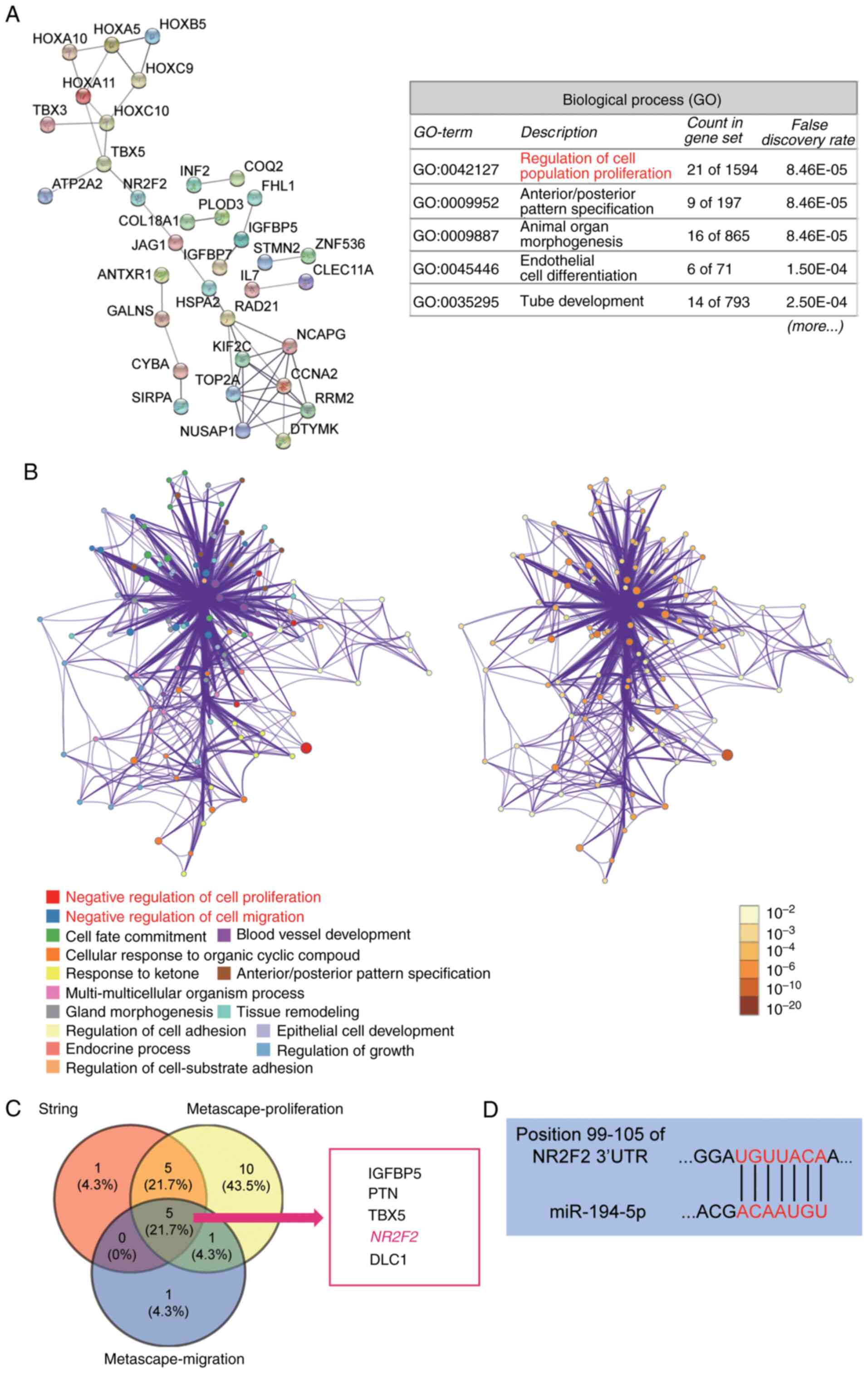
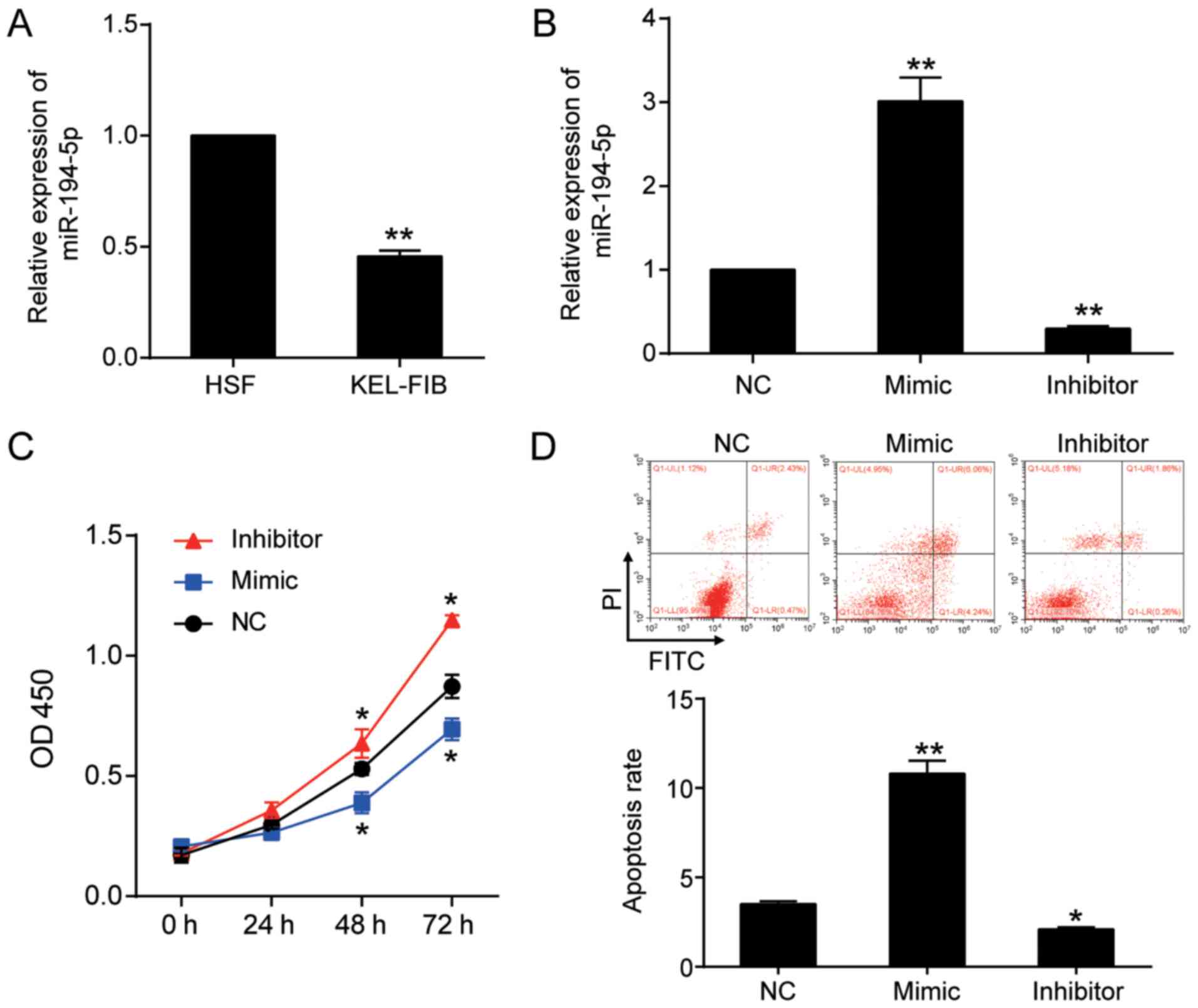
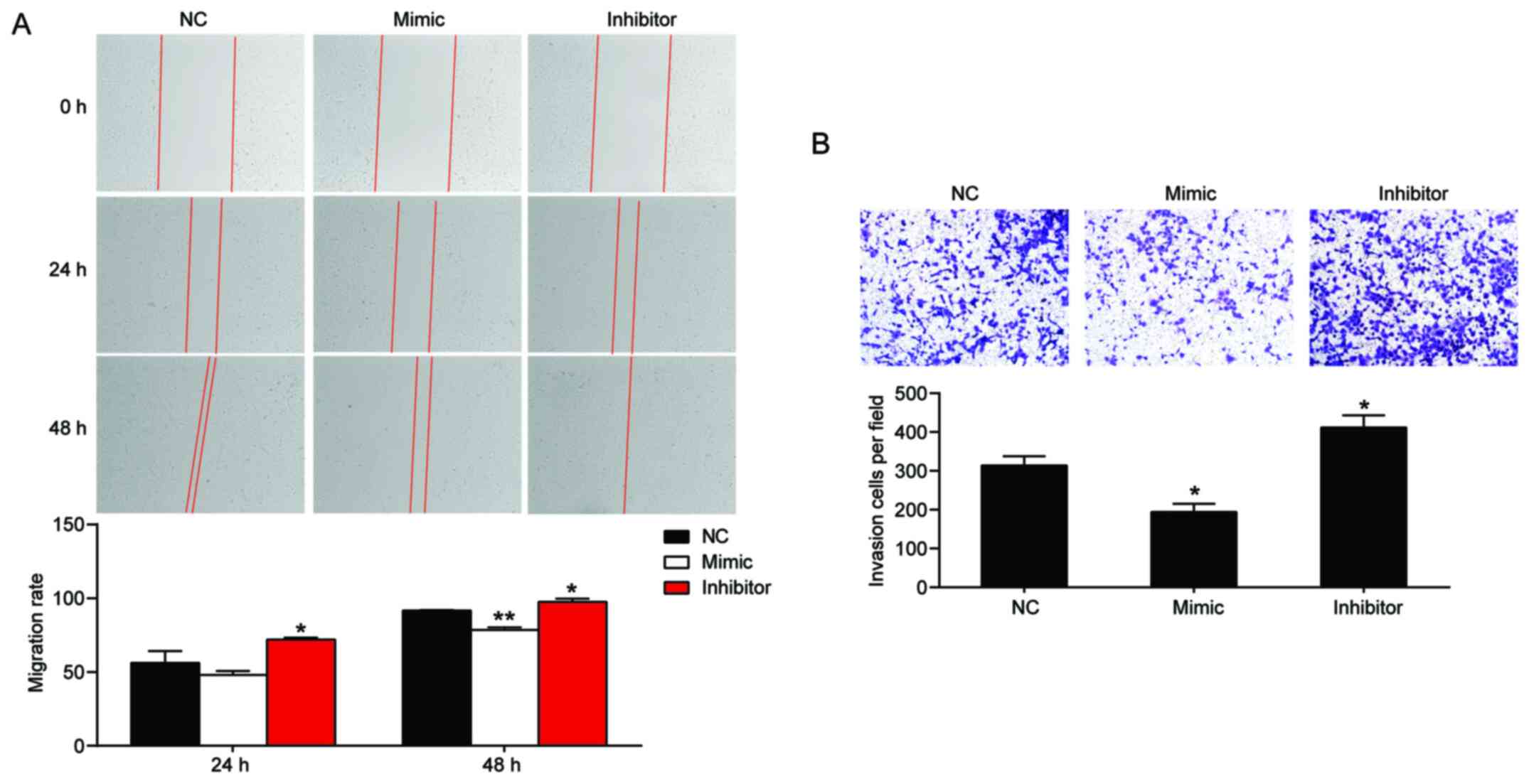
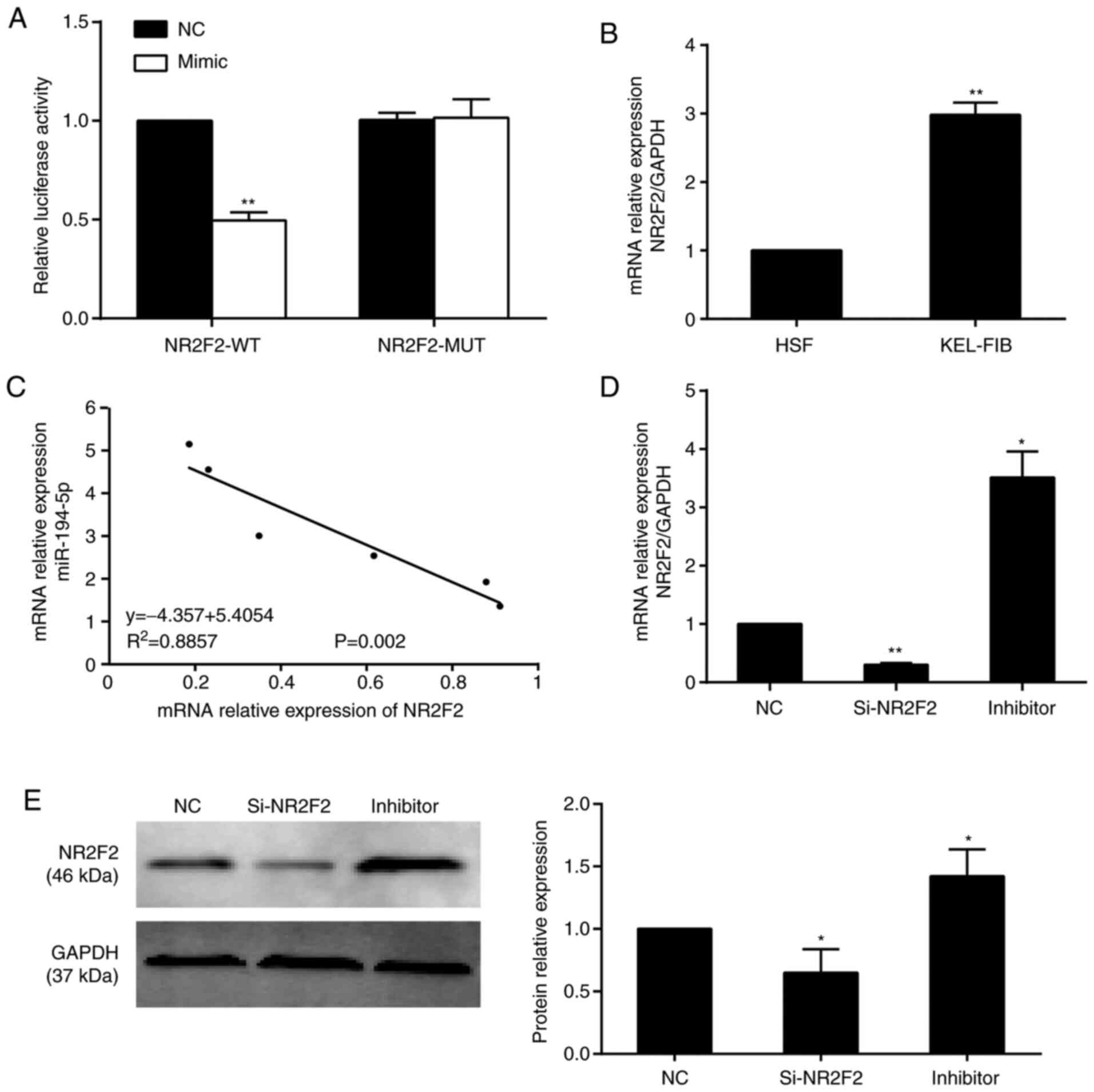
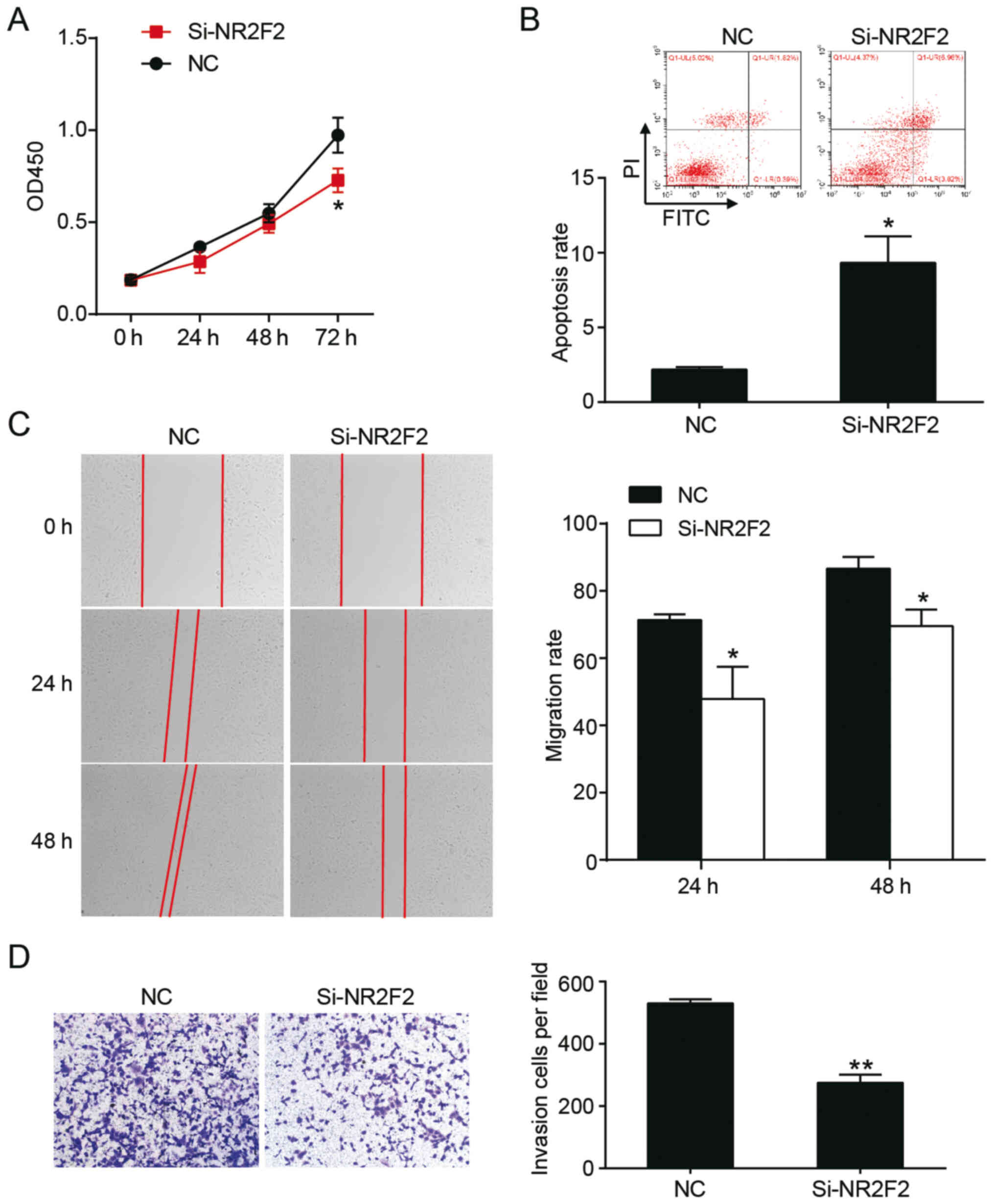
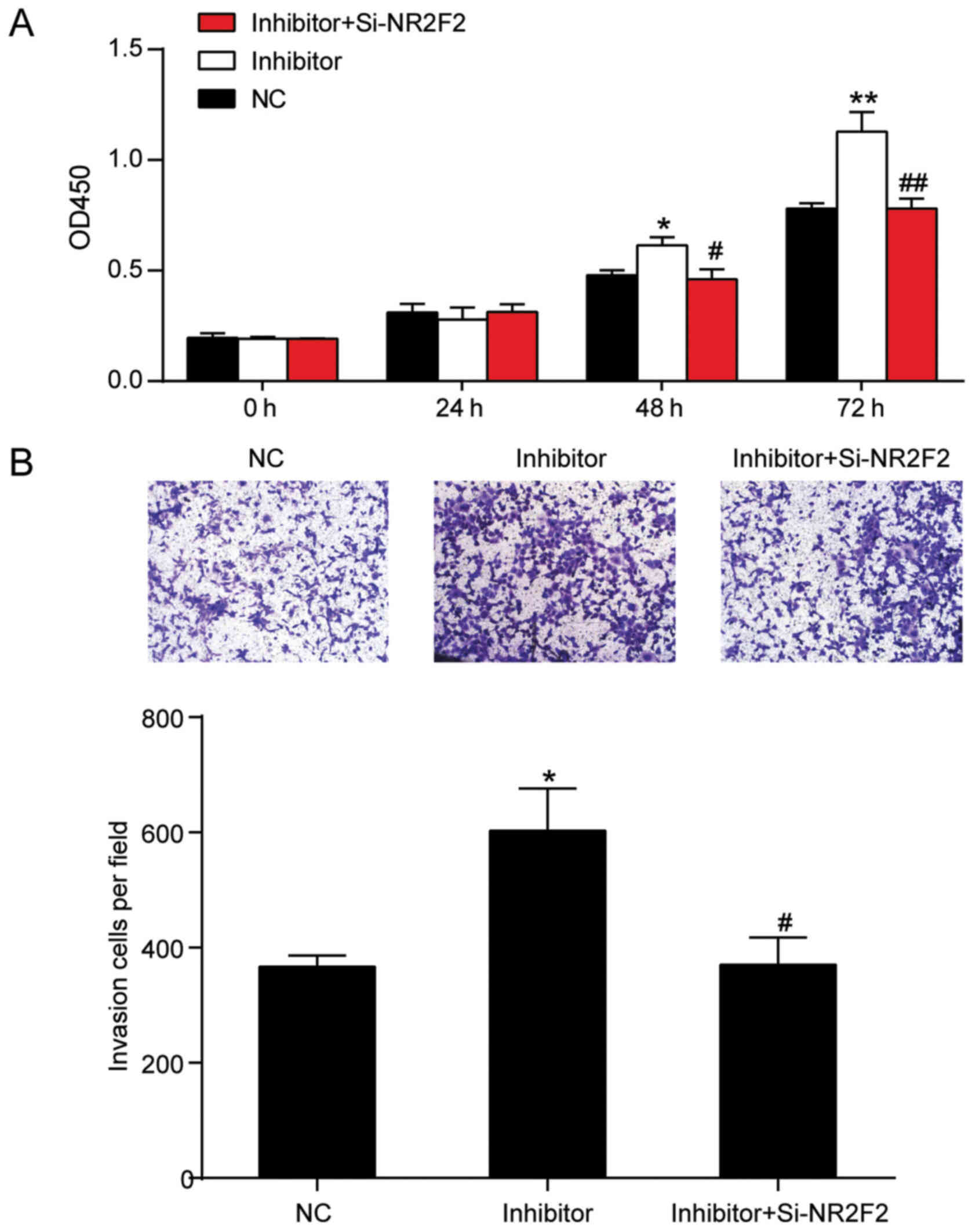
|
1
|
Patel PA, Bailey JK and Yakuboff KP:
Treatment outcomes for keloid scar management in the pediatric burn
population. Burns. 38:767–771. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yao X, Cui X, Wu X, Xu P, Zhu W, Chen X
and Zhao T: Tumor suppressive role of miR-1224-5p in keloid
proliferation, apoptosis and invasion via the TGF-β1/Smad3
signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 495:713–720. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Seifert O and Mrowietz U: Keloid scarring:
Bench and bedside. Arch Dermatol Res. 301:259–272. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Finnerty CC, Jeschke MG, Branski LK,
Barret JP, Dziewulski P and Herndon DN: Hypertrophic scarring: The
greatest unmet challenge after burn injury. Lancet. 388:1427–1436.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Slemp AE and Kirschner RE: Keloids and
scars: A review of keloids and scars, their pathogenesis, risk
factors, and management. Curr Opin Pediatr. 18:396–402. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Berman B, Maderal A and Raphael B: Keloids
and hypertrophic scars: Pathophysiology, classification, and
treatment. Dermatol Surg. 43 (Suppl 1):S3–S18. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhu W, Wu X, Yang B, Yao X, Cui X, Xu P
and Chen X: miR-188-5p regulates proliferation and invasion via
PI3K/Akt/MMP-2/9 signaling in keloids. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
(Shanghai). 51:185–196. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yi R, O'Carroll D, Pasolli HA, Zhang Z,
Dietrich FS, Tarakhovsky A and Fuchs E: Morphogenesis in skin is
governed by discrete sets of differentially expressed microRNAs.
Nat Genet. 38:356–362. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chau BN and Brenner DA: What goes up must
come down: The emerging role of microRNA in fibrosis. Hepatology.
53:4–6. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li Z, Yu X, Shen J, Chan MT and Wu WK:
MicroRNA in intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Prolif.
48:278–283. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yu X, Li Z and Liu J: MiRNAs in primary
cutaneous lymphomas. Cell Prolif. 48:271–277. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li Z, Yu X, Shen J and Jiang Y: MicroRNA
dysregulation in uveal melanoma: A new player enters the game.
Oncotarget. 6:4562–4568. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Di Leva G, Garofalo M and Croce CM:
MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 9:287–314. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ren L, Zhang J, Wang J, Wei J, Liu J, Li
X, Zhu Y, Li Y, Guo C, Duan J, et al: Silica nanoparticles induce
spermatocyte cell apoptosis through microRNA-2861 targeting death
receptor pathway. Chemosphere. 228:709–720. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhao MJ, Xie J, Shu WJ, Wang HY, Bi J,
Jiang W and Du HN: MiR-15b and miR-322 inhibit SETD3 expression to
repress muscle cell differentiation. Cell Death Dis. 10:1832019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Duan L, Duan D, Wei W, Sun Z, Xu H, Guo L
and Wu X: MiR-19b-3p attenuates IL-1β induced extracellular matrix
degradation and inflammatory injury in chondrocytes by targeting
GRK6. Mol Cell Biochem. 459:205–214. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li C, Bai Y, Liu H, Zuo X, Yao H, Xu Y and
Cao M: Comparative study of microRNA profiling in keloid fibroblast
and annotation of differential expressed microRNAs. Acta Biochim
Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 45:692–699. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu Y, Yang D, Xiao Z and Zhang M: miRNA
expression profiles in keloid tissue and corresponding normal skin
tissue. Aesthetic plastic surgery. 36:193–201. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Navab R, Gonzalez-Santos JM, Johnston MR,
Liu J, Brodt P, Tsao MS and Hu J: Expression of chicken ovalbumin
upstream promoter-transcription factor II enhances invasiveness of
human lung carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 64:5097–5105. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Litchfield LM, Appana SN, Datta S and
Klinge CM: COUP-TFII inhibits NFkappaB activation in
endocrine-resistant breast cancer cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
382:358–367. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang W, Liu J, Qiu J, Fu X, Tang Q, Yang
F, Zhao Z and Wang H: MicroRNA-382 inhibits prostate cancer cell
proliferation and metastasis through targeting COUP-TFII. Oncol
Rep. 36:3707–3715. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qin J, Wu SP, Creighton CJ, Dai F, Xie X,
Cheng CM, Frolov A, Ayala G, Lin X, Feng XH, et al: COUP-TFII
inhibits TGF-β-induced growth barrier to promote prostate
tumorigenesis. Nature. 493:236–240. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Smith JC, Boone BE, Opalenik SR, Williams
SM and Russell SB: Gene profiling of keloid fibroblasts shows
altered expression in multiple fibrosis-associated pathways. J
Invest Dermatol. 128:1298–1310. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sidgwick GP and Bayat A: Extracellular
matrix molecules implicated in hypertrophic and keloid scarring. J
Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 26:141–152. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang C and Ogawa R: The link between
hypertension and pathological scarring: Does hypertension cause or
promote keloid and hypertrophic scar pathogenesis? Wound Repair
Regen. 22:462–466. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rutnam ZJ, Wight TN and Yang BB: miRNAs
regulate expression and function of extracellular matrix molecules.
Matrix Biol. 32:74–85. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Meltzer PS: Cancer genomics: Small RNAs
with big impacts. Nature. 435:745–746. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Price C and Chen J: MicroRNAs in cancer
biology and therapy: Current status and perspectives. Genes Dis.
1:53–63. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang Y, Guo B, Hui Q, Li W, Chang P and
Tao K: Downregulation of miR-637 promotes proliferation and
metastasis by targeting Smad3 in keloids. Mol Med Rep.
18:1628–1636. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Qin J, Chen X, Yu-Lee LY, Tsai MJ and Tsai
SY: Nuclear receptor COUP-TFII controls pancreatic islet tumor
angiogenesis by regulating vascular endothelial growth
factor/vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 signaling.
Cancer Res. 70:8812–8821. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bao Y, Gu D, Feng W, Sun X, Wang X, Zhang
X, Shi Q, Cui G, Yu H, Tang C and Deng A: COUP-TFII regulates
metastasis of colorectal adenocarcinoma cells by modulating Snail1.
Br J Cancer. 111:933–943. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Naylor MC and Brissett AE: Current
concepts in the etiology and treatment of keloids. Facial Plast
Surg. 28:504–512. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hou Z, Fan F and Liu P: BTXA regulates the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and autophagy of keloid
fibroblasts via modulating miR-1587/miR-2392 targeted ZEB2. Biosci
Rep. 39:BSR201906792019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jin J, Zhai HF, Jia ZH and Luo XH: Long
non-coding RNA HOXA11-AS induces type I collagen synthesis to
stimulate keloid formation via sponging miR-124-3p and activation
of Smad5 signaling. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 317:C1001–C1010.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jin J, Jia ZH, Luo XH and Zhai HF: Long
non-coding RNA HOXA11-AS accelerates the progression of keloid
formation via miR-124-3p/TGFβR1 axis. Cell Cycle. 19:218–232. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|