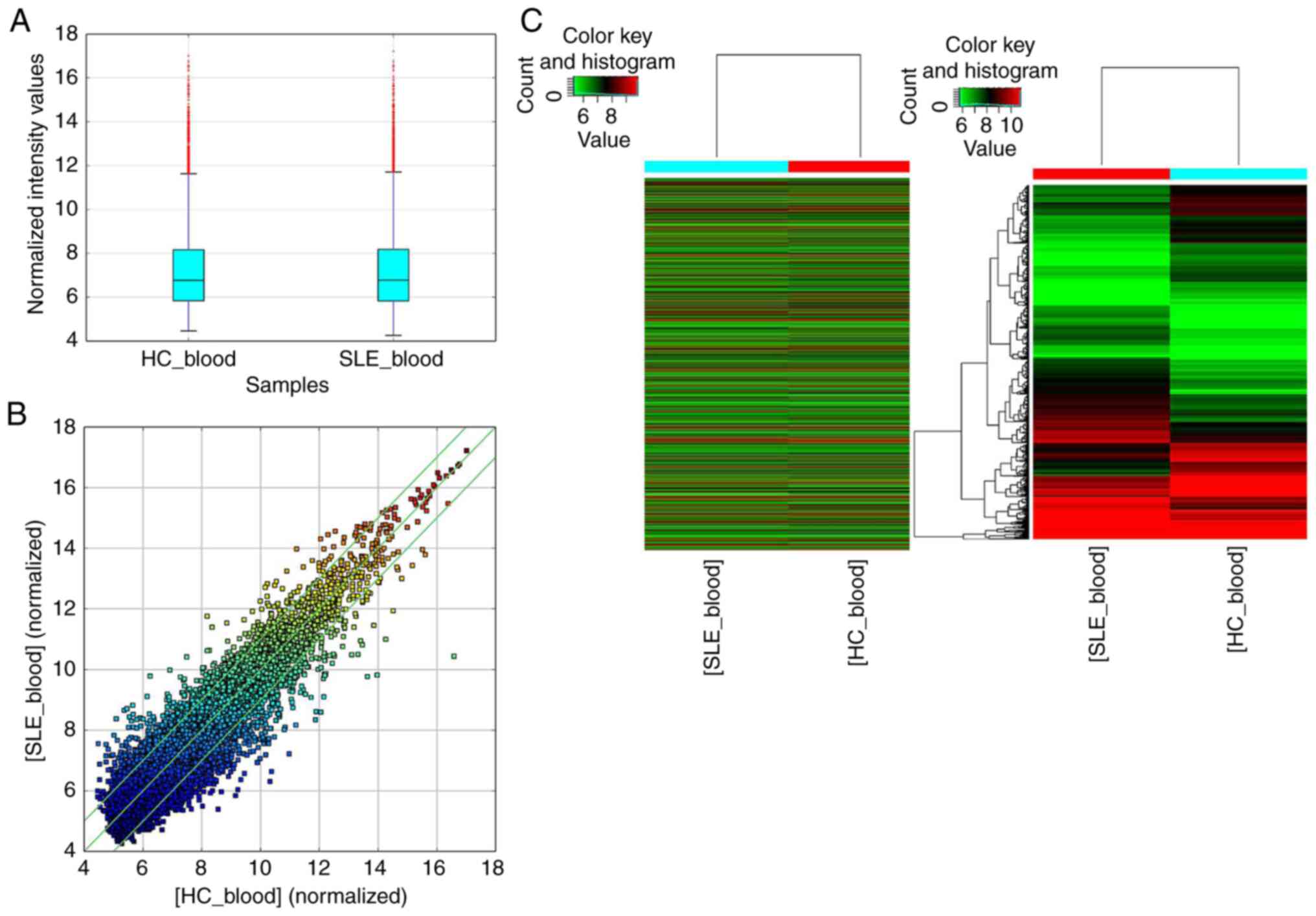
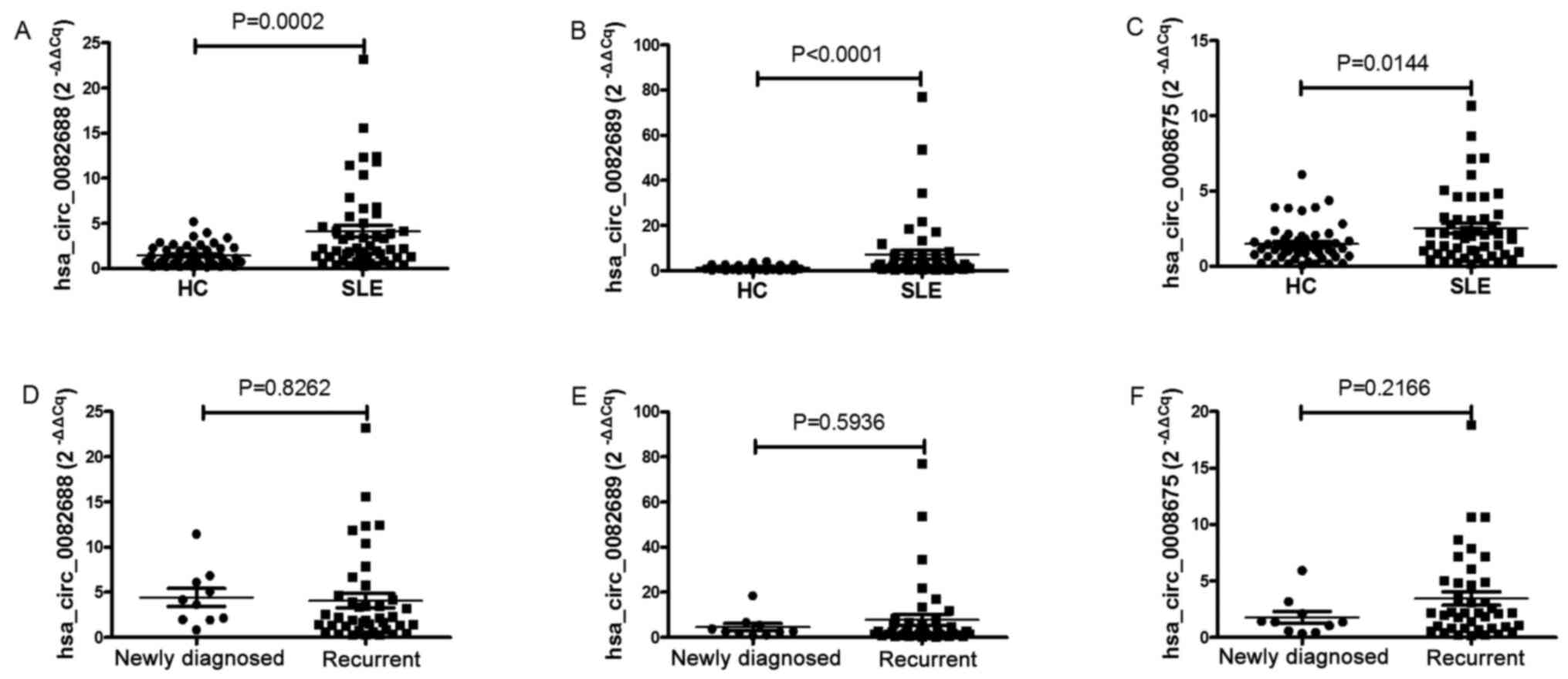
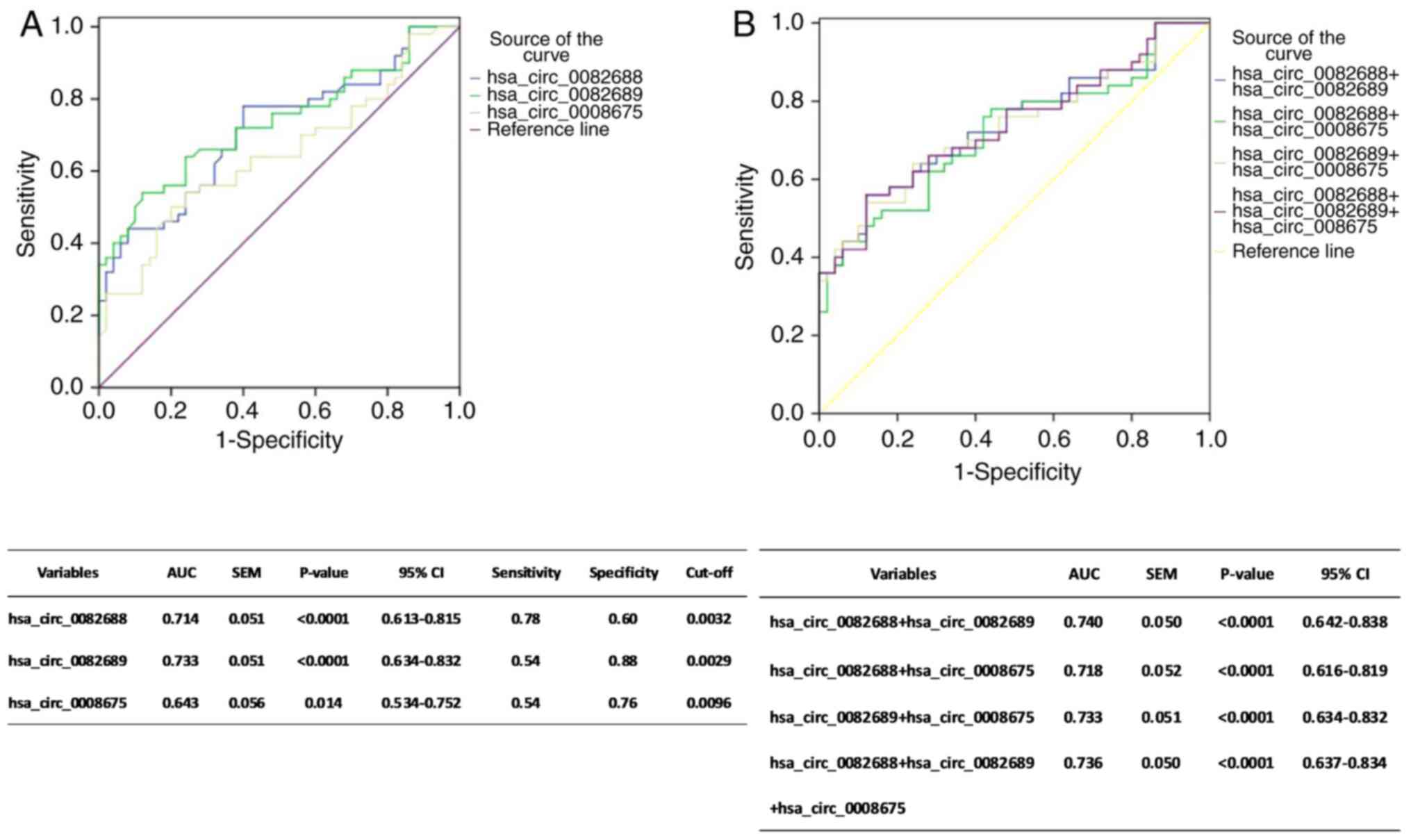
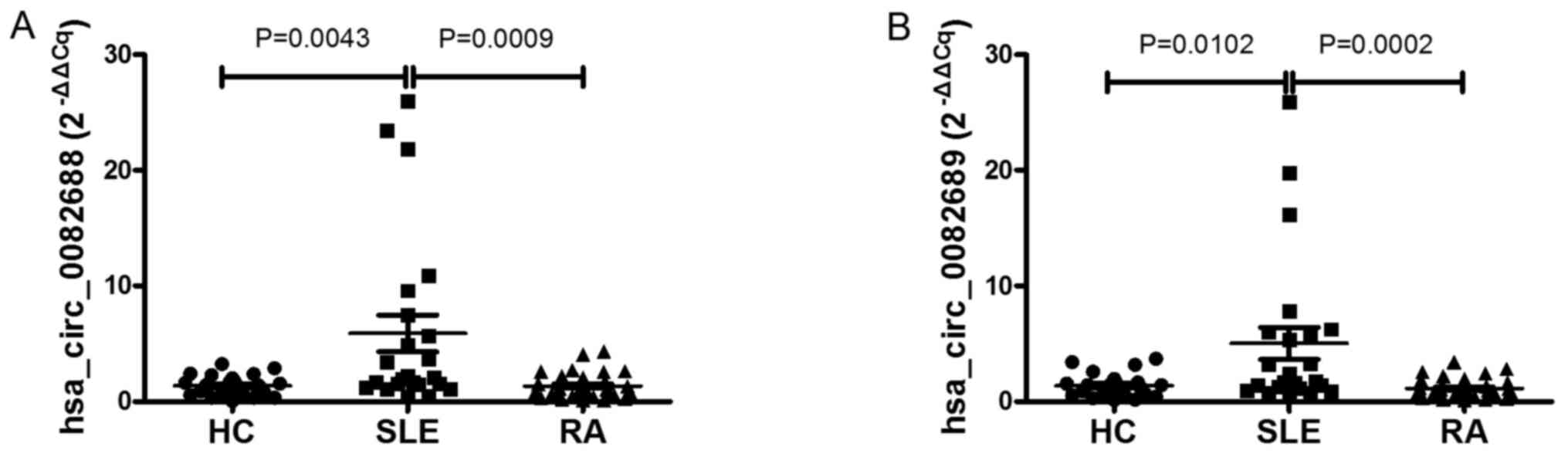
|
1
|
Tsokos GC: Systemic lupus erythematosus. N
Engl J Med. 365:2110–2121. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ruiz-Irastorza G, Ramos-Casals M,
Brito-Zeron P and Khamashta MA: Clinical efficacy and side effects
of antimalarials in systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic
review. Ann Rheum Dis. 69:20–28. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chang NH, Li TT, Kim JJ,
Landolt-Marticorena C, Fortin PR, Gladman DD, Urowitz MB and Wither
JE: Interferon alpha induces altered transitional B cell signaling
and function in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Autoimmun.
58:100–110. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhao M, Liu S, Luo S, Wu H, Tang M, Cheng
W, Zhang Q, Zhang P, Yu X, Xia Y, et al: DNA methylation and mRNA
and microRNA expression of SLE CD4+ T cells correlate with disease
phenotype. J Autoimmun. 54:127–136. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
O'Gorman WE, Hsieh EW, Savig ES,
Gherardini PF, Hernandez JD, Hansmann L, Balboni IM, Utz PJ,
Bendall SC, Fantl WJ, et al: Single-cell systems-level analysis of
human Toll-like receptor activation defines a chemokine signature
in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 136:1326–1336. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lech M, Kantner C, Kulkarni OP, Ryu M,
Vlasova E, Heesemann J, Anz D, Endres S, Kobayashi KS, Flavell RA,
et al: Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-M suppresses
systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 70:2207–2217. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Huang Z, Shi Y, Cai B, Wang L, Wu Y, Ying
B, Qin L, Hu C and Li Y: MALDI-TOF MS combined with magnetic beads
for detecting serum protein biomarkers and establishment of
boosting decision tree model for diagnosis of systemic lupus
erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford). 48:626–631. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ferreira TAR, de Andrade HM, de Pádua PM,
Carvalho MDG, Pires SDF, Oliveira IHR, Lima BSS, Fialho Júnior LC,
Cicarini WB, Chapeourouge DA, et al: Identification of potential
biomarkers for systemic lupus erythematosus diagnosis using
two-dimensional differential gel electrophoresis (2D-DIGE) and mass
spectrometry. Autoimmunity. 50:247–256. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu GC, Li J, Leng RX, Li XP, Li XM, Wang
DG, Pan HF and Ye DQ: Identification of long non-coding RNAs GAS5,
linc0597 and lnc-DC in plasma as novel biomarkers for systemic
lupus erythematosus. Oncotarget. 8:23650–23663. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Barrett SP, Wang PL and Salzman J:
Circular RNA biogenesis can proceed through an exon-containing
lariat precursor. Elife. 4:e075402015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li Z, Huang C, Bao C, Chen L, Lin M, Wang
X, Zhong G, Yu B, Hu W, Dai L, et al: Exon-intron circular RNAs
regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat Struct Mol Biol.
22:256–264. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, Slevin MK,
Burd CE, Liu J, Marzluff WF and Sharpless NE: Circular RNAs are
abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA.
19:141–157. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F,
Krueger J, Rybak A, Maier L, Mackowiak SD, Gregersen LH, Munschauer
M, et al: Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with
regulatory potency. Nature. 495:333–338. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen
JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK and Kjems J: Natural RNA circles function
as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 495:384–388. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jeck WR and Sharpless NE: Detecting and
characterizing circular RNAs. Nat Biotechnol. 32:453–461. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Burd CE, Jeck WR, Liu Y, Sanoff HK, Wang Z
and Sharpless NE: Expression of linear and novel circular forms of
an INK4/ARF-associated non-coding RNA correlates with
atherosclerosis risk. PLoS Genet. 6:e10012332010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hansen TB, Kjems J and Damgaard CK:
Circular RNA and miR-7 in cancer. Cancer Res. 73:5609–5612. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li F, Zhang L, Li W, Deng J, Zheng J, An
M, Lu J and Zhou Y: Circular RNA ITCH has inhibitory effect on ESCC
by suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Oncotarget. 6:6001–6013.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ouyang Q, Wu J, Jiang Z, Zhao J, Wang R,
Lou A, Zhu D, Shi GP and Yang M: Microarray expression profile of
circular RNAs in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from rheumatoid
arthritis patients. Cell Physiol Biochem. 42:651–659. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lin X, Lo HC, Wong DT and Xiao X:
Noncoding RNAs in human saliva as potential disease biomarkers.
Front Genet. 6:1752015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Memczak S, Papavasileiou P, Peters O and
Rajewsky N: Identification and characterization of circular RNAs As
a new class of putative biomarkers in human blood. PLoS One.
10:e01412142015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
You X, Vlatkovic I, Babic A, Will T,
Epstein I, Tushev G, Akbalik G, Wang M, Glock C, Quedenau C, et al:
Neural circular RNAs are derived from synaptic genes and regulated
by development and plasticity. Nat Neurosci. 18:603–610. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Salzman J, Chen RE, Olsen MN, Wang PL and
Brown PO: Cell-type specific features of circular RNA expression.
PLoS Genet. 9:e10037772013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhao Z, Li X, Jian D, Hao P, Rao L and Li
M: Hsa_circ_0054633 in peripheral blood can be used as a diagnostic
biomarker of pre-diabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta
Diabetol. 54:237–245. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao Z, Li X, Gao C, Jian D, Hao P, Rao L
and Li M: Peripheral blood circular RNA hsa_circ_0124644 can be
used as a diagnostic biomarker of coronary artery disease. Sci Rep.
7:399182017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Luo Q, Zhang L, Li X, Fu B, Guo Y, Huang Z
and Li J: Identification of circular RNAs hsa_circ_0044235 and
hsa_circ_0068367 as novel biomarkers for systemic lupus
erythematosus. Int J Mol Med. 44:1462–1472. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hochberg MC: Updating the American college
of rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic
lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 40:17251997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bombardier C, Gladman DD, Urowitz MB,
Caron D and Chang CH: Derivation of the SLEDAI. A disease activity
index for lupus patients. The committee on prognosis studies in
SLE. Arthritis Rheum. 35:630–640. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane
DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, Healey LA, Kaplan SR, Liang MH, Luthra HS,
et al: The American rheumatism association 1987 revised criteria
for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthr Rhuem.
31:315–324. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Luo Q, Li X, Xu C, Zeng L, Ye J, Guo Y,
Huang Z and Li J: Integrative analysis of long non-coding RNAs and
messenger RNA expression profiles in systemic lupus erythematosus.
Mol Med Rep. 17:3489–3496. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Luo Q, Zhang L, Fang L, Fu B, Guo Y, Huang
Z and Li J: Circular RNAs hsa_circ_0000479 in peripheral blood
mononuclear cells as novel biomarkers for systemic lupus
erythematosus. Autoimmunity. 53:167–176. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Soliman S and Mohan C: Lupus nephritis
biomarkers. Clin Immunol. 185:10–20. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Stypinska B and Paradowska-Gorycka A:
Cytokines and MicroRNAs as candidate biomarkers for systemic lupus
erythematosus. Int J Mol Sci. 16:24194–24218. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wu Y, Zhang F, Ma J, Zhang X, Wu L, Qu B,
Xia S, Chen S, Tang Y and Shen N: Association of large intergenic
noncoding RNA expression with disease activity and organ damage in
systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther. 17:1312015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Guo JN, Li J, Zhu CL, Feng WT, Shao JX,
Wan L, Huang MD and He JD: Comprehensive profile of differentially
expressed circular RNAs reveals that hsa_circ_0000069 is
upregulated and promotes cell proliferation, migration, and
invasion in colorectal cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 9:7451–7458.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liang D and Wilusz JE: Short intronic
repeat sequences facilitate circular RNA production. Genes Dev.
28:2233–2247. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ouyang Q, Huang Q, Jiang Z, Zhao J, Shi GP
and Yang M: Using plasma circRNA_002453 as a novel biomarker in the
diagnosis of lupus nephritis. Mol Immunol. 101:531–538. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang MY, Wang JB, Zhu ZW, Li LJ, Liu RS,
Yang XK, Leng RX, Li XM, Pan HF and Ye DQ: Differentially expressed
circular RNAs in systemic lupus erythematosus and their clinical
significance. Biomed Pharmacother. 107:1720–1727. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li S, Zhang J, Tan X, Deng J, Li Y, Piao
Y, Li C, Yang W, Mo W, Sun J, et al: Microarray expression profile
of circular RNAs and mRNAs in children with systemic lupus
erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol. 38:1339–1350. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yi F, Hao Y, Chong X and Zhong W:
Overexpression of microRNA-506-3p aggravates the injury of vascular
endothelial cells in patients with hypertension by downregulating
Beclin1 expression. Exp Ther Med. 15:2844–2850. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pan Q, Gao C, Chen Y, Feng Y, Liu WJ and
Liu HF: Update on the role of autophagy in systemic lupus
erythematosus: A novel therapeutic target. Biomed Pharmacother.
71:190–193. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liang J, Xu L, Zhou F, Liu AM, Ge HX, Chen
YY and Tu M: MALAT1/miR-127-5p regulates osteopontin (OPN)-mediated
proliferation of human chondrocytes through PI3K/Akt pathway. J
Cell Biochem. 119:431–439. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chen H, Shi B, Feng X, Kong W, Chen W,
Geng L, Chen J, Liu R, Li X, Chen W, et al: Leptin and
neutrophil-activating peptide 2 promote mesenchymal stem cell
senescence through activation of the phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/Akt pathway in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.
Arthritis Rheumatol. 67:2383–2393. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Navarro-Quiroz E, Pacheco-Lugo L,
Navarro-Quiroz R, Lorenzi H, España-Puccini P, Díaz-Olmos Y,
Almendrales L, Olave V, Gonzalez-Torres H, Diaz-Perez A, et al:
Profiling analysis of circulating microRNA in peripheral blood of
patients with class IV lupus nephritis. PLoS One. 12:e01879732017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|