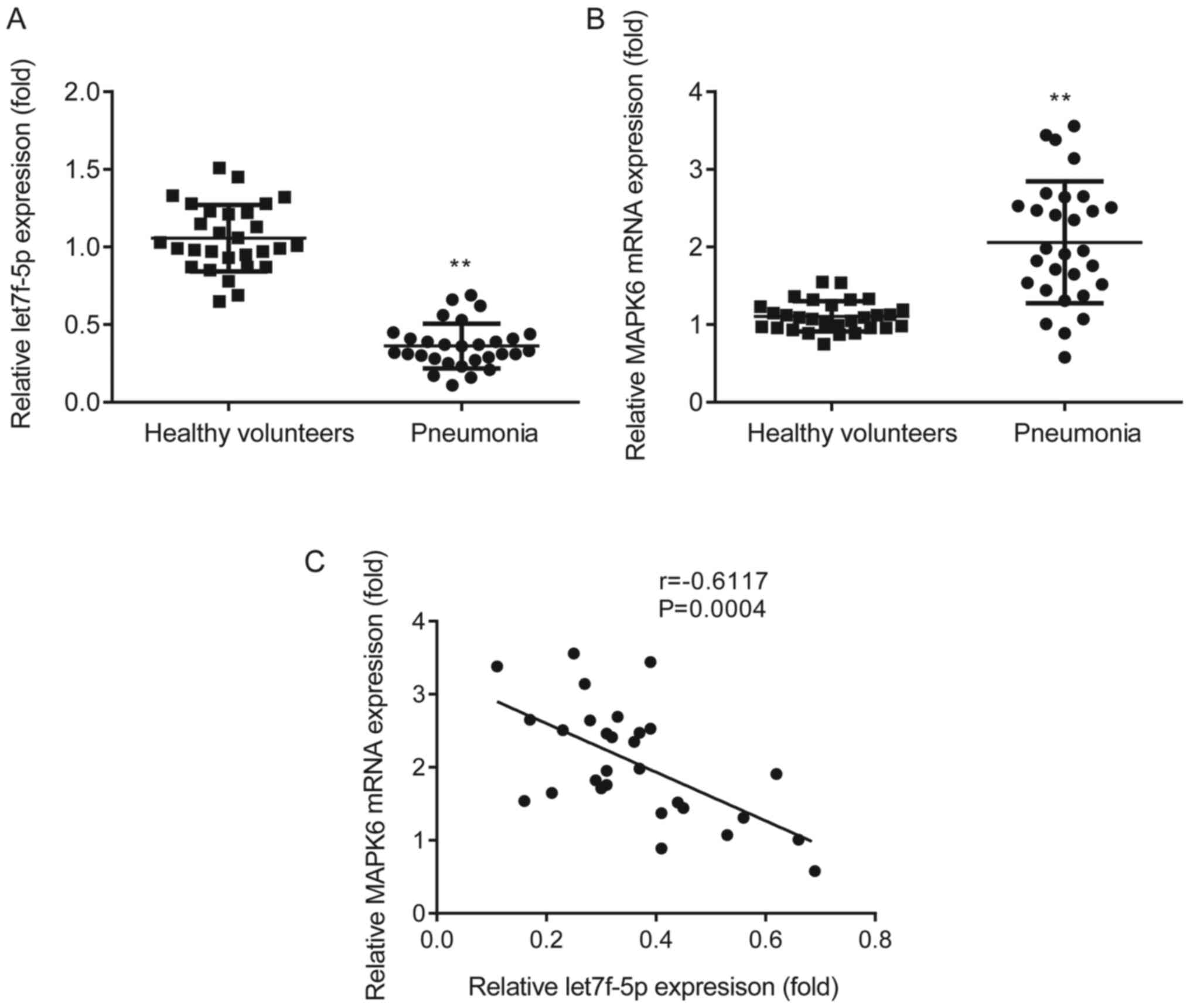
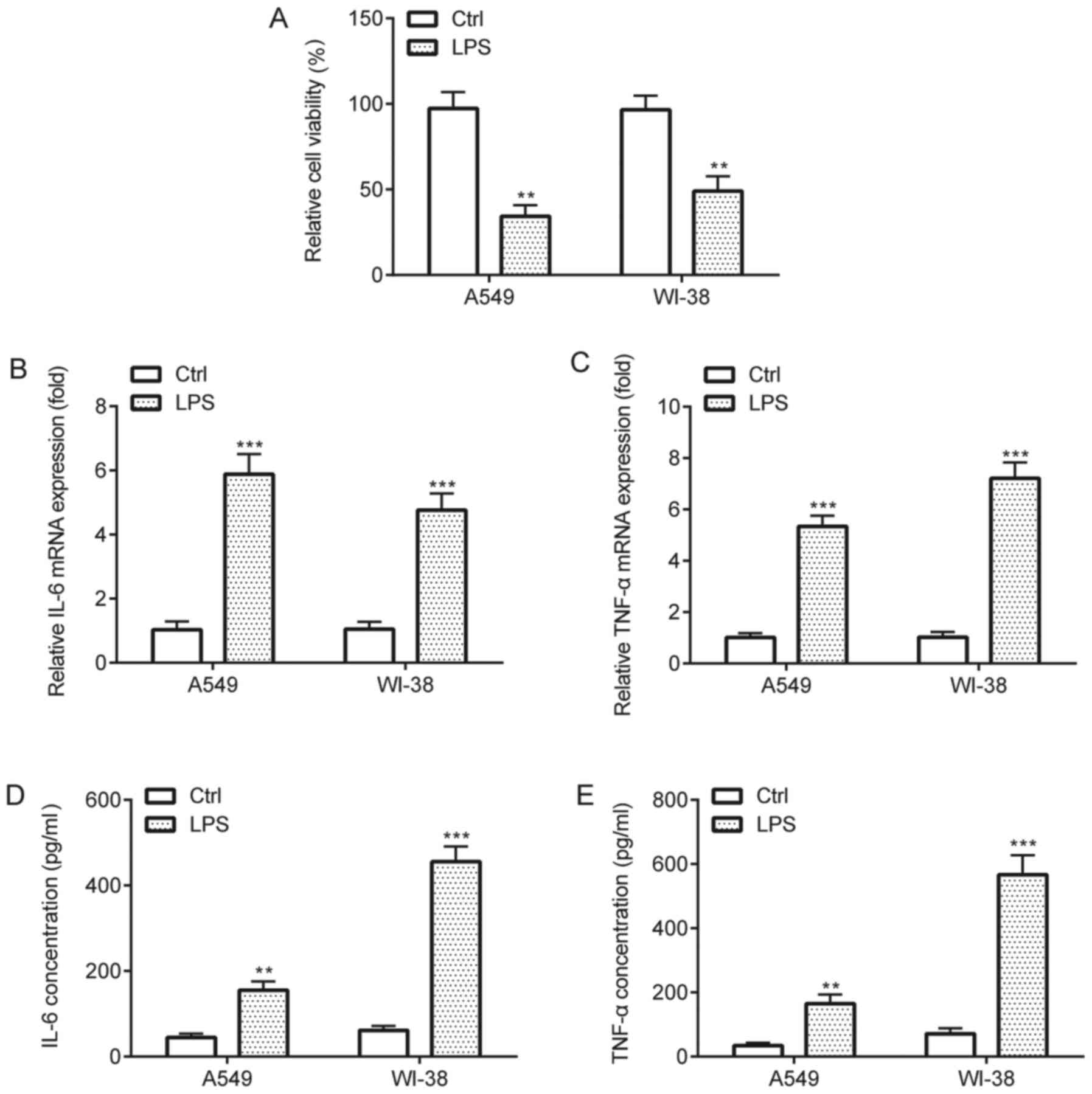
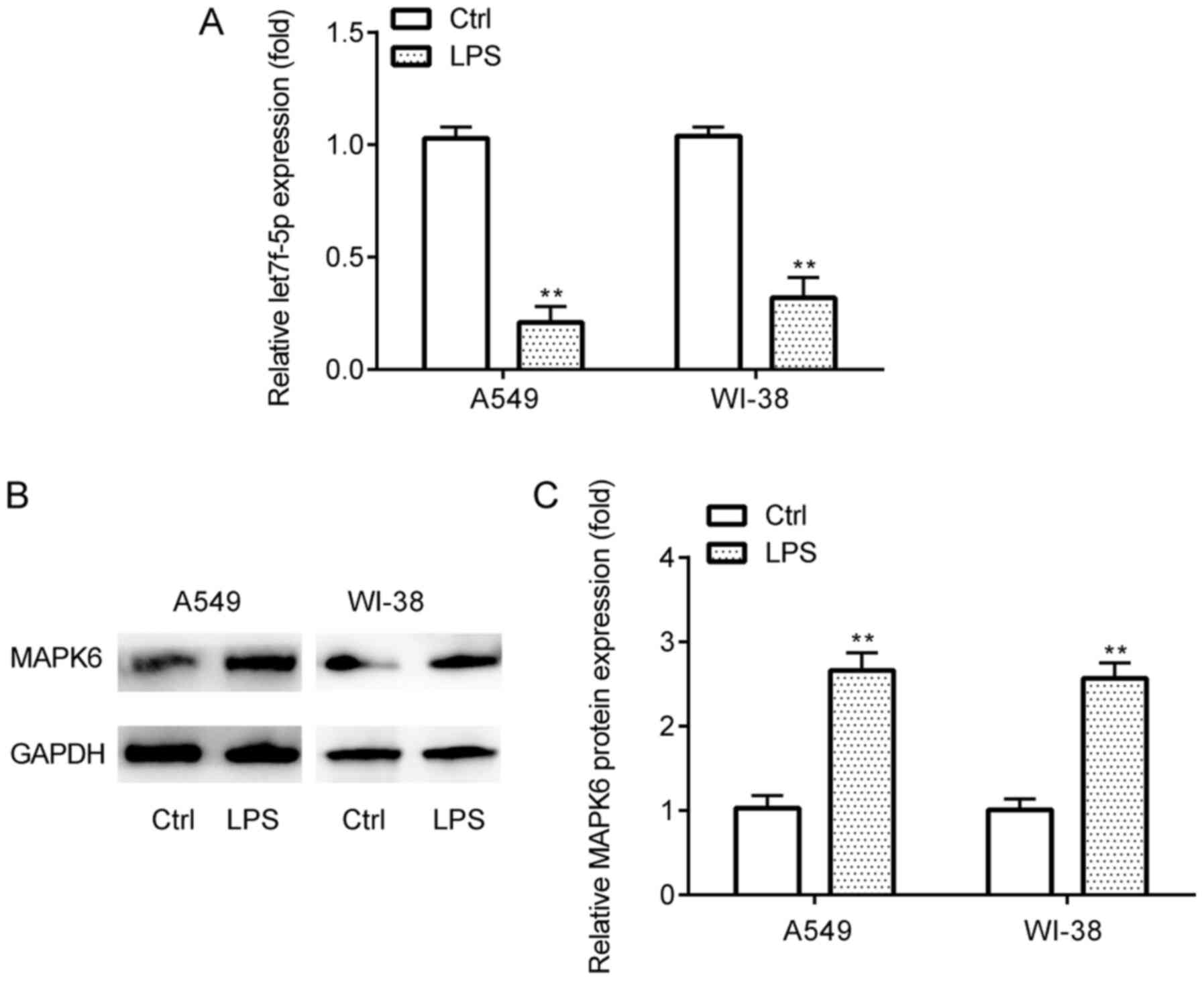
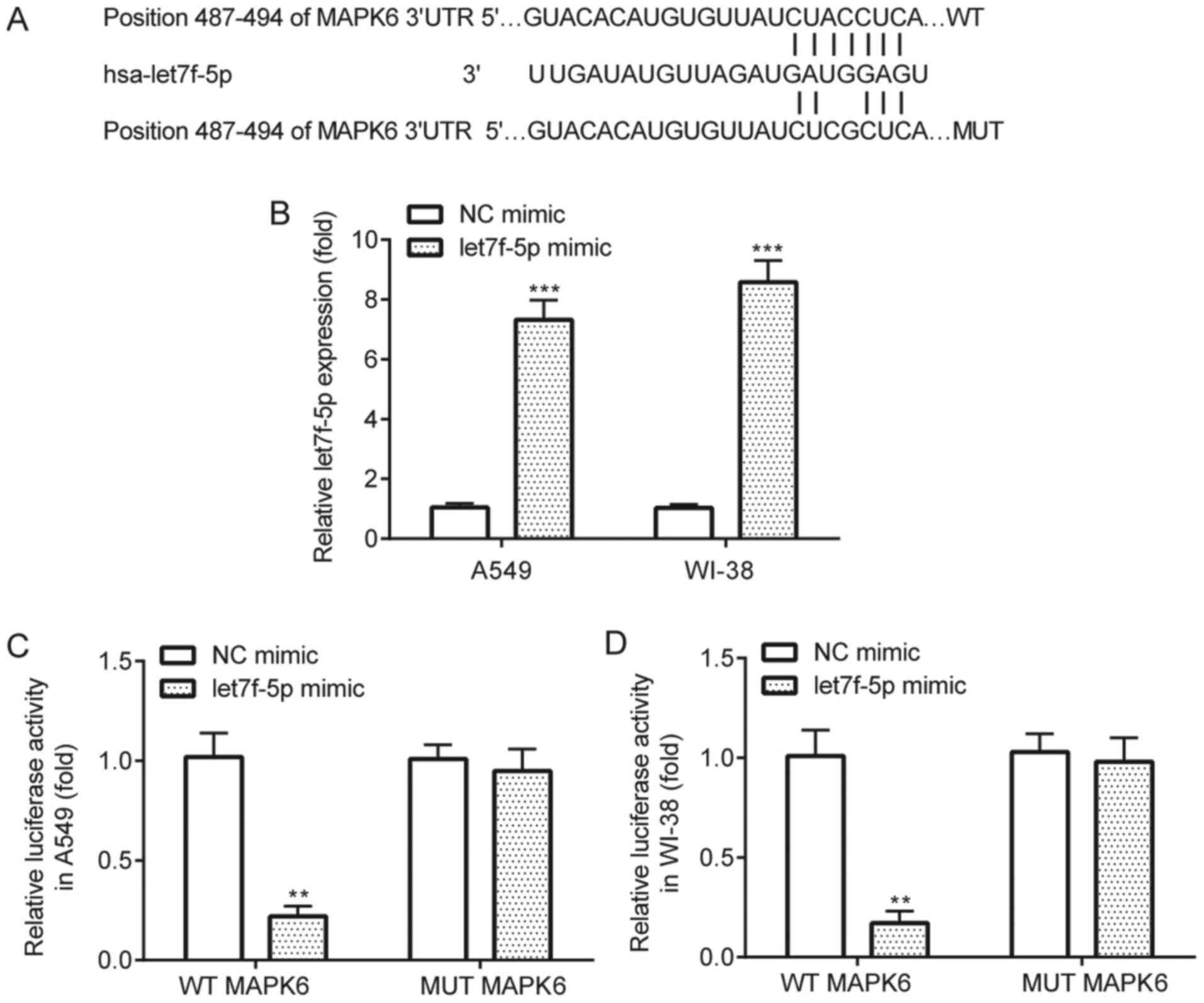
|
1
|
Cillóniz C, Torres A, Niederman M, van der
Eerden M, Chalmers J, Welte T and Blasi F: Community-acquired
pneumonia related to intracellular pathogens. Intensive Care Med.
42:1374–1386. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Korppi M: Diagnosis and treatment of
community-acquired pneumonia in children. Acta Paediatr.
101:702–704. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Simonetti AF, Viasus D, Garcia-Vidal C and
Carratalà J: Management of community-acquired pneumonia in older
adults. Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2:3–16. 2014.
|
|
4
|
Kim GD: Myricetin inhibits angiogenesis by
inducing apoptosis and suppressing PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in
endothelial cells. J Cancer Prev. 22:219–227. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Yu B, Shen Y, Qiao J and Cui Q: Geniposide
attenuates Staphylococcus aureus-induced pneumonia in mice by
inhibiting NF-κB activation. Microb Pathog. 112:117–121. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Rojas M, Woods CR, Mora AL, Xu J and
Brigham KL: Endotoxin-induced lung injury in mice: Structural,
functional, and biochemical responses. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 288:L333–L341. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Didier D and Jean-Damien R: Acute lung
injury and bacterial infection. Clin Chest Med. 26:105–112. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wong KY, Huang X and Chim CS: DNA
methylation of microRNA genes in multiple myeloma. Carcinogenesis.
33:1629–1638. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Fei S, Cao L and Pan L: microRNA3941
targets IGF2 to control LPS-induced acute pneumonia in A549 cells.
Mol Med Rep. 17:4019–4026. 2018.
|
|
10
|
Abd-El-Fattah AA, Sadik NA, Shaker OG and
Aboulftouh ML: Differential microRNAs expression in serum of
patients with lung cancer, pulmonary tuberculosis, and pneumonia.
Cell Biochem Biophys. 67:875–884. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Huang S, Feng C, Zhai YZ, Zhou X, Li B,
Wang LL, Chen W, Lv FQ and Li TS: Identification of miRNA
biomarkers of pneumonia using RNA-sequencing and bioinformatics
analysis. Exp Ther Med. 13:1235–1244. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bai D, Han A and Cong S: The effect of
down-regulation of CCL5 on lipopolysaccharide-induced WI-38
fibroblast injury: A potential role for infantile pneumonia. Iran J
Basic Med Sci. 21:449–454. 2018.
|
|
13
|
Zhou Z, Zhua Y, Gao G and Zhang Y: Long
noncoding RNA SNHG16 targets miR-146a-5p/CCL5 to regulate LPS
induced WI-38 cell apoptosis and inflammation in acute pneumonia.
Life Sci. 228:189–197. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wang Q, Li D, Han Y, Ding X, Xu T and Tang
B: MicroRNA-146 protects A549 and H1975 cells from LPS-induced
apoptosis and inflammation injury. J Biosci. 42:637–645. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Pérez-Herrero E and Fernández-Medarde A:
Advanced targeted therapies in cancer: Drug nanocarriers, the
future of chemotherapy. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 93:52–79. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wang X, Cao L, Wang Y, Wang X, Liu N and
You Y: Regulation of let-7 and its target oncogenes (Review). Oncol
Lett. 3:955–960. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Tan KS, Choi H, Jiang X, Yin L, Seet JE,
Patzel V, Engelward BP and Chow VT: Micro-RNAs in regenerating
lungs: An integrative systems biology analysis of murine influenza
pneumonia. BMC Genomics. 15:5872014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Selvamani A, Sathyan P, Miranda RC and
Sohrabji F: An antagomir to microRNA Let7f promotes neuroprotection
in an ischemic stroke model. PLoS One. 7:e326622012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wang L, Niu X, Hu J, Xing H, Sun M, Wang
J, Jian Q and Yang H: After myocardial ischemia-reperfusion,
miR-29a, and Let7 could affect apoptosis through regulating IGF-1.
Biomed Res Int. 2015:2454122015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Damanakis AI, Eckhardt S, Wunderlich A,
Roth S, Wissniowski TT, Bartsch DK and Di Fazio P: MicroRNAs let7
expression in thyroid cancer: Correlation with their deputed
targets HMGA2 and SLC5A5. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 142:1213–1220.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Eguchi A, Franz N, Kobayashi Y, Iwasa M,
Wagner N, Hildebrand F, Takei Y, Marzi I and Relja B: Circulating
extracellular vesicles and their miR ‘Barcode’ differentiate
alcohol drinkers with liver injury and those without liver injury
in severe trauma patients. Front Med (Lausanne). 6:302019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lv P, Qiu X, Gu Y, Yang X, Xu X and Yang
Y: Long non-coding RNA SNHG6 enhances cell proliferation, migration
and invasion by regulating miR-26a-5p/MAPK6 in breast cancer.
Biomed Pharmacother. 110:294–301. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wu J, Zhao Y, Li F and Qiao B: miR-144-3p:
A novel tumor suppressor targeting MAPK6 in cervical cancer. J
Physiol Biochem. 75:143–152. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Luo M, Sun Q, Zhao H, Tao J and Yan D:
Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 sponges miR-495-3p to enhance myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury via MAPK6 activation. J Cell Physiol.
235:105–113. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhang Y, Su Z, Liu HL, Li L, Wei M, Ge DJ
and Zhang ZJ: Effects of miR-26a-5p on neuropathic pain development
by targeting MAPK6 in in CCI rat models. Biomed Pharmacother.
107:644–649. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Liu YC, Ho HC, Lee MR, Lai KC, Yeh CM, Lin
YM, Ho TY, Hsiang CY and Chung JG: Early induction of
cytokines/cytokine receptors and Cox2, and activation of NF-κB in
4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide-induced murine oral cancer model. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 262:107–116. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Khan J, Noboru N, Young A and Thomas D:
Pro and antiinflammatory cytokine levels (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and
IL-10) in rat model of neuroma. Pathophysiology. 24:155–159. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Berg AS, Inchley CS, Fjaerli HO, Leegaard
TM, Lindbaek M and Nakstad B: Clinical features and inflammatory
markers in pediatric pneumonia: A prospective study. Eur J Pediatr.
176:629–638. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Dai JP, Wang QW, Su Y, Gu LM, Zhao Y, chen
XX, Chen C, Li WZ, Wang GF and Li KS: Emodin inhibition of
influenza A virus replication and influenza viral pneumonia via the
Nrf2, TLR4, p38/JNK and NF-kappaB pathways. Molecules. 22:17542017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yu Q, Zeng K, Ma X, Song F, Jiang Y, Tu P
and Wang X: Resokaempferol-mediated anti-inflammatory effects on
activated macrophages via the inhibition of JAK2/STAT3, NF-κB and
JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 38:104–114.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Gao H and Ward PA: STAT3 and suppressor of
cytokine signaling 3: Potential targets in lung inflammatory
responses. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 11:869–880. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Liu G, Wan Q, Li J, Hu X, Gu X and Xu S:
Circ_0038467 regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory
injury in human bronchial epithelial cells through sponging
miR-338-3p. Thorac Cancer. 11:1297–1308. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Tan W, Gu Z, Leng J, Zou X, Chen H, Min F,
Zhou W, Zhang L and Li G: Let-7f-5p ameliorates inflammation by
targeting NLRP3 in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in
patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Biomed Pharmacother.
118:1093132019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Yao T, Zha D, Hu C and Wu X: Circ_0000285
promotes podocyte injury through sponging miR-654-3p and activating
MAPK6 in diabetic nephropathy. Gene. 747:1446612020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Li ZH, Wang YF, He DD, Zhang XM, Zhou YL,
Yue H, Huang S, Fu Z, Zhang LY, Mao ZQ, et al: Let-7f-5p suppresses
Th17 differentiation via targeting STAT3 in multiple sclerosis.
Aging (Albany NY). 11:4463–4477. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kim SJ, Pham TH, Bak Y, Ryu HW, Oh SR and
Yoon DY: Orientin inhibits invasion by suppressing MMP-9 and IL-8
expression via the PKCα/ERK/AP-1/STAT3-mediated signaling pathways
in TPA-treated MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Phytomedicine. 50:35–42.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhang Y, Zhu Y, Gao G and Zhou Z:
Knockdown XIST alleviates LPS-induced WI-38 cell apoptosis and
inflammation injury via targeting miR-370-3p/TLR4 in acute
pneumonia. Cell Biochem Funct. 37:348–358. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhang L, Dong L, Tang Y, Li M and Zhang M:
miR-146b protects against the inflammation injury in pediatric
pneumonia through MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. Infect Dis (Lond).
52:23–32. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|